Uncategorized
The End Of Moral Hazard And The Dollar’s Debasement
The End Of Moral Hazard And The Dollar’s Debasement
Authored by Simon White, Bloomberg macro strategist,
A full guarantee of all bank deposits…
Authored by Simon White, Bloomberg macro strategist,
A full guarantee of all bank deposits would spell the end of moral hazard and mark the final chapter of the dollar’s multi-decade debasement.
It’s said the cover-up is worse than the crime. With the latest banking crisis in the US, it’s the clean-up that could end up doing far more lasting damage. The failure of SVB et al prompted the FDIC to guarantee that all depositors will be made whole, whether insured or not.
The precedent is being set, with Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen commenting on Tuesday that the US could repeat its actions if other banks became imperiled. She was referring to smaller lenders, and denied the next day that insurance would be “blanket”, but given the regulatory direction of travel over the last forty years, this will inevitability apply to any lender when push comes to shove.
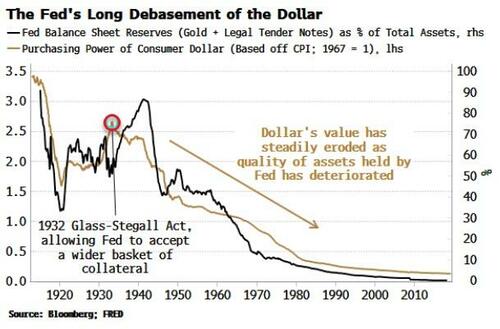
This marks the end of moral hazard and, ultimately, the final desecration of the Fed’s balance sheet.
The dollar is a liability of the central bank; therefore, this would mean further erosion of its real value, compounding the decimation of its purchasing power seen over the last century.
The 1932 Glass-Stegall Act was the beginning of the end, allowing the Fed to accept a wider basket of collateral it could lend against: riskier assets such as longer-term Treasury securities. The falling quality of collateral has continued, with the Fed lending against corporate debt in recent years.
The end result is the Fed’s balance sheet has steadily deteriorated, and with it the real value of the dollar.
A de facto expansion of insurance to all deposits will lead to a further erosion in the Fed’s balance sheet. Why? Firstly, note that deposit-insurance schemes typically lead to less, not more, bank stability.
Several studies have shown that countries with deposit-insurance schemes tend to see more bank failures. The more generous the scheme, the greater the instability.
Source: Columbia University
Moral hazard instills discipline in depositors as they pay attention to the bank’s credit risk (something many depositors in SVB signally failed to do.) It also imposes discipline on banks, incentivizing them to structure their cash flows so that they match through all time, thus mitigating the risk of bank runs (cue SVB again).
Why, then, would greater banking instability lead to a further deterioration in the Fed’s balance sheet? It comes down to how US banking has evolved over the last century.
Banks must manage cash flows from assets and liabilities, and their preference is to minimize their cash position each night in order to maximize the productive use of their capital. There is always a “position making” instrument, a liquid asset that banks can use to park excess cash or make up for shortfalls each day.
In the early days of the Federal Reserve system it was commercial loans and USTs; now it is principally the repo market. A bank can “make position” if it can repo in or repo out securities for funds. But if the market for that collateral freezes up, they’re dead.
This is where the Fed steps in - but as the “dealer of last resort” rather than the lender of last resort.
To ensure market liquidity, the Fed must underwrite funding liquidity. And to do that it must be willing to accept as collateral whatever the banking sector’s position-making instruments are. If it doesn’t, the game’s up.
SVB happened to have a high proportion of USTs and mortgage-backed securities on its balance sheet, making the Fed’s life easy in creating the BTFP (Bank Term Funding Program), which accepts government and government-backed collateral. But this does not get to the heart of the problem. Only a fifth of small banks’ assets are currently shiftable on to the Fed’s balance - less than for larger lenders — leaving them considerably exposed.
Deposit insurance only mitigates banks’ vulnerability to bank runs; it does not insulate them from liquidity or insolvency risk. SVB et al are very likely not the only fragile US banks, and as the economy slows, asset prices fall and delinquencies and bankruptcies rise, we are likely to see more banks needing support.
The logical outcome is that the Fed will have to increasingly accept poorer quality collateral — especially from smaller banks, with their large exposure to residential and commercial real estate. We have been here before, when during the pandemic the Fed began to accept the corporate debt of even junk-rated companies.
Minsky himself stressed the centrality of banking to financial stability, noting that imprudent banks (read: operating without moral hazard) are more likely to finance unproductive projects, which then leads to inflation.
So there we have it. Inflation and a further debasement of the Fed’s balance sheet.
With an abnegation of moral hazard, the long-term value of the dollar doesn’t stand a chance.
Uncategorized
One city held a mass passport-getting event
A New Orleans congressman organized a way for people to apply for their passports en masse.

While the number of Americans who do not have a passport has dropped steadily from more than 80% in 1990 to just over 50% now, a lack of knowledge around passport requirements still keeps a significant portion of the population away from international travel.
Over the four years that passed since the start of covid-19, passport offices have also been dealing with significant backlog due to the high numbers of people who were looking to get a passport post-pandemic.
Related: Here is why it is (still) taking forever to get a passport
To deal with these concurrent issues, the U.S. State Department recently held a mass passport-getting event in the city of New Orleans. Called the "Passport Acceptance Event," the gathering was held at a local auditorium and invited residents of Louisiana’s 2nd Congressional District to complete a passport application on-site with the help of staff and government workers.
'Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required'
"Hey #LA02," Rep. Troy A. Carter Sr. (D-LA), whose office co-hosted the event alongside the city of New Orleans, wrote to his followers on Instagram (META) . "My office is providing passport services at our #PassportAcceptance event. Come apply for your passport, no appointment is required."
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
The event was held on March 14 from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. While it was designed for those who are already eligible for U.S. citizenship rather than as a way to help non-citizens with immigration questions, it helped those completing the application for the first time fill out forms and make sure they have the photographs and identity documents they need. The passport offices in New Orleans where one would normally have to bring already-completed forms have also been dealing with lines and would require one to book spots weeks in advance.
These are the countries with the highest-ranking passports in 2024
According to Carter Sr.'s communications team, those who submitted their passport application at the event also received expedited processing of two to three weeks (according to the State Department's website, times for regular processing are currently six to eight weeks).
While Carter Sr.'s office has not released the numbers of people who applied for a passport on March 14, photos from the event show that many took advantage of the opportunity to apply for a passport in a group setting and get expedited processing.
Every couple of months, a new ranking agency puts together a list of the most and least powerful passports in the world based on factors such as visa-free travel and opportunities for cross-border business.
In January, global citizenship and financial advisory firm Arton Capital identified United Arab Emirates as having the most powerful passport in 2024. While the United States topped the list of one such ranking in 2014, worsening relations with a number of countries as well as stricter immigration rules even as other countries have taken strides to create opportunities for investors and digital nomads caused the American passport to slip in recent years.
A UAE passport grants holders visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 180 of the world’s 198 countries (this calculation includes disputed territories such as Kosovo and Western Sahara) while Americans currently have the same access to 151 countries.
stocks pandemic covid-19 grantsUncategorized
Fast-food chain closes restaurants after Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Several major fast-food chains recently have struggled to keep restaurants open.

Competition in the fast-food space has been brutal as operators deal with inflation, consumers who are worried about the economy and their jobs and, in recent months, the falling cost of eating at home.
Add in that many fast-food chains took on more debt during the covid pandemic and that labor costs are rising, and you have a perfect storm of problems.
It's a situation where Restaurant Brands International (QSR) has suffered as much as any company.
Related: Wendy's menu drops a fan favorite item, adds something new
Three major Burger King franchise operators filed for bankruptcy in 2023, and the chain saw hundreds of stores close. It also saw multiple Popeyes franchisees move into bankruptcy, with dozens of locations closing.
RBI also stepped in and purchased one of its key franchisees.
"Carrols is the largest Burger King franchisee in the United States today, operating 1,022 Burger King restaurants in 23 states that generated approximately $1.8 billion of system sales during the 12 months ended Sept. 30, 2023," RBI said in a news release. Carrols also owns and operates 60 Popeyes restaurants in six states."
The multichain company made the move after two of its large franchisees, Premier Kings and Meridian, saw multiple locations not purchased when they reached auction after Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings. In that case, RBI bought select locations but allowed others to close.
Image source: Chen Jianli/Xinhua via Getty
Another fast-food chain faces bankruptcy problems
Bojangles may not be as big a name as Burger King or Popeye's, but it's a popular chain with more than 800 restaurants in eight states.
"Bojangles is a Carolina-born restaurant chain specializing in craveable Southern chicken, biscuits and tea made fresh daily from real recipes, and with a friendly smile," the chain says on its website. "Founded in 1977 as a single location in Charlotte, our beloved brand continues to grow nationwide."
Like RBI, Bojangles uses a franchise model, which makes it dependent on the financial health of its operators. The company ultimately saw all its Maryland locations close due to the financial situation of one of its franchisees.
Unlike. RBI, Bojangles is not public — it was taken private by Durational Capital Management LP and Jordan Co. in 2018 — which means the company does not disclose its financial information to the public.
That makes it hard to know whether overall softness for the brand contributed to the chain seeing its five Maryland locations after a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing.
Bojangles has a messy bankruptcy situation
Even though the locations still appear on the Bojangles website, they have been shuttered since late 2023. The locations were operated by Salim Kakakhail and Yavir Akbar Durranni. The partners operated under a variety of LLCs, including ABS Network, according to local news channel WUSA9.
The station reported that the owners face a state investigation over complaints of wage theft and fraudulent W2s. In November Durranni and ABS Network filed for bankruptcy in New Jersey, WUSA9 reported.
"Not only do former employees say these men owe them money, WUSA9 learned the former owners owe the state, too, and have over $69,000 in back property taxes."
Former employees also say that the restaurant would regularly purchase fried chicken from Popeyes and Safeway when it ran out in their stores, the station reported.
Bojangles sent the station a comment on the situation.
"The franchisee is no longer in the Bojangles system," the company said. "However, it is important to note in your coverage that franchisees are independent business owners who are licensed to operate a brand but have autonomy over many aspects of their business, including hiring employees and payroll responsibilities."
Kakakhail and Durranni did not respond to multiple requests for comment from WUSA9.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Industrial Production Increased 0.1% in February
From the Fed: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 p…
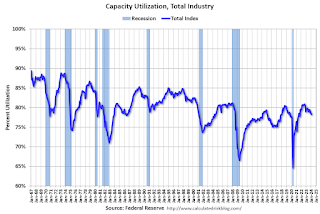
Industrial production edged up 0.1 percent in February after declining 0.5 percent in January. In February, the output of manufacturing rose 0.8 percent and the index for mining climbed 2.2 percent. Both gains partly reflected recoveries from weather-related declines in January. The index for utilities fell 7.5 percent in February because of warmer-than-typical temperatures. At 102.3 percent of its 2017 average, total industrial production in February was 0.2 percent below its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector remained at 78.3 percent in February, a rate that is 1.3 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2023) average.Click on graph for larger image.
emphasis added
This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up from the record low set in April 2020, and above the level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Capacity utilization at 78.3% is 1.3% below the average from 1972 to 2022. This was below consensus expectations.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production increased to 102.3. This is above the pre-pandemic level.
Industrial production was above consensus expectations.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment3 days ago
Spread & Containment3 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















