Spread & Containment
Greenback Trades Higher in Asia before Momentum Stalls in Europe
Overview: The attack on Saudi Arabia’s largest crude terminal reverberated through the capital markets, where sentiment was already fragile, despite the lack of disruption. Brent rose to nearly $71.40, and April WTI to almost $68 extended their gains…

Overview: The attack on Saudi Arabia's largest crude terminal reverberated through the capital markets, where sentiment was already fragile, despite the lack of disruption. Brent rose to nearly $71.40, and April WTI to almost $68 extended their gains for the fourth consecutive session before being fully unwound. Most equity markets fell in the Asia Pacific region, lead by more than a 2% decline in China and nearly as much in Hong Kong. Australia and Singapore bucked the regional trend. Europe's Dow Jones Stoxx 600 is rising for the first time in three days, led by financials and industrials. Utilities and consumer staples are drags. US futures are 0.7%-1.6% lower. The US 10-year yield is knocking on 1.60%, while core European yields are slightly firmer. Peripheral yields are a little softer. The market anticipates that ECB data will show stepped-up purchases last week. The US dollar is riding higher against nearly all the world's currencies today. Among the majors, the Antipodean and Swiss franc are off 0.5%-0.75% to lead the move, and the euro slide extended for a fourth session, during which time it has slipped more than two cents to around $1.1865. The JP Morgan Emerging Market Currency Index is also off for the fourth session and is at its lowest since before last November's US election. Gold began the session higher and tested $1714 before being sold back toward the pre-weekend lows below $1690.
Asia Pacific
Japan's January current account surplus was about half of the economists had expected (JPY647 bln vs. JPY1.253 trillion. The main culprit was the swing in the balance-of-payments trade balance from a JPY695 bln surplus in December to a JPY130 bln deficit in January. Japan also reports some country-specific bond flow data with its current account figures. The notable development was that Japanese investors reduced their buying of European bonds. They bought the least amount of Gilts since at least 2005 and were net sellers of German Bunds. There was a sharp decline in the purchases of Italian and French bonds. Separately, Japanese investors bought the least Australian bonds since last February. Also, of interest, China sold about JPY808.5 bln of Japanese bonds, the most in seven years.
A year ago, China's economy saw the worst of the economic hit from the pandemic. The year-over-year comparison is distorted by the experience. January-February 2020, China's exports fell 17.4%. Here in 2021, they are up 60%, and imports rose by 22%. The trade surplus for the first two months of this year is a whopping $103.25 bln, and the US accounts for nearly half (~$51.3 bln). Separately, citing pests, Beijing announced a ban on imports of pineapples from Taiwan. It usually buys the bulk of Taiwan's crop. For nearly two decades, China has been a strong buyer of Taiwan's agriculture exports. Given Beijing's penchant for using trade as a way to express its disapproval, the situation will be closely monitored.
The divergence of Australia's trade policy from its foreign policy remains stark. Beijing says it has been wronged in 14 ways by Canberra, to which it can add a 15th way. Citing human rights complaints, an Australian broadcaster has suspended China Global Television Network (CGTN). On a separate front, Prime Minister Morrison appeared to be more empathic than some in the media to Italy's (and EU's) decision to block the export of about 250k vaccines to Australia, recognizing that the contagion is hitting Italy harder than his country. The lesson that Morrison and others will likely take away from the episode is the need to have mRNA manufacturing capacity local, which strike us as part of the broader rise of economic nationalism.
The dollar is firm against the yen but is holding a tough below the pre-weekend high near JPY108.65. It has spent hardly any time below JPY108.30. The intraday momentum indicators suggest a consolidative North American session. Last week's price action showed rising yields trumped equity weakness as the driver of the yen. The Australian dollar is trading inside the pre-weekend range (~$0.7620-$0.7730). Here too, the intraday technical indicators suggest a sideways session is likely in North America today. The PBOC set the dollar's reference rate at CNY6.4795. The gap between the fixing and the median forecast in Bloomberg's survey was among the largest in recent weeks. The dollar has finally risen above the highs set in the first trading session of the year (~CNY6.5150) and made it to almost CNY6.5315 before steadying. Despite tightening financial conditions, the PBOC refrained from injecting extra liquidity into the banking system, and money market rates jumped. News that China's official reserves slipped a bit less than expected to $3.205 trillion from $3.211 trillion was taken in stride. There is no doubt that the currency is well managed, though not through an official intervention.
Europe
The US and the EC agreed to a four-month suspension of tariffs over the Airbus-Boeing dispute that resulted. A week earlier, the US and UK struck a similar agreement. This is ultimately a positive development, and there is every reason to expect a formal resolution. Both sides have stopped the offensive behavior. However, a new front is going open shortly. A Chinese company (of which Huawei is the third-largest owner) is laying a 7500-mile underwater cable (called "Peace") that will connect Europe and China. Huawei will also be providing transmission gear and equipment for landing stations. US companies own and operate nearly all of the intercontinental internet and telephone cables. A report estimated that Peace in one second could send the data to stream 90k hours of Netflix. The Nord Stream 2 pipeline brings Russian gas to Germany, bypassing Ukraine. The Chinese cable that first goes overland to Pakistan will terminate in France.
Ahead of the aggregate eurozone's January industrial production report later this week, German and Spanish national figures were released today. Bloomberg's survey found a median forecast for a 0.4% decline in Germany, and instead, industrial output tumbled by 2.5%. The sting was only partly offset by the strong upward revision in the December series to show a 1.9% gain instead of the initial flat report. Spain missed as well, and the December series was revised lower. Industrial production fell 0.7% in January, while Bloomberg's median was for a 0.5% decline. The December gain of 1.1% was revised to 0.8%.
The euro peaked in the middle of last week, a little above $1.2110. It reached $1.1865 today. The 200-day moving average is around $1.1825, while the $1.1890 area marked the (61.8%) retracement of the euro post-US election/vaccine rally. The immediate selling pressure appears to have been satiated in the Europe morning, but it may take a move above $1.1900-$1.1915 to stabilize the technical tone. Sterling has held in better and remains above the pre-weekend low (~$1.3780). While the re-opening of English schools is hopeful, sterling needs to move above $1.39 to boost confidence.
America
News that the private sector jobs surged by 465k last month is welcome, but it is not a game-changer. Fed officials are in the quiet period ahead of next week's FOMC meeting, preventing confirmation. Given Fed Chairman Powell's comments last week, and to be fair, there does not seem to be a dissenting camp at the moment, it seems quite clear that it will take more than one month's report to change the central view. The idea of a possible "Operation Twist" is coming from pundits, not Fed officials.
Despite buying $80 of Treasuries a month, Fed officials still think that yields contain information. It is saying that investors are preparing for a strong recovery from the pandemic. The US Treasury is selling $120 bln of coupons this week, and the corporate issuance calendar is busy too. The exemption of Treasuries and excess reserves (which are created by the Fed when buys Treasuries and Agency MBS) that expires at the end of the month is a potential disrupter. The uncertainty alone is not helpful, but the failure to extend could lead to a jump in rates.
The North American economic diary is light to start the week. The final reading US wholesale trade and inventories are not the stuff that moves the market. Nevertheless, the rise in inventories does underscore another source of economic strength. Inventories had been run down, and replenishing them contributes to GDP. The highlight of the week is the February CPI on Wednesday. Higher food and energy prices will likely lift the headline, but the real base effect kicks in with the March reading. Canada features the central bank meeting (Wednesday) and employment data (Friday). The central bank is not expected to change policy, but its confidence in the medium-term outlook is likely stronger. Canada's labor market is expected to recover from January 213k job loss, which was concentrated in part-time positions (full-time employment rose by 12.6k). Mexico reports its February CPI tomorrow. The year-over-year rate is expected to tick up to 3.75% from almost 3.55%. At the end of the week, Mexico reports January industrial production. A small gain is projected.
Initial follow-through selling saw the US dollar slip briefly below CAD1.2625 in early Asia before rebounding to CAD1.2700 by early Europe. The greenback's recovery faltered, and the intraday momentum indicators suggest a heavier tone is likely. Initial support is seen in the CAD1.2640-CAD1.2660 area. The US dollar bottomed in the first half of last week in front of MXN20.50. Ahead of the weekend, it punched above the 200-day moving average (~MXN21.1650) and has kept going today to reach almost MXN21.6360. Here too, it looks like some short-term buying climax was since in late Asian or early European turnover. The first area of support may be near MXN21.40 and then MXN21.20.
Disclaimer
Government
Harvard Medical School Professor Was Fired Over Not Getting COVID Vaccine
Harvard Medical School Professor Was Fired Over Not Getting COVID Vaccine
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A…

Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
A Harvard Medical School professor who refused to get a COVID-19 vaccine has been terminated, according to documents reviewed by The Epoch Times.
Martin Kulldorff, an epidemiologist, was fired by Mass General Brigham in November 2021 over noncompliance with the hospital’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate after his requests for exemptions from the mandate were denied, according to one document. Mr. Kulldorff was also placed on leave by Harvard Medical School (HMS) because his appointment as professor of medicine there “depends upon” holding a position at the hospital, another document stated.
Mr. Kulldorff asked HMS in late 2023 how he could return to his position and was told he was being fired.
“You would need to hold an eligible appointment with a Harvard-affiliated institution for your HMS academic appointment to continue,” Dr. Grace Huang, dean for faculty affairs, told the epidemiologist and biostatistician.
She said the lack of an appointment, combined with college rules that cap leaves of absence at two years, meant he was being terminated.
Mr. Kulldorff disclosed the firing for the first time this month.
“While I can’t comment on the specifics due to employment confidentiality protections that preclude us from doing so, I can confirm that his employment agreement was terminated November 10, 2021,” a spokesperson for Brigham and Women’s Hospital told The Epoch Times via email.
Mass General Brigham granted just 234 exemption requests out of 2,402 received, according to court filings in an ongoing case that alleges discrimination.
The hospital said previously, “We received a number of exemption requests, and each request was carefully considered by a knowledgeable team of reviewers.”
“A lot of other people received exemptions, but I did not,” Mr. Kulldorff told The Epoch Times.
Mr. Kulldorff was originally hired by HMS but switched departments in 2015 to work at the Department of Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, which is part of Mass General Brigham and affiliated with HMS.
“Harvard Medical School has affiliation agreements with several Boston hospitals which it neither owns nor operationally controls,” an HMS spokesperson told The Epoch Times in an email. “Hospital-based faculty, such as Mr. Kulldorff, are employed by one of the affiliates, not by HMS, and require an active hospital appointment to maintain an academic appointment at Harvard Medical School.”
HMS confirmed that some faculty, who are tenured or on the tenure track, do not require hospital appointments.
Natural Immunity
Before the COVID-19 vaccines became available, Mr. Kulldorff contracted COVID-19. He was hospitalized but eventually recovered.
That gave him a form of protection known as natural immunity. According to a number of studies, including papers from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, natural immunity is better than the protection bestowed by vaccines.
Other studies have found that people with natural immunity face a higher risk of problems after vaccination.
Mr. Kulldorff expressed his concerns about receiving a vaccine in his request for a medical exemption, pointing out a lack of data for vaccinating people who suffer from the same issue he does.
“I already had superior infection-acquired immunity; and it was risky to vaccinate me without proper efficacy and safety studies on patients with my type of immune deficiency,” Mr. Kulldorff wrote in an essay.
In his request for a religious exemption, he highlighted an Israel study that was among the first to compare protection after infection to protection after vaccination. Researchers found that the vaccinated had less protection than the naturally immune.
“Having had COVID disease, I have stronger longer lasting immunity than those vaccinated (Gazit et al). Lacking scientific rationale, vaccine mandates are religious dogma, and I request a religious exemption from COVID vaccination,” he wrote.
Both requests were denied.
Mr. Kulldorff is still unvaccinated.
“I had COVID. I had it badly. So I have infection-acquired immunity. So I don’t need the vaccine,” he told The Epoch Times.
Dissenting Voice
Mr. Kulldorff has been a prominent dissenting voice during the COVID-19 pandemic, countering messaging from the government and many doctors that the COVID-19 vaccines were needed, regardless of prior infection.
He spoke out in an op-ed in April 2021, for instance, against requiring people to provide proof of vaccination to attend shows, go to school, and visit restaurants.
“The idea that everybody needs to be vaccinated is as scientifically baseless as the idea that nobody does. Covid vaccines are essential for older, high-risk people and their caretakers and advisable for many others. But those who’ve been infected are already immune,” he wrote at the time.
Mr. Kulldorff later co-authored the Great Barrington Declaration, which called for focused protection of people at high risk while removing restrictions for younger, healthy people.
Harsh restrictions such as school closures “will cause irreparable damage” if not lifted, the declaration stated.
The declaration drew criticism from Dr. Anthony Fauci, head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and Dr. Rochelle Walensky, who became the head of the CDC, among others.
In a competing document, Dr. Walensky and others said that “relying upon immunity from natural infections for COVID-19 is flawed” and that “uncontrolled transmission in younger people risks significant morbidity(3) and mortality across the whole population.”
“Those who are pushing these vaccine mandates and vaccine passports—vaccine fanatics, I would call them—to me they have done much more damage during this one year than the anti-vaxxers have done in two decades,” Mr. Kulldorff later said in an EpochTV interview. “I would even say that these vaccine fanatics, they are the biggest anti-vaxxers that we have right now. They’re doing so much more damage to vaccine confidence than anybody else.”
Surveys indicate that people have less trust now in the CDC and other health institutions than before the pandemic, and data from the CDC and elsewhere show that fewer people are receiving the new COVID-19 vaccines and other shots.
Support
The disclosure that Mr. Kulldorff was fired drew criticism of Harvard and support for Mr. Kulldorff.
The termination “is a massive and incomprehensible injustice,” Dr. Aaron Kheriaty, an ethics expert who was fired from the University of California–Irvine School of Medicine for not getting a COVID-19 vaccine because he had natural immunity, said on X.
“The academy is full of people who declined vaccines—mostly with dubious exemptions—and yet Harvard fires the one professor who happens to speak out against government policies.” Dr. Vinay Prasad, an epidemiologist at the University of California–San Francisco, wrote in a blog post. “It looks like Harvard has weaponized its policies and selectively enforces them.”
A petition to reinstate Mr. Kulldorff has garnered more than 1,800 signatures.
Some other doctors said the decision to let Mr. Kulldorff go was correct.
“Actions have consequence,” Dr. Alastair McAlpine, a Canadian doctor, wrote on X. He said Mr. Kulldorff had “publicly undermine[d] public health.”
International
“Extreme Events”: US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In “Large Excess Over Trend”
"Extreme Events": US Cancer Deaths Spiked In 2021 And 2022 In "Large Excess Over Trend"
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021…
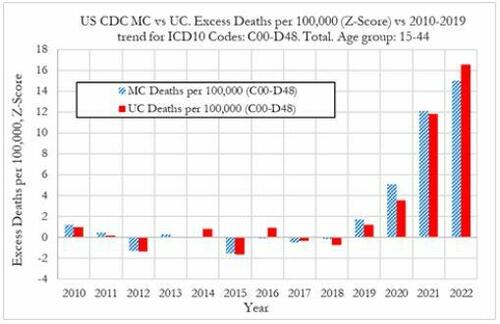
Cancer deaths in the United States spiked in 2021 and 2022 among 15-44 year-olds "in large excess over trend," marking jumps of 5.6% and 7.9% respectively vs. a rise of 1.7% in 2020, according to a new preprint study from deep-dive research firm, Phinance Technologies.

Extreme Events
The report, which relies on data from the CDC, paints a troubling picture.
"We show a rise in excess mortality from neoplasms reported as underlying cause of death, which started in 2020 (1.7%) and accelerated substantially in 2021 (5.6%) and 2022 (7.9%). The increase in excess mortality in both 2021 (Z-score of 11.8) and 2022 (Z-score of 16.5) are highly statistically significant (extreme events)," according to the authors.
That said, co-author, David Wiseman, PhD (who has 86 publications to his name), leaves the cause an open question - suggesting it could either be a "novel phenomenon," Covid-19, or the Covid-19 vaccine.
Cancer deaths in US in 2021 & 2022 in large excess over trend for 15-44 year-olds as extreme events. A novel phenomenon? C19? lockdowns? C19 vaccines? Honored to participate in this work. #CDC where are you? @DowdEdwardhttps://t.co/iUV5oQiWCW pic.twitter.com/uytzaIvvor
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 12, 2024
"The results indicate that from 2021 a novel phenomenon leading to increased neoplasm deaths appears to be present in individuals aged 15 to 44 in the US," reads the report.
The authors suggest that the cause may be the result of "an unexpected rise in the incidence of rapidly growing fatal cancers," and/or "a reduction in survival in existing cancer cases."
They also address the possibility that "access to utilization of cancer screening and treatment" may be a factor - the notion that pandemic-era lockdowns resulted in fewer visits to the doctor. Also noted is that "Cancers tend to be slowly-developing diseases with remarkably stable death rates and only small variations over time," which makes "any temporal association between a possible explanatory factor (such as COVID-19, the novel COVID-19 vaccines, or other factor(s)) difficult to establish."
That said, a ZeroHedge review of the CDC data reveals that it does not provide information on duration of illness prior to death - so while it's not mentioned in the preprint, it can't rule out so-called 'turbo cancers' - reportedly rapidly developing cancers, the existence of which has been largely anecdotal (and widely refuted by the usual suspects).
While the Phinance report is extremely careful not to draw conclusions, researcher "Ethical Skeptic" kicked the barn door open in a Thursday post on X - showing a strong correlation between "cancer incidence & mortality" coinciding with the rollout of the Covid mRNA vaccine.
The argument is over.
— Ethical Skeptic ☀ (@EthicalSkeptic) March 14, 2024
The Covid mRNA Vaxx has cause a sizeable 2021 inflection, and now novel-trend elevation in terms of both cancer incidence & mortality.
Now you know who the liars were all along.
????Incidence = 14.8% excess
????UCoD Mortality = 5.3% excess (lags Incidence) pic.twitter.com/uwN9GMrHl1
Phinance principal Ed Dowd commented on the post, noting that "Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry!"
????Indeed it is…Cancer is suddenly an accelerating growth industry! @EthicalSkeptic provides a chart below showing US Cancer treatment in constant dollars with a current growth rate of 14.8% (6.3% New CAGR) versus long term trend of 1.78% CAGR or $33.8 billion in excess cancer… https://t.co/RIn4R2YZZ7
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Continued:
As a former portfolio manager of of a $14 billion Large Cap Growth Equity portfolio I can definitively say Cancer treatments and the Disabilities have become growth industries that both have inflection points coincidental to the mRNA vaccine rollouts in 2021.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 14, 2024
Chart 1 from… pic.twitter.com/TCt4X1plnM
Bottom line - hard data is showing alarming trends, which the CDC and other agencies have a requirement to explore and answer truthfully - and people are asking #WhereIsTheCDC.
We aren't holding our breath.
Experts are sounding the alarm on a spike in cancer diagnosis worldwide. It is still a mystery. @DowdEdward from Phinance Technologies has also been sounding the alarm for months.
— dr.ir. Carla Peeters (@CarlaPeeters3) March 15, 2024
We are facing a dramatic degradation of the human immune system https://t.co/CPnwP3Oj9G
Wiseman, meanwhile, points out that Pfizer and several other companies are making "significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID."
Pfizer among several companies making significant investments in cancer drugs, post COVID. @DowdEdward @Kevin_McKernan @JesslovesMJK @niki_kyrylenko https://t.co/nefEZYLW1o https://t.co/r505Sbbcq4
— David Wiseman PhD, MRPharmS (@AdhesionsOrg) March 15, 2024
Phinance
We've featured several of Phinance's self-funded deep dives into pandemic data that nobody else is doing. If you'd like to support them, click here.
List of our projects following disturbing tends in deaths, disabilities and absences.
— Edward Dowd (@DowdEdward) March 16, 2024
Link to projects at bottom.
✅ V-Damage Project
✅ Excess Mortality Project
✅ US Disabilities Project
✅ US BLS Absence rates Project
✅ US Cause of Death Project
✅ UK Cause of Death…
Government
“I Can’t Even Save”: Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
"I Can’t Even Save": Americans Are Getting Absolutely Crushed Under Enormous Debt Load
While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great…

While Joe Biden insists that Americans are doing great - suggesting in his State of the Union Address last week that "our economy is the envy of the world," Americans are being absolutely crushed by inflation (which the Biden admin blames on 'shrinkflation' and 'corporate greed'), and of course - crippling debt.
The signs are obvious. Last week we noted that banks' charge-offs are accelerating, and are now above pre-pandemic levels.
...and leading this increase are credit card loans - with delinquencies that haven't been this high since Q3 2011.
On top of that, while credit cards and nonfarm, nonresidential commercial real estate loans drove the quarterly increase in the noncurrent rate, residential mortgages drove the quarterly increase in the share of loans 30-89 days past due.
And while Biden and crew can spin all they want, an average of polls from RealClear Politics shows that just 40% of people approve of Biden's handling of the economy.
Crushed
On Friday, Bloomberg dug deeper into the effects of Biden's "envious" economy on Americans - specifically, how massive debt loads (credit cards and auto loans especially) are absolutely crushing people.
Two years after the Federal Reserve began hiking interest rates to tame prices, delinquency rates on credit cards and auto loans are the highest in more than a decade. For the first time on record, interest payments on those and other non-mortgage debts are as big a financial burden for US households as mortgage interest payments.
According to the report, this presents a difficult reality for millions of consumers who drive the US economy - "The era of high borrowing costs — however necessary to slow price increases — has a sting of its own that many families may feel for years to come, especially the ones that haven’t locked in cheap home loans."
The Fed, meanwhile, doesn't appear poised to cut rates until later this year.
According to a February paper from IMF and Harvard, the recent high cost of borrowing - something which isn't reflected in inflation figures, is at the heart of lackluster consumer sentiment despite inflation having moderated and a job market which has recovered (thanks to job gains almost entirely enjoyed by immigrants).
In short, the debt burden has made life under President Biden a constant struggle throughout America.
"I’m making the most money I've ever made, and I’m still living paycheck to paycheck," 40-year-old Denver resident Nikki Cimino told Bloomberg. Cimino is carrying a monthly mortgage of $1,650, and has $4,000 in credit card debt following a 2020 divorce.

"There's this wild disconnect between what people are experiencing and what economists are experiencing."
CBS: Do you attribute the inflation crisis to the pandemic or Biden?
— RNC Research (@RNCResearch) March 15, 2024
WISCONSIN VOTER: "It's been YEARS now since the pandemic — I'm not buying that anymore. At first I did; I'm not buying that anymore because yogurt is STILL going up in price!" pic.twitter.com/apahb65scB
What's more, according to Wells Fargo, families have taken on debt at a comparatively fast rate - no doubt to sustain the same lifestyle as low rates and pandemic-era stimmies provided. In fact, it only took four years for households to set a record new debt level after paying down borrowings in 2021 when interest rates were near zero.
Meanwhile, that increased debt load is exacerbated by credit card interest rates that have climbed to a record 22%, according to the Fed.
[P]art of the reason some Americans were able to take on a substantial load of non-mortgage debt is because they’d locked in home loans at ultra-low rates, leaving room on their balance sheets for other types of borrowing. The effective rate of interest on US mortgage debt was just 3.8% at the end of last year.
Yet the loans and interest payments can be a significant strain that shapes families’ spending choices. -Bloomberg
And of course, the highest-interest debt (credit cards) is hurting lower-income households the most, as tends to be the case.
The lowest earners also understandably had the biggest increase in credit card delinquencies.
"Many consumers are levered to the hilt — maxed out on debt and barely keeping their heads above water," Allan Schweitzer, a portfolio manager at credit-focused investment firm Beach Point Capital Management told Bloomberg. "They can dog paddle, if you will, but any uptick in unemployment or worsening of the economy could drive a pretty significant spike in defaults."
"We had more money when Trump was president," said Denise Nierzwicki, 69. She and her 72-year-old husband Paul have around $20,000 in debt spread across multiple cards - all of which have interest rates above 20%.

Photographer: Jon Cherry/Bloomberg
During the pandemic, Denise lost her job and a business deal for a bar they owned in their hometown of Lexington, Kentucky. While they applied for Social Security to ease the pain, Denise is now working 50 hours a week at a restaurant. Despite this, they're barely scraping enough money together to service their debt.
The couple blames Biden for what they see as a gloomy economy and plans to vote for the Republican candidate in November. Denise routinely voted for Democrats up until about 2010, when she grew dissatisfied with Barack Obama’s economic stances, she said. Now, she supports Donald Trump because he lowered taxes and because of his policies on immigration. -Bloomberg
Meanwhile there's student loans - which are not able to be discharged in bankruptcy.
"I can't even save, I don't have a savings account," said 29-year-old in Columbus, Ohio resident Brittany Walling - who has around $80,000 in federal student loans, $20,000 in private debt from her undergraduate and graduate degrees, and $6,000 in credit card debt she accumulated over a six-month stretch in 2022 while she was unemployed.
"I just know that a lot of people are struggling, and things need to change," she told the outlet.
The only silver lining of note, according to Bloomberg, is that broad wage gains resulting in large paychecks has made it easier for people to throw money at credit card bills.
Yet, according to Wells Fargo economist Shannon Grein, "As rates rose in 2023, we avoided a slowdown due to spending that was very much tied to easy access to credit ... Now, credit has become harder to come by and more expensive."
According to Grein, the change has posed "a significant headwind to consumption."
Then there's the election
"Maybe the Fed is done hiking, but as long as rates stay on hold, you still have a passive tightening effect flowing down to the consumer and being exerted on the economy," she continued. "Those household dynamics are going to be a factor in the election this year."
Meanwhile, swing-state voters in a February Bloomberg/Morning Consult poll said they trust Trump more than Biden on interest rates and personal debt.
Reverberations
These 'headwinds' have M3 Partners' Moshin Meghji concerned.
"Any tightening there immediately hits the top line of companies," he said, noting that for heavily indebted companies that took on debt during years of easy borrowing, "there's no easy fix."
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Spread & Containment4 days ago
Spread & Containment4 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex

































