Viruses are both the villains and heroes of life as we know it
Viruses have gotten a bad rap for the many illnesses and pandemics they’ve caused. But viruses are also genetic innovators – and possibly the pioneers of using DNA as the genetic blueprint of life.
Viruses have a bad reputation. They are responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic and a long list of maladies that have plagued humanity since time immemorial. Is there anything to celebrate about them?
Many biologists like me believe there is, at least for one specific type of virus – namely, bacteriophages, or viruses that infect bacteria. When the DNA of these viruses is captured by a cell, it may contain instructions that enable that cell to perform new tricks.
The mighty power of bacterial viruses
Bacteriophages, or phages for short, keep bacterial populations in check, both on land and at sea. They kill up to 40% of the oceans’ bacteria every day, helping control bacterial blooms and redistribution of organic matter.
Their ability to selectively kill bacteria also has medical doctors excited. Natural and engineered phages have been successfully used to treat bacterial infections that do not respond to antibiotics. This process, known as phage therapy, could help fight antibiotic resistance.
Recent research points to another important function of phages: They may be nature’s ultimate genetic tinkerers, crafting novel genes that cells can retool to gain new functions.

Phages are the most abundant life form on the planet, with a nonillion – that’s a 1 with 31 zeroes after it – of them floating around the world at any moment. Like all viruses, phages also have high replication and mutation rates, meaning they form many variants with different characteristics each time they reproduce.
Most phages have a rigid shell called a capsid that is filled with their genetic material. In many cases, the shell has more space than the phage needs to store the DNA essential for its replication. This means that phages have room to carry extra genetic baggage: genes that are not actually necessary for the phage’s survival that it can modify at will.
How bacteria retooled a viral switch
To see how this plays out, let’s take a deeper look at the phage life cycle.
Phages come in two main flavors: temperate and virulent. Virulent phages, like many other viruses, operate on an invade-replicate-kill program. They enter the cell, hijack its components, make copies of themselves and burst out.
Temperate phages, on the other hand, play the long game. They fuse their DNA with the cell’s and may lay dormant for years until something triggers their activation. Then they revert to virulent behavior: replicate and burst out.
Many temperate phages use DNA damage as their trigger. It’s sort of a “Houston, we have a problem” signal. If the cell’s DNA is being damaged, that means the DNA of the resident phage is likely to go next, so the phage wisely decides to jump ship. The genes that direct phages to replicate and burst out are turned off unless DNA damage is detected.

Bacteria have retooled the mechanisms controlling that life cycle to generate a complex genetic system that my collaborators and I have been studying for over two decades.
[Research into coronavirus and other news from science Subscribe to The Conversation’s new science newsletter.]
Bacterial cells are also interested in knowing if their DNA is getting busted. If it is, they activate a set of genes that attempt to repair the DNA. This is known as the bacterial SOS response because, if it fails, the cell is toast. Bacteria orchestrate the SOS response using a switch-like protein that responds to DNA damage: It turns on if there is damage and stays off if there isn’t.
Perhaps not surprisingly, bacterial and phage switches are evolutionarily related. This prompts the question: Who invented the switch, bacteria or viruses?
Our previous research and work by other researchers indicates that phages got there first. In our recent report, we discovered that the SOS response of Bacteroidetes, a group of bacteria that comprise up to a half of the bacteria living in your gut, is under control of a phage switch that was retooled to implement the bacteria’s own complex genetic programs. This suggests that bacterial SOS switches are in fact phage switches that got retooled eons ago.

It’s not just bacterial switches that appear to be phage inventions. Beautiful detective work has shown that a bacterial gene needed for cell division also arose through “domestication” of a phage toxin gene. And many bacterial attack systems, such as toxins and the genetic guns used to inject them into cells, as well as the camouflage they use to evade the immune system, are known or suspected to have phage origins.
The upside of viruses
OK, you may think, phages are great, but the viruses that infect us are certainly not cool. Yet there is mounting evidence that the viruses that infect plants and animals are also a major source of genetic innovation in these organisms. Domesticated viral genes have been shown, for instance, to play a key role in the evolution of mammalian placentas and in keeping human skin moist.
Recent evidence suggests that even the nucleus of a cell, which houses DNA, could have also been a viral invention. Researchers have also speculated that the ancestors of today’s viruses may have pioneered the use of DNA as the primary molecule for life. Not a small feat.
So while you may be used to thinking of viruses as the quintessential villains, they are arguably nature’s powerhouses for genetic innovation. Humans are likely here today because of them.
Ivan Erill receives funding from the US National Science Foundation
genome genetic therapy dna pandemic coronavirus covid-19Uncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
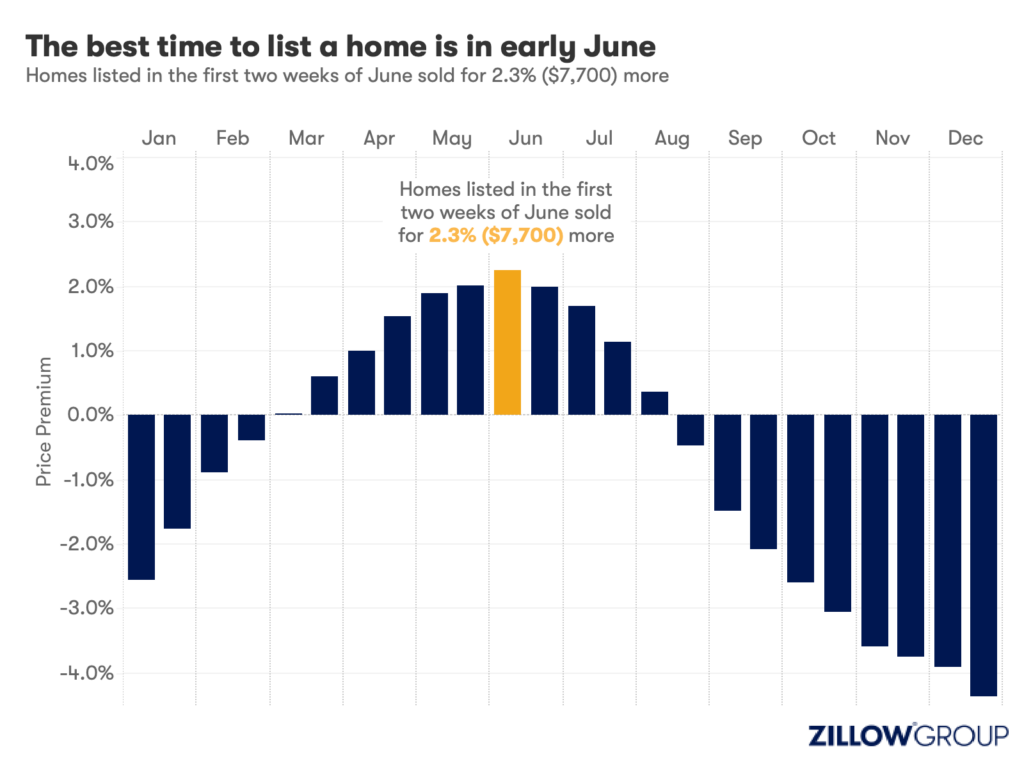
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesGovernment
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat"…
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat" to the health of the US population - a sharp decline from a high of 67% in July 2020.
What's more, the Pew Research Center survey conducted from Feb. 7 to Feb. 11 showed that just 10% of Americans are concerned that they will catch the disease and require hospitalization.
"This data represents a low ebb of public concern about the virus that reached its height in the summer and fall of 2020, when as many as two-thirds of Americans viewed COVID-19 as a major threat to public health," reads the report, which was published March 7.
According to the survey, half of the participants understand the significance of researchers and healthcare providers in understanding and treating long COVID - however 27% of participants consider this issue less important, while 22% of Americans are unaware of long COVID.
What's more, while Democrats were far more worried than Republicans in the past, that gap has narrowed significantly.
"In the pandemic’s first year, Democrats were routinely about 40 points more likely than Republicans to view the coronavirus as a major threat to the health of the U.S. population. This gap has waned as overall levels of concern have fallen," reads the report.
More via the Epoch Times;
The survey found that three in ten Democrats under 50 have received an updated COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older.
Moreover, 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older have received the updated COVID-19 vaccine, while only 24 percent of Republicans ages 65 and older have done so.
“This 42-point partisan gap is much wider now than at other points since the start of the outbreak. For instance, in August 2021, 93 percent of older Democrats and 78 percent of older Republicans said they had received all the shots needed to be fully vaccinated (a 15-point gap),” it noted.
COVID-19 No Longer an Emergency
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently issued its updated recommendations for the virus, which no longer require people to stay home for five days after testing positive for COVID-19.
The updated guidance recommends that people who contracted a respiratory virus stay home, and they can resume normal activities when their symptoms improve overall and their fever subsides for 24 hours without medication.
“We still must use the commonsense solutions we know work to protect ourselves and others from serious illness from respiratory viruses, this includes vaccination, treatment, and staying home when we get sick,” CDC director Dr. Mandy Cohen said in a statement.
The CDC said that while the virus remains a threat, it is now less likely to cause severe illness because of widespread immunity and improved tools to prevent and treat the disease.
“Importantly, states and countries that have already adjusted recommended isolation times have not seen increased hospitalizations or deaths related to COVID-19,” it stated.
The federal government suspended its free at-home COVID-19 test program on March 8, according to a website set up by the government, following a decrease in COVID-19-related hospitalizations.
According to the CDC, hospitalization rates for COVID-19 and influenza diseases remain “elevated” but are decreasing in some parts of the United States.
Government
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says “I Would Support”
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says "I Would Support"
Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump…

Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump into the race to become the next Senate GOP leader, and Elon Musk was quick to support the idea. Republicans must find a successor for periodically malfunctioning Mitch McConnell, who recently announced he'll step down in November, though intending to keep his Senate seat until his term ends in January 2027, when he'd be within weeks of turning 86.
So far, the announced field consists of two quintessential establishment types: John Cornyn of Texas and John Thune of South Dakota. While John Barrasso's name had been thrown around as one of "The Three Johns" considered top contenders, the Wyoming senator on Tuesday said he'll instead seek the number two slot as party whip.
Paul used X to tease his potential bid for the position which -- if the GOP takes back the upper chamber in November -- could graduate from Minority Leader to Majority Leader. He started by telling his 5.1 million followers he'd had lots of people asking him about his interest in running...
Thousands of people have been asking if I'd run for Senate leadership...
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
...then followed up with a poll in which he predictably annihilated Cornyn and Thune, taking a 96% share as of Friday night, with the other two below 2% each.
????????️VOTE NOW ????️ ???? Who would you like to be the next Senate leader?
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
Elon Musk was quick to back the idea of Paul as GOP leader, while daring Cornyn and Thune to follow Paul's lead by throwing their names out for consideration by the Twitter-verse X-verse.
I would support Rand Paul and suspect that other candidates will not actually run polls out of concern for the results, but let’s see if they will!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 8, 2024
Paul has been a stalwart opponent of security-state mass surveillance, foreign interventionism -- to include shoveling billions of dollars into the proxy war in Ukraine -- and out-of-control spending in general. He demonstrated the latter passion on the Senate floor this week as he ridiculed the latest kick-the-can spending package:
This bill is an insult to the American people. The earmarks are all the wasteful spending that you could ever hope to see, and it should be defeated. Read more: https://t.co/Jt8K5iucA4 pic.twitter.com/I5okd4QgDg
— Senator Rand Paul (@SenRandPaul) March 8, 2024
In February, Paul used Senate rules to force his colleagues into a grueling Super Bowl weekend of votes, as he worked to derail a $95 billion foreign aid bill. "I think we should stay here as long as it takes,” said Paul. “If it takes a week or a month, I’ll force them to stay here to discuss why they think the border of Ukraine is more important than the US border.”
Don't expect a Majority Leader Paul to ditch the filibuster -- he's been a hardy user of the legislative delay tactic. In 2013, he spoke for 13 hours to fight the nomination of John Brennan as CIA director. In 2015, he orated for 10-and-a-half-hours to oppose extension of the Patriot Act.
Among the general public, Paul is probably best known as Capitol Hill's chief tormentor of Dr. Anthony Fauci, who was director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease during the Covid-19 pandemic. Paul says the evidence indicates the virus emerged from China's Wuhan Institute of Virology. He's accused Fauci and other members of the US government public health apparatus of evading questions about their funding of the Chinese lab's "gain of function" research, which takes natural viruses and morphs them into something more dangerous. Paul has pointedly said that Fauci committed perjury in congressional hearings and that he belongs in jail "without question."
Musk is neither the only nor the first noteworthy figure to back Paul for party leader. Just hours after McConnell announced his upcoming step-down from leadership, independent 2024 presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr voiced his support:
Mitch McConnell, who has served in the Senate for almost 40 years, announced he'll step down this November.
— Robert F. Kennedy Jr (@RobertKennedyJr) February 28, 2024
Part of public service is about knowing when to usher in a new generation. It’s time to promote leaders in Washington, DC who won’t kowtow to the military contractors or…
In a testament to the extent to which the establishment recoils at the libertarian-minded Paul, mainstream media outlets -- which have been quick to report on other developments in the majority leader race -- pretended not to notice that Paul had signaled his interest in the job. More than 24 hours after Paul's test-the-waters tweet-fest began, not a single major outlet had brought it to the attention of their audience.
That may be his strongest endorsement yet.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex




















