Hickman: 4th-Wave Of COVID-19 Will Push Rates To Zero
Hickman: 4th-Wave Of COVID-19 Will Push Rates To Zero
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Eric Hickman discusses why we should beware of the 4th-Wave of Covid-19…
I know everyone is tired of hearing about the virus….
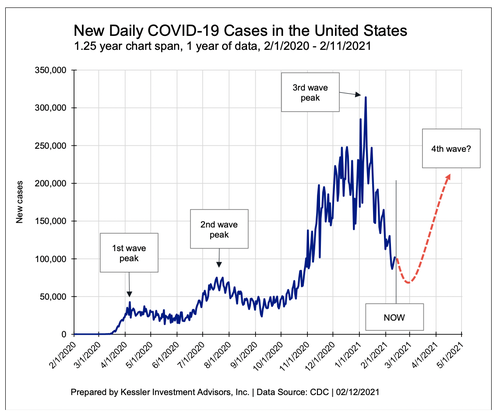
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
Eric Hickman discusses why we should beware of the 4th-Wave of Covid-19...
I know everyone is tired of hearing about the virus. Some think it is overblown by the media, many want to focus on the positives, and others have had their lives upended and want to forget.
There are reasons for optimism. It is a new year with longer days and warmer temperatures. People continue to get inoculated with increasing speed. The approval of new vaccines continues as new cases, deaths, and hospitalizations from the third wave fall (see below). The 1918 Spanish Flu had three waves over about a year; the COVID-19 pandemic has had three over a year as well.
Indeed, this is about over, right?
Tuned Out?
It isn’t over, and financial markets don’t accept that yet. I realize suggesting anything negative about the virus is misanthropic, but the truth matters, and the optics are misleading.
New cases decrease in the third wave because we are past the holidays, not because of vaccinations. It is a common misconception the decrease we’ve seen in the virus is due to vaccinations. The two aren’t related, at least yet.
“The decline in cases is likely a natural drop after record travel followed by indoor holiday gatherings triggered a surge in infections.” – Dr. Sarita Shah, associate professor at Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health.
“We’ve seen these rises and falls in the COVID case counts now a few times, and they seem to really track along holidays or people’s movements,” Shah said.
To Early
“COVID-19 symptoms take between two to 14 days to appear after exposure, and cases peaked precisely two weeks after the Christmas holidays.” – Brittany Baker, undergraduate program coordinator and clinical assistant professor at North Carolina Central University.
Dr. Wafaa El-Sadr, professor of epidemiology and medicine at Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health, said the falling case numbers couldn’t get attributed to the COVID-19 vaccine. Not even a tenth of the population has gotten vaccinated, according to the CDC.
“We’re vaccinating our most vulnerable populations right now, but once we start to move into the broad population, the population that’s driving the numbers. That’s when we’ll start to see an impact on the overall numbers,” Shah said.
She said Americans might start to see the vaccine’s influence on case numbers as early as the summer, but it will be more evident in the fall.
U.S.A Today, 02/06/2021, “Coronavirus cases are falling in the U.S., but experts say it’s not from the COVID-19 vaccine yet.”
New Sars-CoV-2 variants
As with all replicating biological entities, viruses change over time with random mutations to their genetic code (genome) when reproducing. Most mutations do not affect or are detrimental. Still, every once in a while, a random change (or series of changes) will alter a trait that increases its biological fitness – its competitive advantage in its environment. Beneficial mutations get carried forward to new generations, which crowd out the inferior older genome. Such is natural selection.
The process happens at a glacial pace in the life-forms we are most familiar with (say mammals) because reproduction takes years. Viruses replicate in a matter of hours to days, and more specifically, single-strand RNA viruses (of which the coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, is one) replicate faster than other viruses.
Viruses that encode their genome in RNA, such as SARS-CoV-2, HIV and influenza, tend to pick up mutations quickly as they get copied inside their hosts, because enzymes that copy RNA are prone to making errors.
Nature.com, 09/08/2020, “The coronavirus is mutating – does it matter?”
The concerning new Sars-CoV-2 variants emerging from the U.K., South Africa, and Brazil have yet to become dominant in the U.S. On February 7, a study reported that the more transmissible U.K. variant is now “spreading rapidly in the U.S.” It could become the dominant strain by late March. Italy’s health ministry said on February 12 that the U.K. variant makes up 17.8% of cases and will likely become prevalent in the coming months. The vaccine-weakening South African and Brazilian variants got detected in the U.S. in January. There are now several cases dotted around the U.S. They will presumably gain traction as they did in their original countries. This process takes months.
New Variants
The variants detected recently in the U.K. and South Africa have several novel changes in their spike-protein genes.
Scientists think one mutation these variants share could help the virus attach to and enter cells. The recently detected variant from Brazil shares a key spike-protein mutation with the one from South Africa.
“What we’re seeing is exactly what we expect to see. The surface proteins of the virus are under tremendous pressure to change.” – Sean Whelan, a virologist at Washington University in St. Louis.
“All the virus really cares about is multiplying. If it can get into the cells of the [host] and avoid the immune system of that host, it will multiply. Whether it causes the disease is a different question.”
Some scientists worry that South Africa’s variant could be better at evading antibodies produced in response to natural infection and vaccination. Preliminary estimates suggest the variant from the U.K. is 50%–70% more transmissible than earlier versions of the virus. And U.K. scientists said recently that early data suggested it could also be deadlier.
The variants found in the U.K. and South Africa have become the dominant types in countries where they were first detected.
Chart Source: Wall Street Journal
Parallel Evolution
The variant from the U.K. has spread widely abroad. As of late January, it had been reported in 70 countries and territories. The variant from South Africa has been reported in more than 30, while the U.K. variant was detected in more than two dozen U.S. states through late January. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention projected it could become the dominant domestic strain by mid- to late March unless steps are taken to slow it. Variants first found in South Africa and Brazil have also been detected in the U.S.
WSJ, 01/30/2021, “How Coronavirus Mutations Are Taking Over”
Restricting travel between continents may prevent these variants from getting around, but there is another wrinkle to this. In biology, convergent or parallel evolution is a common yet counter-intuitive phenomenon. Independent lineages of a biological entity can arrive at similar evolutionary fitness solutions without any interaction between them. The similarity between the sugar glider (marsupial from Australia) and the flying squirrel (mammal from North America) is an example of this (image below).
Image Source: Getty/Encyclopedia Brittanica/UIG
Mutants
The same phenomenon is happening with Sars-CoV-2 mutations. Critical mutations from the U.K. variant (N501Y) and the one shared by the South African and Brazilian variants (E484K) emerged independently in a now-deceased Boston COVID-19 patient with a prolonged continuous infection. There are quotes from a National Public Radio story below. But for those interested, it is an interesting read (or listen) found at the link below:
Li and his colleagues published their findings in The New England Journal of Medicine in early November 2020 with little fanfare. Then about a month later, the pandemic took a surprising turn – and this peculiar case in Boston took on a new importance.
Scientists in the U.K. and South Africa announced they had detected new variants of the coronavirus. These variants were causing huge surges of COVID-19 in these countries.
When researchers looked at the genes of these variants, guess what they found? A cluster of mutations that looked remarkably similar to the mutations found in the virus from the Boston patient. The sets of mutations weren’t exactly identical, but they shared important characteristics. They both had about 20 mutations, and they shared several key ones, including a mutation (N501Y) known to help the virus bind more tightly to human cells and another mutation (E484K) known to help the virus evade antibody detection.
National Public Radio, 2/5/2021, “Extraordinary Patient Offers Surprising Clues to Origins of Coronavirus Variants”
The virus may optimize itself to known mutations without spreading geographically, weakening the power of travel restrictions.
New Variants Will Emerge
The virus is just a little over one-year-old on its new metaphorical planet of “humans” and is still trying to find an evolutionary best fit. A safe assumption is that more variants will emerge.
“Look, there is going to be a whole cascade of these new variants. The virus moved between species. It migrated from the back end of a pangolin and to humans. And it’s got to adapt to humans. What we see now is it is getting better and better and more efficient at living in humans. And that we can see a set of other mutations coming down the line. So, I think we mustn’t say ‘ahh, well we now know what the mutations are going to look like.’ We don’t. There’s gonna be a set of other ones.”
U.K. Channel 4 news, 01/24/2021, Interview with Prominent Virologist Sir John Bell
Even though vaccination plans for developed-world adults are firming up, the developing world and children are less clear. As long as the virus circulates in humans anywhere, it will find new optimizations that will likely require vaccine alterations.
The more widespread infections remain globally, the more mutations will occur. A lingering pool of cases in poorer countries risks giving birth to resistant strains that force richer economies to lock down and start vaccinating all over again.
Financial Times, 02/05/2021, “The global race between vaccines and mutations”
Taken together, it is probable that the world will have at least one more severe wave of infections this spring and summer – a fourth wave – before the inoculated and previously infected can crowd out those with no protection. Re-vaccination (booster shots) for new variants add to this timeline.
Rates Will Fall Dramatically
Such isn’t doomsday, but at a minimum, it elongates the time until battered industries (hospitality, entertainment) will have a chance to recover. So far, markets continue to believe the pandemic is a net benefit to bigger businesses globally (all-time highs in public companies, see below).
The explanation for this is that it is only the small, non-public companies that are struggling.
That is far-fetched.
The pandemic will cost the world’s public companies in aggregate at some point. I wrote nine months ago that “COVID-19 Defies Hyperbole.” Even though risk-on markets had gone up when I suggested they would go down, I stand by my prediction. Apt fiscal and monetary injections forestalled a deeper contraction. Still, it is a delusion to think we will get out of this for free – especially in a world economy that was overdue for a retraction anyways.
Even without a fourth COVID-19 wave, the negative impact on jobs, rents, consumer demand, tax revenue, and entire economy segments (hospitality, entertainment) has yet to be considered seriously. As they become so, risk-on markets (stocks, commodities, crypto-currencies, houses, and non-G-7 currencies) will drop, and long-term U.S. Treasury yields will fall dramatically.
Spread & Containment
The Coming Of The Police State In America
The Coming Of The Police State In America
Authored by Jeffrey Tucker via The Epoch Times,
The National Guard and the State Police are now…

Authored by Jeffrey Tucker via The Epoch Times,
The National Guard and the State Police are now patrolling the New York City subway system in an attempt to do something about the explosion of crime. As part of this, there are bag checks and new surveillance of all passengers. No legislation, no debate, just an edict from the mayor.
Many citizens who rely on this system for transportation might welcome this. It’s a city of strict gun control, and no one knows for sure if they have the right to defend themselves. Merchants have been harassed and even arrested for trying to stop looting and pillaging in their own shops.
The message has been sent: Only the police can do this job. Whether they do it or not is another matter.
Things on the subway system have gotten crazy. If you know it well, you can manage to travel safely, but visitors to the city who take the wrong train at the wrong time are taking grave risks.
In actual fact, it’s guaranteed that this will only end in confiscating knives and other things that people carry in order to protect themselves while leaving the actual criminals even more free to prey on citizens.
The law-abiding will suffer and the criminals will grow more numerous. It will not end well.
When you step back from the details, what we have is the dawning of a genuine police state in the United States. It only starts in New York City. Where is the Guard going to be deployed next? Anywhere is possible.
If the crime is bad enough, citizens will welcome it. It must have been this way in most times and places that when the police state arrives, the people cheer.
We will all have our own stories of how this came to be. Some might begin with the passage of the Patriot Act and the establishment of the Department of Homeland Security in 2001. Some will focus on gun control and the taking away of citizens’ rights to defend themselves.
My own version of events is closer in time. It began four years ago this month with lockdowns. That’s what shattered the capacity of civil society to function in the United States. Everything that has happened since follows like one domino tumbling after another.
It goes like this:
1) lockdown,
2) loss of moral compass and spreading of loneliness and nihilism,
3) rioting resulting from citizen frustration, 4) police absent because of ideological hectoring,
5) a rise in uncontrolled immigration/refugees,
6) an epidemic of ill health from substance abuse and otherwise,
7) businesses flee the city
8) cities fall into decay, and that results in
9) more surveillance and police state.
The 10th stage is the sacking of liberty and civilization itself.
It doesn’t fall out this way at every point in history, but this seems like a solid outline of what happened in this case. Four years is a very short period of time to see all of this unfold. But it is a fact that New York City was more-or-less civilized only four years ago. No one could have predicted that it would come to this so quickly.
But once the lockdowns happened, all bets were off. Here we had a policy that most directly trampled on all freedoms that we had taken for granted. Schools, businesses, and churches were slammed shut, with various levels of enforcement. The entire workforce was divided between essential and nonessential, and there was widespread confusion about who precisely was in charge of designating and enforcing this.
It felt like martial law at the time, as if all normal civilian law had been displaced by something else. That something had to do with public health, but there was clearly more going on, because suddenly our social media posts were censored and we were being asked to do things that made no sense, such as mask up for a virus that evaded mask protection and walk in only one direction in grocery aisles.
Vast amounts of the white-collar workforce stayed home—and their kids, too—until it became too much to bear. The city became a ghost town. Most U.S. cities were the same.
As the months of disaster rolled on, the captives were let out of their houses for the summer in order to protest racism but no other reason. As a way of excusing this, the same public health authorities said that racism was a virus as bad as COVID-19, so therefore it was permitted.
The protests had turned to riots in many cities, and the police were being defunded and discouraged to do anything about the problem. Citizens watched in horror as downtowns burned and drug-crazed freaks took over whole sections of cities. It was like every standard of decency had been zapped out of an entire swath of the population.
Meanwhile, large checks were arriving in people’s bank accounts, defying every normal economic expectation. How could people not be working and get their bank accounts more flush with cash than ever? There was a new law that didn’t even require that people pay rent. How weird was that? Even student loans didn’t need to be paid.
By the fall, recess from lockdown was over and everyone was told to go home again. But this time they had a job to do: They were supposed to vote. Not at the polling places, because going there would only spread germs, or so the media said. When the voting results finally came in, it was the absentee ballots that swung the election in favor of the opposition party that actually wanted more lockdowns and eventually pushed vaccine mandates on the whole population.
The new party in control took note of the large population movements out of cities and states that they controlled. This would have a large effect on voting patterns in the future. But they had a plan. They would open the borders to millions of people in the guise of caring for refugees. These new warm bodies would become voters in time and certainly count on the census when it came time to reapportion political power.
Meanwhile, the native population had begun to swim in ill health from substance abuse, widespread depression, and demoralization, plus vaccine injury. This increased dependency on the very institutions that had caused the problem in the first place: the medical/scientific establishment.
The rise of crime drove the small businesses out of the city. They had barely survived the lockdowns, but they certainly could not survive the crime epidemic. This undermined the tax base of the city and allowed the criminals to take further control.
The same cities became sanctuaries for the waves of migrants sacking the country, and partisan mayors actually used tax dollars to house these invaders in high-end hotels in the name of having compassion for the stranger. Citizens were pushed out to make way for rampaging migrant hordes, as incredible as this seems.
But with that, of course, crime rose ever further, inciting citizen anger and providing a pretext to bring in the police state in the form of the National Guard, now tasked with cracking down on crime in the transportation system.
What’s the next step? It’s probably already here: mass surveillance and censorship, plus ever-expanding police power. This will be accompanied by further population movements, as those with the means to do so flee the city and even the country and leave it for everyone else to suffer.
As I tell the story, all of this seems inevitable. It is not. It could have been stopped at any point. A wise and prudent political leadership could have admitted the error from the beginning and called on the country to rediscover freedom, decency, and the difference between right and wrong. But ego and pride stopped that from happening, and we are left with the consequences.
The government grows ever bigger and civil society ever less capable of managing itself in large urban centers. Disaster is unfolding in real time, mitigated only by a rising stock market and a financial system that has yet to fall apart completely.
Are we at the middle stages of total collapse, or at the point where the population and people in leadership positions wise up and decide to put an end to the downward slide? It’s hard to know. But this much we do know: There is a growing pocket of resistance out there that is fed up and refuses to sit by and watch this great country be sacked and taken over by everything it was set up to prevent.
Government
Low Iron Levels In Blood Could Trigger Long COVID: Study
Low Iron Levels In Blood Could Trigger Long COVID: Study
Authored by Amie Dahnke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People with inadequate…

Authored by Amie Dahnke via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
People with inadequate iron levels in their blood due to a COVID-19 infection could be at greater risk of long COVID.
A new study indicates that problems with iron levels in the bloodstream likely trigger chronic inflammation and other conditions associated with the post-COVID phenomenon. The findings, published on March 1 in Nature Immunology, could offer new ways to treat or prevent the condition.
Long COVID Patients Have Low Iron Levels
Researchers at the University of Cambridge pinpointed low iron as a potential link to long-COVID symptoms thanks to a study they initiated shortly after the start of the pandemic. They recruited people who tested positive for the virus to provide blood samples for analysis over a year, which allowed the researchers to look for post-infection changes in the blood. The researchers looked at 214 samples and found that 45 percent of patients reported symptoms of long COVID that lasted between three and 10 months.
In analyzing the blood samples, the research team noticed that people experiencing long COVID had low iron levels, contributing to anemia and low red blood cell production, just two weeks after they were diagnosed with COVID-19. This was true for patients regardless of age, sex, or the initial severity of their infection.
According to one of the study co-authors, the removal of iron from the bloodstream is a natural process and defense mechanism of the body.
But it can jeopardize a person’s recovery.
“When the body has an infection, it responds by removing iron from the bloodstream. This protects us from potentially lethal bacteria that capture the iron in the bloodstream and grow rapidly. It’s an evolutionary response that redistributes iron in the body, and the blood plasma becomes an iron desert,” University of Oxford professor Hal Drakesmith said in a press release. “However, if this goes on for a long time, there is less iron for red blood cells, so oxygen is transported less efficiently affecting metabolism and energy production, and for white blood cells, which need iron to work properly. The protective mechanism ends up becoming a problem.”
The research team believes that consistently low iron levels could explain why individuals with long COVID continue to experience fatigue and difficulty exercising. As such, the researchers suggested iron supplementation to help regulate and prevent the often debilitating symptoms associated with long COVID.
“It isn’t necessarily the case that individuals don’t have enough iron in their body, it’s just that it’s trapped in the wrong place,” Aimee Hanson, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Cambridge who worked on the study, said in the press release. “What we need is a way to remobilize the iron and pull it back into the bloodstream, where it becomes more useful to the red blood cells.”
The research team pointed out that iron supplementation isn’t always straightforward. Achieving the right level of iron varies from person to person. Too much iron can cause stomach issues, ranging from constipation, nausea, and abdominal pain to gastritis and gastric lesions.
1 in 5 Still Affected by Long COVID
COVID-19 has affected nearly 40 percent of Americans, with one in five of those still suffering from symptoms of long COVID, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Long COVID is marked by health issues that continue at least four weeks after an individual was initially diagnosed with COVID-19. Symptoms can last for days, weeks, months, or years and may include fatigue, cough or chest pain, headache, brain fog, depression or anxiety, digestive issues, and joint or muscle pain.
Uncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemployment-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges























