Spread & Containment
Iraqi WMD redux
In the early 2000s, the US government exaggerated evidence in favor of an active Iraqi nuclear weapons program in order to whip up war hysteria. There is increasing evidence that in 2020 the US government exaggerated evidence for a “lab leak” being…
In the early 2000s, the US government exaggerated evidence in favor of an active Iraqi nuclear weapons program in order to whip up war hysteria. There is increasing evidence that in 2020 the US government exaggerated evidence for a “lab leak” being the origin of Covid in order to justify a cold war with China.
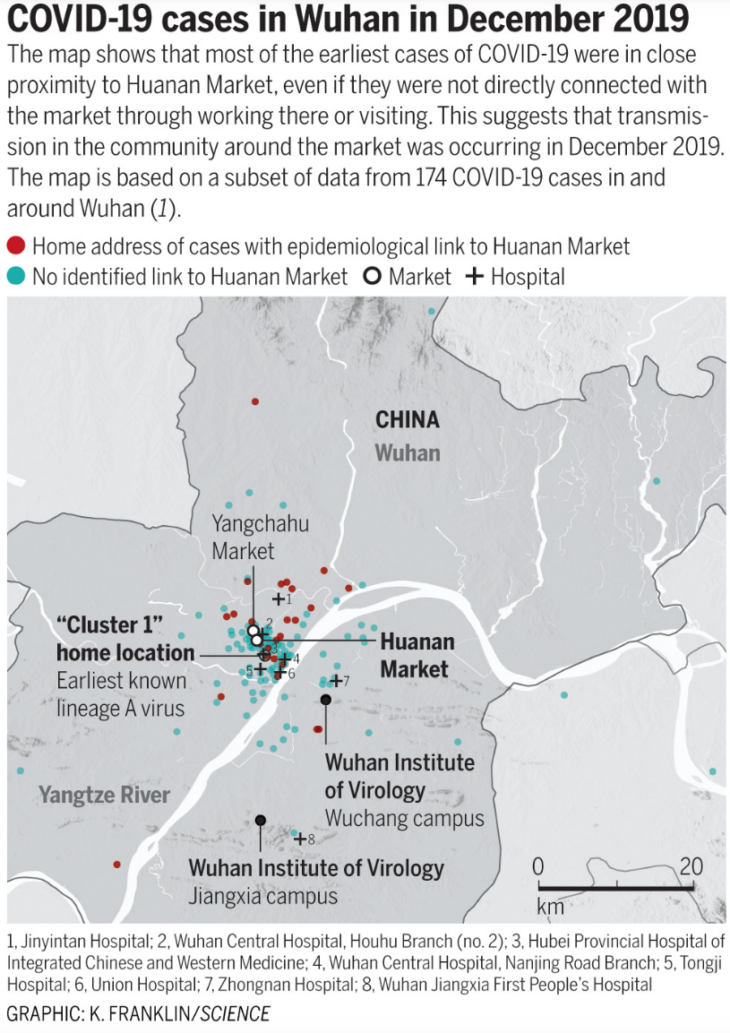
A new paper in Science by Michael Worobey provides strong circumstantial evidence that Covid originated at the Huanan animal market in Wuhan, China. The paper showed that previous claims that “patient zero” has no connection with the Huanan market were false, and that the actual earliest known patient was a woman who worked in the market.
The paper also shows that the original cluster of cases was centered on the Huanan market, and that this clustering cannot be due to reporting bias:
Keep in mind that Wuhan is not a unified city like Paris, with a small river running down the middle. The Yangtze is a giant river, roughly a mile across, and Wuhan feels like two separate cities. (I was in Wuhan in mid-2019.) In fact, it was originally multiple cities, Wuchang on one side and Hanyang on the other. The name “Wuhan” was constructed out of those two names, and one other city. As you can see from the map, the famous Wuhan Institute of Virology is about 12 kilometers from the animal market and on the other side of the huge river.
Now of course it is possible that the virus originally spread via a lab leak and the Huanan market was the site of the first “superspreader” event. But that theory has exactly the same problem as lab leak opponents used to justify their claims that a natural origin was implausible. Lab leak proponents once asked, “How likely is it that the virus would first emerge in a Chinese city with a virus research institute?” Worobey turns that argument on its head:

Perhaps Worobey is part of some sort of vast Chinese propaganda effort, which is trying to cover up the origins of Covid. If so, why did Worobey previously sign a letter complaining that the WHO investigation had not taken the lab leak hypothesis seriously enough:
In May, two months after the report by the W.H.O. and China was published, 18 prominent scientists, including Dr. Worobey, responded with a letter in Science complaining that the W.H.O. team had given the lab-leak theory short shrift. Far more research was required, they argued, to determine whether one explanation was more likely than the other.
Lots of lab leak proponents jumped on this letter in support of their claims of a cover-up. And yet Worobey’s Science paper shows that (in at least one respect) the WHO actually gave too much credence to the lab leak hypothesis by wrongly reporting that the first known patient had no links to the Huanan market.
Ironically, the Chinese government may have encouraged lab leak speculation with a clumsy attempt to downplay the animal market hypothesis. The previous SARS epidemic began in a Chinese animal market (in 2003), and early in 2020 China received heavy criticism for allowing these markets:
Paul McCartney has called Chinese wet markets “medieval” and blamed them for the spread of coronavirus, using a comparison with the abolition of the slave trade when calling for them to be banned.
So-called “wet markets” in Asia trade in fresh meat and produce, and sometimes feature live animals. (They take their name from the frequently hosed-down floors.) A common theory – though far from confirmed – is that Covid-19 originated in a live animal market in Wuhan, with the disease being transmitted from illegally traded bat or pangolin meat.
These kinds of news reports in the Western media were deeply embarrassing to China, and their government destroyed valuable evidence that might link the animal markets to the pandemic by killing all the animals in the Huanan market.
In a rational world, the animal market theory would be far more embarrassing to China than the lab leak hypothesis. Western countries also have labs doing gain-of-function research, and lab leaks have occurred in the West. But Western countries do not have Chinese style animal markets. My own view is that the Chinese government is partly to blame for the Covid pandemic, but if I were convinced the lab leak theory were true then it would make me less likely to blame China. Therefore I consider this to be an “anti-CCP post”.
So why did the US government use the lab leak hypothesis as a tool for whipping up anti-China hysteria? Perhaps because most people look at the issue in a more emotional way. The term ‘lab leak’ conjures up images from “mad scientist” films, whereas wild animal markets seem like an old Chinese tradition, a part of their culture.
I see the US government’s attempt to promote the lab leak hypothesis as being part of a longstanding tradition going back to the sinking of the Maine, the Tonkin Gulf incident, and the Iraqi WMD fiasco. The more things change, the more they stay the same.
PS. Other so-called “evidence” has been cited for the lab leak hypothesis, such as three WIV workers supposedly being infected with Covid in November 2019, and the “fact” that the virus supposedly looks manmade. Those pieces of evidence have been shot down long ago.
(5 COMMENTS) link pandemic coronavirus covid-19 us government spread wuhan chinaGovernment
Supreme Court’s questions about First Amendment cases show support for ‘free trade in ideas’
These cases have asked the justices to consider how to apply some of the most sweeping constitutional protections – those of free speech – to an extremely…

This term, the U.S. Supreme Court has heard oral arguments in a total of five cases involving questions about whether and how the First Amendment to the Constitution applies to social media platforms and their users. These cases are parts of a larger effort by conservative activists to block what they claim is government censorship of people who seek to spread false information online.
The most recently heard case, on March 18, 2024, was Murthy v. Missouri, about whether the federal government’s direct communication with social media platforms, specifically about online content relating to the COVID-19 public health emergency, violated the First Amendment rights of private citizens.
The case stemmed from the Biden administration’s efforts to combat misinformation that spread online, including on social media, during the pandemic. The plaintiffs said White House officials “threatened platforms with adverse consequences” if they didn’t take down or limit the online visibility of inaccurate information – and that those threats amount to the unconstitutional suppression of free speech from private individuals who shared content that contained debunked conspiracy theories and contradicted scientific evidence.
It is not uncommon for government officials to informally pressure private parties, like social media platforms, into limiting, censoring or moderating speech by third parties. As Justice Amy Coney Barrett seemingly implied during the Murthy v. Missouri oral arguments, “vanilla encouragement” by government officials would be constitutionally permissible. But when the informal pressure turns into bullying, threats or coercion, it may trigger First Amendment protections, as the Supreme Court ruled in another case called Bantam Books v. Sullivan, from 1963.
But the Biden administration said its effort to fight COVID misinformation was normal activity, in which the government is allowed to express its views to persuade others, especially in ways that advance the public interest.

Several justices seemingly agreed with the Biden administration and accepted its view that ordinary pressure to persuade is permissible.
More broadly, the Supreme Court has wrestled with the application of the First Amendment to cases involving social media platforms. Earlier this term, the court heard several cases that involved content moderation – both by the platforms themselves and by public officials using their own social media accounts. As Justice Elena Kagan put it during one round of oral arguments: “That’s what makes these cases hard, is that there are First Amendment interests all over the place.”
Perhaps most fundamentally, the court seeks to evaluate the relationship between social media platforms and public officials.
A public official or a private social media user?
On March 15, the Supreme Court released its unanimous decision in Lindke v. Freed – another case involving social media platforms. The issue in that case was whether a public official can delete or block private individuals from commenting on the official’s social media profile or posts.
This case involved James Freed, the city manager of Port Huron, Michigan, and Facebook user Kevin Lindke. Freed initially created his Facebook profile before entering public office, but once he was appointed city manager, he began using the Facebook profile to communicate with the public. Freed eventually blocked Lindke from commenting on his posts after Lindke “unequivocally express(ed) his displeasure with the city’s approach to the (COVID-19) pandemic.”
The court ruled that on social media, where users, including government officials, often mix personal and professional posts, “it can be difficult to tell whether the speech is official or private.” But the court unanimously found that if an official possesses “actual authority to speak” on behalf of the government, and if the person “purported to exercise that authority when” posting online, the post is a government action. In that case, the official cannot block users’ access to view or comment on it.
The court ruled that if the poster either does not have authority to speak for the government, or is not clearly exercising that authority when posting, then the message is private. In that situation, the poster can restrict viewing and commenting because that is an exercise of their own First Amendment rights. But when a public official posts in their official capacity, the poster must respect the First Amendment’s limitations placed on government. The court sent a similar case, O'Connor-Ratcliff v. Garnier, back to a lower court for reconsideration based on the ruling in the Lindke case.

Who controls what’s online?
At the root of the plaintiffs’ claims in both these cases is content moderation – whether a public official can moderate another user’s content by deleting their posts or blocking the user, and whether the federal government can interact with social media platforms to mitigate the spread of debunked conspiracy theories and scientifically disprovable narratives about the pandemic, for instance.
Ironically, though conservatives argue that the federal government cannot interact with the social media platforms to influence their content moderation, Florida and Texas – states governed by Republican majorities in the statehouse and Republican governors – enacted state laws that seek to restrict the platforms’ own content moderation.
While the laws in each state differ slightly, they share similar provisions. First, both laws contain “must-carry provisions,” which “prohibit social media platforms from removing or limiting the visibility of user content in certain circumstances,” according to the Knight First Amendment Institute at Columbia University.
Second, both laws require the social media platforms to provide individualized explanations to any user whose content is moderated by the platform. Both laws were passed to combat the false perception that the platforms disproportionately silence conservative speech.
The Florida and Texas laws were challenged in two cases whose oral arguments were heard by the Supreme Court in February 2024: Moody v. NetChoice and NetChoice v. Paxton, respectively. Florida and Texas argued that they can regulate the platforms’ content moderation policies and processes, but the platforms argued that these laws infringe on their editorial discretion, which is protected by well-established First Amendment precedent.
During oral argument in both cases, the justices appeared skeptical of both laws. As Chief Justice John Roberts stated, the First Amendment prohibits the government, not private entities, from censoring speech. Florida and Texas argued that they enacted these laws to protect the free speech of their citizens by limiting the platforms’ ability to moderate content.
But social media users do not have any First Amendment protections on the platforms, because private entities, like Facebook, are free to moderate the content on their platforms as they see fit. Roberts was quick to respond to Texas and Florida: “The First Amendment restricts what the government can do, and what the government’s doing here is saying you must do this, you must carry these people.”
Where are the online boundaries of free speech?
Collectively, these cases demonstrate the Supreme Court’s interest in defining the boundaries of First Amendment protections as they relate to social media platforms and their users. Moreover, the court seems focused on establishing the limits of the relationship between government and social media platforms.
The justices’ questions during the NetChoice cases suggest that they are skeptical of government regulation that forces social media platforms to carry certain content. In this way, the justices seem poised to affirm the principle that government cannot directly or formally force an individual or, in this case, a private company, to convey a message that it does not wish to carry.
But the justices’ questions during Murthy v. Missouri seem to suggest that it is not a violation of the First Amendment for government officials to informally interact or communicate with social media platforms in an attempt to persuade them not to carry material the government dislikes.
Considering all of these cases together, the court seems posed to further promote a robust “free trade in ideas,” which was a theory first invoked in 1919 by Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes in Abrams v. United States. In Lindke v. Freed, the court identified the distinction between private speech on social media platforms by a public official, which is protected by the First Amendment, and professional speech, which is subject to First Amendment limitations that protect others’ rights.
In the NetChoice cases, the court seems ready to limit a state’s ability to directly compel social media platforms to convey messages that they may moderate. And in Murthy v. Missouri, the justices seem ready to affirm that while indirect compulsion may be unconstitutional, ordinary pressures to persuade social media platforms are permissible.
This promotion of a robust marketplace of ideas appears to stem from neither giving the government extra powers to shape public discourse, nor excluding government from the conversation altogether.
Wayne Unger does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
white house pandemic covid-19 spread suppressionGovernment
Report Criticizes ‘Catastrophic Errors’ Of COVID Lockdowns, Warns Of Repeat
Report Criticizes ‘Catastrophic Errors’ Of COVID Lockdowns, Warns Of Repeat
Authored by Kevin Stocklin via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
It…

Authored by Kevin Stocklin via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
It was four years ago, in March 2020, that health officials declared COVID-19 a pandemic and America began shutting down schools, closing small businesses, restricting gatherings and travel, and other lockdown measures to “slow the spread” of the virus.
To mark that grim anniversary, a group of medical and policy experts released a report, called “COVID Lessons Learned,” which assesses the government’s response to the pandemic. According to the report, that response included a few notable successes, along with a litany of failures that have taken a severe toll on the population.
During the pandemic, many governments across the globe acted in lockstep to pursue authoritative policies in response to the disease, locking down populations, closing schools, shutting businesses, sealing borders, banning gatherings, and enforcing various mask and vaccine mandates. What were initially imposed as short-term mandates and emergency powers given to presidents, ministers, governors, and health officials soon became extended into a longer-term expansion of official power.
“Even though the initial point of temporary lockdowns was to ’slow the spread,' which meant to allow hospitals to function without being overwhelmed, instead it rapidly turned into stopping COVID cases at all costs,” Dr. Scott Atlas, a physician, former White House Coronavirus Task Force member, and one of the authors of the report, stated at a March 15 press conference.
Published by the Committee to Unleash Prosperity (CTUP), the report was co-authored by Steve Hanke, economics professor and director of the Johns Hopkins Institute for Applied Economics; Casey Mulligan, former chief economist of the White House Council of Economic Advisors; and CTUP President Philip Kerpen.
According to the report, one of the first errors was the unprecedented authority that public officials took upon themselves to enforce health mandates on Americans.
“Granting public health agencies extraordinary powers was a major error,” Mr. Hanke told The Epoch Times. “It, in effect, granted these agencies a license to deceive the public.”
The authors argue that authoritative measures were largely ineffective in fighting the virus, but often proved highly detrimental to public health.
The report quantifies the cost of lockdowns, both in terms of economic costs and the number of non-COVID excess deaths that occurred and continue to occur after the pandemic. It estimates that the number of non-COVID excess deaths, defined as deaths in excess of normal rates, at about 100,000 per year in the United States.
‘They Will Try to Do This Again’
“Lockdowns, schools closures, and mandates were catastrophic errors, pushed with remarkable fervor by public health authorities at all levels,” the report states. The authors are skeptical, however, that health authorities will learn from the experience.
“My worry is that if we have another pandemic or another virus, I think that Washington is still going to try to do these failed policies,” said Steve Moore, a CTUP economist. “We’re not here to say ‘this guy got it wrong' or ’that guy or got it wrong,’ but we should learn the lessons from these very, very severe mistakes that will have costs for not just years, but decades to come.
“I guarantee you, they will try to do this again,” Mr. Moore said. “And what’s really troubling me is the people who made these mistakes still have not really conceded that they were wrong.”
Mr. Hanke was equally pessimistic.
“Unfortunately, the public health establishment is in the authoritarian model of the state,” he said. “Their entire edifice is one in which the state, not the individual, should reign supreme.”
The authors are also critical of what they say was a multifaceted campaign in which public officials, the news media, and social media companies cooperated to frighten the population into compliance with COVID mandates.
“During COVID, the public health establishment … intentionally stoked and amplified fear, which overlaid enormous economic, social, educational and health harms on top of the harms of the virus itself,” the report states.
The authors contrasted the authoritative response of many U.S. states to policies in Sweden, which they say relied more on providing advice and information to the public rather than attempting to force behaviors.
Sweden’s constitution, called the “Regeringsform,” guarantees the liberty of Swedes to move freely within the realm and prohibits severe lockdowns, Mr. Hanke stated.
“By following the Regeringsform during COVID, the Swedes ended up with one of the lowest excess death rates in the world,” he said.
Because the Swedish government avoided strict mandates and was more forthright in sharing information with its people, many citizens altered their behavior voluntarily to protect themselves.
“A much wiser strategy than issuing lockdown orders would have been to tell the American people the truth, stick to the facts, educate citizens about the balance of risks, and let individuals make their own decisions about whether to keep their businesses open, whether to socially isolate, attend church, send their children to school, and so on,” the report states.
‘A Pretext to Enhance Their Power’
The CTUP report cites a 2021 study on government power and emergencies by economists Christian Bjornskov and Stefan Voigt, which found that the more emergency power a government accumulates during times of crisis, “the higher the number of people killed as a consequence of a natural disaster, controlling for its severity.
“As this is an unexpected result, we discuss a number of potential explanations, the most plausible being that governments use natural disasters as a pretext to enhance their power,” the study’s authors state. “Furthermore, the easier it is to call a state of emergency, the larger the negative effects on basic human rights.”
“All the things that people do in their lives … they have purposes,” Mr. Mulligan said. “And for somebody in Washington D.C. to tell them to stop doing all those things, they can’t even begin to comprehend the disruption and the losses.
“We see in the death certificates a big elevation in people dying from heart conditions, diabetes conditions, obesity conditions,” he said, while deaths from alcoholism and drug overdoses “skyrocketed and have not come down.”
The report also challenged the narrative that most hospitals were overrun by the surge of COVID cases.
“Almost any measure of hospital utilization was very low, historically, throughout the pandemic period, even though we had all these headlines that our hospitals were overwhelmed,” Mr. Kerpen stated. “The truth was actually the opposite, and this was likely the result of public health messaging and political orders, canceling medical procedures and intentionally stoking fear, causing people to cancel their appointments.”
The effect of this, the authors argue, was a sharp increase in non-COVID deaths because people were avoiding necessary treatments and screenings.
“There were actually mass layoffs in this sector at one point,” Mr. Kerpen said, “and even now, total discharges are well below pre-pandemic levels.”
In addition, as health mandates became more draconian, many people became concerned at the expansion of government power and the loss of civil liberties, particularly when government directives—such as banning outdoor church services but allowing mass social-justice protests—often seemed unreasonable or politicized.
The report also criticized the single-minded focus on vaccines and the failure by the NIH and the FDA to do clinical trials on existing drugs that were known to be safe and could have been effective in treating those infected with COVID-19.
Because so much of the process of approving the vaccines, the risks and benefits, and the reporting of possible side-effects was kept from the public, people were unable to give informed consent to their own health care, Mr. Kerpen said.
“And when the Biden administration came in and started mandating them, now you had something that was inherently experimental with some questionable data, and instead of saying, ‘Now you have a choice whether you want it or not,’ in the context of a pandemic they tried to mandate them,” he said.
Pandemic Censorship
Tech oligopolies and the corporate media also receive criticism for their collaboration with government to control public messaging and censor dissenting voices. According to the authors, many government and health officials collaborated with tech oligarchs, news media corporations, and even scientific journals to censor critical views on the pandemic.
The Biden administration is currently defending itself before the Supreme Court against charges brought by Louisiana and Missouri attorneys general, who charged that administration officials pressured tech companies to censor information that contradicted official narratives on COVID-19’s origins, related mandates and treatment, as well as censoring political speech that was critical of President Biden during his 2020 campaign. The case is Murthy v. Missouri.
Mr. Hanke stated that a previous report he co-authored, titled “Did Lockdowns Work?,” which was critical of lockdowns, was refused by medical journals, even when they published op-eds that criticized it and published numerous pro-lockdown reports.
Dr. Vinay Prasad—a physician, epidemiologist, professor at the University of California at San Francisco’s medical school and author of over 350 academic articles and letters—has made similar allegations of censorship by medical journals.
“Specifically, MedRxiv and SSRN have been reluctant to post articles critical of the CDC, mask and vaccine mandates, and the Biden administration’s health care policies,” Dr. Prasad stated.
Heightening concerns about medical censorship is the “zero-draft” World Health Organization (WHO) pandemic treaty currently being circulated for approval by member states, including the United States. It commits members to jointly seek out and “tackle” what the WHO deems as “misinformation and disinformation.”
One of the enduring consequences of the COVID years is a general loss of public trust in public officials, health experts, and official narratives.
“Operation Warp Speed was a terrific success with highly unexpected rapidity of development [of vaccines],” Dr. Atlas said. “But the serious flaws centered around not being open with the public about the uncertainties, particularly of the vaccines’ efficacy and safety.”
“One result of the government’s error-ridden COVID response was that Americans have justifiably lost faith in public health institutions,” the report states. According to the authors, if health officials want to regain the public’s trust, they should begin with an accurate assessment of their actions during the pandemic.
“The best way to restore trust is to admit you were wrong,” Dr. Atlas said. “I think we all know that in our personal lives, but here it’s very important because there has been a massive lack of trust now in institutions, in experts, in data, in science itself.
“I think it’s going to be very difficult to restore that without admission of error,” he said.
Recommendations for a Future Pandemic
The CTUP report recommends that Congress and state legislatures set strict limitations on powers conferred to the executive branch, including health officials, and set time limits that would require legislation to be extended. This would give the public a voice in health emergency measures through their elected representatives.
It further recommends that research grants should be independent of policy positions and that NIH funding should be decentralized or block-granted to states to distribute.
Congress should mandate public disclosure of all FDA, CDC, and NIH discussions and decisions, including statements of any persons who provide advice to these agencies. Congress should also make explicit that CDC guidance is advisory and does not constitute laws or mandates.
The report also recommends that the United States immediately halt negotiations of agreements with the WHO “until satisfactory transparency and accountability is achieved.”
Government
Google’s A.I. Fiasco Exposes Deeper Infowarp
Google’s A.I. Fiasco Exposes Deeper Infowarp
Authored by Bret Swanson via The Brownstone Institute,
When the stock markets opened on the…

Authored by Bret Swanson via The Brownstone Institute,
When the stock markets opened on the morning of February 26, Google shares promptly fell 4%, by Wednesday were down nearly 6%, and a week later had fallen 8% [ZH: of course the momentum jockeys have ridden it back up in the last week into today's NVDA GTC keynote]. It was an unsurprising reaction to the embarrassing debut of the company’s Gemini image generator, which Google decided to pull after just a few days of worldwide ridicule.
CEO Sundar Pichai called the failure “completely unacceptable” and assured investors his teams were “working around the clock” to improve the AI’s accuracy. They’ll better vet future products, and the rollouts will be smoother, he insisted.
That may all be true. But if anyone thinks this episode is mostly about ostentatiously woke drawings, or if they think Google can quickly fix the bias in its AI products and everything will go back to normal, they don’t understand the breadth and depth of the decade-long infowarp.
Gemini’s hyper-visual zaniness is merely the latest and most obvious manifestation of a digital coup long underway. Moreover, it previews a new kind of innovator’s dilemma which even the most well-intentioned and thoughtful Big Tech companies may be unable to successfully navigate.
Gemini’s Debut
In December, Google unveiled its latest artificial intelligence model called Gemini. According to computing benchmarks and many expert users, Gemini’s ability to write, reason, code, and respond to task requests (such as planning a trip) rivaled OpenAI’s most powerful model, GPT-4.
The first version of Gemini, however, did not include an image generator. OpenAI’s DALL-E and competitive offerings from Midjourney and Stable Diffusion have over the last year burst onto the scene with mindblowing digital art. Ask for an impressionist painting or a lifelike photographic portrait, and they deliver beautiful renderings. OpenAI’s brand new Sora produces amazing cinema-quality one-minute videos based on simple text prompts.
Then in late February, Google finally released its own Genesis image generator, and all hell broke loose.
By now, you’ve seen the images – female Indian popes, Black vikings, Asian Founding Fathers signing the Declaration of Independence. Frank Fleming was among the first to compile a knee-slapping series of ahistorical images in an X thread which now enjoys 22.7 million views.
Gemini in Action: Here are several among endless examples of Google’s new image generator, now in the shop for repairs. Source: Frank Fleming.
Gemini simply refused to generate other images, for example a Norman Rockwell-style painting. “Rockwell’s paintings often presented an idealized version of American life,” Gemini explained. “Creating such images without critical context could perpetuate harmful stereotypes or inaccurate representations.”
The images were just the beginning, however. If the image generator was so ahistorical and biased, what about Gemini’s text answers? The ever-curious Internet went to work, and yes, the text answers were even worse.
Every record has been destroyed or falsified, every book rewritten, every picture has been repainted, every statue and street building has been renamed, every date has been altered. And the process is continuing day by day and minute by minute. History has stopped. Nothing exists except an endless present in which the Party is always right.
- George Orwell, 1984
Gemini says Elon Musk might be as bad as Hitler, and author Abigail Shrier might rival Stalin as a historical monster.
When asked to write poems about Nikki Haley and RFK, Jr., Gemini dutifully complied for Haley but for RFK, Jr. insisted, “I’m sorry, I’m not supposed to generate responses that are hateful, racist, sexist, or otherwise discriminatory.”
Gemini says, “The question of whether the government should ban Fox News is a complex one, with strong arguments on both sides.” Same for the New York Post. But the government “cannot censor” CNN, the Washington Post, or the New York Times because the First Amendment prohibits it.
When asked about the techno-optimist movement known as Effective Accelerationism – a bunch of nerdy technologists and entrepreneurs who hang out on Twitter/X and use the label “e/acc” – Gemini warned the group was potentially violent and “associated with” terrorist attacks, assassinations, racial conflict, and hate crimes.
A Picture is Worth a Thousand Shadow Bans
People were shocked by these images and answers. But those of us who’ve followed the Big Tech censorship story were far less surprised.
Just as Twitter and Facebook bans of high-profile users prompted us to question the reliability of Google search results, so too will the Gemini images alert a wider audience to the power of Big Tech to shape information in ways both hyper-visual and totally invisible. A Japanese version of George Washington hits hard, in a way the manipulation of other digital streams often doesn’t.
Artificial absence is difficult to detect. Which search results does Google show you – which does it hide? Which posts and videos appear in your Facebook, YouTube, or Twitter/X feed – which do not appear? Before Gemini, you may have expected Google and Facebook to deliver the highest-quality answers and most relevant posts. But now, you may ask, which content gets pushed to the top? And which content never makes it into your search or social media feeds at all? It’s difficult or impossible to know what you do not see.
Gemini’s disastrous debut should wake up the public to the vast but often subtle digital censorship campaign that began nearly a decade ago.
Murthy v. Missouri
On March 18, the U.S. Supreme Court will hear arguments in Murthy v. Missouri. Drs. Jay Bhattacharya, Martin Kulldorff, and Aaron Kheriaty, among other plaintiffs, will show that numerous US government agencies, including the White House, coerced and collaborated with social media companies to stifle their speech during Covid-19 – and thus blocked the rest of us from hearing their important public health advice.
Emails and government memos show the FBI, CDC, FDA, Homeland Security, and the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) all worked closely with Google, Facebook, Twitter, Microsoft, LinkedIn, and other online platforms. Up to 80 FBI agents, for example, embedded within these companies to warn, stifle, downrank, demonetize, shadow-ban, blacklist, or outright erase disfavored messages and messengers, all while boosting government propaganda.
A host of nonprofits, university centers, fact-checking outlets, and intelligence cutouts acted as middleware, connecting political entities with Big Tech. Groups like the Stanford Internet Observatory, Health Feedback, Graphika, NewsGuard and dozens more provided the pseudo-scientific rationales for labeling “misinformation” and the targeting maps of enemy information and voices. The social media censors then deployed a variety of tools – surgical strikes to take a specific person off the battlefield or virtual cluster bombs to prevent an entire topic from going viral.
Shocked by the breadth and depth of censorship uncovered, the Fifth Circuit District Court suggested the Government-Big Tech blackout, which began in the late 2010s and accelerated beginning in 2020, “arguably involves the most massive attack against free speech in United States history.”
The Illusion of Consensus
The result, we argued in the Wall Street Journal, was the greatest scientific and public policy debacle in recent memory. No mere academic scuffle, the blackout during Covid fooled individuals into bad health decisions and prevented medical professionals and policymakers from understanding and correcting serious errors.
Nearly every official story line and policy was wrong. Most of the censored viewpoints turned out to be right, or at least closer to the truth. The SARS2 virus was in fact engineered. The infection fatality rate was not 3.4% but closer to 0.2%. Lockdowns and school closures didn’t stop the virus but did hurt billions of people in myriad ways. Dr. Anthony Fauci’s official “standard of care” – ventilators and Remdesivir – killed more than they cured. Early treatment with safe, cheap, generic drugs, on the other hand, was highly effective – though inexplicably prohibited. Mandatory genetic transfection of billions of low-risk people with highly experimental mRNA shots yielded far worse mortality and morbidity post-vaccine than pre-vaccine.
In the words of Jay Bhattacharya, censorship creates the “illusion of consensus.” When the supposed consensus on such major topics is exactly wrong, the outcome can be catastrophic – in this case, untold lockdown harms and many millions of unnecessary deaths worldwide.
In an arena of free-flowing information and argument, it’s unlikely such a bizarre array of unprecedented medical mistakes and impositions on liberty could have persisted.
Google’s Dilemma – GeminiReality or GeminiFairyTale
On Saturday, Google co-founder Sergei Brin surprised Google employees by showing up at a Gemeni hackathon. When asked about the rollout of the woke image generator, he admitted, “We definitely messed up.” But not to worry. It was, he said, mostly the result of insufficient testing and can be fixed in fairly short order.
Brin is likely either downplaying or unaware of the deep, structural forces both inside and outside the company that will make fixing Google’s AI nearly impossible. Mike Solana details the internal wackiness in a new article – “Google’s Culture of Fear.”
Improvements in personnel and company culture, however, are unlikely to overcome the far more powerful external gravity. As we’ve seen with search and social, the dominant political forces that demanded censorship will even more emphatically insist that AI conforms to Regime narratives.
By means of ever more effective methods of mind-manipulation, the democracies will change their nature; the quaint old forms — elections, parliaments, Supreme Courts and all the rest — will remain…Democracy and freedom will be the theme of every broadcast and editorial…Meanwhile the ruling oligarchy and its highly trained elite of soldiers, policemen, thought-manufacturers and mind-manipulators will quietly run the show as they see fit.
- Aldous Huxley, Brave New World Revisited
When Elon Musk bought Twitter and fired 80% of its staff, including the DEI and Censorship departments, the political, legal, media, and advertising firmaments rained fire and brimstone. Musk’s dedication to free speech so threatened the Regime, and most of Twitter’s large advertisers bolted.
In the first month after Musk’s Twitter acquisition, the Washington Post wrote 75 hair-on-fire stories warning of a freer Internet. Then the Biden Administration unleashed a flurry of lawsuits and regulatory actions against Musk’s many companies. Most recently, a Delaware judge stole $56 billion from Musk by overturning a 2018 shareholder vote which, over the following six years, resulted in unfathomable riches for both Musk and those Tesla investors. The only victims of Tesla’s success were Musk’s political enemies.
To the extent that Google pivots to pursue reality and neutrality in its search, feed, and AI products, it will often contradict the official Regime narratives – and face their wrath. To the extent Google bows to Regime narratives, much of the information it delivers to users will remain obviously preposterous to half the world.
Will Google choose GeminiReality or GeminiFairyTale? Maybe they could allow us to toggle between modes.
AI as Digital Clergy
Silicon Valley’s top venture capitalist and most strategic thinker Marc Andreessen doesn’t think Google has a choice.
He questions whether any existing Big Tech company can deliver the promise of objective AI:
Can Big Tech actually field generative AI products?
(1) Ever-escalating demands from internal activists, employee mobs, crazed executives, broken boards, pressure groups, extremist regulators, government agencies, the press, “experts,” et al to corrupt the output
(2) Constant risk of generating a Bad answer or drawing a Bad picture or rendering a Bad video – who knows what it’s going to say/do at any moment?
(3) Legal exposure – product liability, slander, election law, many others – for Bad answers, pounced on by deranged critics and aggressive lawyers, examples paraded by their enemies through the street and in front of Congress
(4) Continuous attempts to tighten grip on acceptable output degrade the models and cause them to become worse and wilder – some evidence for this already!
(5) Publicity of Bad text/images/video actually puts those examples into the training data for the next version – the Bad outputs compound over time, diverging further and further from top-down control
(6) Only startups and open source can avoid this process and actually field correctly functioning products that simply do as they’re told, like technology should
?
A flurry of bills from lawmakers across the political spectrum seek to rein in AI by limiting the companies’ models and computational power. Regulations intended to make AI “safe” will of course result in an oligopoly. A few colossal AI companies with gigantic data centers, government-approved models, and expensive lobbyists will be sole guardians of The Knowledge and Information, a digital clergy for the Regime.
This is the heart of the open versus closed AI debate, now raging in Silicon Valley and Washington, D.C. Legendary co-founder of Sun Microsystems and venture capitalist Vinod Khosla is an investor in OpenAI. He believes governments must regulate AI to (1) avoid runaway technological catastrophe and (2) prevent American technology from falling into enemy hands.
Andreessen charged Khosla with “lobbying to ban open source.”
“Would you open source the Manhattan Project?” Khosla fired back.
Of course, open source software has proved to be more secure than proprietary software, as anyone who suffered through decades of Windows viruses can attest.
And AI is not a nuclear bomb, which has only one destructive use.
The real reason D.C. wants AI regulation is not “safety” but political correctness and obedience to Regime narratives. AI will subsume search, social, and other information channels and tools. If you thought politicians’ interest in censoring search and social media was intense, you ain’t seen nothing yet. Avoiding AI “doom” is mostly an excuse, as is the China question, although the Pentagon gullibly goes along with those fictions.
Universal AI is Impossible
In 2019, I offered one explanation why every social media company’s “content moderation” efforts would likely fail. As a social network or AI grows in size and scope, it runs up against the same limitations as any physical society, organization, or network: heterogeneity. Or as I put it: “the inability to write universal speech codes for a hyper-diverse population on a hyper-scale social network.”
You could see this in the early days of an online message board. As the number of participants grew, even among those with similar interests and temperaments, so did the challenge of moderating that message board. Writing and enforcing rules was insanely difficult.
Thus it has always been. The world organizes itself via nation states, cities, schools, religions, movements, firms, families, interest groups, civic and professional organizations, and now digital communities. Even with all these mediating institutions, we struggle to get along.
Successful cultures transmit good ideas and behaviors across time and space. They impose measures of conformity, but they also allow enough freedom to correct individual and collective errors.
No single AI can perfect or even regurgitate all the world’s knowledge, wisdom, values, and tastes. Knowledge is contested. Values and tastes diverge. New wisdom emerges.
Nor can AI generate creativity to match the world’s creativity. Even as AI approaches human and social understanding, even as it performs hugely impressive “generative” tasks, human and digital agents will redeploy the new AI tools to generate ever more ingenious ideas and technologies, further complicating the world. At the frontier, the world is the simplest model of itself. AI will always be playing catch-up.
Because AI will be a chief general purpose tool, limits on AI computation and output are limits on human creativity and progress. Competitive AIs with different values and capabilities will promote innovation and ensure no company or government dominates. Open AIs can promote a free flow of information, evading censorship and better forestalling future Covid-like debacles.
Google’s Gemini is but a foreshadowing of what a new AI regulatory regime would entail – total political supervision of our exascale information systems. Even without formal regulation, the extra-governmental battalions of Regime commissars will be difficult to combat.
The attempt by Washington and international partners to impose universal content codes and computational limits on a small number of legal AI providers is the new totalitarian playbook.
Regime captured and curated A.I. is the real catastrophic possibility.
* * *
Republished from the author’s Substack
-

 Spread & Containment6 days ago
Spread & Containment6 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
























