International
Monkeypox may not mutate as fast as coronaviruses, but that doesn’t mean it can’t adapt to its new hosts
Monkeypox may not churn out variants at the rate of SARS-CoV-2, but that doesn’t mean we can rest easy.
The recent outbreak of monkeypox virus has called into question the capabilities of these kinds large DNA viruses to evolve, adapt and change their biology.
Compared with small RNA viruses such as coronavirus, monkeypox virus and other large DNA viruses are thought to evolve slowly. Yet there’s clear evidence that this really isn’t a hindrance to these viruses. In fact, they can adapt to new environments like us.
Although most infections remain mild, monkeypox can be a serious life-threatening disease, resulting in sepsis, encephalitis (brain inflammation) and blindness. The most common symptoms are rash and skin lesions, alongside flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes.
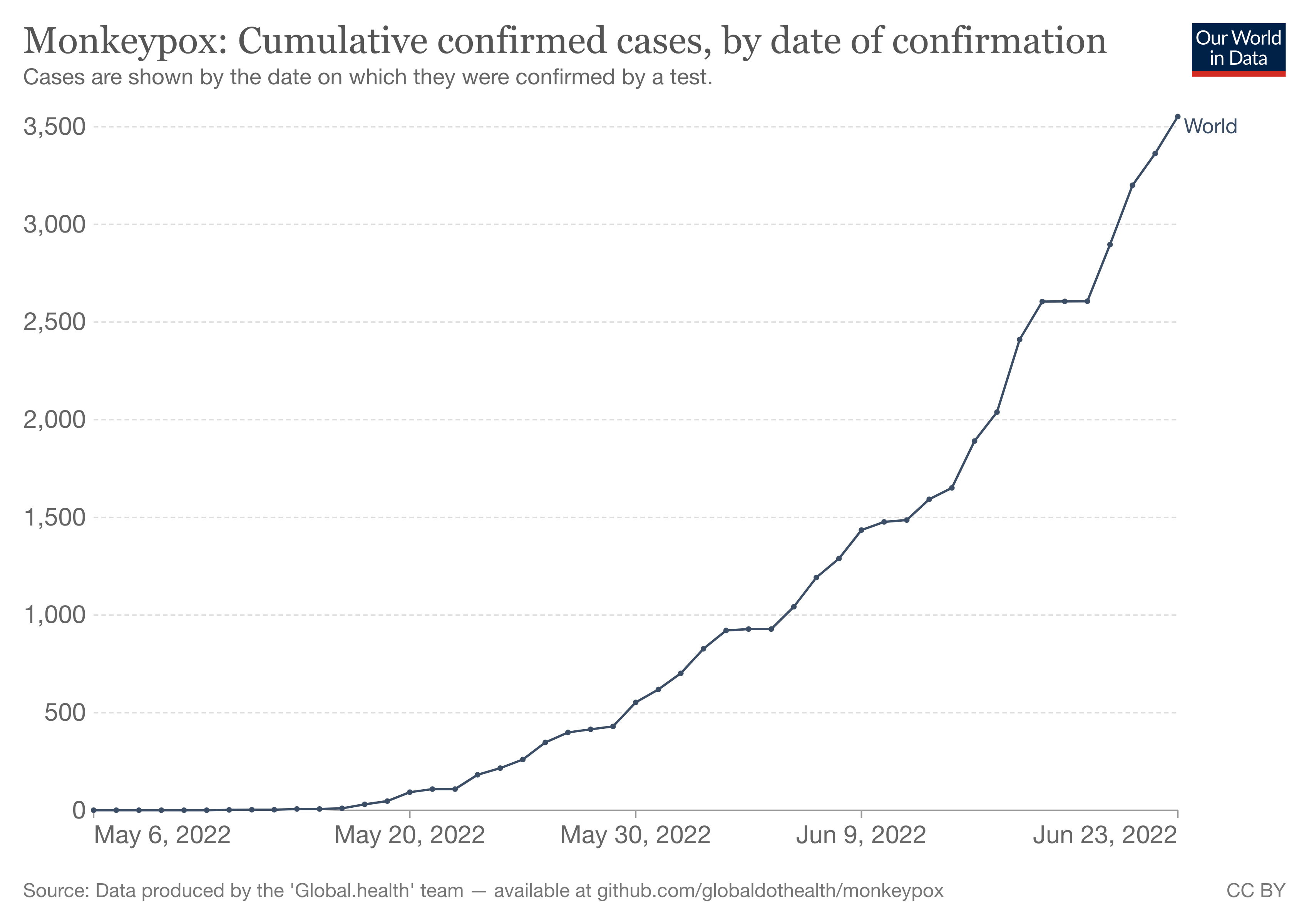
Cumulative monkeypox cases in current outbreak
Monkeypox virus naturally infects wild rodents, such as squirrels and rats, in west and central Africa – but it can jump species into humans and other animals. However, once it has jumped to humans, it cannot keep transmission going and eventually outbreaks die out. This is probably because monkeypox has not adapted itself to its new environment of humans, as spillback into wild rodents from infected humans is unlikely.
Monkeypox is closely related to the viruses that caused smallpox (variola viruses) and the virus that we use to vaccinate and eradicate smallpox (vaccinia virus). This group of viruses, referred to as poxviruses, are a kind of large DNA virus, meaning that their genome is composed of a chemical known as DNA, like our genome. (Coronavirus and related viruses use a cousin molecule called RNA.)
Other DNA viruses are the large DNA viruses adenoviruses and herpesviruses, but also small ones like papillomaviruses and parvoviruses. The viral genomes composed of either DNA or RNA essentially are the instructions to make new viruses, infect us and cause disease. Changes to the instructions can change virus biology.
As we have seen with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, viruses can change how they behave with regards to spreading, disease severity and vaccine sensitivity. This is because of changes accumulating in the virus genome. Virus replication generates diversity in its genome, which can be acted on by evolutionary forces such as natural selection, to increase in frequency and maybe even out-compete older versions.
Evolutionary changes can occur when the virus encounters a new environment that it is not fully adapted to. Although all viruses can evolve rapidly due to their vast population sizes and rapid generation times, RNA viruses are thought to be masters of evolution because they have high mutation rates due to their small size, and many often lack error-correcting ability meaning more mutations occur every time they replicate.
Poxviruses have some characteristics that make them more generalist, including stable infectious particles, giving them more chances to infect. They use very common molecules on your cells to gain entry and infect, unlike SARS-CoV-2 which needs the specific ACE2 protein to gain entry to our cells.
Large DNA viruses such as monkeypox also contain lots of genes that target and manipulate different parts of the immune system.
Room for improvement
However, there’s clear evidence that improvements can be made, because, in humans, monkeypox transmission is relatively inefficient, with long incubation periods.
In general, large DNA viruses such as monkeypox are no different from other viruses, and their mutability is the basis for our ability to track and trace monkeypox outbreaks. They make mistakes and errors accumulate, which can be used as fuel for evolution and biological changes. There’s even evidence from the recent monkeypox outbreak that the host cell is directly mutating the virus genome.
Studies focusing on related poxviruses like the vaccinia virus have even uncovered new tricks they can use, which include rapidly amplifying the number of genes they use to attack our immune system. They could even borrow some of our own genes to help them infect us.
We can’t predict the trajectory that monkeypox evolution will take, so we must take the threat of this virus adapting to its new hosts (humans) seriously. And we need to use all the public health tools at our disposal to halt the current outbreak in all countries – including those where it is endemic.
Connor Bamford receives funding from UKRI, Wellcome Trust, British Medical Association Foundation, SFI.
vaccine genome rna dna coronavirus transmission africaInternational
Red Candle In The Wind
Red Candle In The Wind
By Benjamin PIcton of Rabobank
February non-farm payrolls superficially exceeded market expectations on Friday by…
By Benjamin PIcton of Rabobank
February non-farm payrolls superficially exceeded market expectations on Friday by printing at 275,000 against a consensus call of 200,000. We say superficially, because the downward revisions to prior months totalled 167,000 for December and January, taking the total change in employed persons well below the implied forecast, and helping the unemployment rate to pop two-ticks to 3.9%. The U6 underemployment rate also rose from 7.2% to 7.3%, while average hourly earnings growth fell to 0.2% m-o-m and average weekly hours worked languished at 34.3, equalling pre-pandemic lows.
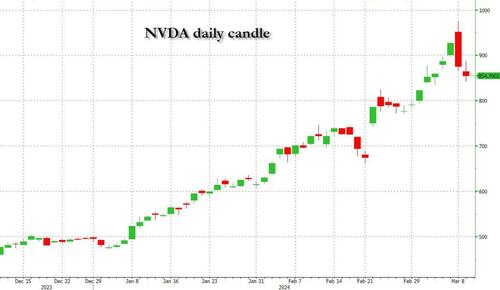
Undeterred by the devil in the detail, the algos sprang into action once exchanges opened. Market darling NVIDIA hit a new intraday high of $974 before (presumably) the humans took over and sold the stock down more than 10% to close at $875.28. If our suspicions are correct that it was the AIs buying before the humans started selling (no doubt triggering trailing stops on the way down), the irony is not lost on us.
The 1-day chart for NVIDIA now makes for interesting viewing, because the red candle posted on Friday presents quite a strong bearish engulfing signal. Volume traded on the day was almost double the 15-day simple moving average, and similar price action is observable on the 1-day charts for both Intel and AMD. Regular readers will be aware that we have expressed incredulity in the past about the durability the AI thematic melt-up, so it will be interesting to see whether Friday’s sell off is just a profit-taking blip, or a genuine trend reversal.
AI equities aside, this week ought to be important for markets because the BTFP program expires today. That means that the Fed will no longer be loaning cash to the banking system in exchange for collateral pledged at-par. The KBW Regional Banking index has so far taken this in its stride and is trading 30% above the lows established during the mini banking crisis of this time last year, but the Fed’s liquidity facility was effectively an exercise in can-kicking that makes regional banks a sector of the market worth paying attention to in the weeks ahead. Even here in Sydney, regulators are warning of external risks posed to the banking sector from scheduled refinancing of commercial real estate loans following sharp falls in valuations.
Markets are sending signals in other sectors, too. Gold closed at a new record-high of $2178/oz on Friday after trading above $2200/oz briefly. Gold has been going ballistic since the Friday before last, posting gains even on days where 2-year Treasury yields have risen. Gold bugs are buying as real yields fall from the October highs and inflation breakevens creep higher. This is particularly interesting as gold ETFs have been recording net outflows; suggesting that price gains aren’t being driven by a retail pile-in. Are gold buyers now betting on a stagflationary outcome where the Fed cuts without inflation being anchored at the 2% target? The price action around the US CPI release tomorrow ought to be illuminating.
Leaving the day-to-day movements to one side, we are also seeing further signs of structural change at the macro level. The UK budget last week included a provision for the creation of a British ISA. That is, an Individual Savings Account that provides tax breaks to savers who invest their money in the stock of British companies. This follows moves last year to encourage pension funds to head up the risk curve by allocating 5% of their capital to unlisted investments.
As a Hail Mary option for a government cruising toward an electoral drubbing it’s a curious choice, but it’s worth highlighting as cash-strapped governments increasingly see private savings pools as a funding solution for their spending priorities.
Of course, the UK is not alone in making creeping moves towards financial repression. In contrast to announcements today of increased trade liberalisation, Australian Treasurer Jim Chalmers has in the recent past flagged his interest in tapping private pension savings to fund state spending priorities, including defence, public housing and renewable energy projects. Both the UK and Australia appear intent on finding ways to open up the lungs of their economies, but government wants more say in directing private capital flows for state goals.
So, how far is the blurring of the lines between free markets and state planning likely to go? Given the immense and varied budgetary (and security) pressures that governments are facing, could we see a re-up of WWII-era Victory bonds, where private investors are encouraged to do their patriotic duty by directly financing government at negative real rates?
That would really light a fire under the gold market.
Spread & Containment
Trump “Clearly Hasn’t Learned From His COVID-Era Mistakes”, RFK Jr. Says
Trump "Clearly Hasn’t Learned From His COVID-Era Mistakes", RFK Jr. Says
Authored by Jeff Louderback via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
President…

Authored by Jeff Louderback via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
President Joe Biden claimed that COVID vaccines are now helping cancer patients during his State of the Union address on March 7, but it was a response on Truth Social from former President Donald Trump that drew the ire of independent presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
During the address, President Biden said: “The pandemic no longer controls our lives. The vaccines that saved us from COVID are now being used to help beat cancer, turning setback into comeback. That’s what America does.”
President Trump wrote: “The Pandemic no longer controls our lives. The VACCINES that saved us from COVID are now being used to help beat cancer—turning setback into comeback. YOU’RE WELCOME JOE. NINE-MONTH APPROVAL TIME VS. 12 YEARS THAT IT WOULD HAVE TAKEN YOU.”
An outspoken critic of President Trump’s COVID response, and the Operation Warp Speed program that escalated the availability of COVID vaccines, Mr. Kennedy said on X, formerly known as Twitter, that “Donald Trump clearly hasn’t learned from his COVID-era mistakes.”
“He fails to recognize how ineffective his warp speed vaccine is as the ninth shot is being recommended to seniors. Even more troubling is the documented harm being caused by the shot to so many innocent children and adults who are suffering myocarditis, pericarditis, and brain inflammation,” Mr. Kennedy remarked.
“This has been confirmed by a CDC-funded study of 99 million people. Instead of bragging about its speedy approval, we should be honestly and transparently debating the abundant evidence that this vaccine may have caused more harm than good.
“I look forward to debating both Trump and Biden on Sept. 16 in San Marcos, Texas.”
Mr. Kennedy announced in April 2023 that he would challenge President Biden for the 2024 Democratic Party presidential nomination before declaring his run as an independent last October, claiming that the Democrat National Committee was “rigging the primary.”
Since the early stages of his campaign, Mr. Kennedy has generated more support than pundits expected from conservatives, moderates, and independents resulting in speculation that he could take votes away from President Trump.
Many Republicans continue to seek a reckoning over the government-imposed pandemic lockdowns and vaccine mandates.
President Trump’s defense of Operation Warp Speed, the program he rolled out in May 2020 to spur the development and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines amid the pandemic, remains a sticking point for some of his supporters.

Operation Warp Speed featured a partnership between the government, the military, and the private sector, with the government paying for millions of vaccine doses to be produced.
President Trump released a statement in March 2021 saying: “I hope everyone remembers when they’re getting the COVID-19 Vaccine, that if I wasn’t President, you wouldn’t be getting that beautiful ‘shot’ for 5 years, at best, and probably wouldn’t be getting it at all. I hope everyone remembers!”
President Trump said about the COVID-19 vaccine in an interview on Fox News in March 2021: “It works incredibly well. Ninety-five percent, maybe even more than that. I would recommend it, and I would recommend it to a lot of people that don’t want to get it and a lot of those people voted for me, frankly.
“But again, we have our freedoms and we have to live by that and I agree with that also. But it’s a great vaccine, it’s a safe vaccine, and it’s something that works.”
On many occasions, President Trump has said that he is not in favor of vaccine mandates.
An environmental attorney, Mr. Kennedy founded Children’s Health Defense, a nonprofit that aims to end childhood health epidemics by promoting vaccine safeguards, among other initiatives.
Last year, Mr. Kennedy told podcaster Joe Rogan that ivermectin was suppressed by the FDA so that the COVID-19 vaccines could be granted emergency use authorization.
He has criticized Big Pharma, vaccine safety, and government mandates for years.
Since launching his presidential campaign, Mr. Kennedy has made his stances on the COVID-19 vaccines, and vaccines in general, a frequent talking point.
“I would argue that the science is very clear right now that they [vaccines] caused a lot more problems than they averted,” Mr. Kennedy said on Piers Morgan Uncensored last April.
“And if you look at the countries that did not vaccinate, they had the lowest death rates, they had the lowest COVID and infection rates.”
Additional data show a “direct correlation” between excess deaths and high vaccination rates in developed countries, he said.
President Trump and Mr. Kennedy have similar views on topics like protecting the U.S.-Mexico border and ending the Russia-Ukraine war.
COVID-19 is the topic where Mr. Kennedy and President Trump seem to differ the most.
Former President Donald Trump intended to “drain the swamp” when he took office in 2017, but he was “intimidated by bureaucrats” at federal agencies and did not accomplish that objective, Mr. Kennedy said on Feb. 5.
Speaking at a voter rally in Tucson, where he collected signatures to get on the Arizona ballot, the independent presidential candidate said President Trump was “earnest” when he vowed to “drain the swamp,” but it was “business as usual” during his term.
John Bolton, who President Trump appointed as a national security adviser, is “the template for a swamp creature,” Mr. Kennedy said.
Scott Gottlieb, who President Trump named to run the FDA, “was Pfizer’s business partner” and eventually returned to Pfizer, Mr. Kennedy said.
Mr. Kennedy said that President Trump had more lobbyists running federal agencies than any president in U.S. history.
“You can’t reform them when you’ve got the swamp creatures running them, and I’m not going to do that. I’m going to do something different,” Mr. Kennedy said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, President Trump “did not ask the questions that he should have,” he believes.
President Trump “knew that lockdowns were wrong” and then “agreed to lockdowns,” Mr. Kennedy said.
He also “knew that hydroxychloroquine worked, he said it,” Mr. Kennedy explained, adding that he was eventually “rolled over” by Dr. Anthony Fauci and his advisers.

MaryJo Perry, a longtime advocate for vaccine choice and a Trump supporter, thinks votes will be at a premium come Election Day, particularly because the independent and third-party field is becoming more competitive.
Ms. Perry, president of Mississippi Parents for Vaccine Rights, believes advocates for medical freedom could determine who is ultimately president.
She believes that Mr. Kennedy is “pulling votes from Trump” because of the former president’s stance on the vaccines.
“People care about medical freedom. It’s an important issue here in Mississippi, and across the country,” Ms. Perry told The Epoch Times.
“Trump should admit he was wrong about Operation Warp Speed and that COVID vaccines have been dangerous. That would make a difference among people he has offended.”
President Trump won’t lose enough votes to Mr. Kennedy about Operation Warp Speed and COVID vaccines to have a significant impact on the election, Ohio Republican strategist Wes Farno told The Epoch Times.
President Trump won in Ohio by eight percentage points in both 2016 and 2020. The Ohio Republican Party endorsed President Trump for the nomination in 2024.
“The positives of a Trump presidency far outweigh the negatives,” Mr. Farno said. “People are more concerned about their wallet and the economy.
“They are asking themselves if they were better off during President Trump’s term compared to since President Biden took office. The answer to that question is obvious because many Americans are struggling to afford groceries, gas, mortgages, and rent payments.
“America needs President Trump.”
Multiple national polls back Mr. Farno’s view.
As of March 6, the RealClearPolitics average of polls indicates that President Trump has 41.8 percent support in a five-way race that includes President Biden (38.4 percent), Mr. Kennedy (12.7 percent), independent Cornel West (2.6 percent), and Green Party nominee Jill Stein (1.7 percent).
A Pew Research Center study conducted among 10,133 U.S. adults from Feb. 7 to Feb. 11 showed that Democrats and Democrat-leaning independents (42 percent) are more likely than Republicans and GOP-leaning independents (15 percent) to say they have received an updated COVID vaccine.
The poll also reported that just 28 percent of adults say they have received the updated COVID inoculation.
The peer-reviewed multinational study of more than 99 million vaccinated people that Mr. Kennedy referenced in his X post on March 7 was published in the Vaccine journal on Feb. 12.
It aimed to evaluate the risk of 13 adverse events of special interest (AESI) following COVID-19 vaccination. The AESIs spanned three categories—neurological, hematologic (blood), and cardiovascular.
The study reviewed data collected from more than 99 million vaccinated people from eight nations—Argentina, Australia, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, New Zealand, and Scotland—looking at risks up to 42 days after getting the shots.
Three vaccines—Pfizer and Moderna’s mRNA vaccines as well as AstraZeneca’s viral vector jab—were examined in the study.
Researchers found higher-than-expected cases that they deemed met the threshold to be potential safety signals for multiple AESIs, including for Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS), cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), myocarditis, and pericarditis.
A safety signal refers to information that could suggest a potential risk or harm that may be associated with a medical product.
The study identified higher incidences of neurological, cardiovascular, and blood disorder complications than what the researchers expected.
President Trump’s role in Operation Warp Speed, and his continued praise of the COVID vaccine, remains a concern for some voters, including those who still support him.
Krista Cobb is a 40-year-old mother in western Ohio. She voted for President Trump in 2020 and said she would cast her vote for him this November, but she was stunned when she saw his response to President Biden about the COVID-19 vaccine during the State of the Union address.
“I love President Trump and support his policies, but at this point, he has to know they [advisers and health officials] lied about the shot,” Ms. Cobb told The Epoch Times.
“If he continues to promote it, especially after all of the hearings they’ve had about it in Congress, the side effects, and cover-ups on Capitol Hill, at what point does he become the same as the people who have lied?” Ms. Cobb added.
“I think he should distance himself from talk about Operation Warp Speed and even admit that he was wrong—that the vaccines have not had the impact he was told they would have. If he did that, people would respect him even more.”
International
There will soon be one million seats on this popular Amtrak route
“More people are taking the train than ever before,” says Amtrak’s Executive Vice President.

While the size of the United States makes it hard for it to compete with the inter-city train access available in places like Japan and many European countries, Amtrak trains are a very popular transportation option in certain pockets of the country — so much so that the country’s national railway company is expanding its Northeast Corridor by more than one million seats.
Related: This is what it's like to take a 19-hour train from New York to Chicago
Running from Boston all the way south to Washington, D.C., the route is one of the most popular as it passes through the most densely populated part of the country and serves as a commuter train for those who need to go between East Coast cities such as New York and Philadelphia for business.
Veronika Bondarenko
Amtrak launches new routes, promises travelers ‘additional travel options’
Earlier this month, Amtrak announced that it was adding four additional Northeastern routes to its schedule — two more routes between New York’s Penn Station and Union Station in Washington, D.C. on the weekend, a new early-morning weekday route between New York and Philadelphia’s William H. Gray III 30th Street Station and a weekend route between Philadelphia and Boston’s South Station.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
According to Amtrak, these additions will increase Northeast Corridor’s service by 20% on the weekdays and 10% on the weekends for a total of one million additional seats when counted by how many will ride the corridor over the year.
“More people are taking the train than ever before and we’re proud to offer our customers additional travel options when they ride with us on the Northeast Regional,” Amtrak Executive Vice President and Chief Commercial Officer Eliot Hamlisch said in a statement on the new routes. “The Northeast Regional gets you where you want to go comfortably, conveniently and sustainably as you breeze past traffic on I-95 for a more enjoyable travel experience.”
Here are some of the other Amtrak changes you can expect to see
Amtrak also said that, in the 2023 financial year, the Northeast Corridor had nearly 9.2 million riders — 8% more than it had pre-pandemic and a 29% increase from 2022. The higher demand, particularly during both off-peak hours and the time when many business travelers use to get to work, is pushing Amtrak to invest into this corridor in particular.
To reach more customers, Amtrak has also made several changes to both its routes and pricing system. In the fall of 2023, it introduced a type of new “Night Owl Fare” — if traveling during very late or very early hours, one can go between cities like New York and Philadelphia or Philadelphia and Washington. D.C. for $5 to $15.
As travel on the same routes during peak hours can reach as much as $300, this was a deliberate move to reach those who have the flexibility of time and might have otherwise preferred more affordable methods of transportation such as the bus. After seeing strong uptake, Amtrak added this type of fare to more Boston routes.
The largest distances, such as the ones between Boston and New York or New York and Washington, are available at the lowest rate for $20.
stocks pandemic japan european-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





















