International
Tweedy, Browne 4Q20 Commentary: New Position In Rubis
Tweedy, Browne commentary for the fourth quarter ended December 2020, discussing their new position in Rubis. Q4 2020 hedge fund letters, conferences and more Also see Tweedy, Browne prospectus here. The cork came off of the champagne bottle in public…
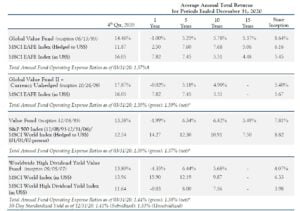

Tweedy, Browne commentary for the fourth quarter ended December 2020, discussing their new position in Rubis.
Get The Full Series in PDF
Get the entire 10-part series on Charlie Munger in PDF. Save it to your desktop, read it on your tablet, or email to your colleagues.

Q4 2020 hedge fund letters, conferences and more
Also see Tweedy, Browne prospectus here.
The cork came off of the champagne bottle in public equity markets during the fourth quarter as vaccine approvals propelled many market indices to new all-time highs, a remarkable achievement in light of the challenges of the last nine months. Proponents of value investing were particularly encouraged as the vaccine news ignited a powerful rally in so called “value stocks,” which in the past have often performed relatively better than their growth counterparts during a robust economic recovery. Many market observers are expecting just such a recovery on the heels of the vaccine roll-out in the coming year. International equities which have also trailed U.S. equities for the better part of the last decade also awakened from their slumber and out-performed their U.S counterparts for the quarter. One cannot help but wonder whether these 4th quarter results are foreshadowing the beginnings of a rotation from all things technology into more value and internationally oriented securities. The Tweedy, Browne Funds did not disappoint during the quarter with each of the four Funds producing strong double digit returns.
Portfolio Overview
Pfizer’s announcement in early November that its COVID vaccine had proven to be 95% effective served to turbocharge returns for global equity markets for the month and quarter. Value stocks, in particular, were beneficiaries of the good news, as the prospects for a receding virus helped to fuel expectations for a strong economic recovery sometime in 2021. In our Fund portfolios, this translated into strong returns in industrial, financial, communication services, consumer discretionary, and materials holdings. This included good results in machinery and aerospace companies such as CNH and Safran; interactive media holdings such as Alphabet (Google) and Baidu; bank and insurance holdings such as DBS Group, Standard Chartered, CNP, and Zurich Insurance Group; auto-related businesses such as Autoliv, Michelin, and Yamaha Motor Co.; and materials holdings such as BASF and Sol SpA. We also had strong returns in beverage companies, Coca-Cola FEMSA and Heineken, and in our last remaining pure oil & gas holding, Total. All of these companies and a host of others enjoyed robust double-digit returns during the quarter.
While most of the Funds’ holdings performed extraordinarily well during the quarter, there were a few that disappointed, including several of our pharmaceutical holdings such as Glaxo, Astellas Pharma, and Roche. We also had poor returns in a number of our consumer staples holdings including Nestlé, Henkel, and Unilever.
As mentioned in the beginning of this report, international equity returns were quite strong during the quarter. This included double-digit returns in most of the Funds’ European holdings which, like value stocks, have tended to benefit from the prospects for a strong economic recovery. European markets tend to have many fewer technology companies and more exposure to older economy companies such as banks, auto-related enterprises, consumer products companies, and pharmaceutical companies. So if value stocks do make a comeback in 2021, as the quarter’s results may be suggesting, we would hope that this might prove beneficial for the Funds’ European holdings, particularly if Europe gets a strong, vaccine-led economic bounce off what has been a deeper bottom for their respective economies.
Most, if not all, of the Asian countries in which the Funds are invested have more effectively responded over time to the onslaught of the virus, and, as a result, their economies have rebounded more quickly from the virusinduced economic downturn. This also held true for their equity markets, as all of the Asian countries in which the Funds are invested (Japan, Hong Kong, Singapore, China, South Korea, Thailand, and the Phillippines) had strong double-digit returns for the quarter. China and Singapore were the most significant contributors to return in our Asian-related holdings, with companies such as Baidu, Shanghai Mechanical, DBS Group and United Overseas Bank leading the way.
New Additions
Despite increasing equity market valuations during the quarter, we remained quite active in terms of new additions to our Fund portfolios. Newly established positions included Conzetta, the small Swiss industrial conglomerate, which the Funds have owned in the past; Enterprise Products, the U.S.-based oil & gas pipeline company; Rubis, the French gas distribution company; Megacable Holdings, the Mexican cable (telecommunications) company; Alten, the French engineering services company; Fukuda Denshi, the Japanese medical products company, which the Funds have owned in the past; Kamigumi, the Japanese port operator; Chinese property management company, A-Living; and Alibaba, the largest e-commerce company in China. At purchase, all of these companies were trading at significant discounts from our estimates of their respective intrinsic values, had strong balance sheets and, in our view, attractive growth prospects. Several of them are small and mid-sized companies, had owner earnings yields (net operating profit after tax/enterprise value) in the 7% to 8% range or higher, were buying back or had plans to buy back a significant number of shares and, in many of the companies, corporate insiders were buying shares at prices at or around what the Funds were paying.
We also added to a number of positions in the Funds’ portfolios, including Alliance Global, Astellas Pharma, CK Huchison, Dali Foods, and Intel.
The markets’ strong advance during the quarter allowed us to sell or reduce our remaining shareholdings in a number of companies that had either met our valuation targets or had disappointed, or whose future prospects had, in our view, become compromised. This included Chokwong Paint, Mediaset, Royal Dutch, and HSBC, among a host of others.
New Position: Rubis
Rubis, a French company predominantly active in emerging markets, was purchased in all four of our Funds during the quarter. The company distributes fuels for vehicles, airplanes, home heating, cooking, and power generation as well as bitumen for road construction and lubricants. They are active in 41 countries and this number is expanding. The activities are largely focused on the Caribbean and East Africa, which together make up roughly 85% of their business volume. The economic model is based on superior and dominant logistics, a musthave product for which there are few available local alternatives, and high market share in small markets with limited competition. As a result, many of their end markets are islands. By way of illustration of Rubis’ approach, the company owns a 71% stake in an oil refinery in the Caribbean, from which it transports refined products with five owned and operated ships to various islands. Rubis controls the whole distribution chain: the refinery, the ships, the local transportation of fuels, and the gas stations. This kind of set-up is difficult to compete with.
Demand for Rubis’s products is underpinned by the fact that in many of their markets, competition from gas and electricity distribution networks is weak or non-existent. As a result, many companies and households in their markets generate their own electricity to run offices, factories and homes, or have back-up generators at the ready. Many people cook and heat their water on liquified petroleum gas (“LPG”) from a tank; there is no alternative.
Fuel for cars is the company’s biggest business, and Rubis operates more than 1,000 gas stations under the Rubis brand in the Caribbean and East Africa. Rubis is often the dominant brand on Caribbean islands, and in East Africa the same position is emerging. Financial results in 2020 were somewhat challenged by the pandemic; the company has forecasted its underlying EBIT to be down around 12% versus 2019, mainly because of aircraft fuel weakness. However, the longer-term outlook for growth, especially in Africa, where they benefit from population growth, urbanization, motorization, and a growing middle class, is good. Rubis also expands by acquiring businesses within logistical reach that have the same economic characteristics that the existing businesses have: small markets, geographical/logistical isolation, and strong market power.
Rubis is committed to a transition to cleaner and transitional fuels such as LPG, which in Africa in many applications competes with coal. The company has introduced energy efficient heat pumps, LNG, and biofuels, in addition to using hydrogen out of its Caribbean refinery to generate electricity in fuel cells. There are solar panels at the refinery. We find Rubis to be a sensible and forward thinking energy distributor committed to providing energy for as many people as possible in their markets, thus contributing to economic growth in places where it is vitally needed to help raise people out of poverty.
Using a cautious 13 times enterprise value to 2021 EBIT to value the business, at purchase Rubis was trading at a significant discount to its appraised intrinsic value. The company is in a net cash position, and traded at a forward price earnings multiple of 12.3 times 2021 estimated earnings per share. The dividend yield was approximately 4.7%. In early December 2020, the company voted to buy back EUR 280 million worth of shares (7.4% of the market cap at the time) over 18 months, and has since started buying. Finally, there were two insider share purchases by Hervé Claquin, a member of the company’s Supervisory Board.
Will Browne’s Announcement
As you may recall, in our recent letter to shareholders that accompanied the Funds’ Semi-Annual Report, we reported that Will Browne, a partner in our business for 42 years, who maintained positions on our Management and Investment Committees, had decided to take a step back. Will withdrew from those positions effective January 1 to become a Senior Advisor to our Investment Committee. As he has said, he will now be able to focus entirely on the part of the business he enjoys the most, the investment process. You can read his announcement here. Will made an immeasurable contribution to our firm during his 42-year tenure, and we are looking forward to many more years of his advice and counsel.
In addition to Will Browne’s announcement, the Management Committee of our firm made some additional appointments just prior to our penning this report. Jay Hill, one of our Managing Directors and a member of the Investment Committee, was appointed to join Tom Shrager, John Spears, and Bob Wyckoff as a member of the Management Committee; and Sean McDonald, one of our analysts, was promoted to Managing Director and has joined the Investment Committee. Both Jay and Sean are long-time employees and equity stakeholders in our firm. They are both extraordinarily capable security analysts, clear thinkers, of impeccable character, and day-in and dayout exhibit the requisite temperament necessary for success as value investors. You can read Jay and Sean’s biographies here.
As we head into the new year, we are grateful for the rapid recovery of equity markets and, in turn, our Fund portfolios off their previous March 2020 lows, and are looking forward to the possibility of better relative returns for value-oriented securities. Many market observers believe that value has never been cheaper in its long history relative to growth. And technology has never been more ascendant, except perhaps in 2000. With speculative fervor afoot in markets, particularly when it comes to all things technology, we take comfort in the businesses that the Funds own, which for the most part (in our view) enjoy strong financial and competitive positions, have prospects for future growth and, most importantly, possess collateral value backing up the prices the Funds have paid for their shares. In a recent article in The Wall Street Journal entitled, What We Already Know About Investing in 2021, Jason Zweig describes the temptation of investors to chase whatever has been “hot,” and quoted Warren Buffett in characterizing the risk associated with excessive valuations, “Geometric progressions eventually forge their own anchors.” Should we have a strong vaccine-induced economic recovery in the coming year, we remain confident and hopeful that our companies will not be held down by such anchors. The same may not be able to be said about many technology companies that have been the beneficiaries of what some might describe as irrational exuberance. We’ll just have to see.
Thank you for investing with us. Stay well.
Roger R. de Bree, Frank H. Hawrylak, Jay Hill, Sean McDonald
Thomas H. Shrager, John D. Spears, Robert Q. Wyckoff, Jr.
Investment Committee
Tweedy, Browne Company LLC
See the full commentary here.
The post Tweedy, Browne 4Q20 Commentary: New Position In Rubis appeared first on ValueWalk.
economic recovery economic growth pandemic emerging markets equities stocks vaccine recovery oil south korea singapore africa japan hong kong european europe chinaInternational
“Extreme Events”: US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In “Large Excess Over Trend”
"Extreme Events": US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In "Large Excess Over Trend"
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021…
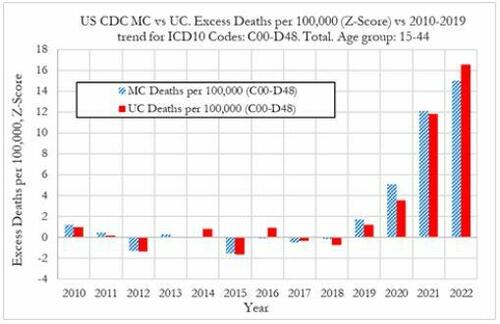
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021 and 2022 among 15-44 year-olds "in large excess over trend," marking jumps of 5.6% and 7.9% respectively vs. a rise of 1.7% in 2020, according to a new preprint study from deep-dive research firm, Phinance Technologies.

Extreme Events
The report, which relies on data from the CDC, paints a troubling picture.
"We show a rise in excess mortality from neoplasms reported as underlying cause of death, which started in 2020 (1.7%) and accelerated substantially in 2021 (5.6%) and 2022 (7.9%). The increase in excess mortality in both 2021 (Z-score of 11.8) and 2022 (Z-score of 16.5) are highly statistically significant (extreme events)," according to the authors.
That said, co-author, David Wiseman, PhD (who has 86 publications to his name), leaves the cause an open question - suggesting it could either be a "novel phenomenon," Covid-19, or the Covid-19 vaccine.
Cancer deaths in US in 2021 & 2022 in large excess over trend for 15-44 year-olds as extreme events. A novel phenomenon? C19? lockdowns? C19 vaccines? Honored to participate in this work. #CDC where are you? @DowdEdwardhttps://t.co/iUV5oQiWCW pic.twitter.com/uytzaIvvor
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 12, 2024
"The results indicate that from 2021 a novel phenomenon leading to increased neoplasm deaths appears to be present in individuals aged 15 to 44 in the US," reads the report.
The authors suggest that the cause may be the result of "an unexpected rise in the incidence of rapidly growing fatal cancers," and/or "a reduction in survival in existing cancer cases."
They also address the possibility that "access to utilization of cancer screening and treatment" may be a factor - the notion that pandemic-era lockdowns resulted in fewer visits to the doctor. Also noted is that "Cancers tend to be slowly-developing diseases with remarkably stable death rates and only small variations over time," which makes "any temporal association between a possible explanatory factor (such as COVID-19, the novel COVID-19 vaccines, or other factor(s)) difficult to establish."
That said, a ZeroHedge review of the CDC data reveals that it does not provide information on duration of illness prior to death - so while it's not mentioned in the preprint, it can't rule out so-called 'turbo cancers' - reportedly rapidly developing cancers, the existence of which has been largely anecdotal (and widely refuted by the usual suspects).
While the Phinance report is extremely careful not to draw conclusions, researcher "Ethical Skeptic" kicked the barn door open in a Thursday post on X - showing a strong correlation between "cancer incidence & mortality" coinciding with the rollout of the Covid mRNA vaccine.
The argument is over.
— Ethical Skeptic ☀ (@EthicalSkeptic) March 14, 2024
The Covid mRNA Vaxx has cause a sizeable 2021 inflection, and now novel-trend elevation in terms of both cancer incidence & mortality.
Now you know who the liars were all along.
????Incidence = 14.8% excess
????UCoD Mortality = 5.3% excess (lags Incidence) pic.twitter.com/uwN9GMrHl1
Phinance principal Ed Dowd commented on the post, noting that "Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry!"
????Indeed it is…Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry! @EthicalSkeptic provides a chart below showing US Cancer treatment in constant dollars with a current growth rate of 14.8% (6.3% New CAGR) versus long term trend of 1.78% CAGR or $33.8 billion in excess cancer… https://t.co/RIn4R2YZZ7
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Continued:
As a former portfolio manager of of a $14 billion Large Cap Growth Equity portfolio I can definitively say Cancer treatments and the Disabilities have become growth industries that both have inflection points coincidental to the mRNA vaccine rollouts in 2021.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Chart 1 from… pic.twitter.com/TCt4X1plnM
Bottom line - hard data is showing alarming trends, which the CDC and other agencies have a requirement to explore and answer truthfully - and people are asking #WhereIsTheCDC.
We aren't holding our breath.
Experts are sounding the alarm on a spike in cancer diagnosis worldwide. It is still a mystery. @DowdEdward from Phinance Technologies has also been sounding the alarm for months.
— dr.ir. Carla Peeters (@CarlaPeeters3) March 15, 2024
We are facing a dramatic degradation of the human immune system https://t.co/CPnwP3Oj9G
Wiseman, meanwhile, points out that Pfizer and several other companies are making "significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID."
Pfizer among several companies making significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID. @DowdEdward @Kevin_McKernan @JesslovesMJK @niki_kyrylenko https://t.co/nefEZYLW1o https://t.co/r505Sbbcq4
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 15, 2024
Phinance
We've featured several of Phinance's self-funded deep dives into pandemic data that nobody else is doing. If you'd like to support them, click here.
List of our projects following disturbing tends in deaths, disabilities and absences.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 16, 2024
Link to projects at bottom.
✅ V-Damage Project
✅ Excess Mortality Project
✅ US Disabilities Project
✅ US BLS Absence rates Project
✅ US Cause of Death Project
✅ UK Cause of Death…
International
Gen Z, The Most Pessimistic Generation In History, May Decide The Election
Gen Z, The Most Pessimistic Generation In History, May Decide The Election
Authored by Mike Shedlock via MishTalk.com,
Young adults are more…
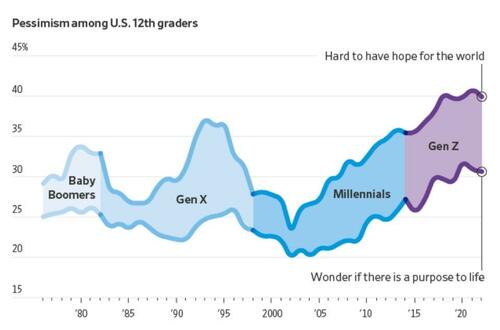
Authored by Mike Shedlock via MishTalk.com,
Young adults are more skeptical of government and pessimistic about the future than any living generation before them.
This is with reason, and it’s likely to decide the election.
Rough Years and the Most Pessimism Ever
The Wall Street Journal has an interesting article on The Rough Years That Turned Gen Z Into America’s Most Disillusioned Voters.
Young adults in Generation Z—those born in 1997 or after—have emerged from the pandemic feeling more disillusioned than any living generation before them, according to long-running surveys and interviews with dozens of young people around the country. They worry they’ll never make enough money to attain the security previous generations have achieved, citing their delayed launch into adulthood, an impenetrable housing market and loads of student debt.
And they’re fed up with policymakers from both parties.
Washington is moving closer to passing legislation that would ban or force the sale of TikTok, a platform beloved by millions of young people in the U.S. Several young people interviewed by The Wall Street Journal said they spend hours each day on the app and use it as their main source of news.
“It’s funny how they quickly pass this bill about this TikTok situation. What about schools that are getting shot up? We’re not going to pass a bill about that?” Gaddie asked. “No, we’re going to worry about TikTok and that just shows you where their head is…. I feel like they don’t really care about what’s going on with humanity.”
Gen Z’s widespread gloominess is manifesting in unparalleled skepticism of Washington and a feeling of despair that leaders of either party can help. Young Americans’ entire political memories are subsumed by intense partisanship and warnings about the looming end of everything from U.S. democracy to the planet. When the darkest days of the pandemic started to end, inflation reached 40-year highs. The right to an abortion was overturned. Wars in Ukraine and the Middle East raged.
Dissatisfaction is pushing some young voters to third-party candidates in this year’s presidential race and causing others to consider staying home on Election Day or leaving the top of the ticket blank. While young people typically vote at lower rates, a small number of Gen Z voters could make the difference in the election, which four years ago was decided by tens of thousands of votes in several swing states.
Roughly 41 million Gen Z Americans—ages 18 to 27—will be eligible to vote this year, according to Tufts University.
Gen Z is among the most liberal segments of the electorate, according to surveys, but recent polling shows them favoring Biden by only a slim margin. Some are unmoved by those who warn that a vote against Biden is effectively a vote for Trump, arguing that isn’t enough to earn their support.
Confidence
When asked if they had confidence in a range of public institutions, Gen Z’s faith in them was generally below that of the older cohorts at the same point in their lives.
One-third of Gen Z Americans described themselves as conservative, according to NORC’s 2022 General Social Survey. That is a larger share identifying as conservative than when millennials, Gen X and baby boomers took the survey when they were the same age, though some of the differences were small and within the survey’s margin of error.
More young people now say they find it hard to have hope for the world than at any time since at least 1976, according to a University of Michigan survey that has tracked public sentiment among 12th-graders for nearly five decades. Young people today are less optimistic than any generation in decades that they’ll get a professional job or surpass the success of their parents, the long-running survey has found. They increasingly believe the system is stacked against them and support major changes to the way the country operates.
Gen Z future Outcome
“It’s the starkest difference I’ve documented in 20 years of doing this research,” said Twenge, the author of the book “Generations.” The pandemic, she said, amplified trends among Gen Z that have existed for years: chronic isolation, a lack of social interaction and a propensity to spend large amounts of time online.
A 2020 study found past epidemics have left a lasting impression on young people around the world, creating a lack of confidence in political institutions and their leaders. The study, which analyzed decades of Gallup World polling from dozens of countries, found the decline in trust among young people typically persists for two decades.
Young people are more likely than older voters to have a pessimistic view of the economy and disapprove of Biden’s handling of inflation, according to the recent Journal poll. Among people under 30, Biden leads Trump by 3 percentage points, 35% to 32%, with 14% undecided and the remaining shares going to third-party candidates, including 10% to independent Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
Economic Reality
Gen Z may be the first generation in US history that is not better off than their parents.
Many have given up on the idea they will ever be able to afford a home.
The economy is allegedly booming (I disagree). Regardless, stress over debt is high with younger millennials and zoomers.
This has been a constant theme of mine for many months.
Credit Card and Auto Delinquencies Soar
Credit card debt surged to a record high in the fourth quarter. Even more troubling is a steep climb in 90 day or longer delinquencies.
Record High Credit Card Debt
Credit card debt rose to a new record high of $1.13 trillion, up $50 billion in the quarter. Even more troubling is the surge in serious delinquencies, defined as 90 days or more past due.
For nearly all age groups, serious delinquencies are the highest since 2011.
Auto Loan Delinquencies
Serious delinquencies on auto loans have jumped from under 3 percent in mid-2021 to to 5 percent at the end of 2023 for age group 18-29.Age group 30-39 is also troubling. Serious delinquencies for age groups 18-29 and 30-39 are at the highest levels since 2010.
For further discussion please see Credit Card and Auto Delinquencies Soar, Especially Age Group 18 to 39
Generational Homeownership Rates
Home ownership rates courtesy of Apartment List
The above chart is from the Apartment List’s 2023 Millennial Homeownership Report
Those struggling with rent are more likely to be Millennials and Zoomers than Generation X, Baby Boomers, or members of the Silent Generation.
The same age groups struggling with credit card and auto delinquencies.
On Average Everything is Great
Average it up, and things look pretty good. This is why we have seen countless stories attempting to explain why people should be happy.
Krugman Blames Partisanship
With the recent rise in consumer sentiment, time to revisit this excellent Briefing Book paper. On reflection, I'd do it a bit differently; same basic conclusion, but I think partisan asymmetry explains even more of the remaining low numbers 1/ https://t.co/4lqm7X4472
— Paul Krugman (@paulkrugman) February 17, 2024
OK, there is a fair amount of partisanship in the polls.
However, Biden isn’t struggling from partisanship alone. If that was the reason, Biden would not be polling so miserably with Democrats in general, blacks, and younger voters.
OK, there is a fair amount of partisanship in the polls.
However, Biden isn’t struggling from partisanship alone. If that was the reason, Biden would not be polling so miserably with Democrats in general, blacks, and younger voters.
This allegedly booming economy left behind the renters and everyone under the age of 40 struggling to make ends meet.
Many Are Addicted to “Buy Now, Pay Later” Plans
Buy Now Pay Later, BNPL, plans are increasingly popular. It’s another sign of consumer credit stress.
For discussion, please see Many Are Addicted to “Buy Now, Pay Later” Plans, It’s a Big Trap
The study did not break things down by home owners vs renters, but I strongly suspect most of the BNPL use is by renters.
What About Jobs?
Another seemingly strong jobs headline falls apart on closer scrutiny. The massive divergence between jobs and employment continued into February.
Nonfarm payrolls and employment levels from the BLS, chart by Mish.
Payrolls vs Employment Gains Since March 2023
-
Nonfarm Payrolls: 2,602,000
-
Employment Level: +144,000
-
Full Time Employment: -284,000
For more details of the weakening labor markets, please see Jobs Up 275,000 Employment Down 184,000
CPI Hot Again
CPI Data from the BLS, chart by Mish.
For discussion of the CPI inflation data for February, please see CPI Hot Again, Rent Up at Least 0.4 Percent for 30 Straight Months
Also note the Producer Price Index (PPI) Much Hotter Than Expected in February
Major Economic Cracks
There are economic cracks in spending, cracks in employment, and cracks in delinquencies.
But there are no cracks in the CPI. It’s coming down much slower than expected. And the PPI appears to have bottomed.
Add it up: Inflation + Recession = Stagflation.
Election Impact
In 2020, younger voters turned out in the biggest wave in history. And they voted for Biden.
Younger voters are not as likely to vote in 2024, and they are less likely to vote for Biden.
Millions of voters will not vote for either Trump or Biden. Net, this will impact Biden more. The base will not decide the election, but the Trump base is far more energized than the Biden base.
If Biden signs a TikTok ban, that alone could tip the election.
If No Labels ever gets its act together, I suspect it will siphon more votes from Biden than Trump. But many will just sit it out.
“We’re just kind of over it,” Noemi Peña, 20, a Tucson, Ariz., resident who works in a juice bar, said of her generation’s attitude toward politics. “We don’t even want to hear about it anymore.” Peña said she might not vote because she thinks it won’t change anything and “there’s just gonna be more fighting.” Biden won Arizona in 2020 by just over 10,000 votes.
The Journal noted nearly one-third of voters under 30 have an unfavorable view of both Biden and Trump, a higher number than all older voters. Sixty-three percent of young voters think neither party adequately represents them.
Young voters in 2020 were energized to vote against Trump. Now they have thrown in the towel.
And Biden telling everyone how great the economy is only rubs salt in the wound.
International
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says “Copper’s Time Is Now”
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says "Copper’s Time Is Now"
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring…
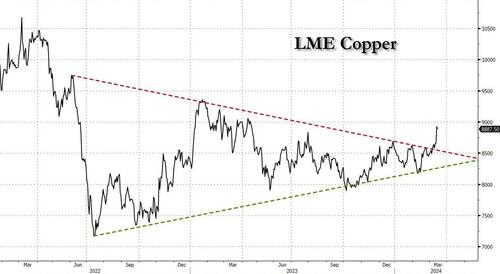
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring speculation about declining global supply, copper has finally broken out, surging to the highest price in the past year, just shy of $9,000 a ton as supply cuts hit the market; At the same time the price of the world's "other" most important mined commodity has diverged, as iron ore has tumbled amid growing demand headwinds out of China's comatose housing sector where not even ghost cities are being built any more.
Copper surged almost 5% this week, ending a months-long spell of inertia, as investors focused on risks to supply at various global mines and smelters. As Bloomberg adds, traders also warmed to the idea that the worst of a global downturn is in the past, particularly for metals like copper that are increasingly used in electric vehicles and renewables.
Yet the commodity crash of recent years is hardly over, as signs of the headwinds in traditional industrial sectors are still all too obvious in the iron ore market, where futures fell below $100 a ton for the first time in seven months on Friday as investors bet that China’s years-long property crisis will run through 2024, keeping a lid on demand.
Indeed, while the mood surrounding copper has turned almost euphoric, sentiment on iron ore has soured since the conclusion of the latest National People’s Congress in Beijing, where the CCP set a 5% goal for economic growth, but offered few new measures that would boost infrastructure or other construction-intensive sectors.
As a result, the main steelmaking ingredient has shed more than 30% since early January as hopes of a meaningful revival in construction activity faded. Loss-making steel mills are buying less ore, and stockpiles are piling up at Chinese ports. The latest drop will embolden those who believe that the effects of President Xi Jinping’s property crackdown still have significant room to run, and that last year’s rally in iron ore may have been a false dawn.
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg notes, on Friday there were fresh signs that weakness in China’s industrial economy is hitting the copper market too, with stockpiles tracked by the Shanghai Futures Exchange surging to the highest level since the early days of the pandemic. The hope is that headwinds in traditional industrial areas will be offset by an ongoing surge in usage in electric vehicles and renewables.
And while industrial conditions in Europe and the US also look soft, there’s growing optimism about copper usage in India, where rising investment has helped fuel blowout growth rates of more than 8% — making it the fastest-growing major economy.
In any case, with the demand side of the equation still questionable, the main catalyst behind copper’s powerful rally is an unexpected tightening in global mine supplies, driven mainly by last year’s closure of a giant mine in Panama (discussed here), but there are also growing worries about output in Zambia, which is facing an El Niño-induced power crisis.
On Wednesday, copper prices jumped on huge volumes after smelters in China held a crisis meeting on how to cope with a sharp drop in processing fees following disruptions to supplies of mined ore. The group stopped short of coordinated production cuts, but pledged to re-arrange maintenance work, reduce runs and delay the startup of new projects. In the coming weeks investors will be watching Shanghai exchange inventories closely to gauge both the strength of demand and the extent of any capacity curtailments.
“The increase in SHFE stockpiles has been bigger than we’d anticipated, but we expect to see them coming down over the next few weeks,” Colin Hamilton, managing director for commodities research at BMO Capital Markets, said by phone. “If the pace of the inventory builds doesn’t start to slow, investors will start to question whether smelters are actually cutting and whether the impact of weak construction activity is starting to weigh more heavily on the market.”
* * *
Few have been as happy with the recent surge in copper prices as Goldman's commodity team, where copper has long been a preferred trade (even if it may have cost the former team head Jeff Currie his job due to his unbridled enthusiasm for copper in the past two years which saw many hedge fund clients suffer major losses).
As Goldman's Nicholas Snowdon writes in a note titled "Copper's time is now" (available to pro subscribers in the usual place)...
... there has been a "turn in the industrial cycle." Specifically according to the Goldman analyst, after a prolonged downturn, "incremental evidence now points to a bottoming out in the industrial cycle, with the global manufacturing PMI in expansion for the first time since September 2022." As a result, Goldman now expects copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25.’
Here are the details:
Previous inflexions in global manufacturing cycles have been associated with subsequent sustained industrial metals upside, with copper and aluminium rising on average 25% and 9% over the next 12 months. Whilst seasonal surpluses have so far limited a tightening alignment at a micro level, we expect deficit inflexions to play out from quarter end, particularly for metals with severe supply binds. Supplemented by the influence of anticipated Fed easing ahead in a non-recessionary growth setting, another historically positive performance factor for metals, this should support further upside ahead with copper the headline act in this regard.
Goldman then turns to what it calls China's "green policy put":
Much of the recent focus on the “Two Sessions” event centred on the lack of significant broad stimulus, and in particular the limited property support. In our view it would be wrong – just as in 2022 and 2023 – to assume that this will result in weak onshore metals demand. Beijing’s emphasis on rapid growth in the metals intensive green economy, as an offset to property declines, continues to act as a policy put for green metals demand. After last year’s strong trends, evidence year-to-date is again supportive with aluminium and copper apparent demand rising 17% and 12% y/y respectively. Moreover, the potential for a ‘cash for clunkers’ initiative could provide meaningful right tail risk to that healthy demand base case. Yet there are also clear metal losers in this divergent policy setting, with ongoing pressure on property related steel demand generating recent sharp iron ore downside.
Meanwhile, Snowdon believes that the driver behind Goldman's long-running bullish view on copper - a global supply shock - continues:
Copper’s supply shock progresses. The metal with most significant upside potential is copper, in our view. The supply shock which began with aggressive concentrate destocking and then sharp mine supply downgrades last year, has now advanced to an increasing bind on metal production, as reflected in this week's China smelter supply rationing signal. With continued positive momentum in China's copper demand, a healthy refined import trend should generate a substantial ex-China refined deficit this year. With LME stocks having halved from Q4 peak, China’s imminent seasonal demand inflection should accelerate a path into extreme tightness by H2. Structural supply underinvestment, best reflected in peak mine supply we expect next year, implies that demand destruction will need to be the persistent solver on scarcity, an effect requiring substantially higher pricing than current, in our view. In this context, we maintain our view that the copper price will surge into next year (GSe 2025 $15,000/t average), expecting copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25’
Another reason why Goldman is doubling down on its bullish copper outlook: gold.
The sharp rally in gold price since the beginning of March has ended the period of consolidation that had been present since late December. Whilst the initial catalyst for the break higher came from a (gold) supportive turn in US data and real rates, the move has been significantly amplified by short term systematic buying, which suggests less sticky upside. In this context, we expect gold to consolidate for now, with our economists near term view on rates and the dollar suggesting limited near-term catalysts for further upside momentum. Yet, a substantive retracement lower will also likely be limited by resilience in physical buying channels. Nonetheless, in the midterm we continue to hold a constructive view on gold underpinned by persistent strength in EM demand as well as eventual Fed easing, which should crucially reactivate the largely for now dormant ETF buying channel. In this context, we increase our average gold price forecast for 2024 from $2,090/toz to $2,180/toz, targeting a move to $2,300/toz by year-end.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Spread & Containment4 days ago
Spread & Containment4 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex































