International
JPM: “We Could Be Just Weeks Away From Cushing Effectively Running Out Of Crude”
JPM: "We Could Be Just Weeks Away From Cushing Effectively Running Out Of Crude"
Back in April 2020, the landlocked West Texas Intermediate crude oil price briefly crashed into negative territory – a stunning turn of events that cost traders.
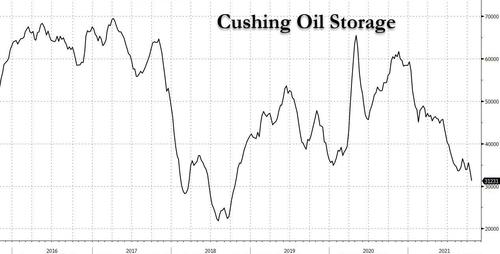
Back in April 2020, the landlocked West Texas Intermediate crude oil price briefly crashed into negative territory - a stunning turn of events that cost traders massive losses - when the spot oil market found itself with an unprecedented glut as there was literally too much oil to be stored, and as such those traders who were assigned delivery would pay others just to take the physical oil off their hands. Well, in just a few weeks we may see the opposite scenario: no physical oil at all in the largest US commercial storage facility, leading to what may be a superspike in the price of oil.
In a note predicting the near-term dynamics of the oil market, JPMorgan's commodity Natasha Kaneva writes that in a world of pervasive nat gas and coal shortages which are forcing the power sector to increasingly turn to oil (boosting demand by 750bkd during winter and drawing inventory by 2.1mmb/d in Nov and Dec), Cushing oil storage - which just dropped to 31.2mm barrels, the lowest since 2018...
... may be just weeks from being "effectively out of crude." The bank's conclusion: "if nothing were to change in the Cushing balance over the next two months, we might expect front WTI spreads to spike to record highs—a “super backwardation” scenario."
Before we get into the meat of the note, first some background which as usual these days, begins with Europe's catastrophic handling of its energy needs.
As JPM notes, the heating season of 2021/2022 is opening with record high global gas prices even as cold winter weather has yet to arrive. Such are the quirks of the natural gas market that, when/if cold winter arrives, demand for gas tends to outpace any source of supply. In the US alone, in a given week in winter, natural gas demand can surge by 50-70 bcf, if not more, with limited response from supply. The situation is so dire at the moment that - JPMorgan observes - "finding even 1 bcf of spare capacity is becoming increasingly difficult."
The good news is that with Russian domestic gas storage sites 97% full, stockpiling should be finalized by November 1, potentially freeing 4-10 bcm of additional shipments to Europe. However, on Monday we reported that Gazprom had booked only 35% of Yamal-Europe exit pipeline capacity for November (same as in October) and chose not to book additional transit volumes via Ukraine, implying that Russia is not currently planning to ship additional gas to Europe at least until Nord Stream 2 is fully authorized.
And as JPM notes, echoing what Goldman said earlier this week, "without additional Russian volumes, the winter weather premium currently embedded in the European natural gas price cannot significantly diminish until outlook for January weather becomes more certain."
In short, even higher nat gas prices are on deck, especially if the winter is cold.
So with record coal and gas prices, the power sector and energy intensive industries are turning to oil, potentially boosting demand by 750 kbd during winter and drawing oil inventory by 2.1 mbd over November and December. Earlier today, Reuters quoted Saudi Arabia's Minister of Energy Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman who confirmed that users switching from gas to oil could account for demand of 500,000-600,000 barrels per day (bpd), adding that the world was now waking up to shortages in the energy sector.
Abdulaziz said the potential switch depended on how severe winter weather would be and how expensive alternative energy prices would be. He outlined a wide range of factors that have led to a recent spike in energy prices, including limited investment in hydrocarbons and infrastructure, low inventories, the lifting of pandemic lockdowns and COVID-19 vaccine uptake rates.
"People all of a sudden woke up to the reality that they are running out of everything: they are ran out of investments, they ran out of stocks and they ran out of … creativity in trying to be attending to real solution that address real issues," Prince Abdulaziz told the CERA Week India Energy Forum.
In any case, in the clearest example yet of market tightness, Cushing crude storage fell to 31.2 mb last week as noted in the chart above. And because operational tank bottoms are likely 20-25% of capacity- or about 20 mb - JPM predicts that "we could be just weeks away from Cushing being effectively out of crude" and adds that "if nothing were to change in the Cushing balance over the next two months, we might expect front WTI spreads to spike to record highs—a “super backwardation” scenario."
If JPM's prediction is correct - and recall just yesterday we published a similar take from Morgan Stanley which now expects a similar "peak supply" scenario playing out, if over the longer term prompting the bank to hike its Q1 2022 price target to $95 from $77.5/bbl - it would have a catastrophic (read higher) impact on the price of oil.
Of course, there are potential mitigating factors: as Kaneva notes, though the dynamics of the US crude balance are different than they were in 2018 and much different than they were in 2014—the last two times Cushing drew down toward operational limits—the market still has a few levers to pull before we worry about such a scenario.
Today, the oil market is already reacting to the possibility that Cushing inventories bottom out and the export arb from the US Gulf Coast to Northwest Europe has been closed since 14 Oct. Consequently, the bank expects US crude exports to fall to an average 2.0-2.2 mbd by mid-November, with most of that ~500 kbd cut coming from flows to Europe.
But while this may be good news for the US, it's even more bad news for Europe - this reduction in flows to Europe would come at a time when European crude markets are already quite tight. According to data from Kpler, Europe crude oil stocks are already at their lowest since late 2018. Since 15 July, Europe crude stocks have fallen 35 mb, a rate of 362 kbd.
European exports aside, and focusing on Cushing inbound flows, JPM notes that last week the Steele City to Cushing section of the Keystone pipeline halted for three days as Keystone shifted flows to Patoka and the pipeline was still flowing at a much lower than normal rate early this week, though flows appear to be back above 400 kbd this morning.
Total Keystone flows fell on Tuesday as flows to Patoka slowed as well. If Keystone flows to Cushing—normally 350-625 kbd—return consistently to normal soon, Cushing would be much closer to balance. However, if the shift in flows is intended to serve as line fill for Capline, Keystone may not be a short-term solution to the Cushing tank bottoms issue.
Capline should require about 5.2 mb of line fill in total. With start-up not planned until 1 Jan, the rate of line fill should not be more than about 100 kbd. While this additional tightness in the PADD 2 crude balance certainly does not help matters at Cushing, it should be more than offset by the continued ramp up of the 760 kbd Line 3 Replacement, JPM suggests.
Finally, flows on the Enbridge Mainline group of pipelines, which includes the Line 3 Replacement, have only increased about 200 kbd since the start of Line 3, which means the potential for much more crude volume flowing into PADD 2 could be just across the horizon, assuming Canadian producers are willing and able to supply them.
International
There will soon be one million seats on this popular Amtrak route
“More people are taking the train than ever before,” says Amtrak’s Executive Vice President.

While the size of the United States makes it hard for it to compete with the inter-city train access available in places like Japan and many European countries, Amtrak trains are a very popular transportation option in certain pockets of the country — so much so that the country’s national railway company is expanding its Northeast Corridor by more than one million seats.
Related: This is what it's like to take a 19-hour train from New York to Chicago
Running from Boston all the way south to Washington, D.C., the route is one of the most popular as it passes through the most densely populated part of the country and serves as a commuter train for those who need to go between East Coast cities such as New York and Philadelphia for business.
Veronika Bondarenko
Amtrak launches new routes, promises travelers ‘additional travel options’
Earlier this month, Amtrak announced that it was adding four additional Northeastern routes to its schedule — two more routes between New York’s Penn Station and Union Station in Washington, D.C. on the weekend, a new early-morning weekday route between New York and Philadelphia’s William H. Gray III 30th Street Station and a weekend route between Philadelphia and Boston’s South Station.
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
According to Amtrak, these additions will increase Northeast Corridor’s service by 20% on the weekdays and 10% on the weekends for a total of one million additional seats when counted by how many will ride the corridor over the year.
“More people are taking the train than ever before and we’re proud to offer our customers additional travel options when they ride with us on the Northeast Regional,” Amtrak Executive Vice President and Chief Commercial Officer Eliot Hamlisch said in a statement on the new routes. “The Northeast Regional gets you where you want to go comfortably, conveniently and sustainably as you breeze past traffic on I-95 for a more enjoyable travel experience.”
Here are some of the other Amtrak changes you can expect to see
Amtrak also said that, in the 2023 financial year, the Northeast Corridor had nearly 9.2 million riders — 8% more than it had pre-pandemic and a 29% increase from 2022. The higher demand, particularly during both off-peak hours and the time when many business travelers use to get to work, is pushing Amtrak to invest into this corridor in particular.
To reach more customers, Amtrak has also made several changes to both its routes and pricing system. In the fall of 2023, it introduced a type of new “Night Owl Fare” — if traveling during very late or very early hours, one can go between cities like New York and Philadelphia or Philadelphia and Washington. D.C. for $5 to $15.
As travel on the same routes during peak hours can reach as much as $300, this was a deliberate move to reach those who have the flexibility of time and might have otherwise preferred more affordable methods of transportation such as the bus. After seeing strong uptake, Amtrak added this type of fare to more Boston routes.
The largest distances, such as the ones between Boston and New York or New York and Washington, are available at the lowest rate for $20.
stocks pandemic japan europeanInternational
The next pandemic? It’s already here for Earth’s wildlife
Bird flu is decimating species already threatened by climate change and habitat loss.

I am a conservation biologist who studies emerging infectious diseases. When people ask me what I think the next pandemic will be I often say that we are in the midst of one – it’s just afflicting a great many species more than ours.
I am referring to the highly pathogenic strain of avian influenza H5N1 (HPAI H5N1), otherwise known as bird flu, which has killed millions of birds and unknown numbers of mammals, particularly during the past three years.
This is the strain that emerged in domestic geese in China in 1997 and quickly jumped to humans in south-east Asia with a mortality rate of around 40-50%. My research group encountered the virus when it killed a mammal, an endangered Owston’s palm civet, in a captive breeding programme in Cuc Phuong National Park Vietnam in 2005.
How these animals caught bird flu was never confirmed. Their diet is mainly earthworms, so they had not been infected by eating diseased poultry like many captive tigers in the region.
This discovery prompted us to collate all confirmed reports of fatal infection with bird flu to assess just how broad a threat to wildlife this virus might pose.
This is how a newly discovered virus in Chinese poultry came to threaten so much of the world’s biodiversity.
The first signs
Until December 2005, most confirmed infections had been found in a few zoos and rescue centres in Thailand and Cambodia. Our analysis in 2006 showed that nearly half (48%) of all the different groups of birds (known to taxonomists as “orders”) contained a species in which a fatal infection of bird flu had been reported. These 13 orders comprised 84% of all bird species.
We reasoned 20 years ago that the strains of H5N1 circulating were probably highly pathogenic to all bird orders. We also showed that the list of confirmed infected species included those that were globally threatened and that important habitats, such as Vietnam’s Mekong delta, lay close to reported poultry outbreaks.
Mammals known to be susceptible to bird flu during the early 2000s included primates, rodents, pigs and rabbits. Large carnivores such as Bengal tigers and clouded leopards were reported to have been killed, as well as domestic cats.
Our 2006 paper showed the ease with which this virus crossed species barriers and suggested it might one day produce a pandemic-scale threat to global biodiversity.
Unfortunately, our warnings were correct.
A roving sickness
Two decades on, bird flu is killing species from the high Arctic to mainland Antarctica.
In the past couple of years, bird flu has spread rapidly across Europe and infiltrated North and South America, killing millions of poultry and a variety of bird and mammal species. A recent paper found that 26 countries have reported at least 48 mammal species that have died from the virus since 2020, when the latest increase in reported infections started.
Not even the ocean is safe. Since 2020, 13 species of aquatic mammal have succumbed, including American sea lions, porpoises and dolphins, often dying in their thousands in South America. A wide range of scavenging and predatory mammals that live on land are now also confirmed to be susceptible, including mountain lions, lynx, brown, black and polar bears.
The UK alone has lost over 75% of its great skuas and seen a 25% decline in northern gannets. Recent declines in sandwich terns (35%) and common terns (42%) were also largely driven by the virus.
Scientists haven’t managed to completely sequence the virus in all affected species. Research and continuous surveillance could tell us how adaptable it ultimately becomes, and whether it can jump to even more species. We know it can already infect humans – one or more genetic mutations may make it more infectious.
At the crossroads
Between January 1 2003 and December 21 2023, 882 cases of human infection with the H5N1 virus were reported from 23 countries, of which 461 (52%) were fatal.
Of these fatal cases, more than half were in Vietnam, China, Cambodia and Laos. Poultry-to-human infections were first recorded in Cambodia in December 2003. Intermittent cases were reported until 2014, followed by a gap until 2023, yielding 41 deaths from 64 cases. The subtype of H5N1 virus responsible has been detected in poultry in Cambodia since 2014. In the early 2000s, the H5N1 virus circulating had a high human mortality rate, so it is worrying that we are now starting to see people dying after contact with poultry again.
It’s not just H5 subtypes of bird flu that concern humans. The H10N1 virus was originally isolated from wild birds in South Korea, but has also been reported in samples from China and Mongolia.
Recent research found that these particular virus subtypes may be able to jump to humans after they were found to be pathogenic in laboratory mice and ferrets. The first person who was confirmed to be infected with H10N5 died in China on January 27 2024, but this patient was also suffering from seasonal flu (H3N2). They had been exposed to live poultry which also tested positive for H10N5.
Species already threatened with extinction are among those which have died due to bird flu in the past three years. The first deaths from the virus in mainland Antarctica have just been confirmed in skuas, highlighting a looming threat to penguin colonies whose eggs and chicks skuas prey on. Humboldt penguins have already been killed by the virus in Chile.

How can we stem this tsunami of H5N1 and other avian influenzas? Completely overhaul poultry production on a global scale. Make farms self-sufficient in rearing eggs and chicks instead of exporting them internationally. The trend towards megafarms containing over a million birds must be stopped in its tracks.
To prevent the worst outcomes for this virus, we must revisit its primary source: the incubator of intensive poultry farms.
Diana Bell does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
genetic pandemic mortality spread deaths south korea south america europe uk chinaInternational
This is the biggest money mistake you’re making during travel
A retail expert talks of some common money mistakes travelers make on their trips.

Travel is expensive. Despite the explosion of travel demand in the two years since the world opened up from the pandemic, survey after survey shows that financial reasons are the biggest factor keeping some from taking their desired trips.
Airfare, accommodation as well as food and entertainment during the trip have all outpaced inflation over the last four years.
Related: This is why we're still spending an insane amount of money on travel
But while there are multiple tricks and “travel hacks” for finding cheaper plane tickets and accommodation, the biggest financial mistake that leads to blown travel budgets is much smaller and more insidious.
This is what you should (and shouldn’t) spend your money on while abroad
“When it comes to traveling, it's hard to resist buying items so you can have a piece of that memory at home,” Kristen Gall, a retail expert who heads the financial planning section at points-back platform Rakuten, told Travel + Leisure in an interview. “However, it's important to remember that you don't need every souvenir that catches your eye.”
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
According to Gall, souvenirs not only have a tendency to add up in price but also weight which can in turn require one to pay for extra weight or even another suitcase at the airport — over the last two months, airlines like Delta (DAL) , American Airlines (AAL) and JetBlue Airways (JBLU) have all followed each other in increasing baggage prices to in some cases as much as $60 for a first bag and $100 for a second one.
While such extras may not seem like a lot compared to the thousands one might have spent on the hotel and ticket, they all have what is sometimes known as a “coffee” or “takeout effect” in which small expenses can lead one to overspend by a large amount.
‘Save up for one special thing rather than a bunch of trinkets…’
“When traveling abroad, I recommend only purchasing items that you can't get back at home, or that are small enough to not impact your luggage weight,” Gall said. “If you’re set on bringing home a souvenir, save up for one special thing, rather than wasting your money on a bunch of trinkets you may not think twice about once you return home.”
Along with the immediate costs, there is also the risk of purchasing things that go to waste when returning home from an international vacation. Alcohol is subject to airlines’ liquid rules while certain types of foods, particularly meat and other animal products, can be confiscated by customs.
While one incident of losing an expensive bottle of liquor or cheese brought back from a country like France will often make travelers forever careful, those who travel internationally less frequently will often be unaware of specific rules and be forced to part with something they spent money on at the airport.
“It's important to keep in mind that you're going to have to travel back with everything you purchased,” Gall continued. “[…] Be careful when buying food or wine, as it may not make it through customs. Foods like chocolate are typically fine, but items like meat and produce are likely prohibited to come back into the country.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemic france-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex























