Gundlach: “People Are Starting To Believe That Stimulus Is Permanent”
Gundlach: "People Are Starting To Believe That Stimulus Is Permanent"
It’s time for Jeff Gundlach to regale DoubleLine fund investors and assorted hangers on with his views of the economy, the stock market and everything else. The title…

It's time for Jeff Gundlach to regale DoubleLine fund investors and assorted hangers on with his views of the economy, the stock market and everything else. The title of the latest webcast is "Looking Backward" although we expect a substantial does of forward looking views and hot takes, including Gundlach's inaugural assessment of the US economy.
Readers can listen to the webcast by clising on the following link or the image below.
The last time we heard from Gundlach, financials were just starting to take off thanks to surging yields. But that was a much smaller move compared to the action we’ve seen since the start of February. Back then, Gundlach pulled up a chart saying U.S. banks are wearing a “normal scuba vest” whereas their Japanese and European counterparts act as if they have an “aqualung vest.” Why? He says negative interest rates. As we noted earlier, US banks may be forced to adopt negative rates as soon as April 1.
As Bloomberg also reminds us, last month Gundlach tweeted that he had been a long-term gold bull and U.S. dollar bear, but has turned neutral on both. Bitcoin may well be the “Stimulus Asset,” he said, a reference to the cryptocurrency’s rally amid a wave of cash pumped into the financial system during the pandemic.
More recently, he noted the divergence below, with Bitcoin rapidly outpacing both gold and the S&P 500’s gains over the past year, adding ominously, “Great dispersions often precede great reversions.” So will Gundlach announce his full-blown endorsement of the cryptocurrency? Stay tuned to find out.
We'll update this post with periodic highlights from the webcast.
Gundlach explains the title of today's webcast “Looking Backward”, which is a nod to a novel written in 1888, and where the protagonist of Edward Bellamy’s socialist-utopian novel goes into a trance in 1887 and awakens in 2000. Gundlach says the novel resembles situations in society today. In the novel the protagonist finds a year 2000 described as having shorter working weeks and equal distribution of goods. In the book, Boston is part of a totally changed world in which the U.S. has been transformed to a socialist utopia, which includes internet and full-benefits retirement at 45.
"So think about this as we go through some of the slides" Gundlach said.
Gundlach starts by showing a chart breaking down the US economy between Nominal GDP, Employment and market cap, with Technology "monopolies" clearly dominating.
He then shows a chart of US economic growth, saying that despite all the stimulus, the US won't be fully out of the recession until we regain the economic growth rate.
The DoubleLine CEO then shows just how much bigger the stimulus at $6.1TN is compared to the Great recession's $1.8TN.
Gundlach then uses one of our favorite charts, the one showing that government accounts for a whopping 27% of all personal income.
Of course, this socialism won't come cheap and the US budget deficit has now hit a record 16.2% of GDP.
Echoing one of our favorite lines, Gundlach says that “80% of the budget is borrowing, so why bother with taxes at all?”
Next, touching on his views on the dollar, Gundlach says that while he has been bullish in recent months, he expects the next move in the dollar to be down after a brief bounce.
Gundlach, who is jumping around like crazy from topic to topic, then slams the "phony" 6.2% unemployment rate pointing to the true US unemployment which is far greater than the official 6MM print, as a result of more than 18MM people receiving various forms of unemployment benefits, more than 10% of the entire US labor force.
Going back to the stock market, Gundlach mentions the “super six” tech stocks again and says it's amazing how high these stocks are valued versus pre-pandemic levels. He then shows surging P/E ratios, saying forward P/E ratios are elevated at 19 but not as high as 1999. Noting that Joe Biden is talking about increased corporate tax rates, Gundlach says P/E ratios could go even higher once that legislation is folded into the valuations.
Which brings us to one of of Gundlach's most bombastic comments so far. Looking at the tremendous outperformance of mega caps relative to micro caps...
... and the tremendous gains in the Nasdaq vs SPX, which recently just took out the dot com higher...
... Gundlach warns that the Nasdaq may see a decline like in 2000-20003 and makes a shocking prediction that "The VIX will go over a 100 during the next downturn."
What could cause such a crash? Perhaps inflation - Gundlach notes that he expects headline inflation to be over 3% for a few months this summer on the back of base effect and stimulus.
It could get worse: Gundlach compares CPI to ISM Prices Paid ans says that one could plausibly predict headline inflation could rise above 4%. "That would really spook the bond market."
As a tangent, Gundlach points out something we have frequently noted, namely that buy purchasing massive amounts of TIPS, the Fed is skewing the TIPS and thus breakevens market.
Gundlach then switches to Gold, and referring to yesterday's plunge in the price of gold to $1,680 he says that that could be the low for gold for this cycle.
He then rapidly shifts to bonds, and saying that while according to German yields, the 10Y is priced correctly...
... the gold/copper ratio suggests that the 10Y should be at 3%.
Gundlach then looks at the "bloodbath" in the long end, and specifically the move in the 30Y, saying it was the largest drawdown since the GFC (charted below), and echoing David Tepper, Gundlach says that "I’d expect a modest or moderate decline in yields on the long-end. It’s overextended sentiment-wise."
The DoubleLine CEO then said what most people know, namely that the only marginal buyer of Treasuries in the past couple of years has been the Fed as Foreigners continue to sell Treasury bonds. Gundlach talks about a “lack of robust, organic demand,” and points to the recent catastrophic seven-year Treasury auction as further evidence.
In short, the "Magic" in "Magic Money Tree" (or MMT) is and has always been the Fed.
Gundlach concludes on a dismal note, criticizing stimulus programs for giving people who make $150,000 a year a pile of money, and extending his criticism to broader debt monetization saying while bemoaning what he says is a reliance on stimulus programs for growth.
Warning that people may be starting to believe stimulus is permanent, he says that “The biggest problem is we’ve become totally addicted to these stimulus programs” adding that while "people may be starting to believe that stimulus is permanent", he worries that "we can see some real need for endless stimulus."
And yet, in a world where a quarter of all personal income comes from the government, stimulus programs need to be kept going because consumers have been “trained” to rely on them. Hammering the point that people could become dependent on these stimulus programs, he said that this is something that tends to be associated more with Europe than the U.S, and warns that we could be seeing “neverending” aid regime stateside.
Welcome to socialism with American characteristics - perpetual universal basic income for everyone, courtesy of a reserve currency... while it lasts. Because as Gundlach warns, China is doing everything in its power (both economic and military) to replace the US as global hegemon.
One final point Gundlach made is that while bond vigilantes can overcome the Fed's effort to keep yields low, the central bank would then launch Yield Curve Control. That said, the Fed isn’t yet at the point where it would implement YCC: “There’s a pretty good shot that they’ll let the 10-year yield go above 2% before they do anything about it."
And in response to a question what is the world's cheapest asset right now, his answer: farmland.
Gundlach's full presentation below.
International
The next pandemic? It’s already here for Earth’s wildlife
Bird flu is decimating species already threatened by climate change and habitat loss.
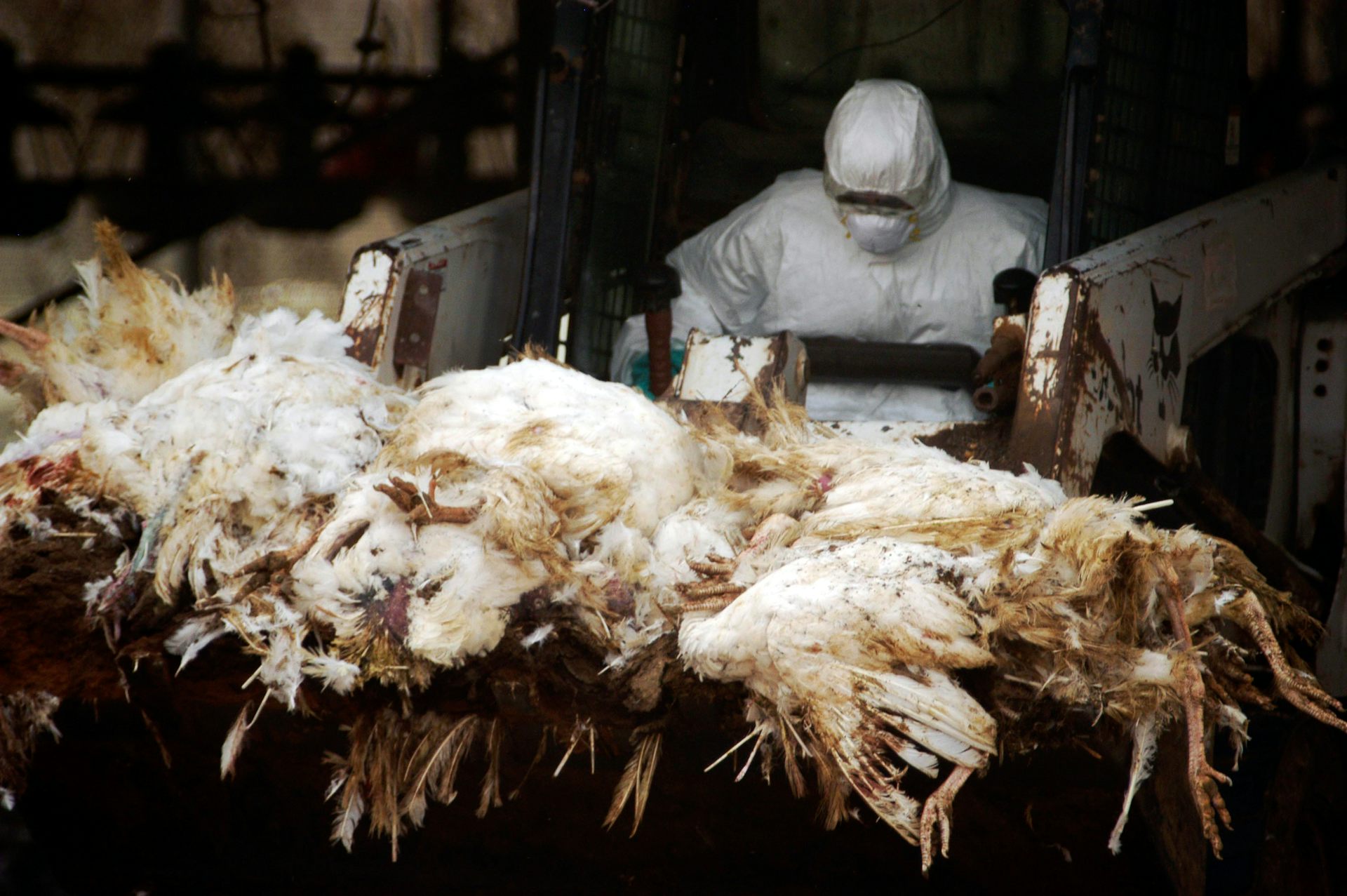

I am a conservation biologist who studies emerging infectious diseases. When people ask me what I think the next pandemic will be I often say that we are in the midst of one – it’s just afflicting a great many species more than ours.
I am referring to the highly pathogenic strain of avian influenza H5N1 (HPAI H5N1), otherwise known as bird flu, which has killed millions of birds and unknown numbers of mammals, particularly during the past three years.
This is the strain that emerged in domestic geese in China in 1997 and quickly jumped to humans in south-east Asia with a mortality rate of around 40-50%. My research group encountered the virus when it killed a mammal, an endangered Owston’s palm civet, in a captive breeding programme in Cuc Phuong National Park Vietnam in 2005.
How these animals caught bird flu was never confirmed. Their diet is mainly earthworms, so they had not been infected by eating diseased poultry like many captive tigers in the region.
This discovery prompted us to collate all confirmed reports of fatal infection with bird flu to assess just how broad a threat to wildlife this virus might pose.
This is how a newly discovered virus in Chinese poultry came to threaten so much of the world’s biodiversity.
The first signs
Until December 2005, most confirmed infections had been found in a few zoos and rescue centres in Thailand and Cambodia. Our analysis in 2006 showed that nearly half (48%) of all the different groups of birds (known to taxonomists as “orders”) contained a species in which a fatal infection of bird flu had been reported. These 13 orders comprised 84% of all bird species.
We reasoned 20 years ago that the strains of H5N1 circulating were probably highly pathogenic to all bird orders. We also showed that the list of confirmed infected species included those that were globally threatened and that important habitats, such as Vietnam’s Mekong delta, lay close to reported poultry outbreaks.
Mammals known to be susceptible to bird flu during the early 2000s included primates, rodents, pigs and rabbits. Large carnivores such as Bengal tigers and clouded leopards were reported to have been killed, as well as domestic cats.
Our 2006 paper showed the ease with which this virus crossed species barriers and suggested it might one day produce a pandemic-scale threat to global biodiversity.
Unfortunately, our warnings were correct.
A roving sickness
Two decades on, bird flu is killing species from the high Arctic to mainland Antarctica.
In the past couple of years, bird flu has spread rapidly across Europe and infiltrated North and South America, killing millions of poultry and a variety of bird and mammal species. A recent paper found that 26 countries have reported at least 48 mammal species that have died from the virus since 2020, when the latest increase in reported infections started.
Not even the ocean is safe. Since 2020, 13 species of aquatic mammal have succumbed, including American sea lions, porpoises and dolphins, often dying in their thousands in South America. A wide range of scavenging and predatory mammals that live on land are now also confirmed to be susceptible, including mountain lions, lynx, brown, black and polar bears.
The UK alone has lost over 75% of its great skuas and seen a 25% decline in northern gannets. Recent declines in sandwich terns (35%) and common terns (42%) were also largely driven by the virus.
Scientists haven’t managed to completely sequence the virus in all affected species. Research and continuous surveillance could tell us how adaptable it ultimately becomes, and whether it can jump to even more species. We know it can already infect humans – one or more genetic mutations may make it more infectious.
At the crossroads
Between January 1 2003 and December 21 2023, 882 cases of human infection with the H5N1 virus were reported from 23 countries, of which 461 (52%) were fatal.
Of these fatal cases, more than half were in Vietnam, China, Cambodia and Laos. Poultry-to-human infections were first recorded in Cambodia in December 2003. Intermittent cases were reported until 2014, followed by a gap until 2023, yielding 41 deaths from 64 cases. The subtype of H5N1 virus responsible has been detected in poultry in Cambodia since 2014. In the early 2000s, the H5N1 virus circulating had a high human mortality rate, so it is worrying that we are now starting to see people dying after contact with poultry again.
It’s not just H5 subtypes of bird flu that concern humans. The H10N1 virus was originally isolated from wild birds in South Korea, but has also been reported in samples from China and Mongolia.
Recent research found that these particular virus subtypes may be able to jump to humans after they were found to be pathogenic in laboratory mice and ferrets. The first person who was confirmed to be infected with H10N5 died in China on January 27 2024, but this patient was also suffering from seasonal flu (H3N2). They had been exposed to live poultry which also tested positive for H10N5.
Species already threatened with extinction are among those which have died due to bird flu in the past three years. The first deaths from the virus in mainland Antarctica have just been confirmed in skuas, highlighting a looming threat to penguin colonies whose eggs and chicks skuas prey on. Humboldt penguins have already been killed by the virus in Chile.

How can we stem this tsunami of H5N1 and other avian influenzas? Completely overhaul poultry production on a global scale. Make farms self-sufficient in rearing eggs and chicks instead of exporting them internationally. The trend towards megafarms containing over a million birds must be stopped in its tracks.
To prevent the worst outcomes for this virus, we must revisit its primary source: the incubator of intensive poultry farms.
Diana Bell does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
genetic pandemic mortality spread deaths south korea south america europe uk chinaUncategorized
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
NY Fed Finds Medium, Long-Term Inflation Expectations Jump Amid Surge In Stock Market Optimism
One month after the inflation outlook tracked…
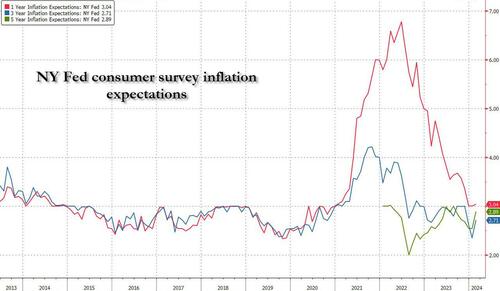
One month after the inflation outlook tracked by the NY Fed Consumer Survey extended their late 2023 slide, with 3Y inflation expectations in January sliding to a record low 2.4% (from 2.6% in December), even as 1 and 5Y inflation forecasts remained flat, moments ago the NY Fed reported that in February there was a sharp rebound in longer-term inflation expectations, rising to 2.7% from 2.4% at the three-year ahead horizon, and jumping to 2.9% from 2.5% at the five-year ahead horizon, while the 1Y inflation outlook was flat for the 3rd month in a row, stuck at 3.0%.
The increases in both the three-year ahead and five-year ahead measures were most pronounced for respondents with at most high school degrees (in other words, the "really smart folks" are expecting deflation soon). The survey’s measure of disagreement across respondents (the difference between the 75th and 25th percentile of inflation expectations) decreased at all horizons, while the median inflation uncertainty—or the uncertainty expressed regarding future inflation outcomes—declined at the one- and three-year ahead horizons and remained unchanged at the five-year ahead horizon.
Going down the survey, we find that the median year-ahead expected price changes increased by 0.1 percentage point to 4.3% for gas; decreased by 1.8 percentage points to 6.8% for the cost of medical care (its lowest reading since September 2020); decreased by 0.1 percentage point to 5.8% for the cost of a college education; and surprisingly decreased by 0.3 percentage point for rent to 6.1% (its lowest reading since December 2020), and remained flat for food at 4.9%.
We find the rent expectations surprising because it is happening just asking rents are rising across the country.
At the same time as consumers erroneously saw sharply lower rents, median home price growth expectations remained unchanged for the fifth consecutive month at 3.0%.
Turning to the labor market, the survey found that the average perceived likelihood of voluntary and involuntary job separations increased, while the perceived likelihood of finding a job (in the event of a job loss) declined. "The mean probability of leaving one’s job voluntarily in the next 12 months also increased, by 1.8 percentage points to 19.5%."
Mean unemployment expectations - or the mean probability that the U.S. unemployment rate will be higher one year from now - decreased by 1.1 percentage points to 36.1%, the lowest reading since February 2022. Additionally, the median one-year-ahead expected earnings growth was unchanged at 2.8%, remaining slightly below its 12-month trailing average of 2.9%.
Turning to household finance, we find the following:
- The median expected growth in household income remained unchanged at 3.1%. The series has been moving within a narrow range of 2.9% to 3.3% since January 2023, and remains above the February 2020 pre-pandemic level of 2.7%.
- Median household spending growth expectations increased by 0.2 percentage point to 5.2%. The increase was driven by respondents with a high school degree or less.
- Median year-ahead expected growth in government debt increased to 9.3% from 8.9%.
- The mean perceived probability that the average interest rate on saving accounts will be higher in 12 months increased by 0.6 percentage point to 26.1%, remaining below its 12-month trailing average of 30%.
- Perceptions about households’ current financial situations deteriorated somewhat with fewer respondents reporting being better off than a year ago. Year-ahead expectations also deteriorated marginally with a smaller share of respondents expecting to be better off and a slightly larger share of respondents expecting to be worse off a year from now.
- The mean perceived probability that U.S. stock prices will be higher 12 months from now increased by 1.4 percentage point to 38.9%.
- At the same time, perceptions and expectations about credit access turned less optimistic: "Perceptions of credit access compared to a year ago deteriorated with a larger share of respondents reporting tighter conditions and a smaller share reporting looser conditions compared to a year ago."
Also, a smaller percentage of consumers, 11.45% vs 12.14% in prior month, expect to not be able to make minimum debt payment over the next three months
Last, and perhaps most humorous, is the now traditional cognitive dissonance one observes with these polls, because at a time when long-term inflation expectations jumped, which clearly suggests that financial conditions will need to be tightened, the number of respondents expecting higher stock prices one year from today jumped to the highest since November 2021... which incidentally is just when the market topped out during the last cycle before suffering a painful bear market.
Spread & Containment
A major cruise line is testing a monthly subscription service
The Cruise Scarlet Summer Season Pass was designed with remote workers in mind.

While going on a cruise once meant disconnecting from the world when between ports because any WiFi available aboard was glitchy and expensive, advances in technology over the last decade have enabled millions to not only stay in touch with home but even work remotely.
With such remote workers and digital nomads in mind, Virgin Voyages has designed a monthly pass that gives those who want to work from the seas a WFH setup on its Scarlet Lady ship — while the latter acronym usually means "work from home," the cruise line is advertising as "work from the helm.”
Related: Royal Caribbean shares a warning with passengers
"Inspired by Richard Branson's belief and track record that brilliant work is best paired with a hearty dose of fun, we're welcoming Sailors on board Scarlet Lady for a full month to help them achieve that perfect work-life balance," Virgin Voyages said in announcing its new promotion. "Take a vacation away from your monotonous work-from-home set up (sorry, but…not sorry) and start taking calls from your private balcony overlooking the Mediterranean sea."
Shutterstock
This is how much it'll cost you to work from a cruise ship for a month
While the single most important feature for successful work at sea — WiFi — is already available for free on Virgin cruises, the new Scarlet Summer Season Pass includes a faster connection, a $10 daily coffee credit, access to a private rooftop, and other member-only areas as well as wash and fold laundry service that Virgin advertises as a perk that will allow one to concentrate on work
More Travel:
- A new travel term is taking over the internet (and reaching airlines and hotels)
- The 10 best airline stocks to buy now
- Airlines see a new kind of traveler at the front of the plane
The pass starts at $9,990 for a two-guest cabin and is available for four monthlong cruises departing in June, July, August, and September — each departs from ports such as Barcelona, Marseille, and Palma de Mallorca and spends four weeks touring around the Mediterranean.
Longer cruises are becoming more common, here's why
The new pass is essentially a version of an upgraded cruise package with additional perks but is specifically tailored to those who plan on working from the ship as an opportunity to market to them.
"Stay connected to your work with the fastest at-sea internet in the biz when you want and log-off to let the exquisite landscape of the Mediterranean inspire you when you need," reads the promotional material for the pass.
Amid the rise of remote work post-pandemic, cruise lines have been seeing growing interest in longer journeys in which many of the passengers not just vacation in the traditional sense but work from a mobile office.
In 2023, Turkish cruise line operator Miray even started selling cabins on a three-year tour around the world but the endeavor hit the rocks after one of the engineers declared the MV Gemini ship the company planned to use for the journey "unseaworthy" and the cruise ship line dealt with a PR scandal that ultimately sank the project before it could take off.
While three years at sea would have set a record as the longest cruise journey on the market, companies such as Royal Caribbean (RCL) (both with its namesake brand and its Celebrity Cruises line) have been offering increasingly long cruises that serve as many people’s temporary homes and cross through multiple continents.
stocks pandemic testing-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex











































