Scorching, Blistering, Highest In A Decade! Powell’s The Voice of Reason Here?
If there is one thing Economists understand very well, it’s mathematics. This is practically all they do, and all that means much to their discipline. If there’s one thing Economists don’t seem either competent with or interested in, it’s the…
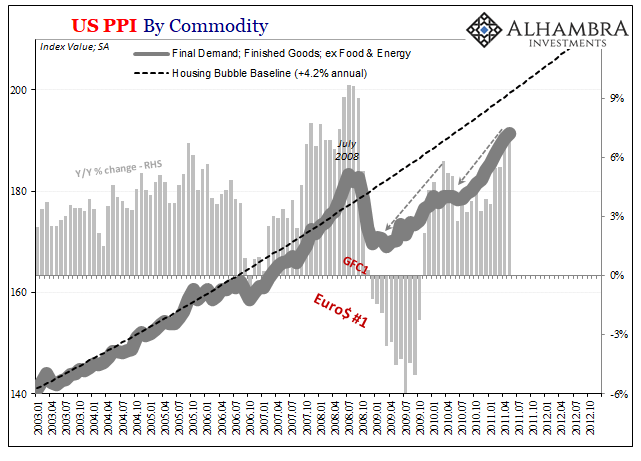
If there is one thing Economists understand very well, it’s mathematics. This is practically all they do, and all that means much to their discipline. If there’s one thing Economists don’t seem either competent with or interested in, it’s the economy. The math is supposed to match the other’s reality, yet rarely does.
There are times, however, when simple calculation is sufficient and (figuratively) on the money (literally, that is the whole other story).
Such was the case around 2011 and 2012. You might remember that period for exorbitant gasoline and food prices triggering FRBNY President Bill Dudley’s iPad debacle, or how restaurants began charging extra for extra napkins, of all things, as paper prices blew upward at a seemingly insane pace.
Both those things as well as other similar outcomes had led to the first of several inflation manias.
The inflation indices were howling, scorching hot according to nearly every Federal Reserve critic who had been “warning” that so much “money printing” could only come home to roost by robbing consumers of purchasing power. Ben Bernanke’s central bank policies – by then two massive QE’s – were sucking the remaining life out of the dollar and, they claimed, hoisting its carcass onto the economy in the form of grossly higher prices.
Bernanke and indeed many Economists took a more rational, appropriately mathematical approach. Understanding how these things work, certainly how they are measured, monetary officials here and elsewhere were suddenly resolute. Prices had gone up, sure, commodities most of all, though when compared to very low prices such as those produced during any deflationary period like the Great “Recession” the rebound from it would naturally come out sizable.
Base effects.
In early 2011, Chairman Bernanke, the guy whose reputation was riding on QE producing inflation, instead told everyone to take a step back and chill.
On the inflation front, we have recently seen significant increases in some highly visible prices, notably for gasoline. Indeed, prices of many commodities have risen lately, largely as a result of the very strong demand from fast-growing emerging market economies, coupled, in some cases, with constraints on supply. Nevertheless, overall inflation remains quite low.
A more subdued trend in prices, Bernanke said, is “not surprising given the substantial slack in the economy.”
Beyond those idiosyncrasies, there was no reason to believe that consumer prices would continue to rise at the rates given from the simple arithmetic of base effects. By April 2011, though the PPI (finished goods) was up 7% year-over-year in that month, a second base effect (below), as Bernanke said earlier in February there remained too much economic ground to cover for it to keep up.
He even used the word transitory in a speech later the same year, in September:
However, inflation is expected to moderate in the coming quarters as these transitory influences wane. In particular, the prices of oil and many other commodities have either leveled off or have come down from their highs.
And that is just what happened. Unlike many others – every other? – in the QE-is-money-printing camp, the Federal Reserve position was grounded by the facts. Consumer and producer prices were rebounding, but that alone didn’t nor wouldn’t settle the matter; rebounds unlike recovery – therefore true inflationary periods – don’t come so easily.


Now where he and Economists went wrong was in how they expected as the economy began to actually recover (remember, they came to believe recovery was being delayed), that’s when inflation pressures would lead to a more sustainable trend in consumer prices which would represented something other than base comparison mathematics.
In 2011, he really should have taken a harder look at exactly why oil and commodities had “leveled off or have come down from their highs.” Instead, never figuring out the whole false dawn mechanics (eurodollars), by 2015 his successor Janet Yellen started using “transitory” for the opposite way and got it all wrong (the disinflationary pressures which kept holding inflation down proved way beyond temporary).

Base effects are, by definition, transitory while any initial price rebound immediately following a deflationary burst (such as either 2009 or 2020), the very definition of reflation, will end up the same way – unless there’s more going on in the economy than those things.
There wasn’t following the Great “Recession” even if for reasons that officials are only recently beginning to explore in useful depth.
Slack is back in 2021, in big way, only nowadays it’s given a more reasonable interpretation (because this time they can blame COVID). Therefore, even Jay Powell is adopting the word transitory, too, except in this case he’s using the original Bernanke version (correctly) rather than the confused vocabulary of Yellen.
From last month:
If we do see what we believe is likely a transitory increase in inflation, where longer-term inflation expectations are broadly stable, I expect that we will be patient.
And that’s exactly what’s been shaping up even as the hysteria in the media, and among the same Fed critics, ramps up to eleven yet again. With PPI data in the US released today, and the finished goods index up a “scorching” 5.98%, the highest in a decade going all the way back to Bernanke’s September 2011 speech, the headlines blare INFLATION while market-based inflation indications shrug.
Base effects contributed much to the rate, as did commodity prices. It really is no different than the initial rebound (Reflation #1) following the Great “Recession.” And next month it will be worse; meaning the rates will be even higher given that they’ll compare to the ultimate lows set during April 2020, and so the rhetoric will certainly surpass them more than they already have for this month’s figures.


Like 2011 heading toward a very troubled 2012, the entire inflation case rests upon what comes next – real inflation is, after all, a sustained trend in consumer prices (and there’s no evidence yet producer prices are grossly distorting them). Even during this year’s reflationary bond sell-off from January to late February, it really wasn’t much of a shift in expectations, certainly nowhere near the hysterically described “historic” rout. In fact, the latest move in it is but a speck when compared to the one Bernanke got (partly) right.
Why is this one so underwhelming in every possible way?
Highest-in-a-decade PPI, blowout payrolls for the same month of March 2021, vaccines, a potential end to the pandemic and the responding governmental overreach, trillions upon trillions, WWII-style fiscal wreckage, all the QE and bank reserves anyone could imagine – and yet, hardly much. Even today, inflation expectations (TIPS breakevens) were down on the day and nominal UST’s were up no more than a market fluctuation.





The key to inflation actually isn’t even contained in the TIPS breakevens; no, a better place to look is real yields which get set based on perceptions of gross economic shortfalls and the like, and they continue to be nowhere near recovery from recovered slack.
Because when even the central bankers are saying “hey, hold on a minute”, that’s saying something. Far be it for me to grow comfortable agreeing with them, I can do the reflation math, too. As I’ve said before, as easy as it might be otherwise, let’s not get carried away here. For one thing, the whole bond market sure isn’t.
Government
Supreme Court Rules Public Officials May Block Their Constituents On Social Media
Supreme Court Rules Public Officials May Block Their Constituents On Social Media
Authored by Matthew Vadum via The Epoch Times (emphasis…

Authored by Matthew Vadum via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Public officials may block people on social media in certain situations, the Supreme Court ruled unanimously on March 15.
At the same time, the court held that public officials who post about topics pertaining to their work on their personal social media accounts are acting on behalf of the government. But such officials can be found liable for violating the First Amendment only when they have been properly authorized by the government to communicate on its behalf.
The case is important because nowadays public officials routinely reach out to voters through social media on the same pages where they discuss personal matters unrelated to government business.
“When a government official posts about job-related topics on social media, it can be difficult to tell whether the speech is official or private,” Justice Amy Coney Barrett wrote for the nation’s highest court.
The case is separate from but brings to mind a lawsuit that several individuals previously filed against former President Donald Trump after he blocked them from accessing his social media account on Twitter, which was later renamed X. The Supreme Court dismissed that case, Biden v. Knight First Amendment Institute, in April 2021 as moot because President Trump had already left office.
At the time of the ruling, the then-Twitter had banned President Trump. When Elon Musk took over the company he reversed that policy.
The new decision in Lindke v. Freed was written by Justice Amy Coney Barrett.
Respondent James Freed, the city manager of Port Huron, Michigan, used a public Facebook account to communicate with his constituents. Petitioner Kevin Lindke, a resident of Port Huron, criticized the municipality’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including accusations of hypocrisy by local officials.
Mr. Freed blocked Mr. Lindke and others and removed their comments, according to Mr. Lindke’s petition.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit ruled for Mr. Freed, finding that he was acting only in a personal capacity and that his activities did not constitute governmental action.
Mr. Freed’s attorney, Victoria Ferres, said during oral arguments before the Supreme Court on Oct. 31, 2023, that her client didn’t give up his rights when using social media.
“This country’s 21 million government employees should have the right to talk publicly about their jobs on personal social media accounts like their private-sector counterparts.”
The position advocated by the other side would unfairly punish government officials, and “will result in uncertainty and self-censorship for this country’s government employees despite this Court repeatedly finding that government employees do not lose their rights merely by virtue of public employment,” she said.
In Lindke v. Freed, the Supreme Court found that a public official who prevents a person from comments on the official’s social media pages engages in governmental action under Section 1983 only if the official had “actual authority” to speak on the government’s behalf on a specific matter and if the official claimed to exercise that authority when speaking in the relevant social media posts.
Section 1983 refers to Title 42, U.S. Code, Section 1983, which allows people to sue government actors for deprivation of civil rights.
Justice Barrett wrote that according to the so-called state action doctrine, the test for “actual authority” must be “rooted in written law or longstanding custom to speak for the State.”
“That authority must extend to speech of the sort that caused the alleged rights deprivation. If the plaintiff cannot make this threshold showing of authority, he cannot establish state action.”
“For social-media activity to constitute state action, an official must not only have state authority—he must also purport to use it,” the justice continued.
“State officials have a choice about the capacity in which they choose to speak.”
Citing previous precedent, Justice Barrett wrote that generally a public employee claiming to speak on behalf of the government acts with state authority when he speaks “in his official capacity or” when he uses his speech to carry out “his responsibilities pursuant to state law.”
“If the public employee does not use his speech in furtherance of his official responsibilities, he is speaking in his own voice.”
The Supreme Court remanded the case to the 6th Circuit with instructions to vacate its judgment and ordered it to conduct “further proceedings consistent with this opinion.”
Also on March 15, the Supreme Court ruled on O’Connor-Ratcliff v. Garnier, a related case. The court’s sparse, unanimous opinion was unsigned.
Petitioners Michelle O’Connor-Ratcliff and T.J. Zane were two elected members of the Poway Unified School District Board of Trustees in California who used their personal Facebook and Twitter accounts to communicate with the public.
Respondents Christopher Garnier and Kimberly Garnier, parents of local students, “spammed Petitioners’ posts and tweets with repetitive comments and replies” so the school board members blocked the respondents from the accounts, according to the petition filed by Ms. O’Connor-Ratcliff and Mr. Zane.
But the Garniers said they were acting in good faith.
“The Garniers left comments exposing financial mismanagement by the former superintendent as well as incidents of racism,” the couple said in a brief.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit found in favor of the Garniers, holding that elected officials using social media accounts were participating in a public forum.
The Supreme Court ruled in a three-page opinion that because the 9th Circuit deviated from the standard the high court articulated in Lindke v. Freed, the 9th Circuit’s decision must be vacated.
The case was remanded to the 9th Circuit “for further proceedings consistent with our opinion” in the Lindke case, the Supreme Court stated.
International
Home buyers must now navigate higher mortgage rates and prices
Rates under 4% came and went during the Covid pandemic, but home prices soared. Here’s what buyers and sellers face as the housing season ramps up.

Springtime is spreading across the country. You can see it as daffodil, camellia, tulip and other blossoms start to emerge.
You can also see it in the increasing number of for sale signs popping up in front of homes, along with the painting, gardening and general sprucing up as buyers get ready to sell.
Which leads to two questions:
- How is the real estate market this spring?
- Where are mortgage rates?
What buyers and sellers face
The housing market is bedeviled with supply shortages, high prices and slow sales.
Mortgage rates are still high and may limit what a buyer can offer and a seller can expect.
Related: Analyst warns that a TikTok ban could lead to major trouble for Apple, Big Tech
And there's a factor not expected that may affect the sales process. Fixed commission rates on home sales are going away in July.
Reports this week and in a week will make the situation clearer for buyers and sellers.
The reports are:
- Housing starts from the U.S. Commerce Department due Tuesday. The consensus estimate is for a seasonally adjusted rate of about 1.4 million homes. These would include apartments, both rentals and condominiums.
- Existing home sales, due Thursday from the National Association of Realtors. The consensus estimate is for a seasonally adjusted sales rate of about 4 million homes. In 2023, some 4.1 million homes were sold, the worst sales rate since 1995.
- New-home sales and prices, due Monday from the Commerce Department. Analysts are expecting a sales rate of 661,000 homes (including condos), up 1.5% from a year ago.
Here is what buyers and sellers need to know about the situation.
Mortgage rates will stay above 5%
That's what most analysts believe. Right now, the rate on a 30-year mortgage is between 6.7% and 7%.
Rates peaked at 8% in October after the Federal Reserve signaled it was done raising interest rates.
The Freddie Mac Primary Mortgage Market Survey of March 14 was at 6.74%.
Freddie Mac buys mortgages from lenders and sells securities to investors. The effect is to replenish lenders' cash levels to make more loans.
A hotter-than-expected Producer Price Index released that day has pushed quotes to 7% or higher, according to data from Mortgage News Daily, which tracks mortgage markets.
TheStreet
On a median-priced home (price: $380,000) and a 20% down payment, that means a principal and interest rate payment of $2,022. The payment does not include taxes and insurance.
Last fall when the 30-year rate hit 8%, the payment would have been $2,230.
In 2021, the average rate was 2.96%, which translated into a payment of $1,275.
Short of a depression, that's a rate that won't happen in most of our lifetimes.
Most economists believe current rates will fall to around 6.3% by the end of the year, maybe lower, depending on how many times the Federal Reserve cuts rates this year.
If 6%, the payment on our median-priced home is $1,823.
But under 5%, absent a nasty recession, fuhgettaboutit.
Supply will be tight, keeping prices up
Two factors are affecting the supply of homes for sale in just about every market.
First: Homeowners who had been able to land a mortgage at 2.96% are very reluctant to sell because they would then have to find a home they could afford with, probably, a higher-cost mortgage.
More economic news:
- Fed members just hat-tipped what's next for interest rates
- Retail sales tumble clouds impact of inflation data
- Jobs report shocker: 353,000 hires crush forecasts, stokes inflation fears
Second, the combination of high prices and high mortgage rates are freezing out thousands of potential buyers, especially those looking for homes in lower price ranges.
Indeed, The Wall Street Journal noted that online brokerage Redfin said only about 20% of homes for sale in February were affordable for the typical household.
And here mortgage rates can play one last nasty trick. If rates fall, that means a buyer can afford to pay more. Sellers and their real-estate agents know this too, and may ask for a higher price.
Covid's last laugh: An inflation surge
Mortgage rates jumped to 8% or higher because since 2022 the Federal Reserve has been fighting to knock inflation down to 2% a year. Raising interest rates was the ammunition to battle rising prices.
In June 2022, the consumer price index was 9.1% higher than a year earlier.
The causes of the worst inflation since the 1970s were:
- Covid-19 pandemic, which caused the global economy to shut down in 2020. When Covid ebbed and people got back to living their lives, getting global supply chains back to normal operation proved difficult.
- Oil prices jumped to record levels because of the recovery from the pandemic recovery and Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
What the changes in commissions means
The long-standing practice of paying real-estate agents will be retired this summer, after the National Association of Realtors settled a long and bitter legal fight.
No longer will the seller necessarily pay 6% of the sale price to split between buyer and seller agents.
Both sellers and buyers will have to negotiate separately the services agents have charged for 100 years or more. These include pre-screening properties, writing sales contracts, and the like. The change will continue a trend of adding costs and complications to the process of buying or selling a home.
Already, interest rates are a complication. In addition, homeowners insurance has become very pricey, especially in communities vulnerable to hurricanes, tornadoes, and forest fires. Florida homeowners have seen premiums jump more than 102% in the last three years. A policy now costs three times more than the national average.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
recession depression pandemic covid-19 stocks fed federal reserve home sales mortgage rates real estate mortgages housing market recovery interest rates oil russia ukraine
Uncategorized
Default: San Francisco Four Seasons Hotel Investors $3 Million Late On Loan As Foreclosure Looms
Default: San Francisco Four Seasons Hotel Investors $3 Million Late On Loan As Foreclosure Looms
Westbrook Partners, which acquired the San…

Westbrook Partners, which acquired the San Francisco Four Seasons luxury hotel building, has been served a notice of default, as the developer has failed to make its monthly loan payment since December, and is currently behind by more than $3 million, the San Francisco Business Times reports.
Westbrook, which acquired the property at 345 California Center in 2019, has 90 days to bring their account current with its lender or face foreclosure.
Related
- Fed Fears "Notable" Financial System Vulnerability As Renowned CRE Investor Tells Team 'Stop All NYC Underwriting'
- The State Of Commercial Real Estate, In Charts
- "Who Could Be Next": Top Canadian Pension Fund Sells Manhattan Office Tower For $1, Sparking Firesale Panic
- "Heightened Risks": Goldman Points To Leading CRE Indicator That Shows Pain Train Not Over
As SF Gate notes, downtown San Francisco hotel investors have had a terrible few years - with interest rates higher than their pre-pandemic levels, and local tourism continuing to suffer thanks to the city's legendary mismanagement that has resulted in overlapping drug, crime, and homelessness crises (which SF Gate characterizes as "a negative media narrative).
Last summer, the owner of San Francisco’s Hilton Union Square and Parc 55 hotels abandoned its loan in the first major default. Industry insiders speculate that loan defaults like this may become more common given the difficult period for investors.
At a visitor impact summit in August, a senior director of hospitality analytics for the CoStar Group reported that there are 22 active commercial mortgage-backed securities loans for hotels in San Francisco maturing in the next two years. Of these hotel loans, 17 are on CoStar’s “watchlist,” as they are at a higher risk of default, the analyst said. -SF Gate
The 155-room Four Seasons San Francisco at Embarcadero currenly occupies the top 11 floors of the iconic skyscrper. After slow renovations, the hotel officially reopened in the summer of 2021.
"Regarding the landscape of the hotel community in San Francisco, the short term is a challenging situation due to high interest rates, fewer guests compared to pre-pandemic and the relatively high costs attached with doing business here," Alex Bastian, President and CEO of the Hotel Council of San Francisco, told SFGATE.
Heightened Risks
In January, the owner of the Hilton Financial District at 750 Kearny St. - Portsmouth Square's affiliate Justice Operating Company - defaulted on the property, which had a $97 million loan on the 544-room hotel taken out in 2013. The company says it proposed a loan modification agreement which was under review by the servicer, LNR Partners.
Meanwhile last year Park Hotels & Resorts gave up ownership of two properties, Parc 55 and Hilton Union Square - which were transferred to a receiver that assumed management.
In the third quarter of 2023, the most recent data available, the Hilton Financial District reported $11.1 million in revenue, down from $12.3 million from the third quarter of 2022. The hotel had a net operating loss of $1.56 million in the most recent third quarter.
Occupancy fell to 88% with an average daily rate of $218 in the third quarter compared with 94% and $230 in the same period of 2022. -SF Chronicle
According to the Chronicle, San Francisco's 2024 convention calendar is lighter than it was last year - in part due to key events leaving the city for cheaper, less crime-ridden places like Las Vegas.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Spread & Containment5 days ago
Spread & Containment5 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex



















