Uncategorized
How do credit scores work? 2 finance professors explain how lenders choose who gets loans and at what interest rate
Trends show credit scores are rising, with nearly half of all US consumers boasting ‘very good’ or ‘excellent’ numbers.

With the cost of borrowing money to buy a home or a car inching ever higher, understanding who gets access to credit, and at what interest rate, is more important for borrowers’ financial health than ever. Lenders base those decisions on the borrowers’ credit scores.
To learn more about credit scores, The Conversation consulted with two finance scholars. Brian Blank is an assistant professor of finance at Mississippi State University with expertise related to how firms allocate capital, as well as the role of credit in mortgage lending. His colleague at Mississippi State, Tom Miller Jr., is a finance professor who has written a book on consumer lending, in addition to providing his expertise to policymakers.
Credit scoring assesses the likelihood of default
Lenders stay in business when borrowers pay back loans.
Some borrowers consistently make prompt payments, while others are slow to repay, and still others default – meaning they do not pay back the money they borrowed. Lenders have a strong business incentive to separate loans that will be paid back from loans that might be paid back.
So how do lenders distinguish between good borrowers and risky ones? They rely on various proprietary credit scoring systems that use past borrower repayment history and other factors to predict the likelihood of future repayment. The three organizations that monitor credit scores in the U.S. are Transunion, Experian and Equifax.
Although 26 million of 258 million credit-eligible Americans lack a credit score, anyone who has ever opened a credit card or other credit account, like a loan, has one. Most people don’t have a credit score before turning 18, which is usually the age applicants can begin opening credit cards in their own name. However, some people still have no credit later in life if they don’t have any accounts for reporting agencies to assess.
Credit scores simply summarize how well individuals repay debt over time. Based on that repayment behavior, the credit scoring system assigns people a single number ranging from 300 to 850. A credit score ranging from 670 to 739 is generally considered to be good, a score in the range of 580 to 669 would be judged fair, and a score less than 579 is classified poor, or subprime.
The two most important factors in credit scores are how promptly past debts have been paid and the amount the individual owes on current debt. The score also takes into account the mix and length of credit, in addition to how new it is.
Credit scores can help lenders decide what interest rate to offer consumers. And they can affect banks’ decisions concerning access to mortgages, credit cards and auto loans.

Recent improvements in consumer credit scores
Average credit scores in the United States have risen from 688 in 2005 to 716 as of August of 2021. They stayed steady at that level through 2022.
While credit card debt is at a record high, the average consumer was using just over a fourth of the revolving credit to which they had access as of September 2022.
As of 2021, nearly half of U.S. consumers had scores considered very good – meaning in the range of 740 to 799 – or excellent (800-850). Six in 10 Americans have a score above 700, consistent with the general trend of record-setting credit scores of the past few years. These trends might, in part, reflect new programs that are designed to note when individuals pay bills like rent and utilities on time, which can help boost scores.
During the first quarter of 2023, people taking out new mortgages had an average credit score of 765, which is one point lower than a year ago but still higher than the pre-pandemic average of 760.
Credit score evolution from the 1980s to the 2020s
Developed in the late 1950s, the first credit scores – FICO scores – were created to build a computerized, objective measure to help lenders make lending decisions. Before then, bankers relied on commercial credit reporting, the same system merchants used to evaluate the creditworthiness of potential customers based on relationships and subjective evaluation.
The FICO credit scoring system was enhanced over the 1960s and ‘70s, and lenders grew to trust computerized credit evaluation systems. Credit scores really began to exert an influence on American borrowers beginning in the 1980s as FICO become widely used.
A major goal of the credit score is to expand the pool of potential borrowers while minimizing the overall default rate of the pool. In this way, lenders can maximize the number of loans they make. Still, credit scores are imperfect predictors, likely because most credit models assume that consumers will continue to act in the same way in the future as they have in the past. In addition, some believe that various risk factors make credit scores imperfect. Credit modelers, however, continue to make progress by making continuous technological innovations. Even FinTech lenders, which strive to go beyond traditional credit models, heavily rely on credit scores to set their interest rates.
Recently, “Buy Now, Pay Later” accounts have been added to credit scoring, while medical debt has been removed.
Credit scores might seem scary but can be useful
Borrowers with poor or limited credit have challenges building more positive credit histories and good credit scores. This challenge is particularly important because credit scores have become more widely used than ever because of the increasing availability of data and growing precision of credit models.
The availability of additional data results in more precise estimates of credit scoring, which can improve access to credit for consumers who repay bills consistently over time. These so-called “boost programs” factor in other payments that consumers routinely make on a monthly schedule. Think of the number of bills that you auto pay. Boost programs add points to your credit score for the bills that you pay consistently.
You can improve your credit score by making wise decisions
Two of the most important ways to improve credit scores are paying bills on time and ensuring that your credit report accurately reflects your payment history. Simply avoiding default is not enough. Timely payments are necessary. Someone who pays the bills every three months is “caught up” every quarter. But that consumer is 90 days delinquent four times a year. Being 90 days delinquent alarms creditors. So, someone who pays the bills every month will have a higher credit score at the end of the year.
Having more credit accounts can also positively affect your credit score because having these accounts shows that many lenders find you creditworthy. As a result, you might benefit from leaving credit accounts open if you make the wise decision not to access that credit. Warning! You must not use that extra credit access to spend more money and accumulate more debt. That decision is unwise.
Why? Because managing the ratio of debt to income is also critical to a good credit score. Debt-to-income ratios of 36% or less generally indicate individuals who have income to put toward savings, which is what all lenders are looking to see and one of the best ways to improve your credit.
Tom Miller Jr. is affiliated with Consumers' Research, a consumer advocacy organization founded in 1929.
D. Brian Blank does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
default pandemic mortgages interest ratesUncategorized
Comments on February Employment Report
The headline jobs number in the February employment report was above expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the …
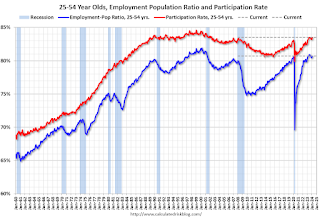
Prime (25 to 54 Years Old) Participation
Since the overall participation rate is impacted by both cyclical (recession) and demographic (aging population, younger people staying in school) reasons, here is the employment-population ratio for the key working age group: 25 to 54 years old.
The 25 to 54 years old participation rate increased in February to 83.5% from 83.3% in January, and the 25 to 54 employment population ratio increased to 80.7% from 80.6% the previous month.
Average Hourly Wages
 The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES).
The graph shows the nominal year-over-year change in "Average Hourly Earnings" for all private employees from the Current Employment Statistics (CES). Wage growth has trended down after peaking at 5.9% YoY in March 2022 and was at 4.3% YoY in February.
Part Time for Economic Reasons
 From the BLS report:
From the BLS report:"The number of people employed part time for economic reasons, at 4.4 million, changed little in February. These individuals, who would have preferred full-time employment, were working part time because their hours had been reduced or they were unable to find full-time jobs."The number of persons working part time for economic reasons decreased in February to 4.36 million from 4.42 million in February. This is slightly above pre-pandemic levels.
These workers are included in the alternate measure of labor underutilization (U-6) that increased to 7.3% from 7.2% in the previous month. This is down from the record high in April 2020 of 23.0% and up from the lowest level on record (seasonally adjusted) in December 2022 (6.5%). (This series started in 1994). This measure is above the 7.0% level in February 2020 (pre-pandemic).
Unemployed over 26 Weeks
 This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more.
This graph shows the number of workers unemployed for 27 weeks or more. According to the BLS, there are 1.203 million workers who have been unemployed for more than 26 weeks and still want a job, down from 1.277 million the previous month.
This is close to pre-pandemic levels.
Job Streak
| Headline Jobs, Top 10 Streaks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year Ended | Streak, Months | |
| 1 | 2019 | 100 |
| 2 | 1990 | 48 |
| 3 | 2007 | 46 |
| 4 | 1979 | 45 |
| 5 | 20241 | 38 |
| 6 tie | 1943 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 1986 | 33 |
| 6 tie | 2000 | 33 |
| 9 | 1967 | 29 |
| 10 | 1995 | 25 |
| 1Currrent Streak | ||
Summary:
The headline monthly jobs number was above consensus expectations; however, December and January payrolls were revised down by 167,000 combined. The participation rate was unchanged, the employment population ratio decreased, and the unemployment rate was increased to 3.9%. Another solid report.
Uncategorized
Immune cells can adapt to invading pathogens, deciding whether to fight now or prepare for the next battle
When faced with a threat, T cells have the decision-making flexibility to both clear out the pathogen now and ready themselves for a future encounter.
How does your immune system decide between fighting invading pathogens now or preparing to fight them in the future? Turns out, it can change its mind.
Every person has 10 million to 100 million unique T cells that have a critical job in the immune system: patrolling the body for invading pathogens or cancerous cells to eliminate. Each of these T cells has a unique receptor that allows it to recognize foreign proteins on the surface of infected or cancerous cells. When the right T cell encounters the right protein, it rapidly forms many copies of itself to destroy the offending pathogen.

Importantly, this process of proliferation gives rise to both short-lived effector T cells that shut down the immediate pathogen attack and long-lived memory T cells that provide protection against future attacks. But how do T cells decide whether to form cells that kill pathogens now or protect against future infections?
We are a team of bioengineers studying how immune cells mature. In our recently published research, we found that having multiple pathways to decide whether to kill pathogens now or prepare for future invaders boosts the immune system’s ability to effectively respond to different types of challenges.
Fight or remember?
To understand when and how T cells decide to become effector cells that kill pathogens or memory cells that prepare for future infections, we took movies of T cells dividing in response to a stimulus mimicking an encounter with a pathogen.
Specifically, we tracked the activity of a gene called T cell factor 1, or TCF1. This gene is essential for the longevity of memory cells. We found that stochastic, or probabilistic, silencing of the TCF1 gene when cells confront invading pathogens and inflammation drives an early decision between whether T cells become effector or memory cells. Exposure to higher levels of pathogens or inflammation increases the probability of forming effector cells.
Surprisingly, though, we found that some effector cells that had turned off TCF1 early on were able to turn it back on after clearing the pathogen, later becoming memory cells.
Through mathematical modeling, we determined that this flexibility in decision making among memory T cells is critical to generating the right number of cells that respond immediately and cells that prepare for the future, appropriate to the severity of the infection.
Understanding immune memory
The proper formation of persistent, long-lived T cell memory is critical to a person’s ability to fend off diseases ranging from the common cold to COVID-19 to cancer.
From a social and cognitive science perspective, flexibility allows people to adapt and respond optimally to uncertain and dynamic environments. Similarly, for immune cells responding to a pathogen, flexibility in decision making around whether to become memory cells may enable greater responsiveness to an evolving immune challenge.
Memory cells can be subclassified into different types with distinct features and roles in protective immunity. It’s possible that the pathway where memory cells diverge from effector cells early on and the pathway where memory cells form from effector cells later on give rise to particular subtypes of memory cells.
Our study focuses on T cell memory in the context of acute infections the immune system can successfully clear in days, such as cold, the flu or food poisoning. In contrast, chronic conditions such as HIV and cancer require persistent immune responses; long-lived, memory-like cells are critical for this persistence. Our team is investigating whether flexible memory decision making also applies to chronic conditions and whether we can leverage that flexibility to improve cancer immunotherapy.
Resolving uncertainty surrounding how and when memory cells form could help improve vaccine design and therapies that boost the immune system’s ability to provide long-term protection against diverse infectious diseases.
Kathleen Abadie was funded by a NSF (National Science Foundation) Graduate Research Fellowships. She performed this research in affiliation with the University of Washington Department of Bioengineering.
Elisa Clark performed her research in affiliation with the University of Washington (UW) Department of Bioengineering and was funded by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship (NSF-GRFP) and by a predoctoral fellowship through the UW Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine (ISCRM).
Hao Yuan Kueh receives funding from the National Institutes of Health.
stimulus covid-19 yuan vaccine stimulusUncategorized
Stock indexes are breaking records and crossing milestones – making many investors feel wealthier
The S&P 500 topped 5,000 on Feb. 9, 2024, for the first time. The Dow Jones Industrial Average will probably hit a new big round number soon t…

The S&P 500 stock index topped 5,000 for the first time on Feb. 9, 2024, exciting some investors and garnering a flurry of media coverage. The Conversation asked Alexander Kurov, a financial markets scholar, to explain what stock indexes are and to say whether this kind of milestone is a big deal or not.
What are stock indexes?
Stock indexes measure the performance of a group of stocks. When prices rise or fall overall for the shares of those companies, so do stock indexes. The number of stocks in those baskets varies, as does the system for how this mix of shares gets updated.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, also known as the Dow, includes shares in the 30 U.S. companies with the largest market capitalization – meaning the total value of all the stock belonging to shareholders. That list currently spans companies from Apple to Walt Disney Co.
The S&P 500 tracks shares in 500 of the largest U.S. publicly traded companies.
The Nasdaq composite tracks performance of more than 2,500 stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange.
The DJIA, launched on May 26, 1896, is the oldest of these three popular indexes, and it was one of the first established.
Two enterprising journalists, Charles H. Dow and Edward Jones, had created a different index tied to the railroad industry a dozen years earlier. Most of the 12 stocks the DJIA originally included wouldn’t ring many bells today, such as Chicago Gas and National Lead. But one company that only got booted in 2018 had stayed on the list for 120 years: General Electric.
The S&P 500 index was introduced in 1957 because many investors wanted an option that was more representative of the overall U.S. stock market. The Nasdaq composite was launched in 1971.
You can buy shares in an index fund that mirrors a particular index. This approach can diversify your investments and make them less prone to big losses.
Index funds, which have only existed since Vanguard Group founder John Bogle launched the first one in 1976, now hold trillions of dollars .
Why are there so many?
There are hundreds of stock indexes in the world, but only about 50 major ones.
Most of them, including the Nasdaq composite and the S&P 500, are value-weighted. That means stocks with larger market values account for a larger share of the index’s performance.
In addition to these broad-based indexes, there are many less prominent ones. Many of those emphasize a niche by tracking stocks of companies in specific industries like energy or finance.
Do these milestones matter?
Stock prices move constantly in response to corporate, economic and political news, as well as changes in investor psychology. Because company profits will typically grow gradually over time, the market usually fluctuates in the short term, while increasing in value over the long term.
The DJIA first reached 1,000 in November 1972, and it crossed the 10,000 mark on March 29, 1999. On Jan. 22, 2024, it surpassed 38,000 for the first time. Investors and the media will treat the new record set when it gets to another round number – 40,000 – as a milestone.
The S&P 500 index had never hit 5,000 before. But it had already been breaking records for several weeks.
Because there’s a lot of randomness in financial markets, the significance of round-number milestones is mostly psychological. There is no evidence they portend any further gains.
For example, the Nasdaq composite first hit 5,000 on March 10, 2000, at the end of the dot-com bubble.
The index then plunged by almost 80% by October 2002. It took 15 years – until March 3, 2015 – for it return to 5,000.
By mid-February 2024, the Nasdaq composite was nearing its prior record high of 16,057 set on Nov. 19, 2021.
Index milestones matter to the extent they pique investors’ attention and boost market sentiment.
Investors afflicted with a fear of missing out may then invest more in stocks, pushing stock prices to new highs. Chasing after stock trends may destabilize markets by moving prices away from their underlying values.
When a stock index passes a new milestone, investors become more aware of their growing portfolios. Feeling richer can lead them to spend more.
This is called the wealth effect. Many economists believe that the consumption boost that arises in response to a buoyant stock market can make the economy stronger.
Is there a best stock index to follow?
Not really. They all measure somewhat different things and have their own quirks.
For example, the S&P 500 tracks many different industries. However, because it is value-weighted, it’s heavily influenced by only seven stocks with very large market values.
Known as the “Magnificent Seven,” shares in Amazon, Apple, Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft, Nvidia and Tesla now account for over one-fourth of the S&P 500’s value. Nearly all are in the tech sector, and they played a big role in pushing the S&P across the 5,000 mark.
This makes the index more concentrated on a single sector than it appears.
But if you check out several stock indexes rather than just one, you’ll get a good sense of how the market is doing. If they’re all rising quickly or breaking records, that’s a clear sign that the market as a whole is gaining.
Sometimes the smartest thing is to not pay too much attention to any of them.
For example, after hitting record highs on Feb. 19, 2020, the S&P 500 plunged by 34% in just 23 trading days due to concerns about what COVID-19 would do to the economy. But the market rebounded, with stock indexes hitting new milestones and notching new highs by the end of that year.
Panicking in response to short-term market swings would have made investors more likely to sell off their investments in too big a hurry – a move they might have later regretted. This is why I believe advice from the immensely successful investor and fan of stock index funds Warren Buffett is worth heeding.
Buffett, whose stock-selecting prowess has made him one of the world’s 10 richest people, likes to say “Don’t watch the market closely.”
If you’re reading this because stock prices are falling and you’re wondering if you should be worried about that, consider something else Buffett has said: “The light can at any time go from green to red without pausing at yellow.”
And the opposite is true as well.
Alexander Kurov does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
dow jones sp 500 nasdaq stocks covid-19-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 month ago
International1 month agoWar Delirium
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges





















