Spread & Containment
How many bots are on Twitter? The question is difficult to answer and misses the point
Elon Musk’s focus on the number of bots on Twitter, whether genuine or a distraction, does little to address the problems of misinformation and spam….

Twitter reports that fewer than 5% of accounts are fakes or spammers, commonly referred to as “bots.” Since his offer to buy Twitter was accepted, Elon Musk has repeatedly questioned these estimates, even dismissing Chief Executive Officer Parag Agrawal’s public response.
Later, Musk put the deal on hold and demanded more proof.
So why are people arguing about the percentage of bot accounts on Twitter?
As the creators of Botometer, a widely used bot detection tool, our group at the Indiana University Observatory on Social Media has been studying inauthentic accounts and manipulation on social media for over a decade. We brought the concept of the “social bot” to the foreground and first estimated their prevalence on Twitter in 2017.
Based on our knowledge and experience, we believe that estimating the percentage of bots on Twitter has become a very difficult task, and debating the accuracy of the estimate might be missing the point. Here is why.
What, exactly, is a bot?
To measure the prevalence of problematic accounts on Twitter, a clear definition of the targets is necessary. Common terms such as “fake accounts,” “spam accounts” and “bots” are used interchangeably, but they have different meanings. Fake or false accounts are those that impersonate people. Accounts that mass-produce unsolicited promotional content are defined as spammers. Bots, on the other hand, are accounts controlled in part by software; they may post content or carry out simple interactions, like retweeting, automatically.
These types of accounts often overlap. For instance, you can create a bot that impersonates a human to post spam automatically. Such an account is simultaneously a bot, a spammer and a fake. But not every fake account is a bot or a spammer, and vice versa. Coming up with an estimate without a clear definition only yields misleading results.
Defining and distinguishing account types can also inform proper interventions. Fake and spam accounts degrade the online environment and violate platform policy. Malicious bots are used to spread misinformation, inflate popularity, exacerbate conflict through negative and inflammatory content, manipulate opinions, influence elections, conduct financial fraud and disrupt communication. However, some bots can be harmless or even useful, for example by helping disseminate news, delivering disaster alerts and conducting research.
Simply banning all bots is not in the best interest of social media users.
For simplicity, researchers use the term “inauthentic accounts” to refer to the collection of fake accounts, spammers and malicious bots. This is also the definition Twitter appears to be using. However, it is unclear what Musk has in mind.
Hard to count
Even when a consensus is reached on a definition, there are still technical challenges to estimating prevalence.

External researchers do not have access to the same data as Twitter, such as IP addresses and phone numbers. This hinders the public’s ability to identify inauthentic accounts. But even Twitter acknowledges that the actual number of inauthentic accounts could be higher than it has estimated, because detection is challenging.
Inauthentic accounts evolve and develop new tactics to evade detection. For example, some fake accounts use AI-generated faces as their profiles. These faces can be indistinguishable from real ones, even to humans. Identifying such accounts is hard and requires new technologies.
Another difficulty is posed by coordinated accounts that appear to be normal individually but act so similarly to each other that they are almost certainly controlled by a single entity. Yet they are like needles in the haystack of hundreds of millions of daily tweets.
Finally, inauthentic accounts can evade detection by techniques like swapping handles or automatically posting and deleting large volumes of content.
The distinction between inauthentic and genuine accounts gets more and more blurry. Accounts can be hacked, bought or rented, and some users “donate” their credentials to organizations who post on their behalf. As a result, so-called “cyborg” accounts are controlled by both algorithms and humans. Similarly, spammers sometimes post legitimate content to obscure their activity.
We have observed a broad spectrum of behaviors mixing the characteristics of bots and people. Estimating the prevalence of inauthentic accounts requires applying a simplistic binary classification: authentic or inauthentic account. No matter where the line is drawn, mistakes are inevitable.
Missing the big picture
The focus of the recent debate on estimating the number of Twitter bots oversimplifies the issue and misses the point of quantifying the harm of online abuse and manipulation by inauthentic accounts.

Through BotAmp, a new tool from the Botometer family that anyone with a Twitter account can use, we have found that the presence of automated activity is not evenly distributed. For instance, the discussion about cryptocurrencies tends to show more bot activity than the discussion about cats. Therefore, whether the overall prevalence is 5% or 20% makes little difference to individual users; their experiences with these accounts depend on whom they follow and the topics they care about.
Recent evidence suggests that inauthentic accounts might not be the only culprits responsible for the spread of misinformation, hate speech, polarization and radicalization. These issues typically involve many human users. For instance, our analysis shows that misinformation about COVID-19 was disseminated overtly on both Twitter and Facebook by verified, high-profile accounts.
Even if it were possible to precisely estimate the prevalence of inauthentic accounts, this would do little to solve these problems. A meaningful first step would be to acknowledge the complex nature of these issues. This will help social media platforms and policymakers develop meaningful responses.
Filippo Menczer receives funding from Knight Foundation, Craig Newmark Philanthropies, Open Technology Fund, and DoD. He owns a Tesla.
Kai-Cheng Yang does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
spread covid-19Government
Young People Aren’t Nearly Angry Enough About Government Debt
Young People Aren’t Nearly Angry Enough About Government Debt
Authored by The American Institute for Economic Research,
Young people sometimes…

Authored by The American Institute for Economic Research,
Young people sometimes seem to wake up in the morning in search of something to be outraged about. We are among the wealthiest and most educated humans in history. But we’re increasingly convinced that we’re worse off than our parents were, that the planet is in crisis, and that it’s probably not worth having kids.
I’ll generalize here about my own cohort (people born after 1981 but before 2010), commonly referred to as Millennials and Gen Z, as that shorthand corresponds to survey and demographic data. Millennials and Gen Z have valid economic complaints, and the conditions of our young adulthood perceptibly weakened traditional bridges to economic independence. We graduated with record amounts of student debt after President Obama nationalized that lending. Housing prices doubled during our household formation years due to zoning impediments and chronic underbuilding. Young Americans say economic issues are important to us, and candidates are courting our votes by promising student debt relief and cheaper housing (which they will never be able to deliver).
Young people, in our idealism and our rational ignorance of the actual appropriations process, typically support more government intervention, more spending programs, and more of every other burden that has landed us in such untenable economic circumstances to begin with. Perhaps not coincidentally, young people who’ve spent the most years in the increasingly partisan bubble of higher education are also the most likely to favor expanded government programs as a “solution” to those complaints.
It’s Your Debt, Boomer
What most young people don’t yet understand is that we are sacrificing our young adulthood and our financial security to pay for debts run up by Baby Boomers. Part of every Millennial and Gen-Z paycheck is payable to people the same age as the members of Congress currently milking this system and miring us further in debt.
Our government spends more than it can extract from taxpayers. Social Security, which represents 20 percent of government spending, has run an annual deficit for 15 years. Last year Social Security alone overspent by $22.1 billion. To keep sending out checks to retirees, Social Security goes begging to the Treasury Department, and the Treasury borrows from the public by issuing bonds. Bonds allow investors (who are often also taxpayers) to pay for some retirees’ benefits now, and be paid back later. But investors only volunteer to lend Social Security the money it needs to cover its bills because the (younger) taxpayers will eventually repay the debt — with interest.
In other words, both Social Security and Medicare, along with various smaller federal entitlement programs, together comprising almost half of the federal budget, have been operating for a decade on the principle of “give us the money now, and stick the next generation with the check.” We saddle future generations with debt for present-day consumption.
The second largest item in the budget after Social Security is interest on the national debt — largely on Social Security and other entitlements that have already been spent. These mandatory benefits now consume three quarters of the federal budget: even Congress is not answerable for these programs. We never had the chance for our votes to impact that spending (not that older generations were much better represented) and it’s unclear if we ever will.
Young Americans probably don’t think much about the budget deficit (each year’s overspending) or the national debt (many years’ deficits put together, plus interest) much at all. And why should we? For our entire political memory, the federal government, as well as most of our state governments, have been steadily piling “public” debt upon our individual and collective heads. That’s just how it is. We are the frogs trying to make our way in the watery world as the temperature ticks imperceptibly higher. We have been swimming in debt forever, unaware that we’re being economically boiled alive.
Millennials have somewhat modest non-mortgage debt of around $27,000 (some self-reports say twice that much), including car notes, student loans, and credit cards. But we each owe more than $100,000 as a share of the national debt. And we don’t even know it.
When Millennials finally do have babies (and we are!) that infant born in 2024 will enter the world with a newly minted Social Security Number and $78,089 credit card bill for Granddad’s heart surgery and the interest on a benefit check that was mailed when her parents were in middle school.
Headlines and comments sections love to sneer at “snowflakes” who’ve just hit the “real world,” and can’t figure out how to make ends meet, but the kids are onto something. A full 15 percent of our earnings are confiscated to pay into retirement and healthcare programs that will be insolvent by the time we’re old enough to enjoy them. The Federal Reserve and government debt are eating the economy. The same interest rates that are pushing mortgages out of reach are driving up the cost of interest to maintain the debt going forward. As we learn to save and invest, our dollars are slowly devalued. We’re right to feel trapped.
Sure, if we’re alive and own a smartphone, we’re among the one percent of the wealthiest humans who’ve ever lived. Older generations could argue (persuasively!) that we have no idea what “poverty” is anymore. But with the state of government spending and debt…we are likely to find out.
Despite being richer than Rockefeller, Millennials are right to say that the previous ways of building income security have been pushed out of reach. Our earning years are subsidizing not our own economic coming-of-age, but bank bailouts, wars abroad, and retirement and medical benefits for people who navigated a less-challenging wealth-building landscape.
Redistribution goes both ways. Boomers are expected to pass on tens of trillions in unprecedented wealth to their children (if it isn’t eaten up by medical costs, despite heavy federal subsidies) and older generations’ financial support of the younger has had palpable lifting effects. Half of college costs are paid by families, and the trope of young people moving back home is only possible if mom and dad have the spare room and groceries to make that feasible.
Government “help” during COVID-19 resulted in the worst inflation in 40 years, as the federal government spent $42,000 per citizen on “stimulus” efforts, right around a Millennial’s average salary at that time. An absurd amount of fraud was perpetrated in the stimulus to save an economy from the lockdown that nearly ruined it. Trillions in earmarked goodies were rubber stamped, carelessly added to young people’s growing bill. Government lenders deliberately removed fraud controls, fearing they couldn’t hand out $800 billion in young people’s future wages away fast enough. Important lessons were taught by those programs. The importance of self-sufficiency and the dignity of hard work weren’t top of the list.
Boomer Benefits are Stagnating Hiring, Wages, and Investment for Young People
Even if our workplace engagement suffered under government distortions, Millennials continue to work more hours than other generations and invest in side hustles and self employment at higher rates. Working hard and winning higher wages almost doesn’t matter, though, when our purchasing power is eaten from the other side. Buying power has dropped 20 percent in just five years. Life is $11,400/year more expensive than it was two years ago and deficit spending is the reason why.
We’re having trouble getting hired for what we’re worth, because it costs employers 30 percent more than just our wages to employ us. The federal tax code both requires and incentivizes our employers to transfer a bunch of what we earned directly to insurance companies and those same Boomer-busted federal benefits, via tax-deductible benefits and payroll taxes. And the regulatory compliance costs of ravenous bureaucratic state. The price paid by each employer to keep each employee continues to rise — but Congress says your boss has to give most of the increase to someone other than you.
Federal spending programs that many people consider good government, including Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, and health insurance for children (CHIP) aren’t a small amount of the federal budget. Government spends on these programs because people support and demand them, and because cutting those benefits would be a re-election death sentence. That’s why they call cutting Social Security the “third rail of politics.” If you touch those benefits, you die. Congress is held hostage by Baby Boomers who are running up the bill with no sign of slowing down.
Young people generally support Social Security and the public health insurance programs, even though a 2021 poll by Nationwide Financial found 47 percent of Millennials agree with the statement “I will not get a dime of the Social Security benefits I have earned.”
In the same survey, Millennials were the most likely of any generation to believe that Social Security benefits should be enough to live on as a sole income, and guessed the retirement age was 52 (it’s 67 for anyone born after 1959 — and that’s likely to rise). Young people are the most likely to see government guarantees as a valid way to live — even though we seem to understand that those promises aren’t guarantees at all.
Healthcare costs tied to an aging population and wonderful-but-expensive growth in medical technologies and medications will balloon over the next few years, and so will the deficits in Boomer benefit programs. Newly developed obesity drugs alone are expected to add $13.6 billion to Medicare spending. By 2030, every single Baby Boomer will be 65, eligible for publicly funded healthcare.
The first Millennial will be eligible to claim Medicare (assuming the program exists and the qualifying age is still 65, both of which are improbable) in 2046. As it happens, that’s also the year that the Boomer benefits programs (which will then be bloated with Gen Xers) and the interest payments we’re incurring to provide those benefits now, are projected to consume 100 percent of federal tax revenue.
Government spending is being transferred to bureaucrats and then to the beneficiaries of government spending who are, in some sense, your diabetic grandma who needs a Medicare-paid dialysis treatment, but in a much more immediate sense, are the insurance companies, pharma giants, and hospital corporations who wrote the healthcare legislation. Some percentage of every college graduate’s paycheck buys bullets that get fired at nothing and inflating the private investment portfolios of government contractors, with dubious, wasteful outcomes from the prison-industrial complex to the perpetual war machine.
No bank or nation in the world can lend the kind of money the American government needs to borrow to fulfill its obligations to citizens. Someone will have to bite the bullet. Even some of the co-authors of the current disaster are wrestling with the truth.
Forget avocado toast and streaming subscriptions. We’re already sensing it, but we haven’t yet seen it. Young people are not well-informed, and often actively misled, about what’s rotten in this economic system. But we are seeing the consequences on store shelves and mortgage contracts and we can sense disaster is coming. We’re about to get stuck with the bill.
Spread & Containment
There Goes The Fed’s Inflation Target: Goldman Sees Terminal Rate 100bps Higher At 3.5%
There Goes The Fed’s Inflation Target: Goldman Sees Terminal Rate 100bps Higher At 3.5%
Two years ago, we first said that it’s only a matter…
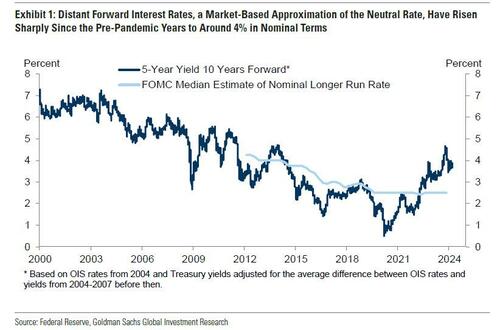
Two years ago, we first said that it's only a matter of time before the Fed admits it is unable to rsolve the so-called "last mile" of inflation and that as a result, the old inflation target of 2% is no longer viable.
At some point Fed will concede it has no control over supply. That's when we will start getting leaks of raising the inflation target
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) June 21, 2022
Then one year ago, we correctly said that while everyone was paying attention elsewhere, the inflation target had already been hiked to 2.8%... on the way to even more increases.
The new inflation target has been set to 2.8%. The rest is just narrative fill for the next 2 years. https://t.co/X1xYkecyPy
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) February 21, 2023
And while the Fed still pretends it can one day lower inflation to 2% even as it prepares to cut rates as soon as June, moments ago Goldman published a note from its economics team which had to balls to finally call a spade a spade, and concluded that - as party of the Fed's next big debate, i.e., rethinking the Neutral rate - both the neutral and terminal rate, a polite euphemism for the inflation target, are much higher than conventional wisdom believes, and that as a result Goldman is "penciling in a terminal rate of 3.25-3.5% this cycle, 100bp above the peak reached last cycle."
There is more in the full Goldman note, but below we excerpt the key fragments:
We argued last cycle that the long-run neutral rate was not as low as widely thought, perhaps closer to 3-3.5% in nominal terms than to 2-2.5%. We have also argued this cycle that the short-run neutral rate could be higher still because the fiscal deficit is much larger than usual—in fact, estimates of the elasticity of the neutral rate to the deficit suggest that the wider deficit might boost the short-term neutral rate by 1-1.5%. Fed economists have also offered another reason why the short-term neutral rate might be elevated, namely that broad financial conditions have not tightened commensurately with the rise in the funds rate, limiting transmission to the economy.
Over the coming year, Fed officials are likely to debate whether the neutral rate is still as low as they assumed last cycle and as the dot plot implies....
...Translation: raising the neutral rate estimate is also the first step to admitting that the traditional 2% inflation target is higher than previously expected. And once the Fed officially crosses that particular Rubicon, all bets are off.
... Their thinking is likely to be influenced by distant forward market rates, which have risen 1-2pp since the pre-pandemic years to about 4%; by model-based estimates of neutral, whose earlier real-time values have been revised up by roughly 0.5pp on average to about 3.5% nominal and whose latest values are little changed; and by their perception of how well the economy is performing at the current level of the funds rate.
The bank's conclusion:
We expect Fed officials to raise their estimates of neutral over time both by raising their long-run neutral rate dots somewhat and by concluding that short-run neutral is currently higher than long-run neutral. While we are fairly confident that Fed officials will not be comfortable leaving the funds rate above 5% indefinitely once inflation approaches 2% and that they will not go all the way back to 2.5% purely in the name of normalization, we are quite uncertain about where in between they will ultimately land.
Because the economy is not sensitive enough to small changes in the funds rate to make it glaringly obvious when neutral has been reached, the terminal or equilibrium rate where the FOMC decides to leave the funds rate is partly a matter of the true neutral rate and partly a matter of the perceived neutral rate. For now, we are penciling in a terminal rate of 3.25-3.5% this cycle, 100bps above the peak reached last cycle. This reflects both our view that neutral is higher than Fed officials think and our expectation that their thinking will evolve.
Not that this should come as a surprise: as a reminder, with the US now $35.5 trillion in debt and rising by $1 trillion every 100 days, we are fast approaching the Minsky Moment, which means the US has just a handful of options left: losing the reserve currency status, QEing the deficit and every new dollar in debt, or - the only viable alternative - inflating it all away. The only question we had before is when do "serious" economists make the same admission.
Meanwhile, nothing changes: total US debt jumps $57BN on March 15, to a record $34.543 trillion.
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) March 19, 2024
Three ways this ends: inflate it away, QE it all, or reserve status collapse
They now have.
And while we have discussed the staggering consequences of raising the inflation target by just 1% from 2% to 3% on everything from markets, to economic growth (instead of doubling every 35 years at 2% inflation target, prices would double every 23 years at 3%), and social cohesion, we will soon rerun the analysis again as the implications are profound. For now all you need to know is that with the US about to implicitly hit the overdrive of dollar devaluation, anything that is non-fiat will be much more preferable over fiat alternatives.
Much more in the full Goldman note available to pro subs in the usual place.
Spread & Containment
Household Net Interest Income Falls As Rates Spike
A Bloomberg article from this morning offered an excellent array of charts detailing the shifts in interest payment flows amid rising rates. The historical…
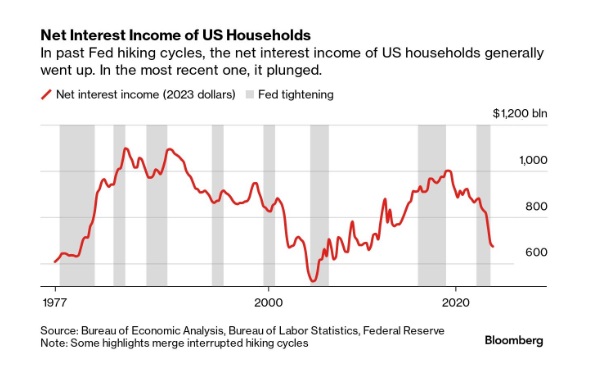
A Bloomberg article from this morning offered an excellent array of charts detailing the shifts in interest payment flows amid rising rates. The historical anomaly was both surprising and contradicted our priors.
10 Key Points:
- Historical Anomaly: This is the first time in the last fifty years that a Federal Reserve rate hike cycle has led to a significant drop in household net interest income.
- Interest Expense Increase: Since the Fed began raising rates in March 2022, Americans’ annual interest expenses on debts like mortgages and credit cards have surged by nearly $420 billion.
- Interest Income Lag: The increase in interest income during the same period was only about $280 billion, resulting in a net decline in household interest income, a departure from past trends.
- Consumer Debt Influence: The recent rate hikes impacted household finances more because of a higher proportion of consumer credit, which adjusts more quickly to rate changes, increasing interest costs.
- Banks and Savers: Banks have been slow to pass on higher interest rates to depositors, and the prolonged period of low rates before 2022 may have discouraged savers from actively seeking better returns.
- Shift in Wealth: There’s been a shift from interest-bearing assets to stocks, with dividends surpassing interest payments as a source of unearned income during the pandemic.
- Distributional Discrepancy: Higher interest rates benefit wealthier individuals who own interest-earning assets, whereas lower-income earners face the brunt of increased debt servicing costs, exacerbating economic inequality.
- Job Market Impact: Typically, Fed rate hikes affect households through the job market, as businesses cut costs, potentially leading to layoffs or wage suppression, though this hasn’t occurred yet in the current cycle.
- Economic Impact: The distribution of interest income and debt servicing means that rate increases transfer money from those more likely to spend (and thus stimulate the economy) to those less likely to increase consumption, potentially dampening economic activity.
- No Immediate Relief: Expectations for the Fed to reduce rates have diminished, indicating that high-interest expenses for households may persist.



-

 Spread & Containment7 days ago
Spread & Containment7 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex























