Uncategorized
Pregnancy is a genetic battlefield – how conflicts of interest pit mom’s and dad’s genes against each other
Genetic conflict may play a role in pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia and gestational diabetes, as well as developmental disorders.

Baby showers. Babymoons. Baby-arrival parties. There are many opportunities to celebrate the 40-week transition to parenthood. Often, these celebrations implicitly assume that pregnancy is cooperative and mutually beneficial to both the parent and the fetus. But this belief obscures a more interesting truth about pregnancy – the mother and the fetus may not be peacefully coexisting in the same body at all.
At the most fundamental level, there is a conflict between the interests of the parent and fetus. While this may sound like the beginning of a thriller, this genetic conflict is a normal part of pregnancy, leading to typical growth and development both during pregnancy and across an individual’s lifetime – something my research focuses on.
However, even though genetic conflict is normal during pregnancy, it can play a role in pregnancy complications and developmental disorders when left unchecked.
What is genetic conflict?
Pregnancy is generally thought of as a period when a new individual is created from a unified blend of genes from their parents. But this is not quite right.
The genes a fetus gets from each parent carry slightly different instructions for development. This means there are contrasting and sometimes conflicting blueprints for how to build the new individual. Conflict over which blueprint to follow for fetal growth and development is the essence of the genetic conflict that occurs during pregnancy.
Moms have to use their bodies to help the fetus grow during pregnancy while dads don’t. This means that the genes the fetus inherits from mom have to not only provide for the current fetus, but also try to keep mom alive and healthy and make sure there are resources left over for a potential future pregnancy. These reserves include both biological resources like glucose, protein, iron and calcium, as well as the time and energy needed to help her children after birth as they grow and develop.
Dad’s genes don’t have this same pressure because they don’t use their bodies to help the fetus grow during pregnancy. A dad’s genes, then, don’t need to ensure that anyone other than the current fetus thrives.
To better understand this situation, pretend that all of the resources a mom can give her children come in the form of a milkshake. Once the milkshake runs out, mom has nothing left to give her children. Maternal genes, therefore, want each child to drink only as much as they need to grow and develop. This ensures that the milkshake can be “shared” across all current and future children.
Paternal genes, on the other hand, have no such guarantee of representation in this mother’s other children – the father of the current child may not be the father of the mother’s potential future children. This lack of guaranteed genetic representation means there is no pressure on the father to “share” the milkshake. The best strategy when it comes to paternal genes, then, is for the fetus to drink as much of the milkshake as they can.
These two strategies play a figurative game of tug of war throughout pregnancy. Both sides are trying to pull fetal development slightly more toward their side. Paternal genes encourage the fetus to grow and develop quickly and take more resources, while maternal genes encourage the fetus to grow and use only what’s necessary for proper development. Conflict over how deeply the embryo implants in the uterus and how quickly the placenta and fetus grow are just a few areas where researchers have documented this tug of war during pregnancy.
The milkshake problem helps researchers determine where to look for genetic conflict by simplifying where trade-offs may take place during pregnancy. Because fetal growth is at the heart of genetic conflict, researchers have focused on processes where conflict over resource transfers from mother to fetus can be observed. These investigations have found that the placenta, a fetal organ responsible for all resource transfers during pregnancy, is dominated by paternally-expressed genes. It releases paternally-derived insulin-like growth factors that make mom less sensitive to her own insulin and hormones that increase maternal blood pressure, both of which ultimately increase the amount of resources the fetus can use to grow during pregnancy but have the potential to harm the mother’s health.
Genetic conflict and pregnancy complications
If genetic conflict goes uncontrolled, it can cause pregnancy complications for the mother and developmental disorders for the child. In fact, there is a growing consensus among researchers that some of the most well-known pregnancy complications like preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, miscarriages and preterm births may best be explained by unchecked genetic conflict.
Despite the potential role that genetic conflict plays in pregnancy complications, current medical treatments are reactive rather than proactive. A pregnant person must show signs of experiencing complications before medical interventions and treatments can take place.
Knowing how unchecked genetic conflict contributes to pregnancy complications could provide researchers another way to develop treatments that are proactive and, ideally, preventive. However, there are currently no treatments for pregnancy complications that consider genetic conflict. Though gestational diabetes can be attributed to underlying genetic conflict, a pregnant person must present with elevated blood sugar levels before doctors can treat underlying conflict over insulin production and blood sugar.
The experiences of pregnant people during the COVID-19 pandemic provide an example of why more research on genetic conflict is needed. During the pandemic, doctors saw both a dramatic decrease in the number of preterm births as well as an increase in the number of stillbirths and miscarriages. Both types of complications are influenced by genetic conflict, but the reasons behind these opposing trends are unclear.
As a woman who was pregnant early in the pandemic, my pregnancy was scary and stressful, spent at home away from the pressures of “normal” life. More research on the complex process of pregnancy and genetic conflict’s role in complications could help researchers better understand how the changes brought by the pandemic produced such wildly different pregnancy outcomes.
Jessica D. Ayers does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
genetic pandemic covid-19Uncategorized
Q4 Update: Delinquencies, Foreclosures and REO
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Q4 Update: Delinquencies, Foreclosures and REO
A brief excerpt: I’ve argued repeatedly that we would NOT see a surge in foreclosures that would significantly impact house prices (as happened followi…
A brief excerpt:
I’ve argued repeatedly that we would NOT see a surge in foreclosures that would significantly impact house prices (as happened following the housing bubble). The two key reasons are mortgage lending has been solid, and most homeowners have substantial equity in their homes..There is much more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/ mortgage rates real estate mortgages pandemic interest rates
...
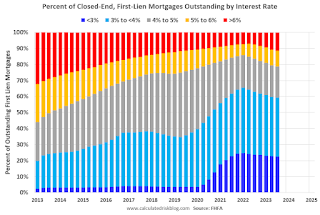
And on mortgage rates, here is some data from the FHFA’s National Mortgage Database showing the distribution of interest rates on closed-end, fixed-rate 1-4 family mortgages outstanding at the end of each quarter since Q1 2013 through Q3 2023 (Q4 2023 data will be released in a two weeks).
This shows the surge in the percent of loans under 3%, and also under 4%, starting in early 2020 as mortgage rates declined sharply during the pandemic. Currently 22.6% of loans are under 3%, 59.4% are under 4%, and 78.7% are under 5%.
With substantial equity, and low mortgage rates (mostly at a fixed rates), few homeowners will have financial difficulties.
Uncategorized
‘Bougie Broke’ – The Financial Reality Behind The Facade
‘Bougie Broke’ – The Financial Reality Behind The Facade
Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Social media users claiming…
Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Social media users claiming to be Bougie Broke share pictures of their fancy cars, high-fashion clothing, and selfies in exotic locations and expensive restaurants. Yet they complain about living paycheck to paycheck and lacking the means to support their lifestyle.
Bougie broke is like “keeping up with the Joneses,” spending beyond one’s means to impress others.
Bougie Broke gives us a glimpse into the financial condition of a growing number of consumers. Since personal consumption represents about two-thirds of economic activity, it’s worth diving into the Bougie Broke fad to appreciate if a large subset of the population can continue to consume at current rates.
The Wealth Divide Disclaimer
Forecasting personal consumption is always tricky, but it has become even more challenging in the post-pandemic era. To appreciate why we share a joke told by Mike Green.
Bill Gates and I walk into the bar…
Bartender: “Wow… a couple of billionaires on average!”
Bill Gates, Jeff Bezos, Elon Musk, Mark Zuckerberg, and other billionaires make us all much richer, on average. Unfortunately, we can’t use the average to pay our bills.
According to Wikipedia, Bill Gates is one of 756 billionaires living in the United States. Many of these billionaires became much wealthier due to the pandemic as their investment fortunes proliferated.
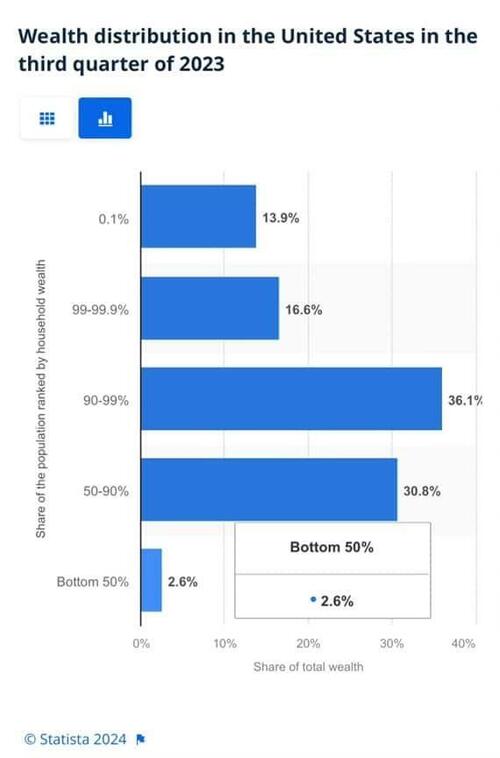
To appreciate the wealth divide, consider the graph below courtesy of Statista. 1% of the U.S. population holds 30% of the wealth. The wealthiest 10% of households have two-thirds of the wealth. The bottom half of the population accounts for less than 3% of the wealth.
The uber-wealthy grossly distorts consumption and savings data. And, with the sharp increase in their wealth over the past few years, the consumption and savings data are more distorted.
Furthermore, and critical to appreciate, the spending by the wealthy doesn’t fluctuate with the economy. Therefore, the spending of the lower wealth classes drives marginal changes in consumption. As such, the condition of the not-so-wealthy is most important for forecasting changes in consumption.
Revenge Spending
Deciphering personal data has also become more difficult because our spending habits have changed due to the pandemic.
A great example is revenge spending. Per the New York Times:
Ola Majekodunmi, the founder of All Things Money, a finance site for young adults, explained revenge spending as expenditures meant to make up for “lost time” after an event like the pandemic.
So, between the growing wealth divide and irregular spending habits, let’s quantify personal savings, debt usage, and real wages to appreciate better if Bougie Broke is a mass movement or a silly meme.
The Means To Consume
Savings, debt, and wages are the three primary sources that give consumers the ability to consume.
Savings
The graph below shows the rollercoaster on which personal savings have been since the pandemic. The savings rate is hovering at the lowest rate since those seen before the 2008 recession. The total amount of personal savings is back to 2017 levels. But, on an inflation-adjusted basis, it’s at 10-year lows. On average, most consumers are drawing down their savings or less. Given that wages are increasing and unemployment is historically low, they must be consuming more.
Now, strip out the savings of the uber-wealthy, and it’s probable that the amount of personal savings for much of the population is negligible. A survey by Payroll.org estimates that 78% of Americans live paycheck to paycheck.
More on Insufficient Savings
The Fed’s latest, albeit old, Report on the Economic Well-Being of U.S. Households from June 2023 claims that over a third of households do not have enough savings to cover an unexpected $400 expense. We venture to guess that number has grown since then. To wit, the number of households with essentially no savings rose 5% from their prior report a year earlier.
Relatively small, unexpected expenses, such as a car repair or a modest medical bill, can be a hardship for many families. When faced with a hypothetical expense of $400, 63 percent of all adults in 2022 said they would have covered it exclusively using cash, savings, or a credit card paid off at the next statement (referred to, altogether, as “cash or its equivalent”). The remainder said they would have paid by borrowing or selling something or said they would not have been able to cover the expense.
Debt
After periods where consumers drained their existing savings and/or devoted less of their paychecks to savings, they either slowed their consumption patterns or borrowed to keep them up. Currently, it seems like many are choosing the latter option. Consumer borrowing is accelerating at a quicker pace than it was before the pandemic.
The first graph below shows outstanding credit card debt fell during the pandemic as the economy cratered. However, after multiple stimulus checks and broad-based economic recovery, consumer confidence rose, and with it, credit card balances surged.
The current trend is steeper than the pre-pandemic trend. Some may be a catch-up, but the current rate is unsustainable. Consequently, borrowing will likely slow down to its pre-pandemic trend or even below it as consumers deal with higher credit card balances and 20+% interest rates on the debt.
The second graph shows that since 2022, credit card balances have grown faster than our incomes. Like the first graph, the credit usage versus income trend is unsustainable, especially with current interest rates.
With many consumers maxing out their credit cards, is it any wonder buy-now-pay-later loans (BNPL) are increasing rapidly?
Insider Intelligence believes that 79 million Americans, or a quarter of those over 18 years old, use BNPL. Lending Tree claims that “nearly 1 in 3 consumers (31%) say they’re at least considering using a buy now, pay later (BNPL) loan this month.”More telling, according to their survey, only 52% of those asked are confident they can pay off their BNPL loan without missing a payment!
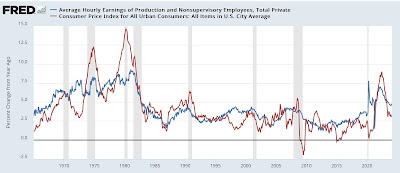
Wage Growth
Wages have been growing above trend since the pandemic. Since 2022, the average annual growth in compensation has been 6.28%. Higher incomes support more consumption, but higher prices reduce the amount of goods or services one can buy. Over the same period, real compensation has grown by less than half a percent annually. The average real compensation growth was 2.30% during the three years before the pandemic.
In other words, compensation is just keeping up with inflation instead of outpacing it and providing consumers with the ability to consume, save, or pay down debt.
It’s All About Employment
The unemployment rate is 3.9%, up slightly from recent lows but still among the lowest rates in the last seventy-five years.
The uptick in credit card usage, decline in savings, and the savings rate argue that consumers are slowly running out of room to keep consuming at their current pace.
However, the most significant means by which we consume is income. If the unemployment rate stays low, consumption may moderate. But, if the recent uptick in unemployment continues, a recession is extremely likely, as we have seen every time it turned higher.
It’s not just those losing jobs that consume less. Of greater impact is a loss of confidence by those employed when they see friends or neighbors being laid off.
Accordingly, the labor market is probably the most important leading indicator of consumption and of the ability of the Bougie Broke to continue to be Bougie instead of flat-out broke!
Summary
There are always consumers living above their means. This is often harmless until their means decline or disappear. The Bougie Broke meme and the ability social media gives consumers to flaunt their “wealth” is a new medium for an age-old message.
Diving into the data, it argues that consumption will likely slow in the coming months. Such would allow some consumers to save and whittle down their debt. That situation would be healthy and unlikely to cause a recession.
The potential for the unemployment rate to continue higher is of much greater concern. The combination of a higher unemployment rate and strapped consumers could accentuate a recession.
Uncategorized
The most potent labor market indicator of all is still strongly positive
– by New Deal democratOn Monday I examined some series from last Friday’s Household survey in the jobs report, highlighting that they more frequently…
- by New Deal democrat
On Monday I examined some series from last Friday’s Household survey in the jobs report, highlighting that they more frequently than not indicated a recession was near or underway. But I concluded by noting that this survey has historically been noisy, and I thought it would be resolved away this time. Specifically, there was strong contrary data from the Establishment survey, backed up by yesterday’s inflation report, to the contrary. Today I’ll examine that, looking at two other series.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges



























