Government
Scientists Instrumental To COVID-19 ‘Natural Origins’ Narrative Received Over $50 Million In NIAID Funding In 2020-2021
Scientists Instrumental To COVID-19 ‘Natural Origins’ Narrative Received Over $50 Million In NIAID Funding In 2020-2021
Authored by Jeff Carlson and Hans Mahncke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Four prominent scientists who played key..

Authored by Jeff Carlson and Hans Mahncke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Four prominent scientists who played key roles in shaping the public narrative around the origin of COVID-19 received substantial increases in grant money from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), headed by Dr. Anthony Fauci, in the subsequent two years, a review of funding data by The Epoch Times has found.
Three of these scientists—Kristian Andersen, Robert Garry, and Michael Farzan—were advisers to a teleconference organized by Fauci held on Feb. 1, 2020, in response to increasing public questions about the origin of the virus.
The scientists were also instrumental in the publication of Proximal Origin, a highly influential paper that promoted a natural origins theory for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and has been frequently cited by the government and media.
Emails released under Freedom of Information Act requests, showed that the scientists had told the senior members of Fauci’s teleconference that they were 60 to 80 percent sure that COVID-19 had come out of a lab.

Notably, despite their private concerns about the origin of the virus, the first draft of Proximal Origin was completed on the same day as the teleconference. Andersen and Garry were co-authors of Proximal Origin and Farzan was acknowledged in the Nature version of Proximal Origin for his participatory discussions in the article’s creation.
Additionally, Fauci’s NIAID provided a substantial increase in funding to EcoHealth’s Peter Daszak, through whom NIAID had funded controversial gain-of-function coronavirus research at the Wuhan Institute of Virology in China.
Some of these funding amounts have continued through 2021—and one of the newest grants will continue through at least 2025.
A significant portion of the funding increase for Daszak, as well as for Andersen and Garry, was provided through NIAID’s creation of the Centers for Research in Emerging Infectious Diseases (CREID).
The program, which was originally referred to as Emerging Infectious Diseases Research Centers (EIDRCs) during the early planning stages in 2019, was formally announced under a new name on Aug. 27, 2020. It is not known why the program was initially delayed or why it was renamed.
The new initiative, described as a global network that involves “multidisciplinary investigations into how and where viruses and other pathogens emerge from wildlife and spillover to cause disease in people,” provided eleven new grants totaling $17 million of new funding in the first year and $82 million in total funding across five years.

Andersen and Garry were the co-recipients of a new $8.9 million 5-year grant made under the CREID initiative that established the West African Research Network for Infectious Diseases (WARN-ID). Daszak was the recipient of a new $7.5 million, 5-year CREID grant that established the Emerging Infectious Diseases: South East Asia Research Collaboration Hub (EID-SEARCH). The other participants of the NIAID CREID program can be found here.
Notably, although the creation of CREID was not publicly announced until Aug. 27, 2020, the Award Notice Date for the grants to Andersen and Garry are listed as May 21, 2020. The CREID grant to Daszak lists an Award Notice Date of June 17, 2020. The timing of Daszak’s grant is particularly noteworthy as it came shortly after President Donald Trump had revoked Daszak’s previous grant from Fauci’s NIAID in April 2020 due to Daszak’s entanglements with the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
Andersen, who had privately told Fauci on Jan. 31, 2020, that the virus “looked engineered,” but later helped spearhead Fauci’s efforts to promote a natural origins narrative, received a total of $7.4 million in funding in 2020 as compared to $4.5 million in grant proceeds in 2019. Andersen’s total grant funding increased to nearly $9 million in 2021. The new CREID grants (co-awarded with Garry) accounted for approximately $1.9 million of his 2020 grant proceeds and $2 million of his grant proceeds in 2021. Included in Andersen’s 2021 figure is a $266,250 CREID grant that was made to Andersen but did not include Garry as a co-recipient.
While it is not known at this point whether there was a connection between the increased funding and the scientists’ involvement in shaping the public natural origins narrative, these new revelations raise an obvious question: How is it that among the thousands of scientists eligible to participate in the much-desired funding from the eleven grants provided by Fauci’s new $82 million CREID initiative, three of those chosen happened to be the same individuals who had led the way in promoting Fauci’s natural origins narrative—despite their private concerns that the virus had been created in a lab.

During the Feb. 1, 2020, teleconference, Andersen claimed to be “60 to 70 percent sure the virus came from a laboratory.” One of Andersen’s Proximal Origin co-authors, Edward Holmes, put that figure even higher, at “80 percent.”
Garry, who told the senior members of Fauci’s teleconference group that he “really can’t think of a plausible natural scenario where you get from the bat virus” to SARS-CoV-2, received $7 million in NIAID grants in 2020 as compared to $5.7 million in 2019. Garry also received $6.6 million in grants in 2021. The new CREID grant (co-awarded with Andersen) accounted for approximately $1.9 million of his 2020 grant proceeds and $1.8 million of his grant proceeds in 2021.
During the Feb. 1, 2020, teleconference, Garry cited the remarkable sequences of mutations that would have to occur for SARS-CoV-2 to arise naturally, telling the group, “I just can’t figure out how this gets accomplished in nature.” However, Garry noted that a lab-created virus would easily explain the virus data he was seeing, telling Fauci’s group that “in the lab, it would be easy to generate the perfect 12 base insert that you wanted.”
Notably, Garry recently admitted in written correspondence with The Intercept that he had been advised not to discuss a lab leak in the Proximal Origin paper, stating, “The major feedback we got from the Feb 1 teleconference was: 1. Don’t try to write a paper at all—it’s unnecessary or 2. If you do write it, don’t mention a lab origin as that will just add fuel to the conspiracists.”
Garry—along with Andersen—must have heeded that directive because on Feb. 1, 2020, the same day as Fauci’s teleconference, both men had helped to complete the first draft of Proximal Origin promoting the idea that the virus had originated in nature. That paper became the media’s and the public health establishment’s go-to evidence for a natural origin for the virus.
The choice of Andersen as a lead author for Proximal Origin is particularly curious as Andersen had no material experience in researching coronaviruses. His stated focus was related to the Zika virus, Ebola virus, West Nile virus, and Lassa virus. It wasn’t until sometime after the Feb. 1 teleconference that he changed his biography to incorporate SARS-CoV-2.

Proximal Origin was published online on Feb. 16, 2020, and sought to exclude the possibility of a lab leak. The article would prove to be highly influential and has been extensively used by Fauci and media organizations in their promotion of the natural origins narrative.
Another recipient of funding under the CREID initiative was EcoHealth president Peter Daszak, who received a total of $1.5 million in both 2020 and 2021. Unlike either Andersen or Garry, proceeds from his CREID grant make up the entirety of his listed NIAID grants in both years. By way of comparison, Daszak had received approximately $662,000 in NIAID grant money in 2019. Put another way, Daszak’s post-pandemic funding increased by approximately 130 percent.
Daszak, who heavily promoted the natural origins narrative, was personally involved in gain-of-function work with the Wuhan Institute of Virology, which continued until at least April 2020. Most prominently, Daszak authored a 2018 research proposal which details the creation of a virus in a lab that bears a remarkable similarity to the defining features of COVID-19.
That proposal, dated March 27, 2018, details EcoHealth’s plans, in conjunction with the Wuhan Institute, to create entirely new coronaviruses through the synthetic combination of preexisting virus backbones. It describes how those viruses were going to be made more virulent in humans by the insertion of a furin cleavage site, a feature that distinguishes COVID-19 from all other SARS-related coronaviruses.
Another scientist who advised the Feb. 1, 2020, teleconference, Michael Farzan, received $9.9 million in grants from Fauci’s NIAID in 2020, followed by another $7.9 million in 2021 and an additional $919,000 at the start of 2022. By comparison, Farzan had received $3.8 million in grant money from NIAID in 2019. Although Farzan received substantial increases in grant funding, none of that money appears to have come under grants provided by the CREID initiative.

Farzan, an immunologist who in 2005 discovered the receptor of the original severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus, had told the senior members of Fauci’s teleconference group in emails that the pandemic likely originated from a lab in which live coronaviruses were passed repeatedly through human-like tissue, accelerating virus mutations with the end result being that one of the mutated viruses may have leaked from the lab. Farzan told Fauci’s group that he placed the likelihood of a leak from a Wuhan lab at 60 to 70 percent.
But in an Oct. 5, 2021, paper, Farzan appeared to agree with conclusions put forth in Proximal Origin, when he claimed that a “comparison of the S protein sequences indicates SARS-CoV-2 may have emerged from the recombination between bat and pangolin coronaviruses.” Farzan, like Andersen, works at the Scripps laboratory.
Government
CDC Warns Thousands Of Children Sent To ER After Taking Common Sleep Aid
CDC Warns Thousands Of Children Sent To ER After Taking Common Sleep Aid
Authored by Jack Phillips via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A…

Authored by Jack Phillips via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) paper released Thursday found that thousands of young children have been taken to the emergency room over the past several years after taking the very common sleep-aid supplement melatonin.
The agency said that melatonin, which can come in gummies that are meant for adults, was implicated in about 7 percent of all emergency room visits for young children and infants “for unsupervised medication ingestions,” adding that many incidents were linked to the ingestion of gummy formulations that were flavored. Those incidents occurred between the years 2019 and 2022.
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the human body to regulate its sleep cycle. Supplements, which are sold in a number of different formulas, are generally taken before falling asleep and are popular among people suffering from insomnia, jet lag, chronic pain, or other problems.
The supplement isn’t regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and does not require child-resistant packaging. However, a number of supplement companies include caps or lids that are difficult for children to open.
The CDC report said that a significant number of melatonin-ingestion cases among young children were due to the children opening bottles that had not been properly closed or were within their reach. Thursday’s report, the agency said, “highlights the importance of educating parents and other caregivers about keeping all medications and supplements (including gummies) out of children’s reach and sight,” including melatonin.
The approximately 11,000 emergency department visits for unsupervised melatonin ingestions by infants and young children during 2019–2022 highlight the importance of educating parents and other caregivers about keeping all medications and supplements (including gummies) out of children’s reach and sight.
The CDC notes that melatonin use among Americans has increased five-fold over the past 25 years or so. That has coincided with a 530 percent increase in poison center calls for melatonin exposures to children between 2012 and 2021, it said, as well as a 420 percent increase in emergency visits for unsupervised melatonin ingestion by young children or infants between 2009 and 2020.
Some health officials advise that children under the age of 3 should avoid taking melatonin unless a doctor says otherwise. Side effects include drowsiness, headaches, agitation, dizziness, and bed wetting.
Other symptoms of too much melatonin include nausea, diarrhea, joint pain, anxiety, and irritability. The supplement can also impact blood pressure.
However, there is no established threshold for a melatonin overdose, officials have said. Most adult melatonin supplements contain a maximum of 10 milligrams of melatonin per serving, and some contain less.
Many people can tolerate even relatively large doses of melatonin without significant harm, officials say. But there is no antidote for an overdose. In cases of a child accidentally ingesting melatonin, doctors often ask a reliable adult to monitor them at home.
Dr. Cora Collette Breuner, with the Seattle Children’s Hospital at the University of Washington, told CNN that parents should speak with a doctor before giving their children the supplement.
“I also tell families, this is not something your child should take forever. Nobody knows what the long-term effects of taking this is on your child’s growth and development,” she told the outlet. “Taking away blue-light-emitting smartphones, tablets, laptops, and television at least two hours before bed will keep melatonin production humming along, as will reading or listening to bedtime stories in a softly lit room, taking a warm bath, or doing light stretches.”
In 2022, researchers found that in 2021, U.S. poison control centers received more than 52,000 calls about children consuming worrisome amounts of the dietary supplement. That’s a six-fold increase from about a decade earlier. Most such calls are about young children who accidentally got into bottles of melatonin, some of which come in the form of gummies for kids, the report said.
Dr. Karima Lelak, an emergency physician at Children’s Hospital of Michigan and the lead author of the study published in 2022 by the CDC, found that in about 83 percent of those calls, the children did not show any symptoms.
However, other children had vomiting, altered breathing, or other symptoms. Over the 10 years studied, more than 4,000 children were hospitalized, five were put on machines to help them breathe, and two children under the age of two died. Most of the hospitalized children were teenagers, and many of those ingestions were thought to be suicide attempts.
Those researchers also suggested that COVID-19 lockdowns and virtual learning forced more children to be at home all day, meaning there were more opportunities for kids to access melatonin. Also, those restrictions may have caused sleep-disrupting stress and anxiety, leading more families to consider melatonin, they suggested.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
International
Red Candle In The Wind
Red Candle In The Wind
By Benjamin PIcton of Rabobank
February non-farm payrolls superficially exceeded market expectations on Friday by…
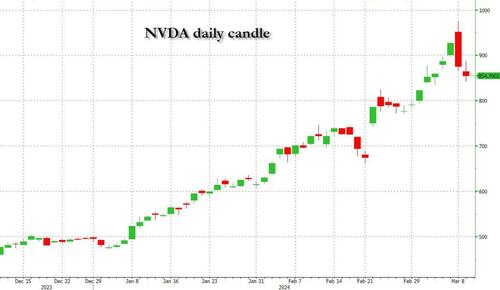
By Benjamin PIcton of Rabobank
February non-farm payrolls superficially exceeded market expectations on Friday by printing at 275,000 against a consensus call of 200,000. We say superficially, because the downward revisions to prior months totalled 167,000 for December and January, taking the total change in employed persons well below the implied forecast, and helping the unemployment rate to pop two-ticks to 3.9%. The U6 underemployment rate also rose from 7.2% to 7.3%, while average hourly earnings growth fell to 0.2% m-o-m and average weekly hours worked languished at 34.3, equalling pre-pandemic lows.
Undeterred by the devil in the detail, the algos sprang into action once exchanges opened. Market darling NVIDIA hit a new intraday high of $974 before (presumably) the humans took over and sold the stock down more than 10% to close at $875.28. If our suspicions are correct that it was the AIs buying before the humans started selling (no doubt triggering trailing stops on the way down), the irony is not lost on us.
The 1-day chart for NVIDIA now makes for interesting viewing, because the red candle posted on Friday presents quite a strong bearish engulfing signal. Volume traded on the day was almost double the 15-day simple moving average, and similar price action is observable on the 1-day charts for both Intel and AMD. Regular readers will be aware that we have expressed incredulity in the past about the durability the AI thematic melt-up, so it will be interesting to see whether Friday’s sell off is just a profit-taking blip, or a genuine trend reversal.
AI equities aside, this week ought to be important for markets because the BTFP program expires today. That means that the Fed will no longer be loaning cash to the banking system in exchange for collateral pledged at-par. The KBW Regional Banking index has so far taken this in its stride and is trading 30% above the lows established during the mini banking crisis of this time last year, but the Fed’s liquidity facility was effectively an exercise in can-kicking that makes regional banks a sector of the market worth paying attention to in the weeks ahead. Even here in Sydney, regulators are warning of external risks posed to the banking sector from scheduled refinancing of commercial real estate loans following sharp falls in valuations.
Markets are sending signals in other sectors, too. Gold closed at a new record-high of $2178/oz on Friday after trading above $2200/oz briefly. Gold has been going ballistic since the Friday before last, posting gains even on days where 2-year Treasury yields have risen. Gold bugs are buying as real yields fall from the October highs and inflation breakevens creep higher. This is particularly interesting as gold ETFs have been recording net outflows; suggesting that price gains aren’t being driven by a retail pile-in. Are gold buyers now betting on a stagflationary outcome where the Fed cuts without inflation being anchored at the 2% target? The price action around the US CPI release tomorrow ought to be illuminating.
Leaving the day-to-day movements to one side, we are also seeing further signs of structural change at the macro level. The UK budget last week included a provision for the creation of a British ISA. That is, an Individual Savings Account that provides tax breaks to savers who invest their money in the stock of British companies. This follows moves last year to encourage pension funds to head up the risk curve by allocating 5% of their capital to unlisted investments.
As a Hail Mary option for a government cruising toward an electoral drubbing it’s a curious choice, but it’s worth highlighting as cash-strapped governments increasingly see private savings pools as a funding solution for their spending priorities.
Of course, the UK is not alone in making creeping moves towards financial repression. In contrast to announcements today of increased trade liberalisation, Australian Treasurer Jim Chalmers has in the recent past flagged his interest in tapping private pension savings to fund state spending priorities, including defence, public housing and renewable energy projects. Both the UK and Australia appear intent on finding ways to open up the lungs of their economies, but government wants more say in directing private capital flows for state goals.
So, how far is the blurring of the lines between free markets and state planning likely to go? Given the immense and varied budgetary (and security) pressures that governments are facing, could we see a re-up of WWII-era Victory bonds, where private investors are encouraged to do their patriotic duty by directly financing government at negative real rates?
That would really light a fire under the gold market.
Government
Fauci Deputy Warned Him Against Vaccine Mandates: Email
Fauci Deputy Warned Him Against Vaccine Mandates: Email
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Mandating COVID-19…

Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
Mandating COVID-19 vaccination was a mistake due to ethical and other concerns, a top government doctor warned Dr. Anthony Fauci after Dr. Fauci promoted mass vaccination.
“Coercing or forcing people to take a vaccine can have negative consequences from a biological, sociological, psychological, economical, and ethical standpoint and is not worth the cost even if the vaccine is 100% safe,” Dr. Matthew Memoli, director of the Laboratory of Infectious Diseases clinical studies unit at the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), told Dr. Fauci in an email.
“A more prudent approach that considers these issues would be to focus our efforts on those at high risk of severe disease and death, such as the elderly and obese, and do not push vaccination on the young and healthy any further.”
Employing that strategy would help prevent loss of public trust and political capital, Dr. Memoli said.
The email was sent on July 30, 2021, after Dr. Fauci, director of the NIAID, claimed that communities would be safer if more people received one of the COVID-19 vaccines and that mass vaccination would lead to the end of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’re on a really good track now to really crush this outbreak, and the more people we get vaccinated, the more assuredness that we’re going to have that we’re going to be able to do that,” Dr. Fauci said on CNN the month prior.
Dr. Memoli, who has studied influenza vaccination for years, disagreed, telling Dr. Fauci that research in the field has indicated yearly shots sometimes drive the evolution of influenza.
Vaccinating people who have not been infected with COVID-19, he said, could potentially impact the evolution of the virus that causes COVID-19 in unexpected ways.
“At best what we are doing with mandated mass vaccination does nothing and the variants emerge evading immunity anyway as they would have without the vaccine,” Dr. Memoli wrote. “At worst it drives evolution of the virus in a way that is different from nature and possibly detrimental, prolonging the pandemic or causing more morbidity and mortality than it should.”
The vaccination strategy was flawed because it relied on a single antigen, introducing immunity that only lasted for a certain period of time, Dr. Memoli said. When the immunity weakened, the virus was given an opportunity to evolve.
Some other experts, including virologist Geert Vanden Bossche, have offered similar views. Others in the scientific community, such as U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention scientists, say vaccination prevents virus evolution, though the agency has acknowledged it doesn’t have records supporting its position.
Other Messages
Dr. Memoli sent the email to Dr. Fauci and two other top NIAID officials, Drs. Hugh Auchincloss and Clifford Lane. The message was first reported by the Wall Street Journal, though the publication did not publish the message. The Epoch Times obtained the email and 199 other pages of Dr. Memoli’s emails through a Freedom of Information Act request. There were no indications that Dr. Fauci ever responded to Dr. Memoli.
Later in 2021, the NIAID’s parent agency, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), and all other federal government agencies began requiring COVID-19 vaccination, under direction from President Joe Biden.
In other messages, Dr. Memoli said the mandates were unethical and that he was hopeful legal cases brought against the mandates would ultimately let people “make their own healthcare decisions.”
“I am certainly doing everything in my power to influence that,” he wrote on Nov. 2, 2021, to an unknown recipient. Dr. Memoli also disclosed that both he and his wife had applied for exemptions from the mandates imposed by the NIH and his wife’s employer. While her request had been granted, his had not as of yet, Dr. Memoli said. It’s not clear if it ever was.
According to Dr. Memoli, officials had not gone over the bioethics of the mandates. He wrote to the NIH’s Department of Bioethics, pointing out that the protection from the vaccines waned over time, that the shots can cause serious health issues such as myocarditis, or heart inflammation, and that vaccinated people were just as likely to spread COVID-19 as unvaccinated people.
He cited multiple studies in his emails, including one that found a resurgence of COVID-19 cases in a California health care system despite a high rate of vaccination and another that showed transmission rates were similar among the vaccinated and unvaccinated.
Dr. Memoli said he was “particularly interested in the bioethics of a mandate when the vaccine doesn’t have the ability to stop spread of the disease, which is the purpose of the mandate.”
The message led to Dr. Memoli speaking during an NIH event in December 2021, several weeks after he went public with his concerns about mandating vaccines.
“Vaccine mandates should be rare and considered only with a strong justification,” Dr. Memoli said in the debate. He suggested that the justification was not there for COVID-19 vaccines, given their fleeting effectiveness.
Julie Ledgerwood, another NIAID official who also spoke at the event, said that the vaccines were highly effective and that the side effects that had been detected were not significant. She did acknowledge that vaccinated people needed boosters after a period of time.
The NIH, and many other government agencies, removed their mandates in 2023 with the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency.
A request for comment from Dr. Fauci was not returned. Dr. Memoli told The Epoch Times in an email he was “happy to answer any questions you have” but that he needed clearance from the NIAID’s media office. That office then refused to give clearance.
Dr. Jay Bhattacharya, a professor of health policy at Stanford University, said that Dr. Memoli showed bravery when he warned Dr. Fauci against mandates.
“Those mandates have done more to demolish public trust in public health than any single action by public health officials in my professional career, including diminishing public trust in all vaccines.” Dr. Bhattacharya, a frequent critic of the U.S. response to COVID-19, told The Epoch Times via email. “It was risky for Dr. Memoli to speak publicly since he works at the NIH, and the culture of the NIH punishes those who cross powerful scientific bureaucrats like Dr. Fauci or his former boss, Dr. Francis Collins.”
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





















