Spread & Containment
Lapse, an app that lets you snap and ‘develop’ rolls of film with groups of friends, raises $11M from GV and others
The relentless march of social media apps’ algorithmic advertising hooks, influencer-leveraged social graphs and UX that begs for endless scrolling have led to viral success and mass-market engagement for the biggest players. But there remains a continuin

The relentless march of social media apps’ algorithmic advertising hooks, influencer-leveraged social graphs and UX that begs for endless scrolling have led to viral success and mass-market engagement for the biggest players. But there remains a continuing gap in the market for products that let us create things like photos and share them with selected friends, without all that other social baggage. Today, one of them is announcing a sizable seed round after seeing strong early interest at its launch.
Lapse, an app that lets users form groups, and then lets those groups collaborate, wherever they are, to take spontaneous pictures on collective “rolls” of 36 photos that are then “developed” — and only shown to the group — 24 hours after the roll has started, with a little bit of chit-chat in between, has raised $11 million in a seed round of funding.
Octopus Ventures and GV (previously called Google Ventures) led the round for the London-based startup of the same name, with Speedinvest and individual investors participating, including Soleio Cuervo, an early Facebook designer that has a track record when it comes to social engagement: he was part of the team that designed Facebook’s “like” button.
This brings the total raised by Lapse to $12.4 million — adding in a $1.4 million pre-seed that came ahead of the company’s launch in September, which was led by Speedinvest, with Claire Nooriala (VP EMEA, Snap Inc.), Matt Robinson (founder of Nested and GoCardless), and Ian Hogarth (founder of SongKick) also participating.
That September launch saw Lapse snap up 10,000 users for its beta test, briefly shoot to the top of Apple’s download charts, and rack up a waitlist of 150,000 — traction that partly explains why it was just a matter of months for the startup to quickly pull together a healthy seed round from a strong list of investors.
Image Credits: Ingrid
Lapse falls into the category of apps that are gaining attention among users and investors for precisely trying to turn some of the mechanics we’ve come to associate with social media on their head.
While Instagram, TikTok and others continue to rack up millions of users, and those millions of users are really regular users, there is a definite seam of people (and parents of people…) who are wary of them and their agendas. They’ve been found to contain a lot of toxic content, and because it’s ultimately hard to control how they are used (and abused) some believe the solution is to abandon them.
On a less severe note, even those that have found a lot of fun, or even business, in mass-market social media apps tire of their relentless push for engagement and exposure and thus want to explore more private or impactful ways of being “social.”
Others in the category include IRL, which was started, the founder has said, on the premise of people using it to create more meaningful social interactions rather than focusing on sharing media with each other or endlessly scrolling to see media posted by people they don’t know.
Created to focus on “in real life” physical events, the app kept itself from the usage graveyard by expanding to, ironically, virtual (that is, not IRL) events as the pandemic kicked off and wore on. Raising a big round earlier this year at a $1 billion+ valuation, IRL made an acquisition earlier this month of a “digital nutrition” app, which it said would help it develop more ethically-focused recommendations.
And closer in concept to Lapse is Dispo, which also makes a nod to the disposable camera roll and wanting to move away from the focus on experiencing things just to share photos of those experiences. It lets people only see what pictures they have taken the day after they’re shot.
The startup also raised money earlier this year, even as the same forces that propelled it to viral interest (it was co-founded by popular YouTuber David Dobrik) turned sour (one of Dobrik’s squad was accused of sexual assault) and left many with a bad taste in their mouth (early investors pulled out and gave up profits, and Dobrik was also removed with any association with it). The app is not exactly eschewing buzzy social media trends, though: in September it started a test to gauge user interest in selling their photos as NFTs.
Lapse was founded by brothers Dan and Ben Silvertown, who travelled to Vietnam together and used a point-and-shoot camera while there as a way of disconnecting and unwinding. They found the experience inspiring enough that they decided to see if they could build an app that recreated that idea of less anxious social posing, while still making something that let users take pictures and share them with groups of friends.
While Lapse leans on the same mechanic as Dispo by focusing on delayed views of photos, it takes a different approach in that it never intends for those pictures to be shared with anyone other than a close social circle.
(Now defunct Path — co-founded by early Facebook employee David Morin to provide a way to share amongst small groups as a counter balance to the wide-angle view taken by his former employer — turned out to be very prescient, if maybe too ahead of its time.)
Lapse is still very much in early stage mode and there is a lot of room for it to be developed further. The only lens that exists on the app currently, for example, is one that takes static photos, from the back of the camera. But the founders say that a lot of thought has gone into that one lens.

Image Credits: Ingrid
“We worked with 30 professional photographers to develop our own image processing agent,” Ben said in an interview. “But we are still only on step one on where we want to go with analogue film in what we think of as a 20-step process.”
I would best describe the filter as having some of the qualities of what a snap might have taken on an old-school point-and-shoot camera. Sounds quaint, and is an interesting way of willfully limiting what has become a very powerful camera experience on the average smartphone, and replacing it with spontaneity but also quite a lot of “bloopers.”
It’s a little like the camera equivalent of when people proactively choose to walk instead of take a vehicle somewhere, or intentionally go through the many steps for a complicated meal instead of just buying it from somewhere: you may be making your life more inconvenient, but maybe for a different kind of end.
In my experience, some of the byproducts of using the Lapse filter were unexpected, and hard to manage but not in a terminal, but fun, way.
They included taking very blurry pictures as the camera doesn’t seem to let you focus, and you can’t take anything but a very inaccurate selfie (or maybe one in a mirror as I eventually did) since there is no front-facing lens, and there is no video, nor any “filters” to play with the image. The ability to snap is surprisingly easy: you take pictures often before you realize that you have, and there are no do-overs.
And my son Abel somehow found a way to take a three-image picture that I never figured out how to take myself.
Those images, when they are developed, are sent into the group chat, where you see them in a super-fast slideshow unless you make the effort to slow things down to see them a little more carefully. And, the app is not without its more conventional social media hooks: you can also save pictures from the roll and share them elsewhere.
Dan tells me that this was initially created to help spread the word about the app, mimicking how, say, TikTok grew by making it very easy to share videos from that app to other platforms and hook in people that way. As it’s still in its early days, he said they have not yet decided if they will keep that hook or eventually turn it off.
So too are specific questions of monetization still being put off, apart from wanting to stay away from advertising.
“We have had some high level thoughts about monetization, but that question will come later,” said Dan. “The strong hypothesis is that we won’t use an ad-based model because it incentivizes as many users as possible and optimizes time on screen — which is one of the reasons you get toxic behavior. We want the focus to be on quality versus quantity.” One idea, he hinted, was a freemium model, “building an app for users at level such that they love it so much that they’ll pay for additional features.” One feature will likely be removing the branding on shared pictures: currently these come with a Lapse-branded frame.
Most of all, though, Lapse seems to be embracing the idea of growing slowly and trying to do so without hype.
The app is not making active user numbers public, but I’ll say that the waitlist of 150,000 is not the full size of the app today, and having investors like GV backing you is one sign that the numbers are good. Those who are allowed in get several invites, and when you get one of these you skip the waitlist. The user engagement has been decent: 15% who download it stay using the app, Ben said. Right now the majority of users are “Gen Z” females, with a whopping 79% of users female and 71% under the age of 24. Some 80% of users currently are U.S.-based.
All these numbers, I suspect, will shift as and when the app matures. And in the spirit of having actual choices among different approaches to social apps, I hope that it does.
“Lapse is a next-generation private social network, launched at a time when consumers are fundamentally rethinking their relationship with traditional players,” said Matthew Chandler, investment manager at Octopus Ventures, in a statement. “With Lapse, the consumer is no longer the product. This dramatic shift in mentality enables users to communicate freely in private groups, and to provide in-the-moment images of their lives. The product design also means users no longer have the social pressures of portraying themselves a certain way and are instead encouraged to be authentic, which has a profound impact on the way we communicate. We are incredibly excited to partner with Dan and Ben as they build the modern platform for image-based memories.”
spread pandemicGovernment
Harvard Medical School Professor Was Fired Over Not Getting COVID Vaccine
Harvard Medical School Professor Was Fired Over Not Getting COVID Vaccine
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A…

Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A Harvard Medical School professor who refused to get a COVID-19 vaccine has been terminated, according to documents reviewed by The Epoch Times.
Martin Kulldorff, an epidemiologist, was fired by Mass General Brigham in November 2021 over noncompliance with the hospital’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate after his requests for exemptions from the mandate were denied, according to one document. Mr. Kulldorff was also placed on leave by Harvard Medical School (HMS) because his appointment as professor of medicine there “depends upon” holding a position at the hospital, another document stated.
Mr. Kulldorff asked HMS in late 2023 how he could return to his position and was told he was being fired.
“You would need to hold an eligible appointment with a Harvard-affiliated institution for your HMS academic appointment to continue,” Dr. Grace Huang, dean for faculty affairs, told the epidemiologist and biostatistician.
She said the lack of an appointment, combined with college rules that cap leaves of absence at two years, meant he was being terminated.
Mr. Kulldorff disclosed the firing for the first time this month.
“While I can’t comment on the specifics due to employment confidentiality protections that preclude us from doing so, I can confirm that his employment agreement was terminated November 10, 2021,” a spokesperson for Brigham and Women’s Hospital told The Epoch Times via email.
Mass General Brigham granted just 234 exemption requests out of 2,402 received, according to court filings in an ongoing case that alleges discrimination.
The hospital said previously, “We received a number of exemption requests, and each request was carefully considered by a knowledgeable team of reviewers.”
“A lot of other people received exemptions, but I did not,” Mr. Kulldorff told The Epoch Times.
Mr. Kulldorff was originally hired by HMS but switched departments in 2015 to work at the Department of Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, which is part of Mass General Brigham and affiliated with HMS.
“Harvard Medical School has affiliation agreements with several Boston hospitals which it neither owns nor operationally controls,” an HMS spokesperson told The Epoch Times in an email. “Hospital-based faculty, such as Mr. Kulldorff, are employed by one of the affiliates, not by HMS, and require an active hospital appointment to maintain an academic appointment at Harvard Medical School.”
HMS confirmed that some faculty, who are tenured or on the tenure track, do not require hospital appointments.
Natural Immunity
Before the COVID-19 vaccines became available, Mr. Kulldorff contracted COVID-19. He was hospitalized but eventually recovered.
That gave him a form of protection known as natural immunity. According to a number of studies, including papers from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, natural immunity is better than the protection bestowed by vaccines.
Other studies have found that people with natural immunity face a higher risk of problems after vaccination.
Mr. Kulldorff expressed his concerns about receiving a vaccine in his request for a medical exemption, pointing out a lack of data for vaccinating people who suffer from the same issue he does.
“I already had superior infection-acquired immunity; and it was risky to vaccinate me without proper efficacy and safety studies on patients with my type of immune deficiency,” Mr. Kulldorff wrote in an essay.
In his request for a religious exemption, he highlighted an Israel study that was among the first to compare protection after infection to protection after vaccination. Researchers found that the vaccinated had less protection than the naturally immune.
“Having had COVID disease, I have stronger longer lasting immunity than those vaccinated (Gazit et al). Lacking scientific rationale, vaccine mandates are religious dogma, and I request a religious exemption from COVID vaccination,” he wrote.
Both requests were denied.
Mr. Kulldorff is still unvaccinated.
“I had COVID. I had it badly. So I have infection-acquired immunity. So I don’t need the vaccine,” he told The Epoch Times.
Dissenting Voice
Mr. Kulldorff has been a prominent dissenting voice during the COVID-19 pandemic, countering messaging from the government and many doctors that the COVID-19 vaccines were needed, regardless of prior infection.
He spoke out in an op-ed in April 2021, for instance, against requiring people to provide proof of vaccination to attend shows, go to school, and visit restaurants.
“The idea that everybody needs to be vaccinated is as scientifically baseless as the idea that nobody does. Covid vaccines are essential for older, high-risk people and their caretakers and advisable for many others. But those who’ve been infected are already immune,” he wrote at the time.
Mr. Kulldorff later co-authored the Great Barrington Declaration, which called for focused protection of people at high risk while removing restrictions for younger, healthy people.
Harsh restrictions such as school closures “will cause irreparable damage” if not lifted, the declaration stated.
The declaration drew criticism from Dr. Anthony Fauci, head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and Dr. Rochelle Walensky, who became the head of the CDC, among others.
In a competing document, Dr. Walensky and others said that “relying upon immunity from natural infections for COVID-19 is flawed” and that “uncontrolled transmission in younger people risks significant morbidity(3) and mortality across the whole population.”
“Those who are pushing these vaccine mandates and vaccine passports—vaccine fanatics, I would call them—to me they have done much more damage during this one year than the anti-vaxxers have done in two decades,” Mr. Kulldorff later said in an EpochTV interview. “I would even say that these vaccine fanatics, they are the biggest anti-vaxxers that we have right now. They’re doing so much more damage to vaccine confidence than anybody else.”
Surveys indicate that people have less trust now in the CDC and other health institutions than before the pandemic, and data from the CDC and elsewhere show that fewer people are receiving the new COVID-19 vaccines and other shots.
Support
The disclosure that Mr. Kulldorff was fired drew criticism of Harvard and support for Mr. Kulldorff.
The termination “is a massive and incomprehensible injustice,” Dr. Aaron Kheriaty, an ethics expert who was fired from the University of California–Irvine School of Medicine for not getting a COVID-19 vaccine because he had natural immunity, said on X.
“The academy is full of people who declined vaccines—mostly with dubious exemptions—and yet Harvard fires the one professor who happens to speak out against government policies.” Dr. Vinay Prasad, an epidemiologist at the University of California–San Francisco, wrote in a blog post. “It looks like Harvard has weaponized its policies and selectively enforces them.”
A petition to reinstate Mr. Kulldorff has garnered more than 1,800 signatures.
Some other doctors said the decision to let Mr. Kulldorff go was correct.
“Actions have consequence,” Dr. Alastair McAlpine, a Canadian doctor, wrote on X. He said Mr. Kulldorff had “publicly undermine[d] public health.”
International
“Extreme Events”: US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In “Large Excess Over Trend”
"Extreme Events": US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In "Large Excess Over Trend"
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021…
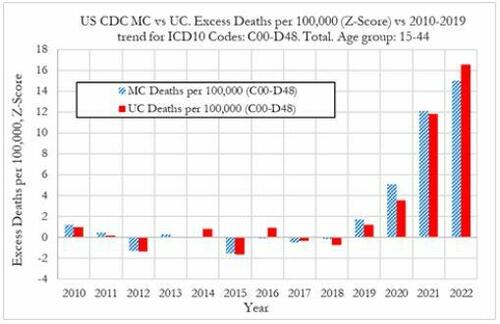
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021 and 2022 among 15-44 year-olds "in large excess over trend," marking jumps of 5.6% and 7.9% respectively vs. a rise of 1.7% in 2020, according to a new preprint study from deep-dive research firm, Phinance Technologies.

Extreme Events
The report, which relies on data from the CDC, paints a troubling picture.
"We show a rise in excess mortality from neoplasms reported as underlying cause of death, which started in 2020 (1.7%) and accelerated substantially in 2021 (5.6%) and 2022 (7.9%). The increase in excess mortality in both 2021 (Z-score of 11.8) and 2022 (Z-score of 16.5) are highly statistically significant (extreme events)," according to the authors.
That said, co-author, David Wiseman, PhD (who has 86 publications to his name), leaves the cause an open question - suggesting it could either be a "novel phenomenon," Covid-19, or the Covid-19 vaccine.
Cancer deaths in US in 2021 & 2022 in large excess over trend for 15-44 year-olds as extreme events. A novel phenomenon? C19? lockdowns? C19 vaccines? Honored to participate in this work. #CDC where are you? @DowdEdwardhttps://t.co/iUV5oQiWCW pic.twitter.com/uytzaIvvor
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 12, 2024
"The results indicate that from 2021 a novel phenomenon leading to increased neoplasm deaths appears to be present in individuals aged 15 to 44 in the US," reads the report.
The authors suggest that the cause may be the result of "an unexpected rise in the incidence of rapidly growing fatal cancers," and/or "a reduction in survival in existing cancer cases."
They also address the possibility that "access to utilization of cancer screening and treatment" may be a factor - the notion that pandemic-era lockdowns resulted in fewer visits to the doctor. Also noted is that "Cancers tend to be slowly-developing diseases with remarkably stable death rates and only small variations over time," which makes "any temporal association between a possible explanatory factor (such as COVID-19, the novel COVID-19 vaccines, or other factor(s)) difficult to establish."
That said, a ZeroHedge review of the CDC data reveals that it does not provide information on duration of illness prior to death - so while it's not mentioned in the preprint, it can't rule out so-called 'turbo cancers' - reportedly rapidly developing cancers, the existence of which has been largely anecdotal (and widely refuted by the usual suspects).
While the Phinance report is extremely careful not to draw conclusions, researcher "Ethical Skeptic" kicked the barn door open in a Thursday post on X - showing a strong correlation between "cancer incidence & mortality" coinciding with the rollout of the Covid mRNA vaccine.
The argument is over.
— Ethical Skeptic ☀ (@EthicalSkeptic) March 14, 2024
The Covid mRNA Vaxx has cause a sizeable 2021 inflection, and now novel-trend elevation in terms of both cancer incidence & mortality.
Now you know who the liars were all along.
????Incidence = 14.8% excess
????UCoD Mortality = 5.3% excess (lags Incidence) pic.twitter.com/uwN9GMrHl1
Phinance principal Ed Dowd commented on the post, noting that "Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry!"
????Indeed it is…Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry! @EthicalSkeptic provides a chart below showing US Cancer treatment in constant dollars with a current growth rate of 14.8% (6.3% New CAGR) versus long term trend of 1.78% CAGR or $33.8 billion in excess cancer… https://t.co/RIn4R2YZZ7
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Continued:
As a former portfolio manager of of a $14 billion Large Cap Growth Equity portfolio I can definitively say Cancer treatments and the Disabilities have become growth industries that both have inflection points coincidental to the mRNA vaccine rollouts in 2021.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Chart 1 from… pic.twitter.com/TCt4X1plnM
Bottom line - hard data is showing alarming trends, which the CDC and other agencies have a requirement to explore and answer truthfully - and people are asking #WhereIsTheCDC.
We aren't holding our breath.
Experts are sounding the alarm on a spike in cancer diagnosis worldwide. It is still a mystery. @DowdEdward from Phinance Technologies has also been sounding the alarm for months.
— dr.ir. Carla Peeters (@CarlaPeeters3) March 15, 2024
We are facing a dramatic degradation of the human immune system https://t.co/CPnwP3Oj9G
Wiseman, meanwhile, points out that Pfizer and several other companies are making "significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID."
Pfizer among several companies making significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID. @DowdEdward @Kevin_McKernan @JesslovesMJK @niki_kyrylenko https://t.co/nefEZYLW1o https://t.co/r505Sbbcq4
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 15, 2024
Phinance
We've featured several of Phinance's self-funded deep dives into pandemic data that nobody else is doing. If you'd like to support them, click here.
List of our projects following disturbing tends in deaths, disabilities and absences.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 16, 2024
Link to projects at bottom.
✅ V-Damage Project
✅ Excess Mortality Project
✅ US Disabilities Project
✅ US BLS Absence rates Project
✅ US Cause of Death Project
✅ UK Cause of Death…
Government
“I Can’t Even Save”: Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
"I Can’t Even Save": Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great…

While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great - suggesting in his State of the Union Address last week that "our economy is the envy of the world," Americans are being absolutely crushed by inflation (which the Biden admin blames on 'shrinkflation' and 'corporate greed'), and of course - crippling debt.
The signs are obvious. Last week we noted that banks' charge-offs are accelerating, and are now above pre-pandemic levels.
...and leading this increase are credit card loans - with delinquencies that haven't been this high since Q3 2011.
On top of that, while credit cards and nonfarm, nonresidential commercial real estate loans drove the quarterly increase in the noncurrent rate, residential mortgages drove the quarterly increase in the share of loans 30-89 days past due.
And while Biden and crew can spin all they want, an average of polls from RealClear Politics shows that just 40% of people approve of Biden's handling of the economy.
Crushed
On Friday, Bloomberg dug deeper into the effects of Biden's "envious" economy on Americans - specifically, how massive debt loads (credit cards and auto loans especially) are absolutely crushing people.
Two years after the Federal Reserve began hiking interest rates to tame prices, delinquency rates on credit cards and auto loans are the highest in more than a decade. For the first time on record, interest payments on those and other non-mortgage debts are as big a financial burden for US households as mortgage interest payments.
According to the report, this presents a difficult reality for millions of consumers who drive the US economy - "The era of high borrowing costs — however necessary to slow price increases — has a sting of its own that many families may feel for years to come, especially the ones that haven’t locked in cheap home loans."
The Fed, meanwhile, doesn't appear poised to cut rates until later this year.
According to a February paper from IMF and Harvard, the recent high cost of borrowing - something which isn't reflected in inflation figures, is at the heart of lackluster consumer sentiment despite inflation having moderated and a job market which has recovered (thanks to job gains almost entirely enjoyed by immigrants).
In short, the debt burden has made life under President Biden a constant struggle throughout America.
"I’m making the most money I've ever made, and I’m still living paycheck to paycheck," 40-year-old Denver resident Nikki Cimino told Bloomberg. Cimino is carrying a monthly mortgage of $1,650, and has $4,000 in credit card debt following a 2020 divorce.

"There's this wild disconnect between what people are experiencing and what economists are experiencing."
CBS: Do you attribute the inflation crisis to the pandemic or Biden?
— RNC Research (@RNCResearch) March 15, 2024
WISCONSIN VOTER: "It's been YEARS now since the pandemic — I'm not buying that anymore. At first I did; I'm not buying that anymore because yogurt is STILL going up in price!" pic.twitter.com/apahb65scB
What's more, according to Wells Fargo, families have taken on debt at a comparatively fast rate - no doubt to sustain the same lifestyle as low rates and pandemic-era stimmies provided. In fact, it only took four years for households to set a record new debt level after paying down borrowings in 2021 when interest rates were near zero.
Meanwhile, that increased debt load is exacerbated by credit card interest rates that have climbed to a record 22%, according to the Fed.
[P]art of the reason some Americans were able to take on a substantial load of non-mortgage debt is because they’d locked in home loans at ultra-low rates, leaving room on their balance sheets for other types of borrowing. The effective rate of interest on US mortgage debt was just 3.8% at the end of last year.
Yet the loans and interest payments can be a significant strain that shapes families’ spending choices. -Bloomberg
And of course, the highest-interest debt (credit cards) is hurting lower-income households the most, as tends to be the case.
The lowest earners also understandably had the biggest increase in credit card delinquencies.
"Many consumers are levered to the hilt — maxed out on debt and barely keeping their heads above water," Allan Schweitzer, a portfolio manager at credit-focused investment firm Beach Point Capital Management told Bloomberg. "They can dog paddle, if you will, but any uptick in unemployment or worsening of the economy could drive a pretty significant spike in defaults."
"We had more money when Trump was president," said Denise Nierzwicki, 69. She and her 72-year-old husband Paul have around $20,000 in debt spread across multiple cards - all of which have interest rates above 20%.

Photographer: Jon Cherry/Bloomberg
During the pandemic, Denise lost her job and a business deal for a bar they owned in their hometown of Lexington, Kentucky. While they applied for Social Security to ease the pain, Denise is now working 50 hours a week at a restaurant. Despite this, they're barely scraping enough money together to service their debt.
The couple blames Biden for what they see as a gloomy economy and plans to vote for the Republican candidate in November. Denise routinely voted for Democrats up until about 2010, when she grew dissatisfied with Barack Obama’s economic stances, she said. Now, she supports Donald Trump because he lowered taxes and because of his policies on immigration. -Bloomberg
Meanwhile there's student loans - which are not able to be discharged in bankruptcy.
"I can't even save, I don't have a savings account," said 29-year-old in Columbus, Ohio resident Brittany Walling - who has around $80,000 in federal student loans, $20,000 in private debt from her undergraduate and graduate degrees, and $6,000 in credit card debt she accumulated over a six-month stretch in 2022 while she was unemployed.
"I just know that a lot of people are struggling, and things need to change," she told the outlet.
The only silver lining of note, according to Bloomberg, is that broad wage gains resulting in large paychecks has made it easier for people to throw money at credit card bills.
Yet, according to Wells Fargo economist Shannon Grein, "As rates rose in 2023, we avoided a slowdown due to spending that was very much tied to easy access to credit ... Now, credit has become harder to come by and more expensive."
According to Grein, the change has posed "a significant headwind to consumption."
Then there's the election
"Maybe the Fed is done hiking, but as long as rates stay on hold, you still have a passive tightening effect flowing down to the consumer and being exerted on the economy," she continued. "Those household dynamics are going to be a factor in the election this year."
Meanwhile, swing-state voters in a February Bloomberg/Morning Consult poll said they trust Trump more than Biden on interest rates and personal debt.
Reverberations
These 'headwinds' have M3 Partners' Moshin Meghji concerned.
"Any tightening there immediately hits the top line of companies," he said, noting that for heavily indebted companies that took on debt during years of easy borrowing, "there's no easy fix."
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Spread & Containment4 days ago
Spread & Containment4 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
















