International
Outdoor education at universities can be a positive legacy of COVID-19
Université de Sherbrooke introduced 10 new outdoor classrooms during COVID-19 and created a guide about outdoor teaching. It will fine-tune outdoor teaching in response to student feedback.


Universities have faced major planning challenges due to COVID-19. While there has been significant media coverage about universities offering students online learning, what has been less discussed is how some activities have continued in face-to-face settings.
My research is concerned with outdoor science education so I have long been engaged in studying outdoor learning. At the Université de Sherbrooke, among our measures to promote student and staff safety during the pandemic was setting up outdoor sheltered and ampitheatre-style learning environments. Since the university was already planning to develop outdoor spaces that could be used for teaching, the pandemic provided an opportunity for pilot testing.
To develop our outdoor learning environments, we appointed a committee with diverse expertise in learning and teaching, health and safety and a variety of logistical and technical considerations such as managing audiovisual resources. Together, we created a guide to support outdoor education in higher education in Canada during the context of COVID-19.

Teaching and learning considerations
In times of pandemic, outdoor classes allow students to meet their professor or classmates in person, when they would not otherwise have had the chance to do so. However, even during regular non-pandemic times, outdoor classes may also allow professors to incorporate outdoor education into their lessons directly on campus.
Outdoor learning environments should be used only when activities have an added value. In other words, not all courses have to be held there. They can be used in a complementary manner with indoor or online learning when they support the learning objectives.
In a university context, outdoor education can have several benefits. It provides the opportunity to draw on the environment to explore different disciplinary knowledge. For example, students might engage with the outdoor environment to learn more about social behaviours on campus; they might explore natural phenomena or examine technical phenomena such as building construction.
Open spaces can also encourage teachers to combine physical activity with educational content. Activities that put students physically in action are associated with the potential to increase academic achievement.
In the university context, where appropriate student accommodations can be made when necessary, this could include field activities with classmates or a guided walk with the teacher to explore the surrounding area.
Some research suggests that for people without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) “inattention and impulsivity are reduced after exposure to natural views and settings,” but it is unclear what these findings could mean for students with ADHD. It is important to consider accessibility when planning to create an inclusive gathering space for all students.
Student and faculty experiences
This fall, a total of 57 teachers made 137 reservations in the 10 outdoor classrooms. Of the 1,275 students who had at least one outdoor activity, 94 per cent were at the undergraduate level. Fifty-seven per cent of them were entering their first year at the university. These outdoor activities allowed them to experience the campus during this time of physical distancing.
The faculty of education and the faculty of arts and humanities were the most represented. Instructors led courses in a wide variety of fields, such as primary science education, drama and film writing, physical activity anatomy, psychology and research methodology.
We conducted a survey to better understand the students’ experience. Most striking was the potentially positive and negative effects of outdoor learning environments on concentration.
While some students mentioned that the outdoors allowed them to be more focused, others mentioned the opposite. These insights highlight the importance of selecting locations that enhance positive stimuli (for example, feeling the warmth of the sun or being surrounded by nature) while reducing nuisance stimuli such as passers-by and ambient noise.
These preliminary observations will lead to first adjustments when our outdoor learning environments reopen in May 2021.
Looking forward
While education at all levels has been shaken over the past months, the pandemic is an opportunity to think about new learning environments. Outdoor settings were an opportunity for students to discover the campus, meet their teacher and develop relationships with new fellow students. Paradoxically, the current context does not allow teachers to fully benefit from one of the important principles of outdoor education: active teaching methods.
Since teachers in higher education institutions are generally not familiar with teaching outdoors, it is essential to develop training or offer a community of practice within the institution to support them. This process must be embedded in a broader change from a paradigm centred on teaching to one centred on student learning.
Much research is being conducted to better understand the effects of experiences with nature on cognitive, physical, mental and educational components for students between kindergarten to Grade 12. In higher education, we still need to develop a co-ordinated research agenda to answer important questions. How can outdoor learning promote inclusiveness in higher education? What teaching methods are most conducive to outdoor learning in higher education?
At Université de Sherbrooke, outdoor learning environments will be a legacy of the pandemic, in terms of both infrastructure and pedagogical practices. I invite all those interested to join us in these new avenues of research.
Jean-Philippe Ayotte-Beaudet has received funding from SSHRC, FQRSC, and MEES.
testing pandemic covid-19 canadaGovernment
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
According to DB’s Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark…
According to DB's Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark week in markets as the last global holdout on negative rates looks set to be removed as the BoJ likely hikes rates from -0.1% tomorrow." That will likely overshadow the FOMC that concludes on Wednesday that will have its own signalling intrigue given recent strong inflation. We also have the RBA meeting tomorrow and the SNB and BoE meetings on Thursday to close out a big week for global central bankers with many EM countries also deciding on policy. We’ll preview the main meetings in more depth below but outside of this we have the global flash PMIs on Thursday as well as inflation reports in Japan (Thursday) and the UK (Wednesday). US housing data also permeates through the week as you'll see in the full global day-by-day week ahead at the end as usual.
Let’s go into detail now, starting with the BoJ tomorrow. We’ve had negative base rates now for 8 years which if is the longest run ever seen for any country in the history of mankind. In fact it is doubtful that pre-historic man was as generous as to charge negative interest rates on lending money prior to this! It also might be one of the longest global runs without any interest rate hikes given the 17 year run that could end tomorrow. So, as Reid puts it, a landmark event.
DB's Chief Japan economist expects the central bank to revise its policy and abandon both NIRP and the multi-tiered current account structure and set rates on all excess reserves at 0.1%. He also sees both the yield curve control (YCC) and the inflation-overshooting commitment ending, replaced by a benchmark for the pace of the bank’s JGB purchasing activity. The house view forecast of 50bps of hikes through 2025 is more hawkish than the market but risks are still tilted to the upside. On Friday, the Japan Trade Union Confederation (Rengo) announced the first tally of the results of this year's shunto spring wage negotiation. The wage increase rate, including the seniority-based wage hike, is 5.28%, which was significantly higher than expected. This year will probably see the highest wage settlements since 1991 which given Japan’s recent history is an incredible turnaround. This wage data news has firmed up expectations for tomorrow.
With regards to the FOMC which concludes on Wednesday, DB economists expect only minor revisions to the meeting statement that saw an overhaul last meeting. With regards to the SEP, the growth and unemployment forecasts are unlikely to change but the 2024 inflation forecasts potentially could; elsewhere, expect the Fed to revise up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast by a tenth to 2.5%, although they see meaningful risks that it gets revised up even higher to 2.6%. In our economists' view, a 2.5% core PCE reading would allow just enough wiggle room to keep the 2024 fed funds rate at 4.6% (75bps of cuts). However, if core PCE inflation were revised up to 2.6%, it would likely entail the Fed moving their base case back to 50bps of cuts, as this would essentially reflect the same forecasts as the September 2023 SEP.
Beyond 2024, DB expect officials to build in less policy easing due to a higher r-star. If two of the eight officials currently at 2.5% move up by 25bps, then the long-run median forecast would edge up to 2.6%. This could be justified by a one-tenth upgrade to the long-run growth forecast. After all this information is released the presser from Powell will of course be heavily scrutinised, especially on how Powell sees recent inflation data. Powell should also provide an update on discussions around QT but it is unlikely they are ready yet to release updated guidance.
One additional global highlight this week might be a big fall in UK inflation on Wednesday, suggesting that headline CPI will slow to 3.4% (vs 4% in January) and core to 4.5% (5.1%). Elsewhere there is plenty of ECB speaker appearances including President Lagarde on Wednesday. They are all highlighted in the day-by-day guide at the end.
Courtesy of DB, here is a day-by-day calendar of events
Monday March 18
- Data: US March New York Fed services business activity, NAHB housing market index, China February retail sales, industrial production, property investment, Eurozone January trade balance, Canada February raw materials, industrial product price index, existing home sales
Tuesday March 19
- Data: US January total net TIC flows, February housing starts, building permits, Japan January capacity utilization, Germany and Eurozone March Zew survey, Eurozone Q4 labour costs, Canada February CPI
- Central banks: BoJ decision, ECB's Guindos speaks, RBA decision
- Auctions: US 20-yr Bond ($13bn, reopening)
Wednesday March 20
- Data: UK February CPI, PPI, RPI, January house price index, China 1-yr and 5-yr loan prime rates, Japan February trade balance, Italy January industrial production, Germany February PPI, Eurozone March consumer confidence, January construction output
- Central banks: Fed's decision, ECB's Lagarde, Lane, De Cos, Schnabel, Nagel and Holzmann speak, BoC summary of deliberations
- Earnings: Tencent, Micron
Thursday March 21
- Data: US, UK, Japan, Germany, France and Eurozone March PMIs, US March Philadelphia Fed business outlook, February leading index, existing home sales, Q4 current account balance, initial jobless claims, UK February public finances, Japan February national CPI, Italy January current account balance, France March manufacturing confidence, February retail sales, ECB January current account, EU27 February new car registrations
- Central banks: BoE decision, SNB decision
- Earnings: Nike, FedEx, Lululemon, BMW, Enel
- Auctions: US 10-yr TIPS ($16bn, reopening)
- Other: European Union summit, through March 22
Friday March 22
- Data: UK March GfK consumer confidence, February retail sales, Germany March Ifo survey, January import price index, Canada January retail sales
* * *
Finally, looking at just the US, Goldman notes that the key economic data releases this week are the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index and existing home sales reports on Thursday. The March FOMC meeting is on Wednesday. The post-meeting statement will be released at 2:00 PM ET, followed by Chair Powell’s press conference at 2:30 PM. There are several speaking engagements from Fed officials this week, including Chair Powell, Vice Chair for Supervision Barr, and President Bostic.
Monday, March 18
- There are no major economic data releases scheduled.
Tuesday, March 19
- 08:30 AM Housing starts, February (GS +9.4%, consensus +7.4%, last -14.8%); Building permits, February (consensus +2.0%, last -0.3%)
Wednesday, March 20
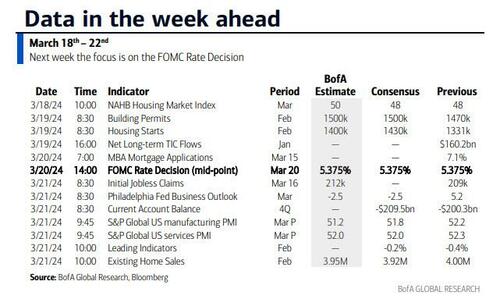
- 02:00 PM FOMC statement, March 19 – March 20 meeting: As discussed in our FOMC preview, we continue to expect the committee to target a first cut in June, but we now expect 3 cuts in 2024 in June, September, and December (vs. 4 previously) given the slightly higher inflation path. We continue to expect 4 cuts in 2025 and now expect 1 final cut in 2026 to an unchanged terminal rate forecast of 3.25-3.5%. The main risk to our expectation is that FOMC participants might be more concerned about the recent inflation data and less convinced that inflation will resume its earlier soft trend. In that case, they might bump up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast to 2.5% and show a 2-cut median.
Thursday, March 21
- 08:30 AM Current account balance, Q4 (consensus -$209.5bn, last -$200.3bn)
- 08:30 AM Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index, March (GS 3.2, consensus -1.3, last 5.2): We estimate that the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index fell 2pt to 3.2 in March. While the measure is elevated relative to other surveys, we expect a boost from the rebound in foreign manufacturing activity and the pickup in US production and freight activity.
- 08:30 AM Initial jobless claims, week ended March 16 (GS 210k, consensus 215k, last 209k): Continuing jobless claims, week ended March 9 (consensus 1,815k, last 1,811k)
- 09:45 AM S&P Global US manufacturing PMI, March preliminary (consensus 51.8, last 52.2): S&P Global US services PMI, March preliminary (consensus 52.0, last 52.3)
- 10:00 AM Existing home sales, February (GS +1.2%, consensus -1.6%, last +3.1%)
- 02:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair Michael for Supervision Barr will participate in a fireside chat in Ann Arbor, MI with students and faculty. A moderated Q&A is expected. On February 14, Barr said the Fed is “confident we are on a path to 2% inflation,” but the recent report showing prices rose faster than anticipated in January “is a reminder that the path back to 2% inflation may be a bumpy one.” Barr also noted that “we need to see continued good data before we can begin the process of reducing the federal funds rate.”
Friday, March 22
- 09:00 AM Fed Reserve Chair Powell speaks: The Federal Reserve Board will host a Fed Listens event in Washington D.C. on “Transitioning to the Post-Pandemic Economy.” Chair Powell will deliver opening remarks. Vice Chair Phillip Jefferson and Fed Governor Michelle Bowman will moderate conversations with leaders from various organizations. On March 6, Chair Powell noted in his congressional testimony that if the economy evolves broadly as expected, it will likely be appropriate to begin dialing back policy restraint at some point this year.
- 12:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Michael Barr will participate in a virtual event on “International Economic and Monetary Design.” A moderated Q&A is expected.
- 04:00 PM Atlanta Fed President Bostic (FOMC voter) speaks: Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic will participate in a moderated conversation at the 2024 Household Finance Conference in Atlanta. On March 4, Bostic said, “I need to see more progress to feel fully confident that inflation is on a sure path to averaging 2% over time.” Bostic also noted, “I expect the first interest rate cut, which I have penciled in for the third quarter, will be followed by a pause in the following meeting.”
Source: DB, Goldman, BofA
Government
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
According to DB’s Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark…

According to DB's Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark week in markets as the last global holdout on negative rates looks set to be removed as the BoJ likely hikes rates from -0.1% tomorrow." That will likely overshadow the FOMC that concludes on Wednesday that will have its own signalling intrigue given recent strong inflation. We also have the RBA meeting tomorrow and the SNB and BoE meetings on Thursday to close out a big week for global central bankers with many EM countries also deciding on policy. We’ll preview the main meetings in more depth below but outside of this we have the global flash PMIs on Thursday as well as inflation reports in Japan (Thursday) and the UK (Wednesday). US housing data also permeates through the week as you'll see in the full global day-by-day week ahead at the end as usual.
Let’s go into detail now, starting with the BoJ tomorrow. We’ve had negative base rates now for 8 years which if is the longest run ever seen for any country in the history of mankind. In fact it is doubtful that pre-historic man was as generous as to charge negative interest rates on lending money prior to this! It also might be one of the longest global runs without any interest rate hikes given the 17 year run that could end tomorrow. So, as Reid puts it, a landmark event.
DB's Chief Japan economist expects the central bank to revise its policy and abandon both NIRP and the multi-tiered current account structure and set rates on all excess reserves at 0.1%. He also sees both the yield curve control (YCC) and the inflation-overshooting commitment ending, replaced by a benchmark for the pace of the bank’s JGB purchasing activity. The house view forecast of 50bps of hikes through 2025 is more hawkish than the market but risks are still tilted to the upside. On Friday, the Japan Trade Union Confederation (Rengo) announced the first tally of the results of this year's shunto spring wage negotiation. The wage increase rate, including the seniority-based wage hike, is 5.28%, which was significantly higher than expected. This year will probably see the highest wage settlements since 1991 which given Japan’s recent history is an incredible turnaround. This wage data news has firmed up expectations for tomorrow.
With regards to the FOMC which concludes on Wednesday, DB economists expect only minor revisions to the meeting statement that saw an overhaul last meeting. With regards to the SEP, the growth and unemployment forecasts are unlikely to change but the 2024 inflation forecasts potentially could; elsewhere, expect the Fed to revise up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast by a tenth to 2.5%, although they see meaningful risks that it gets revised up even higher to 2.6%. In our economists' view, a 2.5% core PCE reading would allow just enough wiggle room to keep the 2024 fed funds rate at 4.6% (75bps of cuts). However, if core PCE inflation were revised up to 2.6%, it would likely entail the Fed moving their base case back to 50bps of cuts, as this would essentially reflect the same forecasts as the September 2023 SEP.
Beyond 2024, DB expect officials to build in less policy easing due to a higher r-star. If two of the eight officials currently at 2.5% move up by 25bps, then the long-run median forecast would edge up to 2.6%. This could be justified by a one-tenth upgrade to the long-run growth forecast. After all this information is released the presser from Powell will of course be heavily scrutinised, especially on how Powell sees recent inflation data. Powell should also provide an update on discussions around QT but it is unlikely they are ready yet to release updated guidance.
One additional global highlight this week might be a big fall in UK inflation on Wednesday, suggesting that headline CPI will slow to 3.4% (vs 4% in January) and core to 4.5% (5.1%). Elsewhere there is plenty of ECB speaker appearances including President Lagarde on Wednesday. They are all highlighted in the day-by-day guide at the end.
Courtesy of DB, here is a day-by-day calendar of events
Monday March 18
- Data: US March New York Fed services business activity, NAHB housing market index, China February retail sales, industrial production, property investment, Eurozone January trade balance, Canada February raw materials, industrial product price index, existing home sales
Tuesday March 19
- Data: US January total net TIC flows, February housing starts, building permits, Japan January capacity utilization, Germany and Eurozone March Zew survey, Eurozone Q4 labour costs, Canada February CPI
- Central banks: BoJ decision, ECB's Guindos speaks, RBA decision
- Auctions: US 20-yr Bond ($13bn, reopening)
Wednesday March 20
- Data: UK February CPI, PPI, RPI, January house price index, China 1-yr and 5-yr loan prime rates, Japan February trade balance, Italy January industrial production, Germany February PPI, Eurozone March consumer confidence, January construction output
- Central banks: Fed's decision, ECB's Lagarde, Lane, De Cos, Schnabel, Nagel and Holzmann speak, BoC summary of deliberations
- Earnings: Tencent, Micron
Thursday March 21
- Data: US, UK, Japan, Germany, France and Eurozone March PMIs, US March Philadelphia Fed business outlook, February leading index, existing home sales, Q4 current account balance, initial jobless claims, UK February public finances, Japan February national CPI, Italy January current account balance, France March manufacturing confidence, February retail sales, ECB January current account, EU27 February new car registrations
- Central banks: BoE decision, SNB decision
- Earnings: Nike, FedEx, Lululemon, BMW, Enel
- Auctions: US 10-yr TIPS ($16bn, reopening)
- Other: European Union summit, through March 22
Friday March 22
- Data: UK March GfK consumer confidence, February retail sales, Germany March Ifo survey, January import price index, Canada January retail sales
* * *
Finally, looking at just the US, Goldman notes that the key economic data releases this week are the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index and existing home sales reports on Thursday. The March FOMC meeting is on Wednesday. The post-meeting statement will be released at 2:00 PM ET, followed by Chair Powell’s press conference at 2:30 PM. There are several speaking engagements from Fed officials this week, including Chair Powell, Vice Chair for Supervision Barr, and President Bostic.
Monday, March 18
- There are no major economic data releases scheduled.
Tuesday, March 19
- 08:30 AM Housing starts, February (GS +9.4%, consensus +7.4%, last -14.8%); Building permits, February (consensus +2.0%, last -0.3%)
Wednesday, March 20
- 02:00 PM FOMC statement, March 19 – March 20 meeting: As discussed in our FOMC preview, we continue to expect the committee to target a first cut in June, but we now expect 3 cuts in 2024 in June, September, and December (vs. 4 previously) given the slightly higher inflation path. We continue to expect 4 cuts in 2025 and now expect 1 final cut in 2026 to an unchanged terminal rate forecast of 3.25-3.5%. The main risk to our expectation is that FOMC participants might be more concerned about the recent inflation data and less convinced that inflation will resume its earlier soft trend. In that case, they might bump up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast to 2.5% and show a 2-cut median.
Thursday, March 21
- 08:30 AM Current account balance, Q4 (consensus -$209.5bn, last -$200.3bn)
- 08:30 AM Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index, March (GS 3.2, consensus -1.3, last 5.2): We estimate that the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index fell 2pt to 3.2 in March. While the measure is elevated relative to other surveys, we expect a boost from the rebound in foreign manufacturing activity and the pickup in US production and freight activity.
- 08:30 AM Initial jobless claims, week ended March 16 (GS 210k, consensus 215k, last 209k): Continuing jobless claims, week ended March 9 (consensus 1,815k, last 1,811k)
- 09:45 AM S&P Global US manufacturing PMI, March preliminary (consensus 51.8, last 52.2): S&P Global US services PMI, March preliminary (consensus 52.0, last 52.3)
- 10:00 AM Existing home sales, February (GS +1.2%, consensus -1.6%, last +3.1%)
- 02:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair Michael for Supervision Barr will participate in a fireside chat in Ann Arbor, MI with students and faculty. A moderated Q&A is expected. On February 14, Barr said the Fed is “confident we are on a path to 2% inflation,” but the recent report showing prices rose faster than anticipated in January “is a reminder that the path back to 2% inflation may be a bumpy one.” Barr also noted that “we need to see continued good data before we can begin the process of reducing the federal funds rate.”
Friday, March 22
- 09:00 AM Fed Reserve Chair Powell speaks: The Federal Reserve Board will host a Fed Listens event in Washington D.C. on “Transitioning to the Post-Pandemic Economy.” Chair Powell will deliver opening remarks. Vice Chair Phillip Jefferson and Fed Governor Michelle Bowman will moderate conversations with leaders from various organizations. On March 6, Chair Powell noted in his congressional testimony that if the economy evolves broadly as expected, it will likely be appropriate to begin dialing back policy restraint at some point this year.
- 12:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Michael Barr will participate in a virtual event on “International Economic and Monetary Design.” A moderated Q&A is expected.
- 04:00 PM Atlanta Fed President Bostic (FOMC voter) speaks: Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic will participate in a moderated conversation at the 2024 Household Finance Conference in Atlanta. On March 4, Bostic said, “I need to see more progress to feel fully confident that inflation is on a sure path to averaging 2% over time.” Bostic also noted, “I expect the first interest rate cut, which I have penciled in for the third quarter, will be followed by a pause in the following meeting.”
Source: DB, Goldman, BofA
International
Free school meals for all may reduce childhood obesity, while easing financial and logistical burdens for families and schools
Since nutrition standards were strengthened in 2010, eating at school provides many students better diet quality compared with other major U.S. food s…
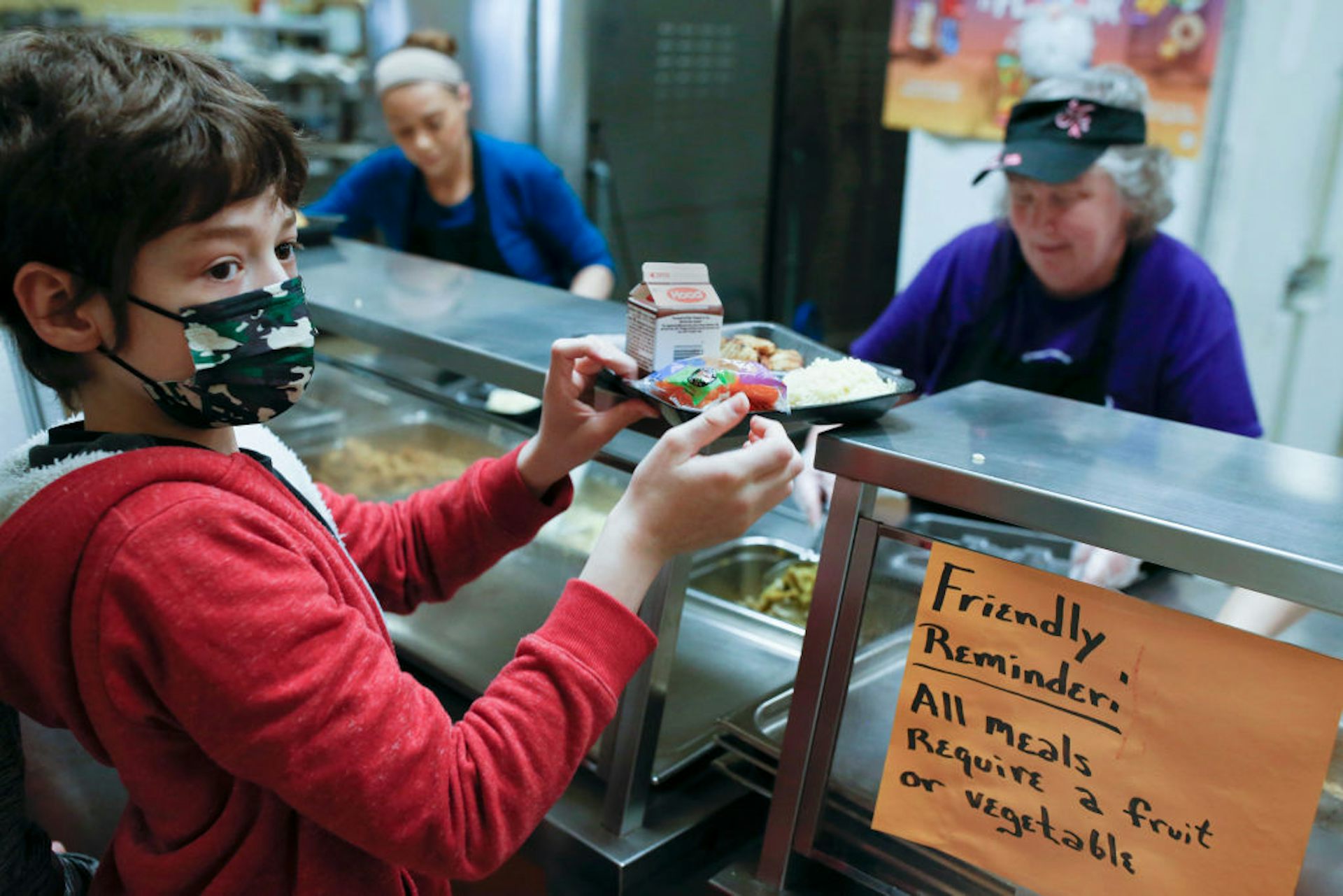

School meals are critical to child health. Research has shown that school meals can be more nutritious than meals from other sources, such as meals brought from home.
A recent study that one of us conducted found the quality of school meals has steadily improved, especially since the 2010 Healthy, Hunger-Free Kids Act strengthened nutrition standards for school meals. In fact, by 2017, another study found that school meals provided the best diet quality of any major U.S. food source.
Many American families became familiar with universal free school meals during the COVID-19 pandemic. To ease the financial and logistical burdens of the pandemic on families and schools, the U.S. Department of Agriculture issued waivers that allowed schools nationwide to provide free breakfast and lunch to all students. However, these waivers expired by the 2022-23 school year.
Since that time, there has been a substantial increase in schools participating in the Community Eligibility Provision, a federal policy that allows schools in high poverty areas to provide free breakfast and lunch to all attending students. The policy became available as an option for low-income schools nationwide in 2014 and was part of the Healthy, Hunger-Free Kids Act. By the 2022-23 school year, over 40,000 schools had adopted the Community Eligibility Provision, an increase of more than 20% over the prior year.
We are public health researchers who study the health effects of nutrition-related policies, particularly those that alleviate poverty. Our newly published research found that the Community Eligibility Provision was associated with a net reduction in the prevalence of childhood obesity.
Improving the health of American children
President Harry Truman established the National School Lunch Program in 1946, with the stated goal of protecting the health and well-being of American children. The program established permanent federal funding for school lunches, and participating schools were required to provide free or reduced-price lunches to children from qualifying households. Eligibility is determined by income based on federal poverty levels, both of which are revised annually.
In 1966, the Child Nutrition Act piloted the School Breakfast Program, which provides free, reduced-price and full-price breakfasts to students. This program was later made permanent through an amendment in 1975.
The Community Eligibility Provision was piloted in several states beginning in 2011 and became an option for eligible schools nationwide beginning in 2014. It operates through the national school lunch and school breakfast programs and expands on these programs.

The policy allows all students in a school to receive free breakfast and lunch, rather than determine eligibility by individual households. Entire schools or school districts are eligible for free lunches if at least 40% of their students are directly certified to receive free meals, meaning their household participated in a means-based safety net program, such as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, or the child is identified as runaway, homeless, in foster care or enrolled in Head Start. Some states also use Medicaid for direct certification.
The Community Eligibility Provision increases school meal participation by reducing the stigma associated with receiving free meals, eliminating the need to complete and process applications and extending access to students in households with incomes above the eligibility threshold for free meals. As of 2023, the eligibility threshold for free meals is 130% of the federal poverty level, which amounts to US$39,000 for a family of four.
Universal free meals and obesity
We analyzed whether providing universal free meals at school through the Community Eligibility Provision was associated with lower childhood obesity before the COVID-19 pandemic.
To do this, we measured changes in obesity prevalence from 2013 to 2019 among 3,531 low-income California schools. We used over 3.5 million body mass index measurements of students in fifth, seventh and ninth grade that were taken annually and aggregated at the school level. To ensure rigorous results, we accounted for differences between schools that adopted the policy and eligible schools that did not. We also followed the same schools over time, comparing obesity prevalence before and after the policy.

We found that schools participating in the Community Eligibility Provision had a 2.4% relative reduction in obesity prevalence compared with eligible schools that did not participate in the provision. Although our findings are modest, even small improvements in obesity levels are notable because effective strategies to reduce obesity at a population level remain elusive. Additionally, because obesity disproportionately affects racially and ethnically marginalized and low-income children, this policy could contribute to reducing health disparities.
The Community Eligibility Provision likely reduces obesity prevalence by substituting up to half of a child’s weekly diet with healthier options and simultaneously freeing up more disposable income for low-to-middle-income families. Families receiving free breakfast and lunch save approximately $4.70 per day per child, or $850 per year. For low-income families, particularly those with multiple school-age children, this could result in meaningful savings that families can use for other health-promoting goods or services.
Expanding access to school meals
Childhood obesity has been increasing over the past several decades. Obesity often continues into adulthood and is linked to a range of chronic health conditions and premature death.
Growing research is showing the benefits of universal free school meals for the health and well-being of children. Along with our study of California schools, other researchers have found an association between universal free school meals and reduced obesity in Chile, South Korea and England, as well as among New York City schools and school districts in New York state.
Studies have also linked the Community Eligibility Provision to improvements in academic performance and reductions in suspensions.
While our research observed a reduction in the prevalence of obesity among schools participating in the Community Eligibility Provision relative to schools that did not, obesity increased over time in both groups, with a greater increase among nonparticipating schools.
Universal free meals policies may slow the rise in childhood obesity rates, but they alone will not be sufficient to reverse these trends. Alongside universal free meals, identifying other population-level strategies to reduce obesity among children is necessary to address this public health issue.
As of 2023, several states have implemented their own universal free school meals policies. States such as California, Maine, Colorado, Minnesota and New Mexico have pledged to cover the difference between school meal expenditures and federal reimbursements. As more states adopt their own universal free meals policies, understanding their effects on child health and well-being, as well as barriers and supports to successfully implementing these programs, will be critical.
Jessica Jones-Smith receives funding from the National Institutes of Health.
Anna Localio does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
south korea mexico pandemic covid-19-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Spread & Containment5 days ago
Spread & Containment5 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















