How The Fed Juices Stocks
How The Fed Juices Stocks
Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
We came across the following bullet points from a Seeking Alpha article titled- The Fed is not Juicing the Stock Market.
It makes for a great headline,..

Authored by Michael Lebowitz via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
We came across the following bullet points from a Seeking Alpha article titled- The Fed is not Juicing the Stock Market.
-
It makes for a great headline, but the Fed is not the cause of this rally.
-
Every dollar the Fed has pumped into the economy is spoken for, and it is not in equities.
-
The truth is a lot more boring and scary than the conspiracy theory.
After explaining how the Fed is not culpable for rising stock prices, the author ends the article with the following challenge:
“So please, I invite anyone to explain to me, like I was a 5-year-old, what exactly is the mechanism that explains “the Fed is juicing the market,” when we know exactly where all the Fed’s money is, and we know that it isn’t in the market.”
We are always up for a challenge.
The following article describes four ways in which the Fed juices the stock market.
Draining the Asset Pool
The Fed conducts monetary policy by governing the Fed Funds Rate. To do this, they buy and sell Treasury securities via open market operations. When the Fed wants to lower rates, they buy Treasury debt. In doing so, they reduce the supply of investible debt, making remaining debt more expensive (lower yield). They most often buy or sell short term Treasury Bills to affect the short term Fed Funds rate. Open market operations also add or drain the banking system’s liquidity to help further hit their target.
More recently, with Fed Funds at zero percent, they have conducted QE or large-scale asset purchases. These operations help manipulate rates across the maturity curve and not just Fed Funds. QE, as with traditional open market operations, reduces supply, boosts prices, and lowers yields.
With knowledge of the Fed’s modus operandi, let’s go swimming.
Think of the asset markets as a big swimming pool. The kiddie pool is for risk-averse investors, and the deep end is home for the riskiest of investors. While the depth of the water varies extensively, the water level is the same throughout the pool.
Imagine the Fed comes to our pool with a giant bucket and removes gallons of water from the shallow end. What happens to the water level for the entire pool? It falls, and consequently, there is less water to swim in. The effect is more obvious in the shallow end as the depth was lower to begin with. Regardless of appearances, the water level in the deep end falls by the same amount.
Some of our risk-averse shallow end swimmers will now take a step or two towards the deep end. They may move from Treasury Bills to short term corporate bonds or mortgages. As investors take on more risk, they start crowding out other investors and pushing everyone toward the deep end.
Less water means less supply of investible assets. The basic laws of supply and demand clearly state that less supply and the same demand result in higher prices.
Leverage
One of the Fed’s recent accomplishments during this economic crisis is fostering easy financial conditions. Such an environment allows companies to borrow and reduce the possibility of default. Another benefit is it encourages investors to use more leverage as borrowing is easier to attain and cheaper.
The two graphs below show borrowing conditions have rarely been easier. Typically a recession has the exact opposite effect on lending conditions.
“U.S. financial conditions are the easiest they’ve been in more than a quarter century as stock markets scale new heights on hopes of an end to the Covid-19 pandemic, according to an index compiled by Goldman Sachs Group Inc.” – Bloomberg 12/14/2020
More leverage allows speculators and traders to amass larger holdings than would otherwise be possible. Much of this leverage comes from the repo markets. Repurchase transactions, or repo, is a loan collateralized with an asset. For example, an investor buys a security, pledges it as collateral, and uses the borrowed funds to buy more assets. The investor holds more assets with the same original investment.
The Fed has been actively providing funds to the repo markets resulting in more liquidity and lower borrowing rates since the fall of 2019. At its peak in March, the Fed supplied over $400 billion in repo funding to the market. This source of funds allowed for the increased demand for assets, and as you would expect, this includes stocks.
Fed Put
Investors are like Pavlov’s dogs. Increasingly they associate Fed actions with more stimulus, easier financial conditions, and higher asset prices. The Fed has responded by becoming more verbally accommodative via talking up policy options when markets hit rough patches.
Fed actions or even words of encouragement become buying opportunities. As such, prices do not decline as much as they might have, and volatility is muted as a result. Muted volatility encourages more investment and speculation as risks, measured using common financial math, such as standard deviation, are perceived to be lower.
More return with less perceived risk encourages more risk-taking, ergo more interest in stocks.
Fed Supports Passive Investing
Reduced volatility and eye-popping returns are increasingly leading investors to focus on momentum and passive strategies. Active investors, forecasting economic and earnings trends, and assessing valuations get left behind in momentum-driven markets. As these investors lose assets or switch to more passive strategies, passive strategies by default play a more prominent role in asset pricing. For more, please read our article: The Market’s Invisible Guardrails Are Missing.
Active investors tend to hold cash to take advantage of opportunities that may occur in the future. Further, at times like today, when valuations are historically extreme, active investors take profits and may not find suitable replacements, also increasing their cash balances.
Passive investors are typically fully invested. Cash, after all, is a performance drag in upward trending markets. They do not sell because of high valuations but switch from one index to another based on momentum.
Due to the steady gravitation from active to passive strategies over the last decade, system-wide cash balances are reduced, and there is more demand to buy assets. As shown below, courtesy SentimentTrader, equity mutual fund cash balances are 70-year lows.
Summary
Our summary is short and sweet, so even a five-year-old can understand.
The Fed juices stocks!
Government
Stock Market Today: Stocks turn lower as factory inflation spikes, retail sales miss target
Stocks will navigate the last major data releases prior to next week’s Fed rate meeting in Washington.

Check back for updates throughout the trading day
U.S. stocks edged lower Thursday following a trio of key economic releases that have added to the current inflation puzzle as investors shift focus to the Federal Reserve's March policy meeting next week in Washington.
Updated at 9:59 AM EDT
Red start
Stocks are now falling sharply following the PPI inflation data and retail sales miss, with the S&P 500 marked 18 points lower, or 0.36%, in the opening half hour of trading.
The Dow, meanwhile, was marked 92 points lower while the Nasdaq slipped 67 points.
Treasury yields are also on the move, with 2-year notes rising 5 basis points on the session to 4.679% and 10-year notes pegged 7 basis points higher at 4.271%.
The probability of a June rate cut has moved below 60% after the higher-than-expected CPI/PPI reports. A week ago this probability was 74% and a month ago it was 82%. pic.twitter.com/9W01oWU96G
— Charlie Bilello (@charliebilello) March 14, 2024
Updated at 9:44 AM EDT
Under Water
Under Armour (UAA) shares slumped firmly lower in early trading following the sportswear group's decision to bring back founder Kevin Plank as CEO, replacing the outgoing Stephanie Linnartz.
Plank, who founded Under Armour in 1996, left the group in May of 2021 just weeks before the group revealed that it was co-operating with investigations from both the Securities and Exchange Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice into the company's revenue recognition accounting.
Under Armour shares were marked 10.6% lower in early trading to change hands at $7.21 each.
Updated at 9:22 AM EDT
Steely resolve
U.S. Steel (X) shares extended their two-day decline Thursday, falling 5.75% in pre-market trading following multiple reports that suggest President Joe Biden will push to prevent Japan's Nippon Steel from buying the Pittsburgh-based group.
Both Reuters and the Associated Press have said Biden will express his views to Prime Minister Kishida Yuko ahead of a planned State Visit next month at the White House.
Related: US Steel soars on $15 billion Nippon Steel takeover; United Steelworkers slams deal
Updated at 8:52 AM EDT
Clear as mud
Retail sales rebounded last month, but the overall tally of $700.7 billion missed Street forecasts and suggests the recent uptick in inflation could be holding back discretionary spending.
A separate reading of factory inflation, meanwhile, showed prices spiking by 1.6%, on the year, and 0.6% on the month, amid a jump in goods prices.
U.S. stocks held earlier gains following the data release, with futures tied to the S&P 500 indicating an opening bell gain of 10 points, while the Dow was called 140 points higher. The Nasdaq, meanwhile, is looking at a more modest 40 point gain.
Benchmark 10-year Treasury note yields edged 3 basis points lower to 4.213% while two-year notes were little-changed at 4.626%.
The #PPI troughed 8 months ago, yet the economic consensus and even the #Fed believes #inflation has been conquered. Forget the forecasts for multiple rate cuts. pic.twitter.com/ZNIiKLWdFA
— Richard Bernstein Advisors (@RBAdvisors) March 14, 2024
Stock Market Today
Stocks finished lower last night, with the S&P 500 ending modestly in the red and the Nasdaq falling around 0.5%. The declines came amid an uptick in Treasury yields tied to concern that inflation pressures have failed to ease over the opening months of the year.
A better-than-expected auction of $22 billion in 30-year bonds, drawing the strongest overall demand since last June, steadied the overall market, but stocks still slipped into the close with an eye towards today's dataset.
The Commerce Department will publish its February reading of factory-gate inflation at 8:30 am Eastern Time. Analysts are expecting a slowdown in the key core reading, which feeds into the Fed's favored PCE price index.
Retail sales figures for the month are also set for an 8:30 am release as investors search for clues on consumer strength, tied to a resilient job market. Those factors could give the Fed more justification to wait until the summer months to begin the first of its three projected rate cuts.
"The case for a gradual but sustained slowdown in growth in consumers’ spending from 2023’s robust pace is persuasive," said Ian Shepherdson of Pantheon Macroeconomics.
"Most households have run down the excess savings accumulated during the pandemic, while the cost of credit has jumped and last year’s plunge in home sales has depressed demand housing-related retail items like furniture and appliances," he added.
Benchmark 10-year Treasury yields are holding steady at 4.196% heading into the start of the New York trading session, while 2-year notes were pegged at 4.628%.
With Fed officials in a quiet period, requiring no public comments ahead of next week's meeting in Washington, the U.S. dollar index is trading in a narrow range against its global peers and was last marked 0.06% higher at 102.852.
On Wall Street, futures tied to the S&P 500 are indicating an opening bell gain of around 19 points, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average indicating a 140-point advance.
The tech-focused Nasdaq, which is up 7.77% for the year, is priced for a gain of around 95 points, with Tesla (TSLA) once again sliding into the red after ending the Wednesday session at a 10-month low.
In Europe, the regionwide Stoxx 600 was marked 0.35% higher in early Frankfurt trading, while Britain's FTSE 100 slipped 0.09% in London.
Overnight in Asia, the Nikkei 225 gained 0.29% as investors looked to a key series of wage negotiation figures from key unions that are likely to see the biggest year-on-year pay increases in three decades.
The broader MSCI ex-Japan benchmark, meanwhile, rose 0.18% into the close of trading.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
bonds pandemic dow jones sp 500 nasdaq ftse stocks rate cut fed federal reserve home sales white house japan europeUncategorized
Walmart and Target make key self-checkout changes to fight theft
Both chains are making changes customers may not like, but self-checkout isn’t going anywhere, according to one industry expert.

In parts of the world, public bathrooms come with a charge, but people pay on the honor system. The money charged allows for better upkeep of the facilities and most people don't mind dropping a small bill or some coins into a lockbox and many of the people who don't are likely dealing with larger problems.
The honor system, however, requires honor. It's based on the idea that most people are trustworthy and that they will pay their fair share.
Related: Beloved mall retailer files Chapter 7 bankruptcy, will liquidate
In the case of a bathroom, people cheating the system are only stealing a low-value service. In the case of self-checkout, a variation on the honor system, people looking to steal by "forgetting" to scan an item can be a very expensive problem.
That has led retailers including Target, Walmart, and Dollar General to make changes. Target has limited the amount of items you can scan at self-checkout at some stores while Dollar General has literally eliminated it in some locations.
Walmart, like Target, has experimented with item limits and limiting the hours of operation for self-checkout. Now, in some stores, the chain has decided to designate some of its self-checkout stations for Walmart+ members and delivery drivers using the Spark app.
Advantage Solutions General Manager Andy Keenan answered some questions about Walmart, self-checkout, and theft from TheStreet via email.
Image source: John Smith/VIEWpress.
What Walmart's self-checkout changes mean
TheStreet: What are the benefits of reserving self-checkout registers for Spark drivers and Walmart+ customers?
Keenan: The benefits include exclusivity and perks of membership, speed, and convenience when shopping.
TheStreet: If this rolls out more broadly, what do you anticipate being the impact on non-Walmart+ customers?
Keenan: There is the potential for non-Walmart+ customers to become agitated, they are losing convenience because they are not enrolled. Customers who are looking for convenience will have fewer options for speed to check out.
TheStreet: Do lane restrictions like limiting lanes to 10 items or fewer help reduce time spent waiting in lines?
Keenan: Yes, but retailers must have a diverse amount of check lane options including 10 items or fewer to ensure that the speed of checkout actually transpires.
TheStreet: Do you believe self-checkout is leading to partial shrink? If so, do you think that this move to shut off self-checkout lanes will help prevent theft in the future?
Keenan: Yes, self-checkout is leading to partial shrink. We believe this tends to be more due to errors in scanning and intentional theft.
There are already front-end transformation tests going on in stores, reducing the number of self-checkouts and shifting back to cashier checkouts in order to measure the reduction in shrink. Early indicators show that a move back to cashier checkouts combined with other shrink initiatives will help prevent theft.
Self-checkout is not going away
While changes are ongoing, Keenan believes self-checkout is here to stay.
“Self-checkout is not, as one recent article called it, a failed experiment. It’s actually part of the next evolution of the retail customer experience, and evolutions take time,” Keenan said in a web post about the findings of the 2024 Advantage Shopper Outlook survey.
He makes it clear that rising labor costs and struggles to find workers make some for of self-checkout inevitable.
“Since the pandemic, there’s been a revolution on hourly labor,” Keenan said. “Labor in certain markets that would cost you $16 an hour now costs you $19 or $20 an hour, and it’s a gig economy. The people who once stood at a checkout stand in the front of a store are now driving for Instacart or DoorDash because the hours are more flexible. They want to make their own schedule, and it’s varied work. Today, most retailers can’t offer that.”
Basically, while there are kinks to work out, self-checkout simply makes sense for retailers.
“The notion that we’re going to pivot away from technology that helps offset labor needs and will ultimately continue to improve customer experience because of some challenges is far-fetched. We need to continue to embrace the technology and realize that it may always be imperfect, but it will always be evolving. The noise that, ‘Oh, self-checkout might not be working,’ that’s just a moment in time,” he added.
bankruptcy pandemicUncategorized
Hitting Home: Housing Affordability in the U.S.
The Issue:
Housing is becoming unaffordable to a widening swathe of the American population. This deteriorating affordability directly impacts American…
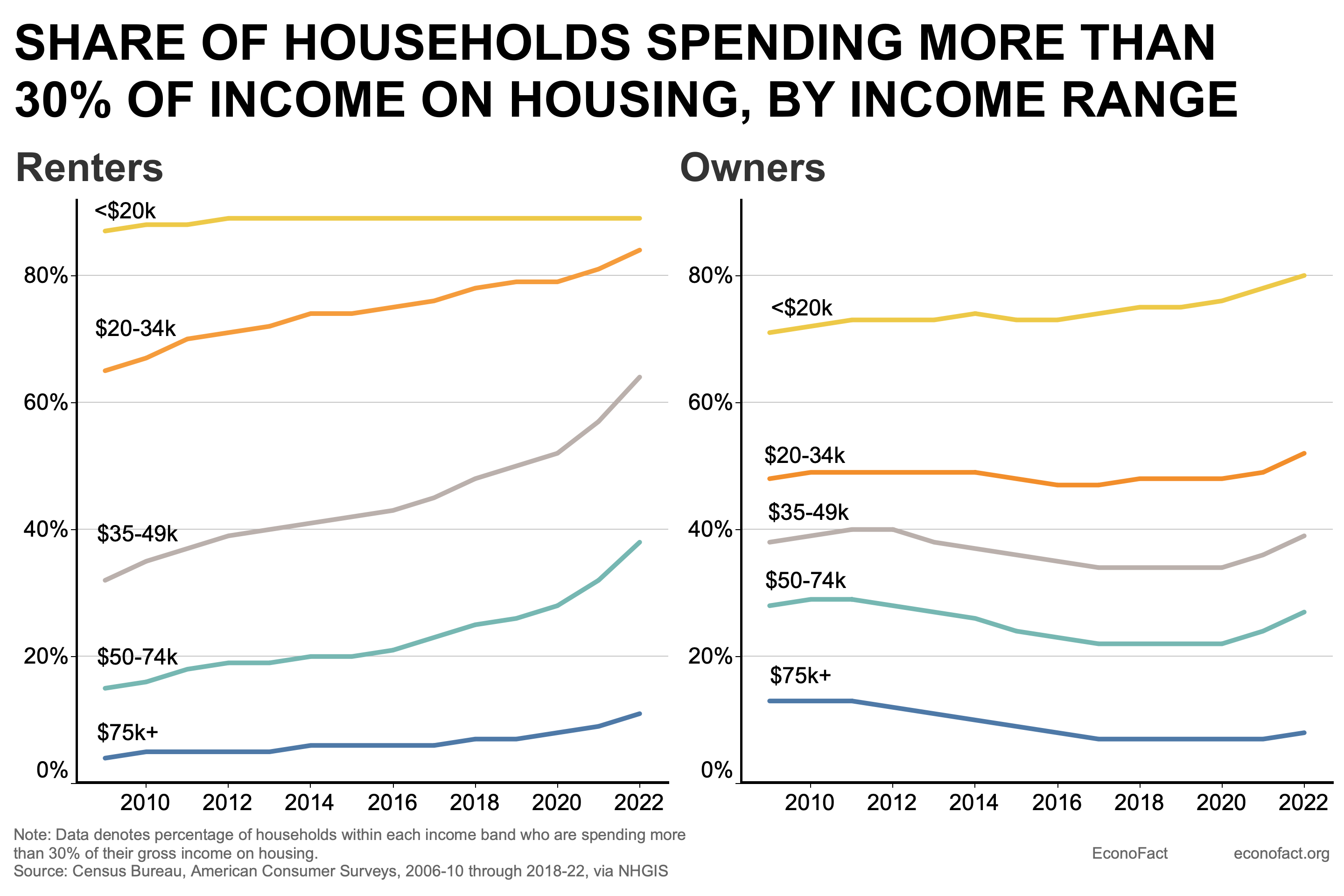
The Issue:
Housing is becoming unaffordable to a widening swathe of the American population. This deteriorating affordability directly impacts American lives, including where people choose to live and work. It has also been cited as a major contributor to key social problems like rising homelessness and worsening child wellbeing.
The Facts:
- Median house prices are now 6 times the median income, up from a range of between 4 and 5 two decades ago. In cities along the coasts, the numbers are higher, exceeding 10 in San Francisco.
- The ratio of median rents to median income has also crept from 25 percent to 30 percent in two decades.
- Households — renters in particular — are increasingly cost-burdened, having to spend more than 30% of their income on rent, mortgage and other housing needs. Among homeowners, about 40 percent of those in the $35-49 income range are cost-burdened. The share of cost-burdened renters in that income range has risen sharply from under 40 percent of households in 2010 to over 60 percent today (see chart).
- Historically, rural and interior areas of the country have been more affordable. But, even prior to the pandemic, migration toward these locations has helped drive faster house price appreciation than in more expensive regions.
- Demographic developments have contributed to the demand-supply imbalance. Supply is crimped by more older Americans opting to age in place. On the demand side, the biggest driver is new household formation. Americans formed about a million new households a year between 2015-2017, but the pace has almost doubled according to the most recent data, largely reflecting a pickup in household formation rates among millennials.
- A long-standing lack of homebuilding, which partly reflects tight regulatory restrictions in many parts of the country, has also contributed to rising home prices.
- More recently, higher interest rates since 2022 have exacerbated these secular trends to make housing even more unaffordable. The mortgage rate on a 30-year home loan soared from 3 ½ percent in early 2022 to nearly 8% in October 2023 as the Fed raised policy interest rates; the mortgage rate had only eased to about 7% in March 2024 as the tightening cycle had peaked. The problem is compounded by mortgage lock-in: higher interest rates have left many homeowners — many of whom bought homes or refinanced at the lows of 2020-21 — with cheaper-than-market mortgages, reluctant to sell their house and reset their mortgage at current, higher rates.
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International6 days ago
International6 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges


























