NY Fed Pres John Williams on coronavirus “We saw signs of concern and we acted promptly and decisively”
NY Fed Pres John Williams on coronavirus “We saw signs of concern and we acted promptly and decisively”


CNBC Exclusive: CNBC Transcript: New York Federal Reserve President John Williams Speaks with CNBC’s Steve Liesman today on handling the coronavirus-fueled crisis.
WHEN: Today, Friday, April 17, 2020
WHERE: CNBC’s “Squawk Box”
Q1 2020 hedge fund letters, conferences and more
Full interview with NY Fed's John Williams on handling the coronavirus-fueled crisis
STEVE LIESMAN: Becky, thanks very much. I’m pleased to be joined by John Williams, the President of the New York Federal Reserve Bank which is really on the frontlines of a lot of the Fed’s response doing the buying and selling and managing a lot of these programs. Good morning, President Williams.
JOHN WILLIAMS: Good morning, Steve.
STEVE LIESMAN: I’m going to start out in a way that was different from how I thought because this morning, John, there’s an air of optimism in the air. The market’s up. The President is announcing a plan to open the economy. There’s a new drug that everybody is excited about. I’m wondering, from an economic point of view, as you look ahead, do you share that optimism now? Are things looking better than you had originally forecast?
JOHN WILLIAMS: Well, this is a rapidly evolving situation and every day, there’s new developments. We try to – we obviously stay on top of that. I still think, you know, we have a lot of economic pain that we’re experiencing today, and that’s likely to continue for some time as these necessary measures that have been taken to limit the spread of coronavirus that continue to hold down the economy. Although I’m hopeful about the eventual bounce back to the economy and the recovery and getting the economy back to full strength, I still think we have some tough days ahead. And that’s why we’re working so hard to support the economy during this difficult period.
STEVE LIESMAN: I want to get to those in a minute. But now, I’m going to start where I was going to normally start, which was yesterday’s jobless claims number, cumulative, John, of 22.5 million over the past several weeks since March 7th. And I don’t think that’s the surprise or really different from what was expected. But I’m wondering, how much when you look at those numbers, do you believe are temporary and can come back very quickly? And what are you thinking about in terms of lasting damage to the economy from this shutdown?
JOHN WILLIAMS: Right. That’s the critical question. Right now, we are seeing the immediate effect that the restrictions and social distancing that have been put into place and that’s shutting down whole sectors of the economy, obviously, hospitality, travel, retail, a lot of areas of the economy have essentially shut down in recent weeks. And that’s why we’re seeing this enormous increase in unemployment, declines -- declines in employment, declines in income. So, I think that is, like you said, the predictable part of this. In terms of looking ahead, you know, we’re watching the data very carefully using a lot of big data and other analytics and not coming to any firm conclusions about how long this will last. And we’re acting in every way we can and doing our utmost to support the economy, however this evolves over the next few months.
In terms of lasting damage, I think that’s a key – a critical question. One of the things that we’re hearing a lot from business contacts and leaders in the community is our concerns that even as the pandemic passes, even as the restrictions are relaxed gradually over time, people may take quite a while before they’re willing to get back on airplanes or trains or go to the theater or go to concerts and things like that. So, I think there are some risks that it takes longer to get that recovery for the economy than just what happens in terms of the formal restrictions that are in place.
One of the things that, you know, we’re very focused on is making sure that businesses and households can get through this period, and that’s what this is about, is making sure credit is flowing and making sure that otherwise healthy businesses can get through this period and be in a good position that once the restrictions are lifted, once the pandemic’s over, they can start their businesses up as fast as possible and get the economy back to full strength.
STEVE LIESMAN: John, Wall Street has a pretty good consensus on an atrocious second quarter but strong rebound in the third quarter. Is that your base case?
JOHN WILLIAMS: Well, definitely we’re seeing, you know, horrible data for the second quarter. We’re already seeing that data, obviously in regional sales, in unemployment and other indicators. So that I agree with in terms of a bounce back, I do think that as we see – when restrictions are relaxed, gradually over time, based on what’s happening with the coronavirus, we will see a return to certain sectors of the economy. In particular, I see construction, which has been hit really hard and it is very important obviously for our economy here in New York, I expect that to be able to bounce back a bit, more quickly than other sectors. I don’t see the economy being back to full strength by the end of the year. It’s going to take us longer to get us back to where we want to be.
STEVE LIESMAN: John, let’s talk about the programs you have in place. The immediate concerns of the Federal Reserve were the Treasury market and the mortgage market and some of the overnight credit markets. Do you feel like those have calmed down? Do you feel like you have a handle on them to the extent where they’re functioning more normally now?
JOHN WILLIAMS: Well, you’re right. That isn’t where we started. Because when the pandemic really started to spread and market participants were, you know, getting more concerned about the economic impact and the uncertainty about that, we saw that enormous tidal wave of money moving from riskier assets and from around the globe into shorter-term safe assets. And the financial system in a way was overwhelmed by that flow of money, and that’s why we saw the illiquidity and some market functioning issues. And what’s really the cornerstone of the global financial system, that’s the U.S. Treasury securities market, and that’s where we intervened most frequently and in enormous scale, in terms of our buying U.S. Treasuries, securities, mortgage-backed securities, and agency commercially backed securities.
That was our initial, where we saw signs of concern and we acted promptly and decisively. We have seen significant improvement in liquidity and market function in those critical sectors. And, you know, my view is if you don’t get those healthy, then it’s impossible to make sure that credit is flowing more generally. So, that’s where we were focused initially. I think those efforts have been successful. We’re still purchasing. But, you know, as we’ve seen, we’ve cut back on the purchases because we’ve seen improvement in those markets. So, we’re seeing liquidity and functioning improving there.
We’re seeing it spill over into other markets. And whether it’s the money market, commercial funds, commercial paper and even corporate bond markets. So, now that we’ve seen, I think, a return to, you know, more stable and better functioning core financial markets, that’s helping all of the markets I think function better. Of course, we have got other programs that are really to support them and support credit flow.
STEVE LIESMAN: Yeah. John, I want to talk about those other programs. There’s two in particular that have raised some criticism about the Federal Reserve. The first one is the Main Street Lending Program. An editorial in "The Journal," actually, two editorials in "The Journal" today, that criticized the Federal Reserve for being too tough on the people who are borrowing not having enough money, not taking enough risk with the Treasury’s money and, of course, involving the banks and it’s going to be too slow to get up and running. What are your responses to that?
JOHN WILLIAMS: I do see the Main Street Program as really an essential part of our approach and the Federal Reserve working with the U.S. Treasury, providing support for the economy and making sure credit is flowing, especially with the small and medium-size businesses. I think it complements the CARES Act, SBA, PPP program and obviously complements our efforts at more broader market functioning and functioning in terms of the large business markets, like the corporate bond market. You know, we are very focused at the Federal Reserve in making sure that this program gets credit flowing immediate, as soon as possible, that it’s hitting the businesses that need it the most and really is done it at scale that addresses the issues that businesses across the country are facing and will face for the next few months.
Clearly, we’ve made an initial announcement at the Federal Reserve around this program. We -- the Federal Reserve also asks for comments and we’re getting a lot of feedback and comments from a variety of stakeholders, businesses, non-profits, and banks to help us make that program as effective as possible. And we’re committed to getting this right and committed to getting this out into the market as soon as we can.
STEVE LIESMAN: John, thanks for joining us this morning. John Williams, the President of the New York Federal Reserve Bank. Joe, back to you from my bureau, where the bureau chief has declared Friday a no tie day.
The post NY Fed Pres John Williams on coronavirus “We saw signs of concern and we acted promptly and decisively” appeared first on ValueWalk.
Uncategorized
Tight inventory and frustrated buyers challenge agents in Virginia
With inventory a little more than half of what it was pre-pandemic, agents are struggling to find homes for clients in Virginia.
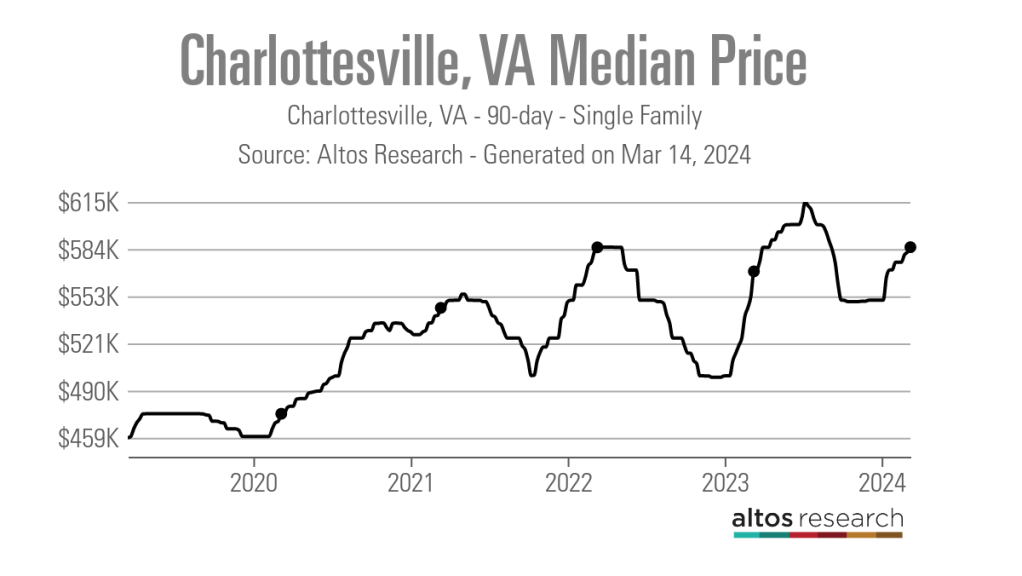
No matter where you are in the state, real estate agents in Virginia are facing low inventory conditions that are creating frustrating scenarios for their buyers.
“I think people are getting used to the interest rates where they are now, but there is just a huge lack of inventory,” said Chelsea Newcomb, a RE/MAX Realty Specialists agent based in Charlottesville. “I have buyers that are looking, but to find a house that you love enough to pay a high price for — and to be at over a 6.5% interest rate — it’s just a little bit harder to find something.”
Newcomb said that interest rates and higher prices, which have risen by more than $100,000 since March 2020, according to data from Altos Research, have caused her clients to be pickier when selecting a home.
“When rates and prices were lower, people were more willing to compromise,” Newcomb said.
Out in Wise, Virginia, near the westernmost tip of the state, RE/MAX Cavaliers agent Brett Tiller and his clients are also struggling to find suitable properties.
“The thing that really stands out, especially compared to two years ago, is the lack of quality listings,” Tiller said. “The slightly more upscale single-family listings for move-up buyers with children looking for their forever home just aren’t coming on the market right now, and demand is still very high.”
Statewide, Virginia had a 90-day average of 8,068 active single-family listings as of March 8, 2024, down from 14,471 single-family listings in early March 2020 at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Altos Research. That represents a decrease of 44%.

In Newcomb’s base metro area of Charlottesville, there were an average of only 277 active single-family listings during the same recent 90-day period, compared to 892 at the onset of the pandemic. In Wise County, there were only 56 listings.
Due to the demand from move-up buyers in Tiller’s area, the average days on market for homes with a median price of roughly $190,000 was just 17 days as of early March 2024.
“For the right home, which is rare to find right now, we are still seeing multiple offers,” Tiller said. “The demand is the same right now as it was during the heart of the pandemic.”
According to Tiller, the tight inventory has caused homebuyers to spend up to six months searching for their new property, roughly double the time it took prior to the pandemic.
For Matt Salway in the Virginia Beach metro area, the tight inventory conditions are creating a rather hot market.
“Depending on where you are in the area, your listing could have 15 offers in two days,” the agent for Iron Valley Real Estate Hampton Roads | Virginia Beach said. “It has been crazy competition for most of Virginia Beach, and Norfolk is pretty hot too, especially for anything under $400,000.”
According to Altos Research, the Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News housing market had a seven-day average Market Action Index score of 52.44 as of March 14, making it the seventh hottest housing market in the country. Altos considers any Market Action Index score above 30 to be indicative of a seller’s market.

Further up the coastline on the vacation destination of Chincoteague Island, Long & Foster agent Meghan O. Clarkson is also seeing a decent amount of competition despite higher prices and interest rates.
“People are taking their time to actually come see things now instead of buying site unseen, and occasionally we see some seller concessions, but the traffic and the demand is still there; you might just work a little longer with people because we don’t have anything for sale,” Clarkson said.
“I’m busy and constantly have appointments, but the underlying frenzy from the height of the pandemic has gone away, but I think it is because we have just gotten used to it.”
While much of the demand that Clarkson’s market faces is for vacation homes and from retirees looking for a scenic spot to retire, a large portion of the demand in Salway’s market comes from military personnel and civilians working under government contracts.
“We have over a dozen military bases here, plus a bunch of shipyards, so the closer you get to all of those bases, the easier it is to sell a home and the faster the sale happens,” Salway said.
Due to this, Salway said that existing-home inventory typically does not come on the market unless an employment contract ends or the owner is reassigned to a different base, which is currently contributing to the tight inventory situation in his market.
Things are a bit different for Tiller and Newcomb, who are seeing a decent number of buyers from other, more expensive parts of the state.
“One of the crazy things about Louisa and Goochland, which are kind of like suburbs on the western side of Richmond, is that they are growing like crazy,” Newcomb said. “A lot of people are coming in from Northern Virginia because they can work remotely now.”
With a Market Action Index score of 50, it is easy to see why people are leaving the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria market for the Charlottesville market, which has an index score of 41.
In addition, the 90-day average median list price in Charlottesville is $585,000 compared to $729,900 in the D.C. area, which Newcomb said is also luring many Virginia homebuyers to move further south.

“They are very accustomed to higher prices, so they are super impressed with the prices we offer here in the central Virginia area,” Newcomb said.
For local buyers, Newcomb said this means they are frequently being outbid or outpriced.
“A couple who is local to the area and has been here their whole life, they are just now starting to get their mind wrapped around the fact that you can’t get a house for $200,000 anymore,” Newcomb said.
As the year heads closer to spring, triggering the start of the prime homebuying season, agents in Virginia feel optimistic about the market.
“We are seeing seasonal trends like we did up through 2019,” Clarkson said. “The market kind of soft launched around President’s Day and it is still building, but I expect it to pick right back up and be in full swing by Easter like it always used to.”
But while they are confident in demand, questions still remain about whether there will be enough inventory to support even more homebuyers entering the market.
“I have a lot of buyers starting to come off the sidelines, but in my office, I also have a lot of people who are going to list their house in the next two to three weeks now that the weather is starting to break,” Newcomb said. “I think we are going to have a good spring and summer.”
real estate housing market pandemic covid-19 interest ratesSpread & Containment
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
‘Excess Mortality Skyrocketed’: Tucker Carlson and Dr. Pierre Kory Unpack ‘Criminal’ COVID Response
As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded…

As the global pandemic unfolded, government-funded experimental vaccines were hastily developed for a virus which primarily killed the old and fat (and those with other obvious comorbidities), and an aggressive, global campaign to coerce billions into injecting them ensued.
Then there were the lockdowns - with some countries (New Zealand, for example) building internment camps for those who tested positive for Covid-19, and others such as China welding entire apartment buildings shut to trap people inside.
It was an egregious and unnecessary response to a virus that, while highly virulent, was survivable by the vast majority of the general population.
Oh, and the vaccines, which governments are still pushing, didn't work as advertised to the point where health officials changed the definition of "vaccine" multiple times.
Tucker Carlson recently sat down with Dr. Pierre Kory, a critical care specialist and vocal critic of vaccines. The two had a wide-ranging discussion, which included vaccine safety and efficacy, excess mortality, demographic impacts of the virus, big pharma, and the professional price Kory has paid for speaking out.
Keep reading below, or if you have roughly 50 minutes, watch it in its entirety for free on X:
Ep. 81 They’re still claiming the Covid vax is safe and effective. Yet somehow Dr. Pierre Kory treats hundreds of patients who’ve been badly injured by it. Why is no one in the public health establishment paying attention? pic.twitter.com/IekW4Brhoy
— Tucker Carlson (@TuckerCarlson) March 13, 2024
"Do we have any real sense of what the cost, the physical cost to the country and world has been of those vaccines?" Carlson asked, kicking off the interview.
"I do think we have some understanding of the cost. I mean, I think, you know, you're aware of the work of of Ed Dowd, who's put together a team and looked, analytically at a lot of the epidemiologic data," Kory replied. "I mean, time with that vaccination rollout is when all of the numbers started going sideways, the excess mortality started to skyrocket."
When asked "what kind of death toll are we looking at?", Kory responded "...in 2023 alone, in the first nine months, we had what's called an excess mortality of 158,000 Americans," adding "But this is in 2023. I mean, we've had Omicron now for two years, which is a mild variant. Not that many go to the hospital."
'Safe and Effective'
Tucker also asked Kory why the people who claimed the vaccine were "safe and effective" aren't being held criminally liable for abetting the "killing of all these Americans," to which Kory replied: "It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and effective] was a predetermined conclusion. There was no data to support that, but it was agreed upon that it would be presented as safe and effective."
Tucker Carlson Asks the Forbidden Question
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
He wants to know why the people who made the claim “safe and effective” aren’t being held to criminal liability for abetting the “killing of all these Americans.”
DR. PIERRE KORY: “It’s my kind of belief, looking back, that [safe and… pic.twitter.com/Icnge18Rtz
Carlson and Kory then discussed the different segments of the population that experienced vaccine side effects, with Kory noting an "explosion in dying in the youngest and healthiest sectors of society," adding "And why did the employed fare far worse than those that weren't? And this particularly white collar, white collar, more than gray collar, more than blue collar."
Kory also said that Big Pharma is 'terrified' of Vitamin D because it "threatens the disease model." As journalist The Vigilant Fox notes on X, "Vitamin D showed about a 60% effectiveness against the incidence of COVID-19 in randomized control trials," and "showed about 40-50% effectiveness in reducing the incidence of COVID-19 in observational studies."
Dr. Pierre Kory: Big Pharma is ‘TERRIFIED’ of Vitamin D
— The Vigilant Fox ???? (@VigilantFox) March 14, 2024
Why?
Because “It threatens the DISEASE MODEL.”
A new meta-analysis out of Italy, published in the journal, Nutrients, has unearthed some shocking data about Vitamin D.
Looking at data from 16 different studies and 1.26… pic.twitter.com/q5CsMqgVju
Professional costs
Kory - while risking professional suicide by speaking out, has undoubtedly helped save countless lives by advocating for alternate treatments such as Ivermectin.
Kory shared his own experiences of job loss and censorship, highlighting the challenges of advocating for a more nuanced understanding of vaccine safety in an environment often resistant to dissenting voices.
"I wrote a book called The War on Ivermectin and the the genesis of that book," he said, adding "Not only is my expertise on Ivermectin and my vast clinical experience, but and I tell the story before, but I got an email, during this journey from a guy named William B Grant, who's a professor out in California, and he wrote to me this email just one day, my life was going totally sideways because our protocols focused on Ivermectin. I was using a lot in my practice, as were tens of thousands of doctors around the world, to really good benefits. And I was getting attacked, hit jobs in the media, and he wrote me this email on and he said, Dear Dr. Kory, what they're doing to Ivermectin, they've been doing to vitamin D for decades..."
"And it's got five tactics. And these are the five tactics that all industries employ when science emerges, that's inconvenient to their interests. And so I'm just going to give you an example. Ivermectin science was extremely inconvenient to the interests of the pharmaceutical industrial complex. I mean, it threatened the vaccine campaign. It threatened vaccine hesitancy, which was public enemy number one. We know that, that everything, all the propaganda censorship was literally going after something called vaccine hesitancy."
Money makes the world go 'round
Carlson then hit on perhaps the most devious aspect of the relationship between drug companies and the medical establishment, and how special interests completely taint science to the point where public distrust of institutions has spiked in recent years.
"I think all of it starts at the level the medical journals," said Kory. "Because once you have something established in the medical journals as a, let's say, a proven fact or a generally accepted consensus, consensus comes out of the journals."
"I have dozens of rejection letters from investigators around the world who did good trials on ivermectin, tried to publish it. No thank you, no thank you, no thank you. And then the ones that do get in all purportedly prove that ivermectin didn't work," Kory continued.
"So and then when you look at the ones that actually got in and this is where like probably my biggest estrangement and why I don't recognize science and don't trust it anymore, is the trials that flew to publication in the top journals in the world were so brazenly manipulated and corrupted in the design and conduct in, many of us wrote about it. But they flew to publication, and then every time they were published, you saw these huge PR campaigns in the media. New York Times, Boston Globe, L.A. times, ivermectin doesn't work. Latest high quality, rigorous study says. I'm sitting here in my office watching these lies just ripple throughout the media sphere based on fraudulent studies published in the top journals. And that's that's that has changed. Now that's why I say I'm estranged and I don't know what to trust anymore."
Vaccine Injuries
Carlson asked Kory about his clinical experience with vaccine injuries.
"So how this is how I divide, this is just kind of my perception of vaccine injury is that when I use the term vaccine injury, I'm usually referring to what I call a single organ problem, like pericarditis, myocarditis, stroke, something like that. An autoimmune disease," he replied.
"What I specialize in my practice, is I treat patients with what we call a long Covid long vaxx. It's the same disease, just different triggers, right? One is triggered by Covid, the other one is triggered by the spike protein from the vaccine. Much more common is long vax. The only real differences between the two conditions is that the vaccinated are, on average, sicker and more disabled than the long Covids, with some pretty prominent exceptions to that."
Watch the entire interview above, and you can support Tucker Carlson's endeavors by joining the Tucker Carlson Network here...
Uncategorized
These Cities Have The Highest (And Lowest) Share Of Unaffordable Neighborhoods In 2024
These Cities Have The Highest (And Lowest) Share Of Unaffordable Neighborhoods In 2024
Authored by Sam Bourgi via CreditNews.com,
Homeownership…

Authored by Sam Bourgi via CreditNews.com,
Homeownership is one of the key pillars of the American dream. But for many families, the idyllic fantasy of a picket fence and backyard barbecues remains just that—a fantasy.
Thanks to elevated mortgage rates, sky-high house prices, and scarce inventory, millions of American families have been locked out of the opportunity to buy a home in many cities.
To shed light on America’s housing affordability crisis, Creditnews Research ranked the 50 most populous cities by the percentage of neighborhoods within reach for the typical married-couple household to buy a home in.
The study reveals a stark reality, with many cities completely out of reach for the most affluent household type. Not only that, the unaffordability has radically worsened in recent years.
Comparing how affordability has changed since Covid, Creditnews Research discovered an alarming pattern—indicating consistently more unaffordable housing in all but three cities.
Fortunately, there’s still hope for households seeking to put down roots in more affordable cities—especially for those looking beyond Los Angeles, New York, Boston, San Jone, and Miami.
The typical American family has a hard time putting down roots in many parts of the country. In 11 of the top 50 cities, at least 50% of neighborhoods are out of reach for the average married-couple household. The affordability gap has widened significantly since Covid; in fact, no major city has reported an improvement in affordability post-pandemic.
Sam Bourgi, Senior Analyst at Creditnews
Key findings
-
The most unaffordable cities are Los Angeles, Boston, St. Louis, and San Jose; in each city, 100% of neighborhoods are out of reach for for married-couple households earning a median income;
-
The most affordable cities are Cleveland, Hartford, and Memphis—in these cities, the typical family can afford all neighborhoods;
-
None of the top 50 cities by population saw an improvement in affordable neighborhoods post-pandemic;
-
California recorded the biggest spike in unaffordable neighborhoods since pre-Covid;
-
The share of unaffordable neighborhoods has increased the most since pre-Covid in San Jose (70 percentage points), San Diego (from 57.8 percentage points), and Riverside-San Bernardino (51.9 percentage points);
-
Only three cities have seen no change in housing affordability since pre-Covid: Cleveland, Memphis, and Hartford. They’re also the only cities that had 0% of unaffordable neighborhoods before Covid.
Cities with the highest share of unaffordable neighborhoods
With few exceptions, the most unaffordable cities for married-couple households tend to be located in some of the nation’s most expensive housing markets.
Four cities in the ranking have an unaffordability percentage of 100%—indicating that the median married-couple household couldn’t qualify for an average home in any neighborhood.
The following are the cities ranked from the least affordable to the most:
-
Los Angeles, CA: Housing affordability in Los Angeles has deteriorated over the last five years, as average incomes have failed to keep pace with rising property values and elevated mortgage rates. The median household income of married-couple families in LA is $117,056, but even at that rate, 100% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable.
-
St. Louis, MO: It may be surprising to see St. Louis ranking among the most unaffordable housing markets for married-couple households. But a closer look reveals that the Mound City was unaffordable even before Covid. In 2019, 98% of the city’s neighborhoods were unaffordable—way worse than Los Angeles, Boston, or San Jose.
-
Boston, MA: Boston’s housing affordability challenges began long before Covid but accelerated after the pandemic. Before Covid, married couples earning a median income were priced out of 90.7% of Boston’s neighborhoods. But that figure has since jumped to 100%, despite a comfortable median household income of $172,223.
-
San Jose, CA: Nestled in Silicon Valley, San Jose has long been one of the most expensive cities for housing in America. But things have gotten far worse since Covid, as 100% of its neighborhoods are now out of reach for the average family. Perhaps the most shocking part is that the median household income for married-couple families is $188,403—much higher than the national average.
-
San Diego, CA: Another California city, San Diego, is among the most unaffordable places in the country. Despite boasting a median married-couple household income of $136,297, 95.6% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable.
-
San Francisco, CA: San Francisco is another California city with a high married-couple median income ($211,585) but low affordability. The percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods for these homebuyers stands at 89.2%.
-
New York, NY: As one of the most expensive cities in America, New York is a difficult housing market for married couples with dual income. New York City’s share of unaffordable neighborhoods is 85.9%, marking a 33.4% rise from pre-Covid times.
-
Miami, FL: Partly due to a population boom post-Covid, Miami is now one of the most unaffordable cities for homebuyers. Roughly four out of five (79.4%) of Miami’s neighborhoods are out of reach price-wise for married-couple families. That’s a 34.7% increase from 2019.
-
Nashville, TN: With Nashville’s population growth rebounding to pre-pandemic levels, the city has also seen greater affordability challenges. In the Music City, 73.7% of neighborhoods are considered unaffordable for married-couple households—an increase of 11.9% from pre-Covid levels.
-
Richmond, VA: Rounding out the bottom 10 is Richmond, where 55.9% of the city’s 161 neighborhoods are unaffordable for married-couple households. That’s an 11.9% increase from pre-Covid levels.
Cities with the lowest share of unaffordable neighborhoods
All the cities in our top-10 ranking have less than 10% unaffordable neighborhoods—meaning the average family can qualify for a home in at least 90% of the city.
Interestingly, these cities are also outside the top 15 cities by population, and eight are in the bottom half.
The following are the cities ranked from the most affordable to the least:
-
Hartford, CT: Hartford ranks first with the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods at 0%, unchanged since pre-Covid times. Married couples earning a median income of $135,612 can afford to live in any of the city’s 16 neighborhoods. Interestingly, Hartford is the smallest city to rank in the top 10.
-
Memphis, TN: Like Hartford, Memphis has 0% unaffordable neighborhoods, meaning any married couple earning a median income of $101,734 can afford an average homes in any of the city’s 12 neighborhoods. The percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods also stood at 0% before Covid.
-
Cleveland, OH: The Midwestern city of Cleveland is also tied for first, with the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods at 0%. That means households with a median-couple income of $89,066 can qualify for an average home in all of the city’s neighborhoods. Cleveland is also among the three cities that have seen no change in unaffordability compared to 2019.
-
Minneapolis, MN: The largest city in the top 10, Minneapolis’ share of unaffordable neighborhoods stood at 2.41%, up slightly from 2019. Married couples earning the median income ($149,214) have access to the vast majority of the city’s 83 neighborhoods.
-
Baltimore, MD: Married-couple households in Baltimore earn a median income of $141,634. At that rate, they can afford to live in 97.3% of the city’s 222 neighborhoods, making only 2.7% of neighborhoods unaffordable. That’s up from 0% pre-Covid.
-
Louisville, KY: Louisville is a highly competitive market for married households. For married-couple households earning a median wage, only 3.6% of neighborhoods are unaffordable, up 11.9% from pre-Covid times.
-
Cincinnati, OH: The second Ohio city in the top 10 ranks close to Cleveland in population but has a much higher median married-couple household income of $129,324. Only 3.6% of the city’s neighborhoods are unaffordable, up slightly from pre-pandemic levels.
-
Indianapolis, IN: Another competitive Midwestern market, only 4.4% of Indianapolis is unaffordable, making the vast majority of the city’s 92 neighborhoods accessible to the average married couple. Still, the percentage of unaffordable neighborhoods before Covid was less than 1%.
-
Oklahoma City, OK: Before Covid, Oklahoma City had 0% neighborhoods unaffordable for married-couple households earning the median wage. It has since increased to 4.69%, which is still tiny compared to the national average.
-
Kansas City, MO: Kansas City has one of the largest numbers of neighborhoods in the top 50 cities. Its married-couple residents can afford to live in nearly 95% of them, making only 5.6% of neighborhoods out of reach. Like Indiana, Kansas City’s share of unaffordable neighborhoods was less than 1% before Covid.
The biggest COVID losers
What's particularly astonishing about the current housing market is just how quickly affordability has declined since Covid.
Even factoring in the market correction after the 2022 peak, the price of existing homes is still nearly one-third higher than before Covid. Mortgage rates have also more than doubled since early 2022.
Combined, the rising home prices and interest rates led to the worst mortgage affordability in more than 40 years.
Against this backdrop, it’s hardly surprising that unaffordability increased in 47 of the 50 cities studied and remained flat in the other three. No city reported improved affordability in 2024 compared to 2019.
The biggest increases are led by San Jose (70 percentage points), San Diego (57.8 percentage points), Riverside-San Bernardino (51.9 percentage points), Sacramento (43 percentage points), Orlando (37.4 percentage points), Miami (34.7 percentage points), and New York City (33.4 percentage points).
The following cities in our study are ranked by the largest percentage point change in unaffordable neighborhoods since pre-Covid:
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges























