Government
“Pandora’s Box Of Harms”: How Public Health Erred On Side Of Catastrophe
"Pandora’s Box Of Harms": How Public Health Erred On Side Of Catastrophe
Authored by Brian McGlinchey via Stark Realities,
Throughout the…

Authored by Brian McGlinchey via Stark Realities,
Throughout the Covid-19 pandemic, proponents of lockdowns, shelter-in-place orders, mask mandates and other coercive government interventions have characterized these measures as benevolently “erring on the side of caution.” Now, as the grim toll of those public health measures comes into ever-sharper focus, it’s increasingly clear those characterizations were terribly wrong.
What’s less readily apparent, however, is how the very use of the “erring on the side of caution” framing was injurious in itself—by thwarting reasoned debate of public health policies, diverting attention from unintended consequences, and buffering the Covid regime’s architects from accountability.
To understand how the misuse of “erring on the side of caution” performed a sort of mass hypnosis that coaxed populations into two years of submission to disastrous, overreaching policies, consider how the expression is typically used.
In everyday life, one might err on the side of caution by:
- Leaving for the airport an extra 30 minutes early
- Carrying an umbrella when there’s a 25% chance of rain
- Opting for a less-challenging ski slope
- Going back into the house to make sure the iron is unplugged
- Getting a second medical opinion
Generally speaking, “erring on the side of caution” in everyday life means lowering risk with a precaution that has a negligible cost.
When mandate proponents portrayed their edicts as “erring on the side of caution,” it had the effect of tacitly assuring the public—and themselves—that there’d be little or no harm associated with extreme measures like:
- Shutting down businesses for months at a time
- Knowingly forcing millions of people into unemployment
- Halting in-person attendance at schools and colleges
- Ordering people of all ages and risk profiles to wear masks
- Denying people opportunities to socialize, recreate and enjoy living
That implicit low-downside assurance not only fostered unthinking support for draconian measures among citizens and experts alike, it also cultivated an atmosphere of intolerance toward those who questioned the wisdom of these interventions and predicted the great many harms that have resulted.
“Overconfident, unnuanced messaging conditioned us to assume that all dissenting opinions are misinformation rather than reflections of good faith disagreement or differing priorities,” write Rutgers professors Jacob Hale Russell and Dennis Patterson in their essay, The Mask Debacle. “In doing so, elites drove out scientific research that might have separated valuable interventions from the less valuable.”
Of course, in addition to its implicit assurance that a risk-reduction measure comes at little cost, “erring on the side of caution” conveys an assumption that the precaution will actually be effective.
That hasn’t been the case with Covid mandates. Though many continue embracing the illusion of government control over Covid, the contrary studies and real-world observations are stacking far too high to be denied any longer by the intellectually honest among us.
Charts via Ian Miller at Unmasked
Public Health Threw Out the Playbook and Threw Pandora’s Box Wide Open
The masses who’ve chanted “I trust science,” as they praise each government intervention and idolize those who impose them, are likely unaware that, before Covid-19, the well-considered scientific consensus was against lockdowns, broad quarantines and masking outside of hospital settings—particular for a virus like Covid-19 that has a 99% survival rate for most age groups.
For example, a 2006 paper published by the Center for Biosecurity of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center—focusing on mitigation measures against another contagious respiratory illness, pandemic influenza—reads like a warning label against many of the policies inflicted on humanity in the face of Covid-19:
-
“There is no basis for recommending quarantine either of groups or individuals. The problems in implementing such measures are formidable, and secondary effects of absenteeism and community disruption as well as possible adverse consequences…are likely to be considerable.”
-
“Widespread closures [of schools, restaurants, churches, recreations centers, etc] would almost certainly have serious adverse social and economic effects.”
-
“The ordinary surgical mask does little to prevent inhalation of small droplets bearing influenza virus…There are few data available to support the efficacy of N95 or surgical masks outside a healthcare setting. N95 masks need to be fit-tested to be efficacious.”
The point of that and other pre-2020 research into pandemic mitigation was to be prepared, in times of crisis, with policies that reflected a well-reasoned and dispassionate weighing of costs and benefits.
However, when the pandemic arrived, panicking public health officials and academics threw out the playbook and took their policy inspiration from the government that was first to confront the virus. Sadly for the world, that was communist China.
The breadth of the resulting harms from the ensuing plunge into public health authoritarianism is staggering. Far from erring on the side of caution…
Public health erred on the side of a mental health crisis. Anxiety and depression have surged, particularly among adolescents and young adults, where symptoms have doubled during the pandemic.
“I have never been as busy in my life and I’ve never seen my colleagues as busy,” New York psychiatrist Valentine Raiteri told CNBC. “I can’t refer people to other people because everybody is full.”
Public health erred on the side of juvenile suicide attempts. In the summer of 2020, emergency room visits for potential suicides by children leapt over 22% compared to the summer of 2019.
Public health erred on the side of drug overdoses. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, overdose deaths surged 30% in 2020 to a record-high of more than 93,000. Among the factors cited: social isolation, people using drugs alone, and decreased access to treatment.
Public health erred on the side of auto fatalities. Traffic deaths had been on a general downtrend since the 60s, reaching a near-record low in 2019. However, even with shutdown-lightened traffic, deaths jumped 17.5% in the summer of 2020 compared to 2019, and kept rising into 2021.
Blame increased drug and alcohol use, along with psychological fallout from people being denied life’s fundamental pleasures. University of Texas cognitive scientist Art Markman told The New York Times that anger and aggression behind the wheel in part reflects “two years of having to stop ourselves from doing things that we’d like to do.”
Public health erred on the side of domestic violence. A review of 32 studies found an increase in domestic violence around the world, with the increases most intense during the first week of lockdowns. “The home confinement led to constant contact between perpetrators and victims, resulting in increased violence and decreased reports,” the researchers found.
Public health erred on the side of riots, arson and looting. It’s my own conviction that 2020’s eruption of summer violence following a Minneapolis police officer’s callous homicide of George Floyd was greatly magnified by the period of forced mass confinement that preceded it.
Floyd’s death was a match dropped into a tinderbox of humanity confined to veritable house arrest. People blocked from restaurants and bars were suddenly granted a societal waiver to venture out into enormous crowds, where they found excitement, socialization and, far too often, a senselessly destructive means of venting months of pent-up energy, anxiety and frustration. It stands as the costliest civil unrest episode in American history.
Public health erred on the side of confining people where the virus is transmitted most. Lockdowns ordered people away from workplaces, schools, restaurants and bars and into their homes, where New York contract tracers found 74% of Covid spread was happening, compared to just 1.4% in bars and restaurants and even less in schools and workplaces.
Public health erred on the side of obesity. According to the CDC, “the risk of severe COVID-19 illness increases sharply with higher BMI [Body Mass Index].” So what happens when public health “experts” shut down schools, workplaces and recreation options and told people to stay home to stay “safe”?
The CDC found that, in 2020, the rate by which BMI increased among 2- to 19-year olds doubled. Another study found that 48% of adults gained weight during the pandemic, with those who were already overweight most likely to add even more. Among other factors, the study pointed to psychological distress and having schoolchildren at home.
Public health erred against fresh air, exercise and Vitamin D. Governments raced to shut down playgrounds, basketball courts and other outdoor recreation facilities. In a move that’s profoundly emblematic of heavy-handed, counterproductive authoritarianism in the age of Covid, the city of San Clemente, California filled a skate park with 37 tons of sand.
Public health erred on the side of impaired child development. “We find that children born during the pandemic have significantly reduced verbal, motor, and overall cognitive performance compared to children born pre-pandemic,” say the authors of a study from Paediatric Emergency Research in the UK and Ireland (PERUKI).
“Results highlight that even in the absence of direct SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 illness, the environmental changes associated [with the] COVID-19 pandemic [are] significantly and negatively affecting infant and child development.”
Public health erred on the side of learning loss. Children are less vulnerable to Covid-19 than they are to the flu, and rarely transmit it to teachers. Unfortunately, American public health officials and teacher unions prevailed in halting in-person instruction (and socialization) in favor of “remote learning.”
It was a poor substitute that fell hardest on the youngest learners. For example, according to curriculum and assessment provider Amplify, the percentage of first-graders scoring at or above the goals for their grade in mid-school-year dropped from 58% before the pandemic to just 44% this year.
Public health erred on the side of pointlessly masking schoolchildren. When schools did open, mask mandates abounded—despite children’s relative invulnerability to the virus and the documented rarity of in-school transmission. A Spanish study showed no discernible difference in transmission among 5-year-olds—who aren’t required to mask—and 6 year olds, who are.
“Masking is a psychological stressor for children and disrupts learning. Covering the lower half of the face of both teacher and pupil reduces the ability to communicate,” wrote Neeraj Sood, director of the Covid Initiative at USC, and Jay Bhattacharya, professor of medicine at Stanford. “Positive emotions such as laughing and smiling become less recognizable, and negative emotions get amplified. Bonding between teachers and students takes a hit.”
“Most of the masks worn by most kids for most of the pandemic have likely done nothing to change the velocity or trajectory of the virus,” writes University of California associate professor of epidemiology and biostatistics Vinay Prasad. “The loss to children remains difficult to capture in hard data, but will likely become clear in the years to come.”
Public health erred on the side of giving masked people a false sense of security. As I wrote in August, “Covid-19 particles are astoundingly small. Hard as it is to imagine, the imperceptible gaps in surgical masks can be 1,000 times the size of a viral particle. Gaps in cloth masks are well larger.” That’s to say nothing of the respirated air that simply goes around the mask’s edges.
Earlier in the pandemic, questioning cloth masks triggered outrage and swift social media censorship. Now, even mandate-happy CNN medical analyst Leanna Wen has declared they’re “little more than facial decorations.” Mask skepticism is sprouting elsewhere in mainstream media; the Washington Post and Bloomberg even published an essay titled “Mask Mandates Didn’t Make Much of a Difference Anyway.”
Chart via Ian Miller at Unmasked
When public health officials exaggerated the power of masks, they did more than promote pointless discomfort and a dystopian way of life. “Naively fooled to think that masks would protect them, some older high-risk people did not socially distance properly, and some died from Covid-19 because of it,” said epidemiologist, biostatistician and former Harvard Medical School professor Martin Kulldorff.
Public health erred on the side of killing small businesses. Thanks in large part to government’s targeting of so-called “non-essential businesses,” the first year of the pandemic brought an additional 200,000 business closures over prior levels.
Public health erred on the side of harming women’s careers. Women comprise a greater proportion of the sectors hid hardest by lockdowns, and the closing of schools and child care centers prompted many more women than men to put their careers on hold.
Public health erred on the side of inflation. To offset the massive economic destruction inflicted by public health shutdowns, the federal government plunged into an astounding spending spree, handing out cash to individuals, businesses and city and state governments.
It was money the government didn’t have, so the Federal Reserve essentially created it out of thin air. Pushing all that new fiat money into circulation debases the currency, fueling today’s surging price inflation—which is a stealth tax with no maximum rate, which hits poor people hardest.
Note: Lockdowns and other mandates weren’t the exclusive driver of many of the various harms I’ve described; general fear of the virus also contributed to some of them. However, it should also be noted that public health officials—and media that overwhelmingly emphasized negative stories—whipped up a level of fear that led people to overstate the level of danger actually posed by the virus.
There’s one more way in which characterizing lockdowns and other mandates as “erring on the side of caution” plays a psychological trick: Since the phrase is embedded with the notion of good intentions, it conditions citizens to be forgiving of the bureaucrats and politicians who imposed them.
Note, however, that in most everyday usage of “erring on the side of caution,” the choice to “err” is made voluntarily by individuals who bear the consequences of their own decisions—or by others, like an airplane pilot or a surgeon, to whom we’ve voluntarily and unmistakably granted control of our well-being.
The grim impacts of lockdowns and other mandates, however, were coercively imposed on society, to say nothing of the fact that so many of the edicts represented gross usurpations of power and violations of human rights.
On top of all that, the edicts were reinforced by Orwellian censorship and ostracism leveled at those who dared raise questions that have now proven valid.
So make no mistake: Overreaching public health officials and politicians—and the journalists-in-name-only who served as their mindless, unquestioning megaphones—have fully earned our withering condemnation. Indeed, holding them accountable is essential to sparing ourselves and future generations from repeating this dystopian chapter of human history.
* * *
Stark Realities undermines official narratives, demolishes conventional wisdom and exposes fundamental myths across the political spectrum. Read more and subscribe at starkrealities.substack.com
Government
“I Can’t Even Save”: Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
"I Can’t Even Save": Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great…

While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great - suggesting in his State of the Union Address last week that "our economy is the envy of the world," Americans are being absolutely crushed by inflation (which the Biden admin blames on 'shrinkflation' and 'corporate greed'), and of course - crippling debt.
The signs are obvious. Last week we noted that banks' charge-offs are accelerating, and are now above pre-pandemic levels.
...and leading this increase are credit card loans - with delinquencies that haven't been this high since Q3 2011.
On top of that, while credit cards and nonfarm, nonresidential commercial real estate loans drove the quarterly increase in the noncurrent rate, residential mortgages drove the quarterly increase in the share of loans 30-89 days past due.
And while Biden and crew can spin all they want, an average of polls from RealClear Politics shows that just 40% of people approve of Biden's handling of the economy.
Crushed
On Friday, Bloomberg dug deeper into the effects of Biden's "envious" economy on Americans - specifically, how massive debt loads (credit cards and auto loans especially) are absolutely crushing people.
Two years after the Federal Reserve began hiking interest rates to tame prices, delinquency rates on credit cards and auto loans are the highest in more than a decade. For the first time on record, interest payments on those and other non-mortgage debts are as big a financial burden for US households as mortgage interest payments.
According to the report, this presents a difficult reality for millions of consumers who drive the US economy - "The era of high borrowing costs — however necessary to slow price increases — has a sting of its own that many families may feel for years to come, especially the ones that haven’t locked in cheap home loans."
The Fed, meanwhile, doesn't appear poised to cut rates until later this year.
According to a February paper from IMF and Harvard, the recent high cost of borrowing - something which isn't reflected in inflation figures, is at the heart of lackluster consumer sentiment despite inflation having moderated and a job market which has recovered (thanks to job gains almost entirely enjoyed by immigrants).
In short, the debt burden has made life under President Biden a constant struggle throughout America.
"I’m making the most money I've ever made, and I’m still living paycheck to paycheck," 40-year-old Denver resident Nikki Cimino told Bloomberg. Cimino is carrying a monthly mortgage of $1,650, and has $4,000 in credit card debt following a 2020 divorce.

"There's this wild disconnect between what people are experiencing and what economists are experiencing."
CBS: Do you attribute the inflation crisis to the pandemic or Biden?
— RNC Research (@RNCResearch) March 15, 2024
WISCONSIN VOTER: "It's been YEARS now since the pandemic — I'm not buying that anymore. At first I did; I'm not buying that anymore because yogurt is STILL going up in price!" pic.twitter.com/apahb65scB
What's more, according to Wells Fargo, families have taken on debt at a comparatively fast rate - no doubt to sustain the same lifestyle as low rates and pandemic-era stimmies provided. In fact, it only took four years for households to set a record new debt level after paying down borrowings in 2021 when interest rates were near zero.
Meanwhile, that increased debt load is exacerbated by credit card interest rates that have climbed to a record 22%, according to the Fed.
[P]art of the reason some Americans were able to take on a substantial load of non-mortgage debt is because they’d locked in home loans at ultra-low rates, leaving room on their balance sheets for other types of borrowing. The effective rate of interest on US mortgage debt was just 3.8% at the end of last year.
Yet the loans and interest payments can be a significant strain that shapes families’ spending choices. -Bloomberg
And of course, the highest-interest debt (credit cards) is hurting lower-income households the most, as tends to be the case.
The lowest earners also understandably had the biggest increase in credit card delinquencies.
"Many consumers are levered to the hilt — maxed out on debt and barely keeping their heads above water," Allan Schweitzer, a portfolio manager at credit-focused investment firm Beach Point Capital Management told Bloomberg. "They can dog paddle, if you will, but any uptick in unemployment or worsening of the economy could drive a pretty significant spike in defaults."
"We had more money when Trump was president," said Denise Nierzwicki, 69. She and her 72-year-old husband Paul have around $20,000 in debt spread across multiple cards - all of which have interest rates above 20%.

Photographer: Jon Cherry/Bloomberg
During the pandemic, Denise lost her job and a business deal for a bar they owned in their hometown of Lexington, Kentucky. While they applied for Social Security to ease the pain, Denise is now working 50 hours a week at a restaurant. Despite this, they're barely scraping enough money together to service their debt.
The couple blames Biden for what they see as a gloomy economy and plans to vote for the Republican candidate in November. Denise routinely voted for Democrats up until about 2010, when she grew dissatisfied with Barack Obama’s economic stances, she said. Now, she supports Donald Trump because he lowered taxes and because of his policies on immigration. -Bloomberg
Meanwhile there's student loans - which are not able to be discharged in bankruptcy.
"I can't even save, I don't have a savings account," said 29-year-old in Columbus, Ohio resident Brittany Walling - who has around $80,000 in federal student loans, $20,000 in private debt from her undergraduate and graduate degrees, and $6,000 in credit card debt she accumulated over a six-month stretch in 2022 while she was unemployed.
"I just know that a lot of people are struggling, and things need to change," she told the outlet.
The only silver lining of note, according to Bloomberg, is that broad wage gains resulting in large paychecks has made it easier for people to throw money at credit card bills.
Yet, according to Wells Fargo economist Shannon Grein, "As rates rose in 2023, we avoided a slowdown due to spending that was very much tied to easy access to credit ... Now, credit has become harder to come by and more expensive."
According to Grein, the change has posed "a significant headwind to consumption."
Then there's the election
"Maybe the Fed is done hiking, but as long as rates stay on hold, you still have a passive tightening effect flowing down to the consumer and being exerted on the economy," she continued. "Those household dynamics are going to be a factor in the election this year."
Meanwhile, swing-state voters in a February Bloomberg/Morning Consult poll said they trust Trump more than Biden on interest rates and personal debt.
Reverberations
These 'headwinds' have M3 Partners' Moshin Meghji concerned.
"Any tightening there immediately hits the top line of companies," he said, noting that for heavily indebted companies that took on debt during years of easy borrowing, "there's no easy fix."
International
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says “Copper’s Time Is Now”
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says "Copper’s Time Is Now"
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring…
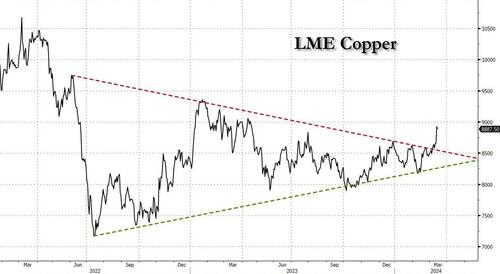
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring speculation about declining global supply, copper has finally broken out, surging to the highest price in the past year, just shy of $9,000 a ton as supply cuts hit the market; At the same time the price of the world's "other" most important mined commodity has diverged, as iron ore has tumbled amid growing demand headwinds out of China's comatose housing sector where not even ghost cities are being built any more.
Copper surged almost 5% this week, ending a months-long spell of inertia, as investors focused on risks to supply at various global mines and smelters. As Bloomberg adds, traders also warmed to the idea that the worst of a global downturn is in the past, particularly for metals like copper that are increasingly used in electric vehicles and renewables.
Yet the commodity crash of recent years is hardly over, as signs of the headwinds in traditional industrial sectors are still all too obvious in the iron ore market, where futures fell below $100 a ton for the first time in seven months on Friday as investors bet that China’s years-long property crisis will run through 2024, keeping a lid on demand.
Indeed, while the mood surrounding copper has turned almost euphoric, sentiment on iron ore has soured since the conclusion of the latest National People’s Congress in Beijing, where the CCP set a 5% goal for economic growth, but offered few new measures that would boost infrastructure or other construction-intensive sectors.
As a result, the main steelmaking ingredient has shed more than 30% since early January as hopes of a meaningful revival in construction activity faded. Loss-making steel mills are buying less ore, and stockpiles are piling up at Chinese ports. The latest drop will embolden those who believe that the effects of President Xi Jinping’s property crackdown still have significant room to run, and that last year’s rally in iron ore may have been a false dawn.
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg notes, on Friday there were fresh signs that weakness in China’s industrial economy is hitting the copper market too, with stockpiles tracked by the Shanghai Futures Exchange surging to the highest level since the early days of the pandemic. The hope is that headwinds in traditional industrial areas will be offset by an ongoing surge in usage in electric vehicles and renewables.
And while industrial conditions in Europe and the US also look soft, there’s growing optimism about copper usage in India, where rising investment has helped fuel blowout growth rates of more than 8% — making it the fastest-growing major economy.
In any case, with the demand side of the equation still questionable, the main catalyst behind copper’s powerful rally is an unexpected tightening in global mine supplies, driven mainly by last year’s closure of a giant mine in Panama (discussed here), but there are also growing worries about output in Zambia, which is facing an El Niño-induced power crisis.
On Wednesday, copper prices jumped on huge volumes after smelters in China held a crisis meeting on how to cope with a sharp drop in processing fees following disruptions to supplies of mined ore. The group stopped short of coordinated production cuts, but pledged to re-arrange maintenance work, reduce runs and delay the startup of new projects. In the coming weeks investors will be watching Shanghai exchange inventories closely to gauge both the strength of demand and the extent of any capacity curtailments.
“The increase in SHFE stockpiles has been bigger than we’d anticipated, but we expect to see them coming down over the next few weeks,” Colin Hamilton, managing director for commodities research at BMO Capital Markets, said by phone. “If the pace of the inventory builds doesn’t start to slow, investors will start to question whether smelters are actually cutting and whether the impact of weak construction activity is starting to weigh more heavily on the market.”
* * *
Few have been as happy with the recent surge in copper prices as Goldman's commodity team, where copper has long been a preferred trade (even if it may have cost the former team head Jeff Currie his job due to his unbridled enthusiasm for copper in the past two years which saw many hedge fund clients suffer major losses).
As Goldman's Nicholas Snowdon writes in a note titled "Copper's time is now" (available to pro subscribers in the usual place)...
... there has been a "turn in the industrial cycle." Specifically according to the Goldman analyst, after a prolonged downturn, "incremental evidence now points to a bottoming out in the industrial cycle, with the global manufacturing PMI in expansion for the first time since September 2022." As a result, Goldman now expects copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25.’
Here are the details:
Previous inflexions in global manufacturing cycles have been associated with subsequent sustained industrial metals upside, with copper and aluminium rising on average 25% and 9% over the next 12 months. Whilst seasonal surpluses have so far limited a tightening alignment at a micro level, we expect deficit inflexions to play out from quarter end, particularly for metals with severe supply binds. Supplemented by the influence of anticipated Fed easing ahead in a non-recessionary growth setting, another historically positive performance factor for metals, this should support further upside ahead with copper the headline act in this regard.
Goldman then turns to what it calls China's "green policy put":
Much of the recent focus on the “Two Sessions” event centred on the lack of significant broad stimulus, and in particular the limited property support. In our view it would be wrong – just as in 2022 and 2023 – to assume that this will result in weak onshore metals demand. Beijing’s emphasis on rapid growth in the metals intensive green economy, as an offset to property declines, continues to act as a policy put for green metals demand. After last year’s strong trends, evidence year-to-date is again supportive with aluminium and copper apparent demand rising 17% and 12% y/y respectively. Moreover, the potential for a ‘cash for clunkers’ initiative could provide meaningful right tail risk to that healthy demand base case. Yet there are also clear metal losers in this divergent policy setting, with ongoing pressure on property related steel demand generating recent sharp iron ore downside.
Meanwhile, Snowdon believes that the driver behind Goldman's long-running bullish view on copper - a global supply shock - continues:
Copper’s supply shock progresses. The metal with most significant upside potential is copper, in our view. The supply shock which began with aggressive concentrate destocking and then sharp mine supply downgrades last year, has now advanced to an increasing bind on metal production, as reflected in this week's China smelter supply rationing signal. With continued positive momentum in China's copper demand, a healthy refined import trend should generate a substantial ex-China refined deficit this year. With LME stocks having halved from Q4 peak, China’s imminent seasonal demand inflection should accelerate a path into extreme tightness by H2. Structural supply underinvestment, best reflected in peak mine supply we expect next year, implies that demand destruction will need to be the persistent solver on scarcity, an effect requiring substantially higher pricing than current, in our view. In this context, we maintain our view that the copper price will surge into next year (GSe 2025 $15,000/t average), expecting copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25’
Another reason why Goldman is doubling down on its bullish copper outlook: gold.
The sharp rally in gold price since the beginning of March has ended the period of consolidation that had been present since late December. Whilst the initial catalyst for the break higher came from a (gold) supportive turn in US data and real rates, the move has been significantly amplified by short term systematic buying, which suggests less sticky upside. In this context, we expect gold to consolidate for now, with our economists near term view on rates and the dollar suggesting limited near-term catalysts for further upside momentum. Yet, a substantive retracement lower will also likely be limited by resilience in physical buying channels. Nonetheless, in the midterm we continue to hold a constructive view on gold underpinned by persistent strength in EM demand as well as eventual Fed easing, which should crucially reactivate the largely for now dormant ETF buying channel. In this context, we increase our average gold price forecast for 2024 from $2,090/toz to $2,180/toz, targeting a move to $2,300/toz by year-end.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs.
Government
Moderna turns the spotlight on long Covid with new initiatives
Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital…

Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital campaign debuted Friday along with a co-sponsored event in Detroit offering free CT scans, which will also be used in ongoing long Covid research.
In a new video, a young woman describes her three-year battle with long Covid, which includes losing her job, coping with multiple debilitating symptoms and dealing with the negative effects on her family. She ends by saying, “The only way to prevent long Covid is to not get Covid” along with an on-screen message about where to find Covid-19 vaccines through the vaccines.gov website.
“Last season we saw people would get a flu shot, but they didn’t always get a Covid shot,” said Moderna’s Chief Brand Officer Kate Cronin. “People should get their flu shot, but they should also get their Covid shot. There’s no risk of long flu, but there is the risk of long-term effects of Covid.”
It’s Moderna’s “first effort to really sound the alarm,” she said, and the debut coincides with the second annual Long Covid Awareness Day.
An estimated 17.6 million Americans are living with long Covid, according to the latest CDC data. About four million of them are out of work because of the condition, resulting in an estimated $170 billion in lost wages.
While HHS anted up $45 million in grants last year to expand long Covid support initiatives along with public health campaigns, the condition is still often ignored and underfunded.
“It’s not just about the initial infection of Covid, but also if you get it multiple times, your risks goes up significantly,” Cronin said. “It’s important that people understand that.”
grants covid-19 cdc hhs-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment3 days ago
Spread & Containment3 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex




































