The Urge to Surge
The US dollar pulled back, and long-term yields softened last week, but the economic surge has only just begun. The more than 900k rise last month’s non-farm payrolls and the jump in auto sales will set the tone for this month’s economic data, and invest

The US dollar pulled back, and long-term yields softened last week, but the economic surge has only just begun. The more than 900k rise last month's non-farm payrolls and the jump in auto sales will set the tone for this month's economic data, and investors will get a taste of it next week. The US data will be robust in absolute terms but also relative to other countries.
France and Spain have already revised their growth forecasts this year, and Bundesbank President Weidmann hinted that it may do the same for Germany. The market has written off Q1 and probably Q2 as well.
Singapore is the first to report Q1 GDP. It is expected to have expanded by around 1% after growing 3.8% in Q4 20. It would be the slowest paces since the contraction in the first two quarters of last year. China will be the first of the large countries to report. The world's second-largest economy appears to have slowed by half or more in Q1 after a 2.6% quarter-over-quarter pace in Q4 20. March trade figures are due before the GDP figures, but other March data, including retail sales, industrial production, and fixed-asset investment, are released simultaneously.
The key question is, what happens next? China has taken measures, including discouraging loan growth (which will not be evident in the March lending figures) and other actions that could have a cooling-off effect on entrepreneurship. Can China find its mojo? The IMF apparently thinks so as it revised its projection for Chinese growth this year to 8.4% from 8.1% made three months ago, and said that China's economy will generate 20% of the world's growth in the five-year period beginning this year.
The IMF has caught up to market forecasts, but this year's growth is an aberration, and economists expect China's growth in 2022 and 2023 to fall below 6%. As the shift from rural to the city is well advanced and the productivity catch-up gains largely captured, the growth impulse has slowed. With two exceptions (2010 and 2017), Chinese growth has been slowing every year since 2007. This year is an anomaly in the opposite direction of last year's, but the average over the two years is probably close to the new normal.
The IMF also boosted its projection for US growth this year to 6.4%, up from the 5.1% estimate in January. It optimistically anticipates 4.4% growth in 2022, a third faster than Fed officials' median projection. Private-sector economists seem to be closer to the IMF's assessment for next year than the Fed's. This may help explain why the market has fully priced a rate hike more than a year before the median Fed forecast in March despite the official statements.
The macro story that will dominate next week is the surge in US economic activity in March and a jump in headline CPI above 2%. On the one hand, everyone recognizes that US growth is accelerating. On the other hand, the pace, like we saw with the employment report, may surprise economists. The data will not just appear strong, followed by some weather-induced weakness in February. It will be eye-popping in absolute terms, quantifying the surge driven by the massive fiscal and monetary stimulus, the wealth effect of rising equity and real estate prices (and crypto, judging from what is happening in the art world).
March CPI will be reported on April 13, and the base effect will kick in. Headline CPI is expected to rise by 0.4%-0.5% in the month. That would put the Q1 annualized rate over 4% in its own right, but the year-over-year rate will be flattered by the fact that last March CPI fell by 0.3%. The peak of the base effect is happening this month. In April 2020, CPI fell by 0.7%. March's year-over-year rate will jump toward 2.5% from 1.7% in February and further in April.
The core is going to show a milder base effect. In March 2020, it was flat and fell by 0.4% in April. This year core prices were flat in January and rose by 0.1% in February. A 0.2% increase is expected in next week's report. A 0.1% monthly average is the same as in Q4 20. Still, the core rate on a year-over-year basis is likely to return to the upper end of the H2 20 pace around 1.6%-1.7%.
Real sector data for March will surge. The much stronger than expected auto sales suggest a jump in retail sales, which account for a bit more than 40% of overall personal consumption expenditures. Core retail sales, which exclude auto, gasoline, building materials, and food services, are expected to soar by 5.5%, says the Bloomberg survey's median forecast, helped by the second check from the federal government in the past four months.
Less than an hour after the retail sales report, March industrial output figures will be released. A rise of almost 3% is expected after a 2.2% decline in March. It may be the strongest since last July. The shortage of semiconductor chips could begin stunting the recovery of auto production. GM, for example, announced last week it was reducing more production at North American plants due to the lack of sufficient chips. It warned that this bottleneck could shave operating profits this year by $1.5-$2.0 bln. Ford also indicated it would be idling more plants but is planning on making it up in the summer.
Meanwhile, and few in the American press are drawing the connection, but US sanctions against Huawei (the largest Chinese consumer of chips) and SMIC (China's leading chip manufacturer) exacerbates the industry strains. Export controls were imposed last week on three other Chinese semiconductor firms (seven entities in all) for helping develop a supercomputer in China that has military as well as civilian applications. The Biden administration hosts a public/private summit on the chip shortage at the start of the new week. As TSMC and Intel have shown, even if for different reasons, staying at the cutting edge of chip fabrication is not a one-time expense but a heavy and continuous significant investment.
Capacity utilization rates are expected to jump after the weather-induced decline in February. The utilization rate, which fell to almost 64% last April and May, has seen a V-shaped recovery. The capacity utilization rate peaked in January at 75.4% and is expected to make a new post-crash high in March. Bloomberg's survey median forecast is for it to rise to 75.7%. The 10- and 20-year average rates converge around 76.5%. It raises questions about the ability to invest the $2.8 trillion of stimulus that has been approved in December 2020 and March 2021. If not, rising prices will allocate the scarcity.
The week's real sector data reports will conclude on April 16 with a jump in housing starts. Of course, starts were initially paralyzed in the early days of the pandemic and collapsed to five-year lows last April but surged in the remainder of the year and finished 2020 at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1.67 mln, the strongest since 2006. Starts fell by more than 15% in the first two months of the year, mostly due to abysmal weather. That pushed February starts to a 1.42 mln unit pace, the slowest since last August. The median forecast (Bloomberg survey) calls for a nearly 14% increase. Such an increase would lift March starts to a 1.61 mln unit pace, which would be the second-best since last year's trough behind December.
The market reaction to the news will be an important reflection of psychology and position. The dollar edged only a little higher after the stronger than expected employment data. While the 10-year yield rose, it gave it all back and more in the sessions that followed. There has been a pullback in the dollar and yields that suggest positioning was also adjusted, at least on the margins. Also, after a couple weeks' hiatus, the US Treasury is selling $110 bln of coupons next week. If the dollar cannot rally or yields do not rise, more participants may conclude that the divergence theme has been fully discounted.
Disclaimer
real estate pandemic us dollar cryptoUncategorized
Economic Earthquake Ahead? The Cracks Are Spreading Fast
Economic Earthquake Ahead? The Cracks Are Spreading Fast
Authored by Brandon Smith via Alt-Market.us,
One of my favorite false narratives…

Authored by Brandon Smith via Alt-Market.us,
One of my favorite false narratives floating around corporate media platforms has been the argument that the American people “just don’t seem to understand how good the economy really is right now.” If only they would look at the stats, they would realize that we are in the middle of a financial renaissance, right? It must be that people have been brainwashed by negative press from conservative sources…
I have to laugh at this notion because it’s a very common one throughout history – it’s an assertion made by almost every single political regime right before a major collapse. These people always say the same things, and when you study economics as long as I have you can’t help but throw up your hands and marvel at their dedication to the propaganda.
One example that comes to mind immediately is the delusional optimism of the “roaring” 1920s and the lead up to the Great Depression. At the time around 60% of the U.S. population was living in poverty conditions (according to the metrics of the decade) earning less than $2000 a year. However, in the years after WWI ravaged Europe, America’s economic power was considered unrivaled.
The 1920s was an era of mass production and rampant consumerism but it was all fueled by easy access to debt, a condition which had not really existed before in America. It was this illusion of prosperity created by the unchecked application of credit that eventually led to the massive stock market bubble and the crash of 1929. This implosion, along with the Federal Reserve’s policy of raising interest rates into economic weakness, created a black hole in the U.S. financial system for over a decade.
There are two primary tools that various failing regimes will often use to distort the true conditions of the economy: Debt and inflation. In the case of America today, we are experiencing BOTH problems simultaneously and this has made certain economic indicators appear healthy when they are, in fact, highly unstable. The average American knows this is the case because they see the effects everyday. They see the damage to their wallets, to their buying power, in the jobs market and in their quality of life. This is why public faith in the economy has been stuck in the dregs since 2021.
The establishment can flash out-of-context stats in people’s faces, but they can’t force the populace to see a recovery that simply does not exist. Let’s go through a short list of the most faulty indicators and the real reasons why the fiscal picture is not a rosy as the media would like us to believe…
The “miracle” labor market recovery
In the case of the U.S. labor market, we have a clear example of distortion through inflation. The $8 trillion+ dropped on the economy in the first 18 months of the pandemic response sent the system over the edge into stagflation land. Helicopter money has a habit of doing two things very well: Blowing up a bubble in stock markets and blowing up a bubble in retail. Hence, the massive rush by Americans to go out and buy, followed by the sudden labor shortage and the race to hire (mostly for low wage part-time jobs).
The problem with this “miracle” is that inflation leads to price explosions, which we have already experienced. The average American is spending around 30% more for goods, services and housing compared to what they were spending in 2020. This is what happens when you have too much money chasing too few goods and limited production.
The jobs market looks great on paper, but the majority of jobs generated in the past few years are jobs that returned after the covid lockdowns ended. The rest are jobs created through monetary stimulus and the artificial retail rush. Part time low wage service sector jobs are not going to keep the country rolling for very long in a stagflation environment. The question is, what happens now that the stimulus punch bowl has been removed?
Just as we witnessed in the 1920s, Americans have turned to debt to make up for higher prices and stagnant wages by maxing out their credit cards. With the central bank keeping interest rates high, the credit safety net will soon falter. This condition also goes for businesses; the same businesses that will jump headlong into mass layoffs when they realize the party is over. It happened during the Great Depression and it will happen again today.
Cracks in the foundation
We saw cracks in the narrative of the financial structure in 2023 with the banking crisis, and without the Federal Reserve backstop policy many more small and medium banks would have dropped dead. The weakness of U.S. banks is offset by the relative strength of the U.S. dollar, which lures in foreign investors hoping to protect their wealth using dollar denominated assets.
But something is amiss. Gold and bitcoin have rocketed higher along with economically sensitive assets and the dollar. This is the opposite of what’s supposed to happen. Gold and BTC are supposed to be hedges against a weak dollar and a weak economy, right? If global faith in the dollar and in the U.S. economy is so high, why are investors diving into protective assets like gold?
Again, as noted above, inflation distorts everything.
Tens of trillions of extra dollars printed by the Fed are floating around and it’s no surprise that much of that cash is flooding into the economy which simply pushes higher right along with prices on the shelf. But, gold and bitcoin are telling us a more honest story about what’s really happening.
Right now, the U.S. government is adding around $600 billion per month to the national debt as the Fed holds rates higher to fight inflation. This debt is going to crush America’s financial standing for global investors who will eventually ask HOW the U.S. is going to handle that growing millstone? As I predicted years ago, the Fed has created a perfect Catch-22 scenario in which the U.S. must either return to rampant inflation, or, face a debt crisis. In either case, U.S. dollar-denominated assets will lose their appeal and their prices will plummet.
“Healthy” GDP is a complete farce
GDP is the most common out-of-context stat used by governments to convince the citizenry that all is well. It is yet another stat that is entirely manipulated by inflation. It is also manipulated by the way in which modern governments define “economic activity.”
GDP is primarily driven by spending. Meaning, the higher inflation goes, the higher prices go, and the higher GDP climbs (to a point). Eventually prices go too high, credit cards tap out and spending ceases. But, for a short time inflation makes GDP (as well as retail sales) look good.
Another factor that creates a bubble is the fact that government spending is actually included in the calculation of GDP. That’s right, every dollar of your tax money that the government wastes helps the establishment by propping up GDP numbers. This is why government spending increases will never stop – It’s too valuable for them to spend as a way to make the economy appear healthier than it is.
The REAL economy is eclipsing the fake economy
The bottom line is that Americans used to be able to ignore the warning signs because their bank accounts were not being directly affected. This is over. Now, every person in the country is dealing with a massive decline in buying power and higher prices across the board on everything – from food and fuel to housing and financial assets alike. Even the wealthy are seeing a compression to their profit and many are struggling to keep their businesses in the black.
The unfortunate truth is that the elections of 2024 will probably be the turning point at which the whole edifice comes tumbling down. Even if the public votes for change, the system is already broken and cannot be repaired without a complete overhaul.
We have consistently avoided taking our medicine and our disease has gotten worse and worse.
People have lost faith in the economy because they have not faced this kind of uncertainty since the 1930s. Even the stagflation crisis of the 1970s will likely pale in comparison to what is about to happen. On the bright side, at least a large number of Americans are aware of the threat, as opposed to the 1920s when the vast majority of people were utterly conned by the government, the banks and the media into thinking all was well. Knowing is the first step to preparing.
The second step is securing your own financial future – that’s where physical precious metals can play a role. Diversifying your savings with inflation-resistant, uninflatable assets whose intrinsic value doesn’t rely on a counterparty’s promise to pay adds resilience to your savings. That’s the main reason physical gold and silver have been the safe haven store-of-value assets of choice for centuries (among both the elite and the everyday citizen).
* * *
As the world moves away from dollars and toward Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), is your 401(k) or IRA really safe? A smart and conservative move is to diversify into a physical gold IRA. That way your savings will be in something solid and enduring. Get your FREE info kit on Gold IRAs from Birch Gold Group. No strings attached, just peace of mind. Click here to secure your future today.
Uncategorized
Wendy’s teases new $3 offer for upcoming holiday
The Daylight Savings Time promotion slashes prices on breakfast.

Daylight Savings Time, or the practice of advancing clocks an hour in the spring to maximize natural daylight, is a controversial practice because of the way it leaves many feeling off-sync and tired on the second Sunday in March when the change is made and one has one less hour to sleep in.
Despite annual "Abolish Daylight Savings Time" think pieces and online arguments that crop up with unwavering regularity, Daylight Savings in North America begins on March 10 this year.
Related: Coca-Cola has a new soda for Diet Coke fans
Tapping into some people's very vocal dislike of Daylight Savings Time, fast-food chain Wendy's (WEN) is launching a daylight savings promotion that is jokingly designed to make losing an hour of sleep less painful and encourage fans to order breakfast anyway.
Image source: Wendy's.
Promotion wants you to compensate for lost sleep with cheaper breakfast
As it is also meant to drive traffic to the Wendy's app, the promotion allows anyone who makes a purchase of $3 or more through the platform to get a free hot coffee, cold coffee or Frosty Cream Cold Brew.
More Food + Dining:
- Taco Bell menu tries new take on an American classic
- McDonald's menu goes big, brings back fan favorites (with a catch)
- The 10 best food stocks to buy now
Available during the Wendy's breakfast hours of 6 a.m. and 10:30 a.m. (which, naturally, will feel even earlier due to Daylight Savings), the deal also allows customers to buy any of its breakfast sandwiches for $3. Items like the Sausage, Egg and Cheese Biscuit, Breakfast Baconator and Maple Bacon Chicken Croissant normally range in price between $4.50 and $7.
The choice of the latter is quite wide since, in the years following the pandemic, Wendy's has made a concerted effort to expand its breakfast menu with a range of new sandwiches with egg in them and sweet items such as the French Toast Sticks. The goal was both to stand out from competitors with a wider breakfast menu and increase traffic to its stores during early-morning hours.
Wendy's deal comes after controversy over 'dynamic pricing'
But last month, the chain known for the square shape of its burger patties ignited controversy after saying that it wanted to introduce "dynamic pricing" in which the cost of many of the items on its menu will vary depending on the time of day. In an earnings call, chief executive Kirk Tanner said that electronic billboards would allow restaurants to display various deals and promotions during slower times in the early morning and late at night.
Outcry was swift and Wendy's ended up walking back its plans with words that they were "misconstrued" as an intent to surge prices during its most popular periods.
While the company issued a statement saying that any changes were meant as "discounts and value offers" during quiet periods rather than raised prices during busy ones, the reputational damage was already done since many saw the clarification as another way to obfuscate its pricing model.
"We said these menuboards would give us more flexibility to change the display of featured items," Wendy's said in its statement. "This was misconstrued in some media reports as an intent to raise prices when demand is highest at our restaurants."
The Daylight Savings Time promotion, in turn, is also a way to demonstrate the kinds of deals Wendy's wants to promote in its stores without putting up full-sized advertising or posters for what is only relevant for a few days.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemicUncategorized
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In Recent History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Inside The Most Ridiculous Jobs Report In Recent History: Record 1.2 Million Immigrant Jobs Added In One Month
Last month we though that the…
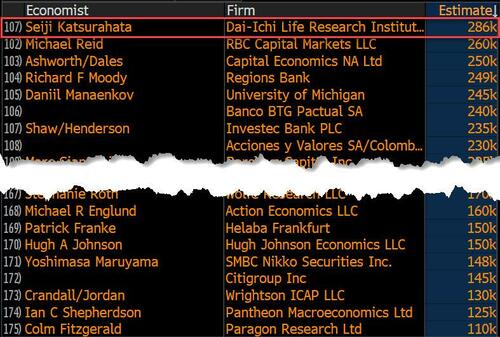
Last month we though that the January jobs report was the "most ridiculous in recent history" but, boy, were we wrong because this morning the Biden department of goalseeked propaganda (aka BLS) published the February jobs report, and holy crap was that something else. Even Goebbels would blush.
What happened? Let's take a closer look.
On the surface, it was (almost) another blockbuster jobs report, certainly one which nobody expected, or rather just one bank out of 76 expected. Starting at the top, the BLS reported that in February the US unexpectedly added 275K jobs, with just one research analyst (from Dai-Ichi Research) expecting a higher number.
Some context: after last month's record 4-sigma beat, today's print was "only" 3 sigma higher than estimates. Needless to say, two multiple sigma beats in a row used to only happen in the USSR... and now in the US, apparently.
Before we go any further, a quick note on what last month we said was "the most ridiculous jobs report in recent history": it appears the BLS read our comments and decided to stop beclowing itself. It did that by slashing last month's ridiculous print by over a third, and revising what was originally reported as a massive 353K beat to just 229K, a 124K revision, which was the biggest one-month negative revision in two years!
Of course, that does not mean that this month's jobs print won't be revised lower: it will be, and not just that month but every other month until the November election because that's the only tool left in the Biden admin's box: pretend the economic and jobs are strong, then revise them sharply lower the next month, something we pointed out first last summer and which has not failed to disappoint once.
In the past month the Biden department of goalseeking stuff higher before revising it lower, has revised the following data sharply lower:
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) August 30, 2023
- Jobs
- JOLTS
- New Home sales
- Housing Starts and Permits
- Industrial Production
- PCE and core PCE
To be fair, not every aspect of the jobs report was stellar (after all, the BLS had to give it some vague credibility). Take the unemployment rate, after flatlining between 3.4% and 3.8% for two years - and thus denying expectations from Sahm's Rule that a recession may have already started - in February the unemployment rate unexpectedly jumped to 3.9%, the highest since February 2022 (with Black unemployment spiking by 0.3% to 5.6%, an indicator which the Biden admin will quickly slam as widespread economic racism or something).
And then there were average hourly earnings, which after surging 0.6% MoM in January (since revised to 0.5%) and spooking markets that wage growth is so hot, the Fed will have no choice but to delay cuts, in February the number tumbled to just 0.1%, the lowest in two years...
... for one simple reason: last month's average wage surge had nothing to do with actual wages, and everything to do with the BLS estimate of hours worked (which is the denominator in the average wage calculation) which last month tumbled to just 34.1 (we were led to believe) the lowest since the covid pandemic...
... but has since been revised higher while the February print rose even more, to 34.3, hence why the latest average wage data was once again a product not of wages going up, but of how long Americans worked in any weekly period, in this case higher from 34.1 to 34.3, an increase which has a major impact on the average calculation.
While the above data points were examples of some latent weakness in the latest report, perhaps meant to give it a sheen of veracity, it was everything else in the report that was a problem starting with the BLS's latest choice of seasonal adjustments (after last month's wholesale revision), which have gone from merely laughable to full clownshow, as the following comparison between the monthly change in BLS and ADP payrolls shows. The trend is clear: the Biden admin numbers are now clearly rising even as the impartial ADP (which directly logs employment numbers at the company level and is far more accurate), shows an accelerating slowdown.
But it's more than just the Biden admin hanging its "success" on seasonal adjustments: when one digs deeper inside the jobs report, all sorts of ugly things emerge... such as the growing unprecedented divergence between the Establishment (payrolls) survey and much more accurate Household (actual employment) survey. To wit, while in January the BLS claims 275K payrolls were added, the Household survey found that the number of actually employed workers dropped for the third straight month (and 4 in the past 5), this time by 184K (from 161.152K to 160.968K).
This means that while the Payrolls series hits new all time highs every month since December 2020 (when according to the BLS the US had its last month of payrolls losses), the level of Employment has not budged in the past year. Worse, as shown in the chart below, such a gaping divergence has opened between the two series in the past 4 years, that the number of Employed workers would need to soar by 9 million (!) to catch up to what Payrolls claims is the employment situation.
There's more: shifting from a quantitative to a qualitative assessment, reveals just how ugly the composition of "new jobs" has been. Consider this: the BLS reports that in February 2024, the US had 132.9 million full-time jobs and 27.9 million part-time jobs. Well, that's great... until you look back one year and find that in February 2023 the US had 133.2 million full-time jobs, or more than it does one year later! And yes, all the job growth since then has been in part-time jobs, which have increased by 921K since February 2023 (from 27.020 million to 27.941 million).
Here is a summary of the labor composition in the past year: all the new jobs have been part-time jobs!
But wait there's even more, because now that the primary season is over and we enter the heart of election season and political talking points will be thrown around left and right, especially in the context of the immigration crisis created intentionally by the Biden administration which is hoping to import millions of new Democratic voters (maybe the US can hold the presidential election in Honduras or Guatemala, after all it is their citizens that will be illegally casting the key votes in November), what we find is that in February, the number of native-born workers tumbled again, sliding by a massive 560K to just 129.807 million. Add to this the December data, and we get a near-record 2.4 million plunge in native-born workers in just the past 3 months (only the covid crash was worse)!
The offset? A record 1.2 million foreign-born (read immigrants, both legal and illegal but mostly illegal) workers added in February!
Said otherwise, not only has all job creation in the past 6 years has been exclusively for foreign-born workers...

... but there has been zero job-creation for native born workers since June 2018!
This is a huge issue - especially at a time of an illegal alien flood at the southwest border...
... and is about to become a huge political scandal, because once the inevitable recession finally hits, there will be millions of furious unemployed Americans demanding a more accurate explanation for what happened - i.e., the illegal immigration floodgates that were opened by the Biden admin.
Which is also why Biden's handlers will do everything in their power to insure there is no official recession before November... and why after the election is over, all economic hell will finally break loose. Until then, however, expect the jobs numbers to get even more ridiculous.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 hours ago
International7 hours agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International1 month ago
International1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex








































