Government
Keynesians and Market Monetarists Didn’t See Inflation Coming
The government’s latest report puts the twelve-month official consumer price inflation rate at 8.5 percent, the highest since December 1981:
As economists…
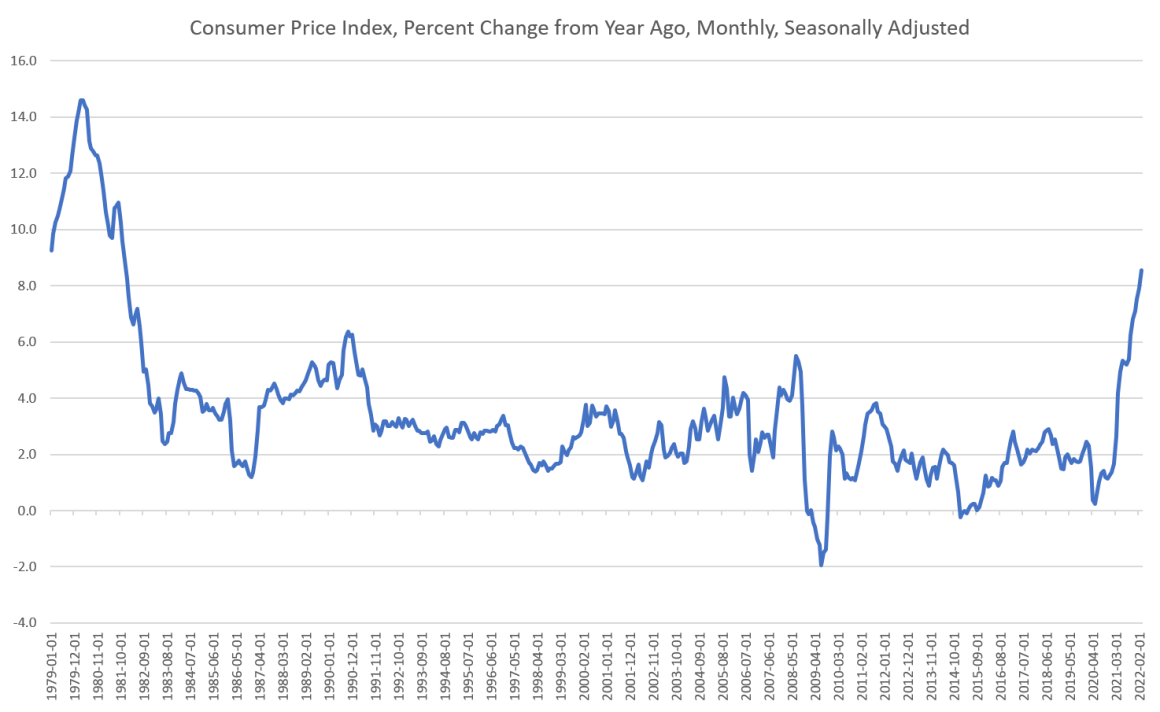
The government’s latest report puts the twelve-month official consumer price inflation rate at 8.5 percent, the highest since December 1981:
As economists debate the causes of, and cure for, this price inflation, it’s worth recounting which schools of thought saw it coming. Although individuals can be nuanced, generally speaking the Austrians have been warning that the Fed’s reckless policies threaten the dollar. In contrast, as I will document in this article, two of the leaders of the Keynesian and market monetarist schools didn’t see this coming at all.
My Worst Professional Mistake
Before diving into it, I need to address a problem: my hands-down worst professional mistake occurred during the early years of the Fed’s “QE” (quantitative easing) programs, when I made bets on (consumer price) inflation with two economist colleagues. I ended up losing those bets and thereby gave Paul Krugman the opportunity to lecture me on my intellectual dishonesty because I clung to my (ostensibly falsified) Austrian model even after my prediction blew up in my face. Indeed, if you check out my Wikipedia entry, you’ll see that apparently my life story is that I was born, got my PhD, and lost an inflation bet—in that order. (For those interested in the details, I summarize the episode with relevant links in this postmortem blog post. I also participated in a 2014 Reason symposium along with Peter Schiff and others, commenting on the lack of inflation.)
Ever since the rounds of QE failed to yield surging consumer price inflation at the scale some of us warned of, the Keynesians and market monetarists understandably ran victory laps, saying that they were to be trusted over those permabear Cassandra Austrians. (To be sure, the market monetarists were far more civil about it than the prominent Keynesians.) So it is not with gloating or vindictiveness that I write the present article, but rather I do it to set the record straight and document for posterity that the leading Keynesians and market monetarists totally missed this bout of price inflation.
The Keynesians Camp: Paul Krugman and Klaus Schwab
Let’s do the fun one first: Paul Krugman has not fared well in light of our current inflationary experience. As late as June 2021, Krugman wrote an article in the New York Times titled “The Week Inflation Panic Died.” Here are some key excerpts, with my bold added, and keep in mind that when Krugman wrote this, the most recent Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation rate was only 4.9 percent:
Remember when everyone was panicking about inflation, warning ominously about 1970s-type stagflation? OK, many people are still saying such things, some because that’s what they always say, some because that’s what they say when there’s a Democratic president….
But for those paying closer attention to the flow of new information, inflation panic is, you know, so last week.Seriously, both recent data and recent statements from the Federal Reserve have, well, deflated the case for a sustained outbreak of inflation … [T]o panic over inflation, you had to believe either that the Fed’s model of how inflation works is all wrong or that the Fed would lack the political courage to cool off the economy if it were to become dangerously overheated.
Both beliefs have now lost most of whatever credibility they may have had….The Fed has been arguing that recent price rises are similarly transitory … The Fed’s view has been that this episode, like the inflation blip of 2010–11, will soon be over.
And it’s now looking as if the Fed was right ...
…. Monetary doomsayers have been wrong again and again since the early 1980s, when Milton Friedman kept predicting an inflation resurgence that never arrived. Why the eagerness to party like it’s 1979?To be fair, government support for the economy is much stronger now than it was during the Obama years, so it makes more sense to worry about inflation this time around. But the vehemence of the inflation rhetoric has been wildly disproportionate to the actual risks—and those risks now seem even smaller than they did a few weeks ago.
Of course, Krugman’s confident dismissal of those Biden-hating doomsayers blew up in his face, as CPI inflation kept ratcheting higher and higher. In a December 2021 NYT column, Krugman threw in the towel and admitted he had been wrong, but in his own special way (again, with my bolding):
The current bout of inflation came on suddenly…. Even once the inflation numbers shot up, many economists—myself included—argued that the surge was likely to prove transitory. But at the very least it’s now clear that “transitory” inflation will last longer than most of us on that team expected….
… I believe that what we’re seeing mainly reflects the inherent dislocations from the pandemic, rather than, say, excessive government spending. I also believe that inflation will subside over the course of the next year and that we shouldn’t take any drastic action. But reasonable economists disagree, and they could be right….
The latest projections from board members and Fed presidents are for the interest rate the Fed controls to rise next year, but by less than one percentage point, and for the unemployment rate to keep falling.
Perhaps surprisingly, my own position on policy substance isn’t all that different from either Furman’s or the Fed’s. I think inflation is mainly bottlenecks and other transitory factors and will come down, but I’m not certain, and I am definitely open to the possibility that the Fed should raise rates, possibly before the middle of next year….
Maybe the real takeaway here should be how little we know about where we are in this strange economic episode. Economists like me who didn’t expect much inflation were wrong, but economists who did predict inflation were arguably right for the wrong reasons, and nobody really knows what’s coming.
For those keeping score at home, remember that when I pointed out that Keynesians Christina Romer and Jared Bernstein had been notoriously wrong in their forecasts of unemployment following the Obama stimulus package, Krugman told us that “some predictions matter more than others.” So this time around, Krugman can’t argue that his botched inflation predictions are irrelevant. Instead, as we see above, he’s claiming that his opponents were right but for the wrong reasons. Even when Krugman is wrong, he’s still better than his enemies!
And for the sake of completeness, let’s reproduce this quotation from Klaus Schwab (who has doctoral degrees in both economics and engineering) and Thierry Malleret in COVID-19: The Great Reset. Writing in July 2020, Schwab and Malleret claimed:
At this current juncture, it is hard to imagine how inflation could pick up anytime soon…. The combination of potent, long-term, structural trends like ageing and technology … and an exceptionally high unemployment rate that will constrain wages for years puts strong downward pressure on inflation. In the post-pandemic era, strong consumer demand is unlikely. (p. 70)
So when he’s not plotting to take over the world, Klaus Schwab is making erroneous inflation predictions.
The Leader of the Market Monetarists, Scott Sumner
As I said earlier, the market monetarists are far more civil than Krugman, Brad DeLong, and some other leading Keynesians. (And as far as I know, they’re not bent on world domination either.) But to repeat myself: since 2008, the one trump card the market monetarists had in their rivalry with the Austrians was that many of us prematurely warned about consumer price inflation à la the 1970s, whereas the market monetarists relied on TIPS (Treasury inflation-protected securities) yields and other market indicators to reassure their readers that inflation wouldn’t be a problem.
In that context, then, it’s very interesting that Scott Sumner, founder and leader of the market monetarists, wrote a blog post entitled, “Fed Policy: The Golden Age Begins,” in January 2020. Here are the key excerpts, with my bold:
We are entering a golden age of central banking, where the Fed will become more effective and come closer to hitting its targets than at any other time in history. Over the next few decades, inflation will stay close to 2% and the unemployment rate will generally be relatively low and stable. And this certainly won’t be due to fiscal policy, which is currently the most recklessly pro-cyclical in American history.
… Fed policy is becoming more effective because it is edging gradually in a market monetarist direction….
If they continue moving in this direction, then NGDP [nominal gross domestic product] growth will continue to become more stable, the business cycle will continue to moderate, inflation will stay in the low single digits, and unemployment will stay relatively low and stable.
It won’t be perfect; the business cycle is not quite dead. There will be an occasional recession. But the business cycle is definitely on life support….
As an analogy, when I was young I would frequently read about airliners crashing in the US…. My daughter is a junior in college and doesn’t recall a single major airline crash in the US, excluding a couple of small commuter planes in the 2000s…. After each crash, problems were fixed and planes got a bit safer.
Recessions and airline crashes: They are getting less frequent, and for the exact same reason.
Before closing, let me deal with the obvious response from the market monetarist camp: They could defend Sumner’s claims by arguing that the Fed only strayed from the ideal path because of covid. Well, sure, but Sumner was still wrong for placing so much faith in central bankers and their “independence.”
Furthermore, as I explain in my chapter on market monetarism in this book, Sumner’s criterion of “NGDP growth” as a measure of tight or loose policy is almost a tautology. It is close to me arguing, “We will continue to see rising prices because of the Fed’s reckless policies, unless demand growth subsides, in which case we won’t.”
recession unemployment pandemic covid-19 stimulus qe fed federal reserve trump unemployment stimulusInternational
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says “Copper’s Time Is Now”
Copper Soars, Iron Ore Tumbles As Goldman Says "Copper’s Time Is Now"
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring…
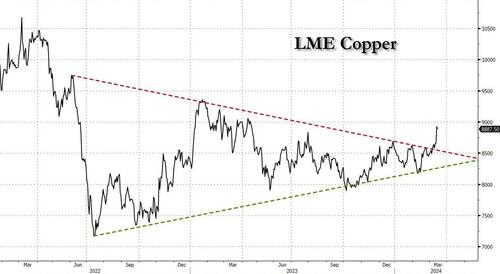
After languishing for the past two years in a tight range despite recurring speculation about declining global supply, copper has finally broken out, surging to the highest price in the past year, just shy of $9,000 a ton as supply cuts hit the market; At the same time the price of the world's "other" most important mined commodity has diverged, as iron ore has tumbled amid growing demand headwinds out of China's comatose housing sector where not even ghost cities are being built any more.
Copper surged almost 5% this week, ending a months-long spell of inertia, as investors focused on risks to supply at various global mines and smelters. As Bloomberg adds, traders also warmed to the idea that the worst of a global downturn is in the past, particularly for metals like copper that are increasingly used in electric vehicles and renewables.
Yet the commodity crash of recent years is hardly over, as signs of the headwinds in traditional industrial sectors are still all too obvious in the iron ore market, where futures fell below $100 a ton for the first time in seven months on Friday as investors bet that China’s years-long property crisis will run through 2024, keeping a lid on demand.
Indeed, while the mood surrounding copper has turned almost euphoric, sentiment on iron ore has soured since the conclusion of the latest National People’s Congress in Beijing, where the CCP set a 5% goal for economic growth, but offered few new measures that would boost infrastructure or other construction-intensive sectors.
As a result, the main steelmaking ingredient has shed more than 30% since early January as hopes of a meaningful revival in construction activity faded. Loss-making steel mills are buying less ore, and stockpiles are piling up at Chinese ports. The latest drop will embolden those who believe that the effects of President Xi Jinping’s property crackdown still have significant room to run, and that last year’s rally in iron ore may have been a false dawn.
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg notes, on Friday there were fresh signs that weakness in China’s industrial economy is hitting the copper market too, with stockpiles tracked by the Shanghai Futures Exchange surging to the highest level since the early days of the pandemic. The hope is that headwinds in traditional industrial areas will be offset by an ongoing surge in usage in electric vehicles and renewables.
And while industrial conditions in Europe and the US also look soft, there’s growing optimism about copper usage in India, where rising investment has helped fuel blowout growth rates of more than 8% — making it the fastest-growing major economy.
In any case, with the demand side of the equation still questionable, the main catalyst behind copper’s powerful rally is an unexpected tightening in global mine supplies, driven mainly by last year’s closure of a giant mine in Panama (discussed here), but there are also growing worries about output in Zambia, which is facing an El Niño-induced power crisis.
On Wednesday, copper prices jumped on huge volumes after smelters in China held a crisis meeting on how to cope with a sharp drop in processing fees following disruptions to supplies of mined ore. The group stopped short of coordinated production cuts, but pledged to re-arrange maintenance work, reduce runs and delay the startup of new projects. In the coming weeks investors will be watching Shanghai exchange inventories closely to gauge both the strength of demand and the extent of any capacity curtailments.
“The increase in SHFE stockpiles has been bigger than we’d anticipated, but we expect to see them coming down over the next few weeks,” Colin Hamilton, managing director for commodities research at BMO Capital Markets, said by phone. “If the pace of the inventory builds doesn’t start to slow, investors will start to question whether smelters are actually cutting and whether the impact of weak construction activity is starting to weigh more heavily on the market.”
* * *
Few have been as happy with the recent surge in copper prices as Goldman's commodity team, where copper has long been a preferred trade (even if it may have cost the former team head Jeff Currie his job due to his unbridled enthusiasm for copper in the past two years which saw many hedge fund clients suffer major losses).
As Goldman's Nicholas Snowdon writes in a note titled "Copper's time is now" (available to pro subscribers in the usual place)...
... there has been a "turn in the industrial cycle." Specifically according to the Goldman analyst, after a prolonged downturn, "incremental evidence now points to a bottoming out in the industrial cycle, with the global manufacturing PMI in expansion for the first time since September 2022." As a result, Goldman now expects copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25.’
Here are the details:
Previous inflexions in global manufacturing cycles have been associated with subsequent sustained industrial metals upside, with copper and aluminium rising on average 25% and 9% over the next 12 months. Whilst seasonal surpluses have so far limited a tightening alignment at a micro level, we expect deficit inflexions to play out from quarter end, particularly for metals with severe supply binds. Supplemented by the influence of anticipated Fed easing ahead in a non-recessionary growth setting, another historically positive performance factor for metals, this should support further upside ahead with copper the headline act in this regard.
Goldman then turns to what it calls China's "green policy put":
Much of the recent focus on the “Two Sessions” event centred on the lack of significant broad stimulus, and in particular the limited property support. In our view it would be wrong – just as in 2022 and 2023 – to assume that this will result in weak onshore metals demand. Beijing’s emphasis on rapid growth in the metals intensive green economy, as an offset to property declines, continues to act as a policy put for green metals demand. After last year’s strong trends, evidence year-to-date is again supportive with aluminium and copper apparent demand rising 17% and 12% y/y respectively. Moreover, the potential for a ‘cash for clunkers’ initiative could provide meaningful right tail risk to that healthy demand base case. Yet there are also clear metal losers in this divergent policy setting, with ongoing pressure on property related steel demand generating recent sharp iron ore downside.
Meanwhile, Snowdon believes that the driver behind Goldman's long-running bullish view on copper - a global supply shock - continues:
Copper’s supply shock progresses. The metal with most significant upside potential is copper, in our view. The supply shock which began with aggressive concentrate destocking and then sharp mine supply downgrades last year, has now advanced to an increasing bind on metal production, as reflected in this week's China smelter supply rationing signal. With continued positive momentum in China's copper demand, a healthy refined import trend should generate a substantial ex-China refined deficit this year. With LME stocks having halved from Q4 peak, China’s imminent seasonal demand inflection should accelerate a path into extreme tightness by H2. Structural supply underinvestment, best reflected in peak mine supply we expect next year, implies that demand destruction will need to be the persistent solver on scarcity, an effect requiring substantially higher pricing than current, in our view. In this context, we maintain our view that the copper price will surge into next year (GSe 2025 $15,000/t average), expecting copper to rise to $10,000/t by year-end and then $12,000/t by end of Q1-25’
Another reason why Goldman is doubling down on its bullish copper outlook: gold.
The sharp rally in gold price since the beginning of March has ended the period of consolidation that had been present since late December. Whilst the initial catalyst for the break higher came from a (gold) supportive turn in US data and real rates, the move has been significantly amplified by short term systematic buying, which suggests less sticky upside. In this context, we expect gold to consolidate for now, with our economists near term view on rates and the dollar suggesting limited near-term catalysts for further upside momentum. Yet, a substantive retracement lower will also likely be limited by resilience in physical buying channels. Nonetheless, in the midterm we continue to hold a constructive view on gold underpinned by persistent strength in EM demand as well as eventual Fed easing, which should crucially reactivate the largely for now dormant ETF buying channel. In this context, we increase our average gold price forecast for 2024 from $2,090/toz to $2,180/toz, targeting a move to $2,300/toz by year-end.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs.
Government
Moderna turns the spotlight on long Covid with new initiatives
Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital…

Moderna’s latest Covid effort addresses the often-overlooked chronic condition of long Covid — and encourages vaccination to reduce risks. A digital campaign debuted Friday along with a co-sponsored event in Detroit offering free CT scans, which will also be used in ongoing long Covid research.
In a new video, a young woman describes her three-year battle with long Covid, which includes losing her job, coping with multiple debilitating symptoms and dealing with the negative effects on her family. She ends by saying, “The only way to prevent long Covid is to not get Covid” along with an on-screen message about where to find Covid-19 vaccines through the vaccines.gov website.
“Last season we saw people would get a flu shot, but they didn’t always get a Covid shot,” said Moderna’s Chief Brand Officer Kate Cronin. “People should get their flu shot, but they should also get their Covid shot. There’s no risk of long flu, but there is the risk of long-term effects of Covid.”
It’s Moderna’s “first effort to really sound the alarm,” she said, and the debut coincides with the second annual Long Covid Awareness Day.
An estimated 17.6 million Americans are living with long Covid, according to the latest CDC data. About four million of them are out of work because of the condition, resulting in an estimated $170 billion in lost wages.
While HHS anted up $45 million in grants last year to expand long Covid support initiatives along with public health campaigns, the condition is still often ignored and underfunded.
“It’s not just about the initial infection of Covid, but also if you get it multiple times, your risks goes up significantly,” Cronin said. “It’s important that people understand that.”
grants covid-19 cdc hhsGovernment
Consequences Minus Truth
Consequences Minus Truth
Authored by James Howard Kunstler via Kunstler.com,
“People crave trust in others, because God is found there.”
-…

Authored by James Howard Kunstler via Kunstler.com,
“People crave trust in others, because God is found there.”
- Dom de Bailleul
The rewards of civilization have come to seem rather trashy in these bleak days of late empire; so, why even bother pretending to be civilized? This appears to be the ethos driving our politics and culture now. But driving us where? Why, to a spectacular sort of crack-up, and at warp speed, compared to the more leisurely breakdown of past societies that arrived at a similar inflection point where Murphy’s Law replaced the rule of law.
The US Military Academy at West point decided to “upgrade” its mission statement this week by deleting the phrase Duty, Honor, Country that summarized its essential moral orientation. They replaced it with an oblique reference to “Army Values,” without spelling out what these values are, exactly, which could range from “embrace the suck” to “charlie foxtrot” to “FUBAR” — all neatly applicable to our country’s current state of perplexity and dread.
Are you feeling more confident that the US military can competently defend our country? Probably more like the opposite, because the manipulation of language is being used deliberately to turn our country inside-out and upside-down. At this point we probably could not successfully pacify a Caribbean island if we had to, and you’ve got to wonder what might happen if we have to contend with countless hostile subversive cadres who have slipped across the border with the estimated nine-million others ushered in by the government’s welcome wagon.
Momentous events await. This Monday, the Supreme Court will entertain oral arguments on the case Missouri, et al. v. Joseph R. Biden, Jr., et al. The integrity of the First Amendment hinges on the decision. Do we have freedom of speech as set forth in the Constitution? Or is it conditional on how government officials feel about some set of circumstances? At issue specifically is the government’s conduct in coercing social media companies to censor opinion in order to suppress so-called “vaccine hesitancy” and to manipulate public debate in the 2020 election. Government lawyers have argued that they were merely “communicating” with Twitter, Facebook, Google, and others about “public health disinformation and election conspiracies.”
You can reasonably suppose that this was our government’s effort to disable the truth, especially as it conflicted with its own policy and activities — from supporting BLM riots to enabling election fraud to mandating dubious vaccines. Former employees of the FBI and the CIA were directly implanted in social media companies to oversee the carrying-out of censorship orders from their old headquarters. The former general counsel (top lawyer) for the FBI, James Baker, slid unnoticed into the general counsel seat at Twitter until Elon Musk bought the company late in 2022 and flushed him out. The so-called Twitter Files uncovered by indy reporters Matt Taibbi, Michael Shellenberger, and others, produced reams of emails from FBI officials nagging Twitter execs to de-platform people and bury their dissent. You can be sure these were threats, not mere suggestions.
One of the plaintiffs joined to Missouri v. Biden is Dr. Martin Kulldorff, a biostatistician and professor at the Harvard Medical School, who opposed Covid-19 lockdowns and vaccine mandates. He was one of the authors of the open letter called The Great Barrington Declaration (October, 2020) that articulated informed medical dissent for a bamboozled public. He was fired from his job at Harvard just this past week for continuing his refusal to take the vaccine. Harvard remains among a handful of institutions that still require it, despite massive evidence that it is ineffective and hazardous. Like West Point, maybe Harvard should ditch its motto, Veritas, Latin for “truth.”
A society hostile to truth can’t possibly remain civilized, because it will also be hostile to reality. That appears to be the disposition of the people running things in the USA these days. The problem, of course, is that this is not a reality-optional world, despite the wishes of many Americans (and other peoples of Western Civ) who wish it would be.
Next up for us will be “Joe Biden’s” attempt to complete the bankruptcy of our country with $7.3-trillion proposed budget, 20 percent over the previous years spending, based on a $5-billion tax increase. Good luck making that work. New York City alone is faced with paying $387 a day for food and shelter for each of an estimated 64,800 illegal immigrants, which amounts to $9.15-billion a year. The money doesn’t exist, of course. New York can thank “Joe Biden’s” executive agencies for sticking them with this unbearable burden. It will be the end of New York City. There will be no money left for public services or cultural institutions. That’s the reality and that’s the truth.
A financial crack-up is probably the only thing short of all-out war that will get the public’s attention at this point. I wouldn’t be at all surprised if it happened next week. Historians of the future, stir-frying crickets and fiddleheads over their campfires will marvel at America’s terminal act of gluttony: managing to eat itself alive.
* * *
Support his blog by visiting Jim’s Patreon Page or Substack
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex


























