Investigators from Weill Cornell Medicine and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have discovered how a drug for multiple sclerosis interacts with its targets, a finding that may pave the way for better treatments.
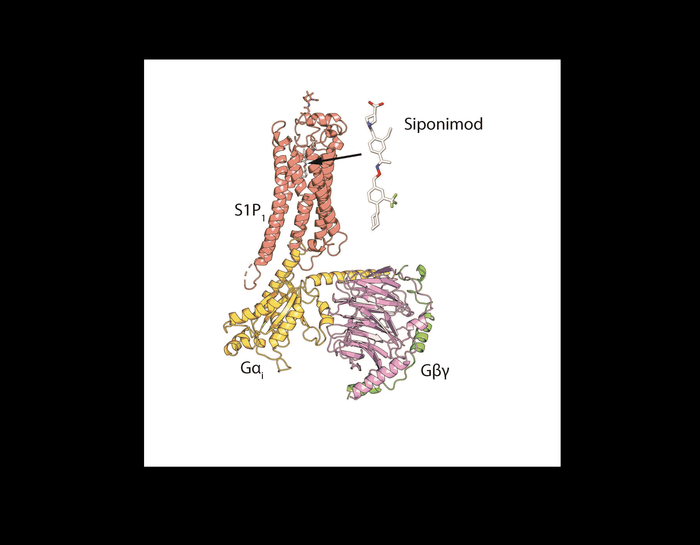
The study, published Feb. 8 in Nature Communications, details the precise molecular structure of the multiple sclerosis drug siponimod as it interacts with its target, the human S1P receptor 1 (S1P1), and off-target receptors using a cutting-edge electron microscopy technique called cryo-EM. This knowledge could help scientists develop drugs for the disease that are less likely to miss their targets.
“This discovery will help us improve drugs for multiple sclerosis and reduce their side effects,” said the study’s co-senior author Dr. Xin-Yun Huang, professor of physiology and biophysics at Weill Cornell Medicine.
In patients with multiple sclerosis, immune cells called lymphocytes attack and destroy the protective sheath around nerve cells, causing progressive neurologic symptoms. Scientists developed immune-suppressing drugs that block the release of these lymphocytes from the lymph nodes by binding to S1P1 receptors. But the first-generation version of these drugs could also bind to related receptors including S1P3, which caused unwanted side effects including an abnormal heart rhythm. To address this problem, scientists created next-generation medications like siponimod that bind more selectively to S1P1 and another receptor called S1P5. But this didn’t eliminate all unwanted side effects.
The new study, co-led by Dr. Shian Liu, a research associate at Weill Cornell Medicine, and Navid Paknejad, a graduate student at Memorial Sloan Kettering, reveals how siponimod binds to these two receptors and the features of the molecule that prevent it from binding to unwanted targets like S1P2, S1P3 and S1P4. Scientists can use this information to modify the drug to help it attach more tightly to its target (S1P1) and less likely to bind with unintended target (S1P5), reducing the risk of side effects.
“This new structural information will help us develop the next generation of multiple sclerosis drugs,” Dr. Huang said.
The study also helps explain how naturally occurring lipids can regulate the immune system, the nervous system and lung function. The team found that nearly identical lipids called sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid assumed very different shapes when bound to their target receptors.
“Lipids are highly plastic molecules, and the structures reveal how the receptors leverage subtle differences in the lipids structures to discriminate between them,” said co-senior author Dr. Richard Hite, a structural biologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering and an assistant professor in the biochemistry and structural biology and the physiology, biophysics and systems biology programs at the Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences.
“This explains how lipids can play very different roles in the body even though their chemical structures are very similar,” Dr. Huang said.
The finding highlights the importance of carefully designing lipid-based drugs to prevent them from missing their targets. “We need to make lipid-based drugs that are very specific to reduce the risk of side effects,” he said.
These new insights may help scientists develop improved treatments for other autoimmune diseases like inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis and systemic lupus. They might also help scientists create lipid-based therapies for conditions that affect the brain or lungs. For example, Dr. Huang noted that there are currently lipid-based drugs in clinical trials to reduce lung stiffening in patients with COVID-19.
Many Weill Cornell Medicine physicians and scientists maintain relationships and collaborate with external organizations to foster scientific innovation and provide expert guidance. The institution makes these disclosures public to ensure transparency. For this information, see profile for Dr. Xin-Yun Huang.
Journal
Nature Communications