Government
SECURE Act 2.0. What Investors Need To Know.
As a small part of the recent omnibus bill, the SECURE Act 2.0 is now a reality. Investors need to know about H.R. 2954 and additional provisions to enhance…
As a small part of the recent omnibus bill, the SECURE Act 2.0 is now a reality. Investors need to know about H.R. 2954 and additional provisions to enhance retirement readiness. The SECURE Act 2.0 is the combination of three separate bills.
First, the bipartisan measure is a strong incentive for diligent savers and wealthier investors wrapped up in a bountiful bow for Wall Street and financial services firms.
Remember, over half of American households don’t or can’t save enough for retirement. The SECURE Act is like a shiny new car they can’t afford to drive.
As a result, several formidable changes are coming in 2023. Here’s what investors need to know about the SECURE Act 2.0.
Required Minimum Distributions get another overhaul.
RMDs are distributions that investors of a specific age must take from retirement accounts. For 2023, the newest legislation raises the RMD age to 73 and 75 beginning January 1, 2033.
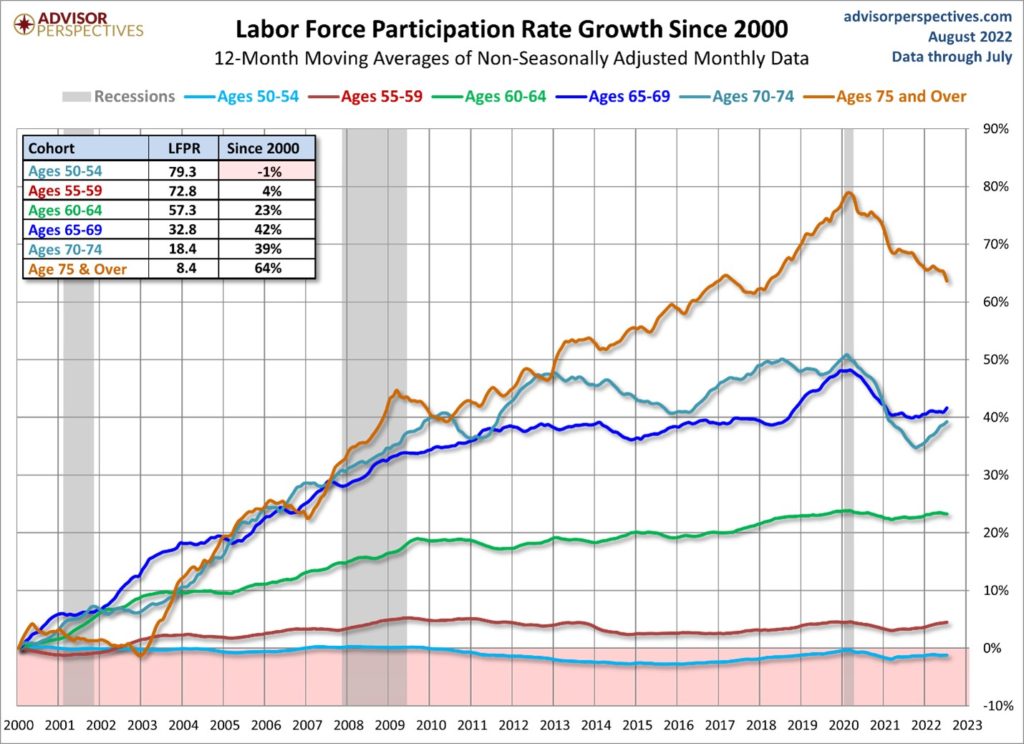
This change makes sense—sort of. Although Labor Force Participation has fallen since 2020, there’s no doubt long term that older workers remain in the workforce longer. I expect 60 and 70-somethings to continue working for several reasons, primarily due to longer life expectancies and inadequate retirement savings: A deadly combination.
So, for some, an RMD is a nuisance and unnecessary as distributions result in forced tax liability. But, according to IRA specialist and CPA Ed Slott, over 80% of people subject to RMDs withdraw more than the minimum because they need the money.
At RIA, our financial planning team advocates unconventional wisdom. In other words, investors should draw down their pre-tax retirement accounts before their RMD deadlines and convert the proceeds to Roth or deposit them in after-tax accounts for greater tax control throughout retirement.
Unfortunately, the bill does not clarify the ten-year rule for distributions from non-spousal IRAs inherited in 2020 and 2021. The IRS is waiving withdrawal penalties on non-spousal inherited IRAs until 2023. Click here to read. I expect the IRS to provide a formal ruling (hopefully) by mid-year.
Penalty relief for late RMDs.
Next, the onerous 50% excise tax for missing required minimum distributions is reduced to 25%, and if corrected promptly, the penalty is reduced to 10%. A correction window is defined as the period of time beginning when the tax is imposed concerning a shortfall from a retirement plan.
So, what is the window?
The earlier the date the IRS demands payment or the last day of the second taxable year that begins after the end of the taxable year in which the tax is imposed. For example, if you miss your RMD in 2023, you’ll have the earliest when notified, or December 31, 2024, to take the distribution.
The excise tax on excess contributions relief.
Also, it’s not uncommon to accidentally overcontribute to retirement accounts. Remember that a 6% excise tax is owed yearly as long as the excess remains in the account.
In the SECURE Act 2.0, a statute of limitations has been created. Taxpayers have three years from when a return would have been required to be filed, excluding extensions.
One-time election for Qualified Charitable Distributions to split-interest entities.
Qualified Charitable Distributions are popular for RMD retirees who look to donate directly to a qualified charity from their retirement accounts. Distributions cannot exceed $100,000 a year. The SECURE Act 2.0 allows a $50,000 one-time deductible contribution to fund a charitable remainder annuity or unitrust.
Retroactive first-year elective deferrals for sole proprietors.
For sole proprietors looking to establish Solo 401ks, they have until their tax filing deadlines (without extensions) to fund a plan. Previously, these retirement accounts required establishment and funding by December 31. Under the new rules, individual business owners have until their tax filing deadline in 2023 to establish and fund their Solo 401k accounts for 2022.
Retirement savings lost and found.
On average, workers change jobs six times during their lifetimes. I expect that multiplier to increase due to post-pandemic work trends. Along the way, they collect retirement accounts like Beanie Babies and forget they exist.
Also, in consultation with the Treasury Department, the Secretary of Labor will establish an online searchable database for forgotten or ‘lost’ retirement plans within two years. Account holders will be able to locate the plan administrators and contact information.
Expanding automatic enrollment in newly-establishment retirement plans.
Newly created 401k or 403b plans will require, during the first year of participation, no less than 3% and not more than 10% unless the participant specifically elects not to have such contributions made or select contributions at a different percentage. Businesses in existence for less than three years are exempt.
Modification of credit for small employer pension plan startup costs.
An employer with 50 employees or fewer is eligible for an enhanced tax credit for start-up plans beginning January 1, 2023. The credit will cover 100% of the startup costs of up to $5,000 for three years. Businesses with more than 50 employees will still receive tax credits subject to limitations based on dollars and a credit phase-in based on the number of employees exceeding 50.
Enhancement of Saver’s Credit.
To encourage retirement savings, the Act outlines a simple 50% refundable saver’s credit rate subject to AGI limitations and phaseouts. In the case of a joint return, the AGI threshold is $48,000, with a phaseout of full credit beginning at $35,000 for couples filing jointly. Single filers would phase out at AGIs over $24,000.
The Saver’s Credit threshold and phaseout amounts adjust for inflation after 2026. The enhancement to the Saver’s Credit applies to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2026.
Indexing IRA catch-up limit as part of the SECURE Act 2.0 – what investors need to know.
The $1,000 IRA catch-up limits for people aged 50 and over, indexed for inflation beginning in 2024. Catch-up contributions to retirement plans increase from $6,500 to $10,000 for eligible participants who would attain the ages 62, 63, 64, but not 65 before the close of 2023. Also, these catch-ups index for inflation.
Treatment of student loan payments as elective deferrals for purposes of matching contributions.
Student loan debt payments are 401(k), 403(b), or SIMPLE IRA employee deferrals and qualify for employer plan matching. As a result, an employee can qualify for matching contributions by making student loan payments and, at the same time, save for retirement, thanks to their employer.
Small immediate financial incentives for contributing to a plan.
Employers can use de minimis financial incentives as employee encouragement to contribute to retirement plans pursuant to a salary reduction agreement. To clarify, employers may use gift cards and cash as dangling fiscal carrots to encourage plan participation.
Improving coverage for part-time workers.
There’s an incentive for part-time workers to participate in company retirement accounts as the SECURE Act 2.0 reduces the service requirements for eligibility from three years to the first consecutive 24-month period.
Qualifying longevity annuity contacts. A crucial element of the SECURE Act 2.0 and what investors need to know.
Our RIA financial planners adhere to rules to help clients manage longevity risk. Most of our clients maximize Social Security retirement benefits for guaranteed income. We believe many retirees will require guaranteed income options to complement Social Security and traditional asset portfolios. Finally, the government is warming up to annuity contracts’ benefits (it’s a slow thaw).
Before the SECURE Act, the maximum premium could not exceed 25% of a retirement account balance or $125,000. Beginning in 2023, the percentage limitation is history, and the maximum premium raised to $200,000.
SIMPLE and SEP Roth IRA options.
Another ‘what the heck too so long?’ moment. Beginning in 2023, SIMPLE IRAs and SEP plan Roth options will be available.
Optional treatment of employer matching contributions as Roth contributions.
Above all, this one is big. Before SECURE Act 2.0, employer matching contributions were always pre-tax. With the SECURE Act 2.0, finally, matching contributions may also be Roth. Keep in mind that such contributions are not excludable from gross income.
Other notable provisions:
Emergency savings enhancements are a big change with the SECURE Act 2.0. and what investors need to know.
Plan participants can withdraw $1,000 yearly without early-withdrawal penalties and must repay in full within three years. Employees must wait another three full years to withdraw again unless paid off sooner. These annual withdrawals are subject to federal and state income taxes. In addition, employers may offer a ‘rainy-day’ account whereby employees contribute $2,500 a year and are allowed four penalty-free withdrawals per year.

Excess 529 contributions to Roth transfer.
Excess 529 contributions can roll over to Roth accounts beginning in 2024. However, there are specific rules and limitations to keep in mind.
Transfer restrictions include:
1. A lifetime transfer cap of $35,000.
2. Rollovers are subject to annual Roth IRA contribution limits ($6,500 in 2023).
3. 529 accounts must be open for 15 years.
4. Transfers may only be made to the beneficiary’s Roth IRA (usually a child).
Hardship withdrawal provisions.
Additional hardship withdrawal provisions are created for victims of domestic abuse, military members, and their spouses. For hardcore tax geeks, read the bill here.
There are several drawbacks to the SECURE Act 2.0. I outline a couple of them.
Greater opportunity for retirement plan leakage. A disappointing element of the SECURE Act 2.0. what investors need to know.
For instance, many workers treat retirement accounts like piggy banks because the government allows withdrawals for several reasons, including first-time home purchases. As a result, retirement plan leakage is a serious, ongoing concern.
Financial pundits must stop the zealous promotion of tax-deferred accounts and help the masses PRIORITIZE and PLAN how to save and invest. At RIA, we’ve established a savings hierarchy.
For example, the crucial first financial step is a financial vulnerability cushion (one year of living expenses in reserve, preferably an online, FDIC-insured online bank). For people who don’t have an emergency reserve, we recommend investing in their company retirement plan only up to the employer match.
RIA recommends increasing pre or post-tax retirement account contributions only after an FVC is funded. As a result, many young people we counsel do not need to tap long-term investment vehicles for emergencies or new homes.
A 2021 Joint Committee on Taxation report outlines how retirement accounts have more holes than Swiss cheese. Leakage occurs when an individual, 20 to 50 years old, takes defined contributions or IRA distributions that exceed contributions the individual makes to those accounts in the same year.
Per the report, leakage is estimated at roughly 22%. The SECURE Act may have its heart in the proper place with emergency saving account options. I approve of the withdrawal provisions for terminally ill patients and the expansion of Roth options. But it seems as if with each new Act, the mark is missed when it comes to leakage. At these times, defined benefits accounts or pensions are sorely missed. Zero leakage. Greater retirement success.
This brings me to my next beef.
America Deserves A Defined Benefit Plan Option For The Masses.
Regardless of its intent, the SECURE Act benefits the wealthiest of savers. And that’s ok – but there will still be millions of workers who lack adequate coverage.
What about a government and private sector alliance to create a national pension vehicle for all workers? In a recent Bloomberg Opinion piece, Teresa Ghilarducci, the Schwartz Professor of Economics at the New School for Social Research, outlines how a bipartisan retirement bill for universal coverage is on the table.
Subsequently, the Retirement Savings for Americans Act of 2022 (RSSA) is a true retirement plan concept that will be introduced in the new Congress. Workers without a plan would automatically enroll in a low-cost defined contribution plan at a 3% contribution rate. Covered workers would receive a match from the federal government. No pre-retirement distribution options would be offered, thus eliminating the danger of leakage.
Read Teresa’s latest opinion here.
In conclusion, the SECURE Act 2.0 is one of the most comprehensive retirement bills in recent history. However, there’s still much more to be done for workers not covered by employer plans.
Regardless, retirees, especially those nearing required distribution age, should work closely with their financial and tax partners to incorporate SECURE Act 2.0 changes into their planning.
Naturally, the five Certified Financial Planners at RIA are here to assist with the SECURE Act 2.0 and what investors need to know.
The post SECURE Act 2.0. What Investors Need To Know. appeared first on RIA.
irs pandemic congress treatmentGovernment
President Biden Delivers The “Darkest, Most Un-American Speech Given By A President”
President Biden Delivers The "Darkest, Most Un-American Speech Given By A President"
Having successfully raged, ranted, lied, and yelled through…

Having successfully raged, ranted, lied, and yelled through the State of The Union, President Biden can go back to his crypt now.
Whatever 'they' gave Biden, every American man, woman, and the other should be allowed to take it - though it seems the cocktail brings out 'dark Brandon'?
Tl;dw: Biden's Speech tonight ...
-
Fund Ukraine.
-
Trump is threat to democracy and America itself.
-
Abortion is good.
-
American Economy is stronger than ever.
-
Inflation wasn't Biden's fault.
-
Illegals are Americans too.
-
Republicans are responsible for the border crisis.
-
Trump is bad.
-
Biden stands with trans-children.
-
J6 was the worst insurrection since the Civil War.
(h/t @TCDMS99)
Tucker Carlson's response sums it all up perfectly:
"that was possibly the darkest, most un-American speech given by an American president. It wasn't a speech, it was a rant..."
Carlson continued: "The true measure of a nation's greatness lies within its capacity to control borders, yet Bid refuses to do it."
"In a fair election, Joe Biden cannot win"
And concluded:
“There was not a meaningful word for the entire duration about the things that actually matter to people who live here.”
Victor Davis Hanson added some excellent color, but this was probably the best line on Biden:
"he doesn't care... he lives in an alternative reality."
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) March 8, 2024
* * *
Watch SOTU Live here...
* * *
Mises' Connor O'Keeffe, warns: "Be on the Lookout for These Lies in Biden's State of the Union Address."
On Thursday evening, President Joe Biden is set to give his third State of the Union address. The political press has been buzzing with speculation over what the president will say. That speculation, however, is focused more on how Biden will perform, and which issues he will prioritize. Much of the speech is expected to be familiar.
The story Biden will tell about what he has done as president and where the country finds itself as a result will be the same dishonest story he's been telling since at least the summer.
He'll cite government statistics to say the economy is growing, unemployment is low, and inflation is down.
Something that has been frustrating Biden, his team, and his allies in the media is that the American people do not feel as economically well off as the official data says they are. Despite what the White House and establishment-friendly journalists say, the problem lies with the data, not the American people's ability to perceive their own well-being.
As I wrote back in January, the reason for the discrepancy is the lack of distinction made between private economic activity and government spending in the most frequently cited economic indicators. There is an important difference between the two:
-
Government, unlike any other entity in the economy, can simply take money and resources from others to spend on things and hire people. Whether or not the spending brings people value is irrelevant
-
It's the private sector that's responsible for producing goods and services that actually meet people's needs and wants. So, the private components of the economy have the most significant effect on people's economic well-being.
Recently, government spending and hiring has accounted for a larger than normal share of both economic activity and employment. This means the government is propping up these traditional measures, making the economy appear better than it actually is. Also, many of the jobs Biden and his allies take credit for creating will quickly go away once it becomes clear that consumers don't actually want whatever the government encouraged these companies to produce.
On top of all that, the administration is dealing with the consequences of their chosen inflation rhetoric.
Since its peak in the summer of 2022, the president's team has talked about inflation "coming back down," which can easily give the impression that it's prices that will eventually come back down.
But that's not what that phrase means. It would be more honest to say that price increases are slowing down.
Americans are finally waking up to the fact that the cost of living will not return to prepandemic levels, and they're not happy about it.
The president has made some clumsy attempts at damage control, such as a Super Bowl Sunday video attacking food companies for "shrinkflation"—selling smaller portions at the same price instead of simply raising prices.
In his speech Thursday, Biden is expected to play up his desire to crack down on the "corporate greed" he's blaming for high prices.
In the name of "bringing down costs for Americans," the administration wants to implement targeted price ceilings - something anyone who has taken even a single economics class could tell you does more harm than good. Biden would never place the blame for the dramatic price increases we've experienced during his term where it actually belongs—on all the government spending that he and President Donald Trump oversaw during the pandemic, funded by the creation of $6 trillion out of thin air - because that kind of spending is precisely what he hopes to kick back up in a second term.
If reelected, the president wants to "revive" parts of his so-called Build Back Better agenda, which he tried and failed to pass in his first year. That would bring a significant expansion of domestic spending. And Biden remains committed to the idea that Americans must be forced to continue funding the war in Ukraine. That's another topic Biden is expected to highlight in the State of the Union, likely accompanied by the lie that Ukraine spending is good for the American economy. It isn't.
It's not possible to predict all the ways President Biden will exaggerate, mislead, and outright lie in his speech on Thursday. But we can be sure of two things. The "state of the Union" is not as strong as Biden will say it is. And his policy ambitions risk making it much worse.
* * *
The American people will be tuning in on their smartphones, laptops, and televisions on Thursday evening to see if 'sloppy joe' 81-year-old President Joe Biden can coherently put together more than two sentences (even with a teleprompter) as he gives his third State of the Union in front of a divided Congress.
President Biden will speak on various topics to convince voters why he shouldn't be sent to a retirement home.
The state of our union under President Biden: three years of decline. pic.twitter.com/Da1KOIb3eR
— Speaker Mike Johnson (@SpeakerJohnson) March 7, 2024
According to CNN sources, here are some of the topics Biden will discuss tonight:
Economic issues: Biden and his team have been drafting a speech heavy on economic populism, aides said, with calls for higher taxes on corporations and the wealthy – an attempt to draw a sharp contrast with Republicans and their likely presidential nominee, Donald Trump.
Health care expenses: Biden will also push for lowering health care costs and discuss his efforts to go after drug manufacturers to lower the cost of prescription medications — all issues his advisers believe can help buoy what have been sagging economic approval ratings.
Israel's war with Hamas: Also looming large over Biden's primetime address is the ongoing Israel-Hamas war, which has consumed much of the president's time and attention over the past few months. The president's top national security advisers have been working around the clock to try to finalize a ceasefire-hostages release deal by Ramadan, the Muslim holy month that begins next week.
An argument for reelection: Aides view Thursday's speech as a critical opportunity for the president to tout his accomplishments in office and lay out his plans for another four years in the nation's top job. Even though viewership has declined over the years, the yearly speech reliably draws tens of millions of households.
Sources provided more color on Biden's SOTU address:
The speech is expected to be heavy on economic populism. The president will talk about raising taxes on corporations and the wealthy. He'll highlight efforts to cut costs for the American people, including pushing Congress to help make prescription drugs more affordable.
Biden will talk about the need to preserve democracy and freedom, a cornerstone of his re-election bid. That includes protecting and bolstering reproductive rights, an issue Democrats believe will energize voters in November. Biden is also expected to promote his unity agenda, a key feature of each of his addresses to Congress while in office.
Biden is also expected to give remarks on border security while the invasion of illegals has become one of the most heated topics among American voters. A majority of voters are frustrated with radical progressives in the White House facilitating the illegal migrant invasion.
It is probable that the president will attribute the failure of the Senate border bill to the Republicans, a claim many voters view as unfounded. This is because the White House has the option to issue an executive order to restore border security, yet opts not to do so
Maybe this is why?
Most Americans are still unaware that the census counts ALL people, including illegal immigrants, for deciding how many House seats each state gets!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 7, 2024
This results in Dem states getting roughly 20 more House seats, which is another strong incentive for them not to deport illegals.
While Biden addresses the nation, the Biden administration will be armed with a social media team to pump propaganda to at least 100 million Americans.
"The White House hosted about 70 creators, digital publishers, and influencers across three separate events" on Wednesday and Thursday, a White House official told CNN.
Not a very capable social media team...
The State of Confusion https://t.co/C31mHc5ABJ
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) March 7, 2024
The administration's move to ramp up social media operations comes as users on X are mostly free from government censorship with Elon Musk at the helm. This infuriates Democrats, who can no longer censor their political enemies on X.
Meanwhile, Democratic lawmakers tell Axios that the president's SOTU performance will be critical as he tries to dispel voter concerns about his elderly age. The address reached as many as 27 million people in 2023.
"We are all nervous," said one House Democrat, citing concerns about the president's "ability to speak without blowing things."
The SOTU address comes as Biden's polling data is in the dumps.
BetOnline has created several money-making opportunities for gamblers tonight, such as betting on what word Biden mentions the most.
As well as...
We will update you when Tucker Carlson's live feed of SOTU is published.
Fuck it. We’ll do it live! Thursday night, March 7, our live response to Joe Biden’s State of the Union speech. pic.twitter.com/V0UwOrgKvz
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) March 6, 2024
International
What is intersectionality and why does it make feminism more effective?
The social categories that we belong to shape our understanding of the world in different ways.

The way we talk about society and the people and structures in it is constantly changing. One term you may come across this International Women’s Day is “intersectionality”. And specifically, the concept of “intersectional feminism”.
Intersectionality refers to the fact that everyone is part of multiple social categories. These include gender, social class, sexuality, (dis)ability and racialisation (when people are divided into “racial” groups often based on skin colour or features).
These categories are not independent of each other, they intersect. This looks different for every person. For example, a black woman without a disability will have a different experience of society than a white woman without a disability – or a black woman with a disability.
An intersectional approach makes social policy more inclusive and just. Its value was evident in research during the pandemic, when it became clear that women from various groups, those who worked in caring jobs and who lived in crowded circumstances were much more likely to die from COVID.
A long-fought battle
American civil rights leader and scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw first introduced the term intersectionality in a 1989 paper. She argued that focusing on a single form of oppression (such as gender or race) perpetuated discrimination against black women, who are simultaneously subjected to both racism and sexism.
Crenshaw gave a name to ways of thinking and theorising that black and Latina feminists, as well as working-class and lesbian feminists, had argued for decades. The Combahee River Collective of black lesbians was groundbreaking in this work.
They called for strategic alliances with black men to oppose racism, white women to oppose sexism and lesbians to oppose homophobia. This was an example of how an intersectional understanding of identity and social power relations can create more opportunities for action.
These ideas have, through political struggle, come to be accepted in feminist thinking and women’s studies scholarship. An increasing number of feminists now use the term “intersectional feminism”.
The term has moved from academia to feminist activist and social justice circles and beyond in recent years. Its popularity and widespread use means it is subjected to much scrutiny and debate about how and when it should be employed. For example, some argue that it should always include attention to racism and racialisation.
Recognising more issues makes feminism more effective
In writing about intersectionality, Crenshaw argued that singular approaches to social categories made black women’s oppression invisible. Many black feminists have pointed out that white feminists frequently overlook how racial categories shape different women’s experiences.
One example is hair discrimination. It is only in the 2020s that many organisations in South Africa, the UK and US have recognised that it is discriminatory to regulate black women’s hairstyles in ways that render their natural hair unacceptable.
This is an intersectional approach. White women and most black men do not face the same discrimination and pressures to straighten their hair.

“Abortion on demand” in the 1970s and 1980s in the UK and USA took no account of the fact that black women in these and many other countries needed to campaign against being given abortions against their will. The fight for reproductive justice does not look the same for all women.
Similarly, the experiences of working-class women have frequently been rendered invisible in white, middle class feminist campaigns and writings. Intersectionality means that these issues are recognised and fought for in an inclusive and more powerful way.
In the 35 years since Crenshaw coined the term, feminist scholars have analysed how women are positioned in society, for example, as black, working-class, lesbian or colonial subjects. Intersectionality reminds us that fruitful discussions about discrimination and justice must acknowledge how these different categories affect each other and their associated power relations.
This does not mean that research and policy cannot focus predominantly on one social category, such as race, gender or social class. But it does mean that we cannot, and should not, understand those categories in isolation of each other.
Ann Phoenix does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
africa uk pandemicInternational
Biden defends immigration policy during State of the Union, blaming Republicans in Congress for refusing to act
A rising number of Americans say that immigration is the country’s biggest problem. Biden called for Congress to pass a bipartisan border and immigration…

President Joe Biden delivered the annual State of the Union address on March 7, 2024, casting a wide net on a range of major themes – the economy, abortion rights, threats to democracy, the wars in Gaza and Ukraine – that are preoccupying many Americans heading into the November presidential election.
The president also addressed massive increases in immigration at the southern border and the political battle in Congress over how to manage it. “We can fight about the border, or we can fix it. I’m ready to fix it,” Biden said.
But while Biden stressed that he wants to overcome political division and take action on immigration and the border, he cautioned that he will not “demonize immigrants,” as he said his predecessor, former President Donald Trump, does.
“I will not separate families. I will not ban people from America because of their faith,” Biden said.
Biden’s speech comes as a rising number of American voters say that immigration is the country’s biggest problem.
Immigration law scholar Jean Lantz Reisz answers four questions about why immigration has become a top issue for Americans, and the limits of presidential power when it comes to immigration and border security.

1. What is driving all of the attention and concern immigration is receiving?
The unprecedented number of undocumented migrants crossing the U.S.-Mexico border right now has drawn national concern to the U.S. immigration system and the president’s enforcement policies at the border.
Border security has always been part of the immigration debate about how to stop unlawful immigration.
But in this election, the immigration debate is also fueled by images of large groups of migrants crossing a river and crawling through barbed wire fences. There is also news of standoffs between Texas law enforcement and U.S. Border Patrol agents and cities like New York and Chicago struggling to handle the influx of arriving migrants.
Republicans blame Biden for not taking action on what they say is an “invasion” at the U.S. border. Democrats blame Republicans for refusing to pass laws that would give the president the power to stop the flow of migration at the border.
2. Are Biden’s immigration policies effective?
Confusion about immigration laws may be the reason people believe that Biden is not implementing effective policies at the border.
The U.S. passed a law in 1952 that gives any person arriving at the border or inside the U.S. the right to apply for asylum and the right to legally stay in the country, even if that person crossed the border illegally. That law has not changed.
Courts struck down many of former President Donald Trump’s policies that tried to limit immigration. Trump was able to lawfully deport migrants at the border without processing their asylum claims during the COVID-19 pandemic under a public health law called Title 42. Biden continued that policy until the legal justification for Title 42 – meaning the public health emergency – ended in 2023.
Republicans falsely attribute the surge in undocumented migration to the U.S. over the past three years to something they call Biden’s “open border” policy. There is no such policy.
Multiple factors are driving increased migration to the U.S.
More people are leaving dangerous or difficult situations in their countries, and some people have waited to migrate until after the COVID-19 pandemic ended. People who smuggle migrants are also spreading misinformation to migrants about the ability to enter and stay in the U.S.

3. How much power does the president have over immigration?
The president’s power regarding immigration is limited to enforcing existing immigration laws. But the president has broad authority over how to enforce those laws.
For example, the president can place every single immigrant unlawfully present in the U.S. in deportation proceedings. Because there is not enough money or employees at federal agencies and courts to accomplish that, the president will usually choose to prioritize the deportation of certain immigrants, like those who have committed serious and violent crimes in the U.S.
The federal agency Immigration and Customs Enforcement deported more than 142,000 immigrants from October 2022 through September 2023, double the number of people it deported the previous fiscal year.
But under current law, the president does not have the power to summarily expel migrants who say they are afraid of returning to their country. The law requires the president to process their claims for asylum.
Biden’s ability to enforce immigration law also depends on a budget approved by Congress. Without congressional approval, the president cannot spend money to build a wall, increase immigration detention facilities’ capacity or send more Border Patrol agents to process undocumented migrants entering the country.

4. How could Biden address the current immigration problems in this country?
In early 2024, Republicans in the Senate refused to pass a bill – developed by a bipartisan team of legislators – that would have made it harder to get asylum and given Biden the power to stop taking asylum applications when migrant crossings reached a certain number.
During his speech, Biden called this bill the “toughest set of border security reforms we’ve ever seen in this country.”
That bill would have also provided more federal money to help immigration agencies and courts quickly review more asylum claims and expedite the asylum process, which remains backlogged with millions of cases, Biden said. Biden said the bipartisan deal would also hire 1,500 more border security agents and officers, as well as 4,300 more asylum officers.
Removing this backlog in immigration courts could mean that some undocumented migrants, who now might wait six to eight years for an asylum hearing, would instead only wait six weeks, Biden said. That means it would be “highly unlikely” migrants would pay a large amount to be smuggled into the country, only to be “kicked out quickly,” Biden said.
“My Republican friends, you owe it to the American people to get this bill done. We need to act,” Biden said.
Biden’s remarks calling for Congress to pass the bill drew jeers from some in the audience. Biden quickly responded, saying that it was a bipartisan effort: “What are you against?” he asked.
Biden is now considering using section 212(f) of the Immigration and Nationality Act to get more control over immigration. This sweeping law allows the president to temporarily suspend or restrict the entry of all foreigners if their arrival is detrimental to the U.S.
This obscure law gained attention when Trump used it in January 2017 to implement a travel ban on foreigners from mainly Muslim countries. The Supreme Court upheld the travel ban in 2018.
Trump again also signed an executive order in April 2020 that blocked foreigners who were seeking lawful permanent residency from entering the country for 60 days, citing this same section of the Immigration and Nationality Act.
Biden did not mention any possible use of section 212(f) during his State of the Union speech. If the president uses this, it would likely be challenged in court. It is not clear that 212(f) would apply to people already in the U.S., and it conflicts with existing asylum law that gives people within the U.S. the right to seek asylum.
Jean Lantz Reisz does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
congress senate trump pandemic covid-19 mexico ukraine-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 Government1 month ago
Government1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges
























