Government
Global Stocks Plunge On Bank, Election, Virus Fears; Treasuries, Dollar Spike
Global Stocks Plunge On Bank, Election, Virus Fears; Treasuries, Dollar Spike
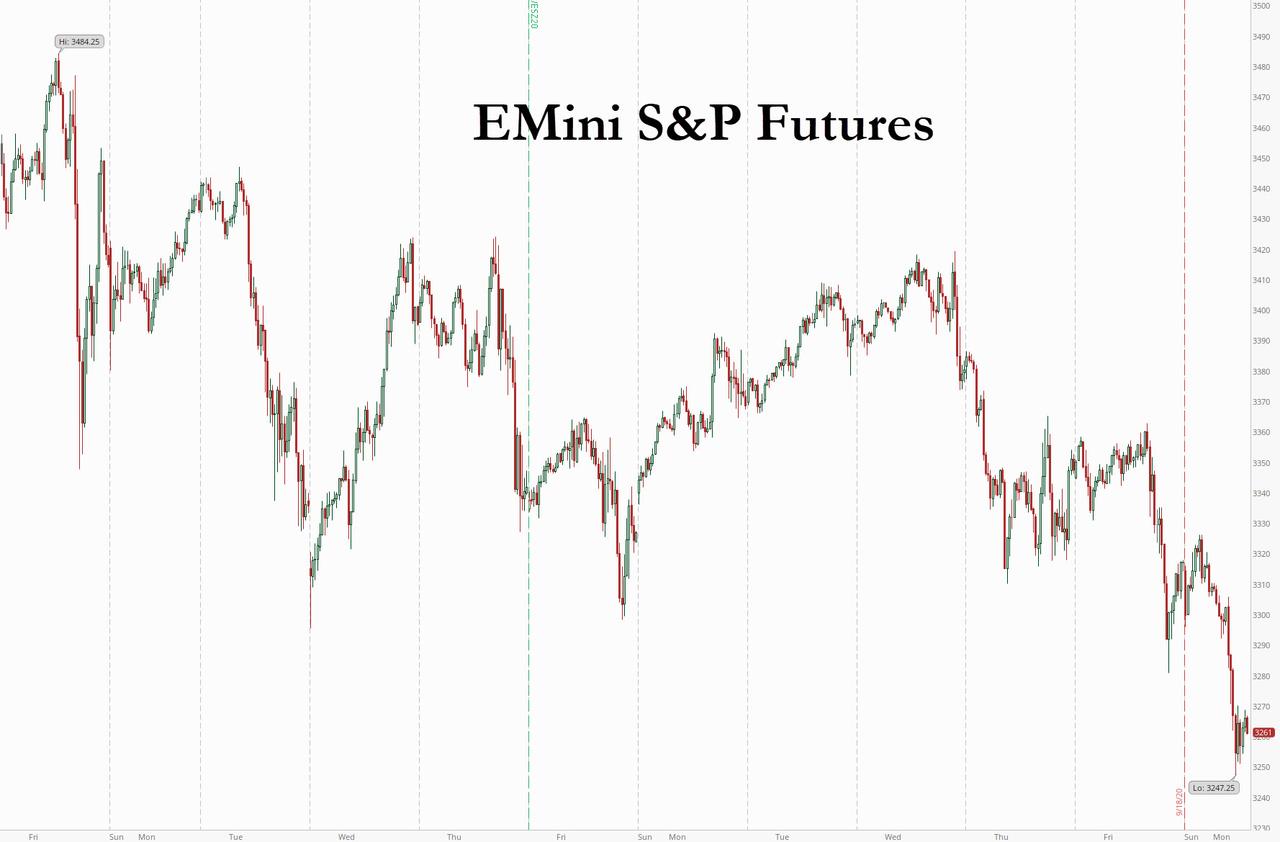
Global markets tumbled on Monday, as S&P futures slid below 3,300 after failing to hold 50DMA support on Friday, and with European stocks falling the most since July as investors worried about renewed covid lockdowns across European countries and a report detailing suspicious transactions at international banks, with a lack of U.S. stimulus and concerns about how the death of Ruth Bader Ginsburg would impact what are already set to be extremely contested elections also hit sentiment.
U.S. stock index futures dropped 1.8% on Monday hit by bank stocks following media reports that several global banks moved sums of allegedly illicit funds over nearly two decades. Shares in JPMorgan Chase and Bank of New York Mellon Corp fell 4% and 3.3%, respectively, after a after a report by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists that said lenders “kept profiting from powerful and dangerous players” in the past two decades even after the U.S. imposed penalties. HSBC Holdings Plc fell to the lowest since 1995 and European bank shares slumped (more here).
Shares of airlines, hotels and cruise operators led declines in premarket trading, tracking their European peers as the UK signaled the possibility of a second national lockdown. Marriott International, Hilton Worldwide and Hyatt Hotels Corp dropped between 1.5% and 3.6%, while casino operators Wynn Resorts, MGM Resorts International and Las Vegas Sands Corp shed between 2.7% and 6.0%. Tech giants including Apple, Facebook and Amazon.com which had dominated Wall Street's rally since April, slid between 1.5% and 2.6% in early deals.
Nikola crashed 27.9% after its founder Trevor Milton stepped down as executive chairman, as the U.S. electric-truck maker battles allegations from a short-seller that it misled investors and automakers. General Motors which took an 11% stake in Nikola for about $2 billion earlier this month, slipped 3.7%.
Another round of business restrictions would also threaten a nascent recovery in the wider economy, analysts said, and could spark a flight from equities. The first round of lockdowns in March had led the benchmark S&P 500 to suffer its worst monthly decline since the global financial crisis.
"The market remains concerned about the broader risk emulating from the U.S: Covid, the Supreme Court fight and the upcoming presidential elections,” said Peter Rosenstreich, head of market strategy at Swissquote Bank SA. “With U.S. tech stocks looking weak, the need to jump right into U.S. assets feels less critical."
The MSCI world equity index was down 0.5%. European indexes opened lower, with the pan-European STOXX 600 down 1.7% at its lowest in nearly two weeks. London's FTSE 100 was at a two-week low, down 2.4% and Germany's DAX fell 2%, led by banking shares which slid after a media report on how several global banks moved large sums of allegedly illicit funds over nearly two decades. HSBC shares tumbled to a 25-year low in Hong Kong.
Investors have also turned more cautious about Europe following a sharp uptick in new COVID-19 cases. European countries including Denmark, Greece and Spain have introduced new restrictions on activity. According to Reuters, Britain is considering a second national lockdown as new cases rise by at least 6,000 per day. Germany’s health minister said the rising new infections in countries like France, Austria and the Netherlands is worrying. Investors will be looking ahead to flash PMI data on Wednesday for the first hints of how economies have fared in September.
"Concerns are rising that the summer recovery is probably as good as it gets when it comes to the recent rebound in economic activity," wrote Michael Hewson, chief market analyst at CMC Markets UK. "This reality combined with the growing realisation that a vaccine remains many months away, despite President (Donald) Trump’s claims to the contrary, has made investors increasingly nervous, as we head into an autumn that could see lockdowns reimposed."
Earlier in the session, Asian stocks fell, led by materials and finance, after rising in the last session. The Shanghai Composite Index retreated 0.6%, with Sanxiang Advanced and Shandong Shida posting the biggest slides.
Emerging-market stocks and currencies headed for their biggest declines this month as surging coronavirus cases and uncertainty about additional US fiscal support dented demand for risky assets. The Mexican peso and South African rand led the retreat among peers as the U.S. political battle over who will be the next Supreme Court justice - following the death of Ruth Bader Ginsburg six weeks before Election Day - also weighed on sentiment. South Africa’s stock market was the worst performer, with the main benchmark headed for its longest losing streak since May 2019. The average spread on developing-nation dollar debt widened by 2 basis points.
Seven members of the Fed will speak this week - including chairman Jerome Powell appearing before Congressional committees - so investors will be looking for hints to determine the dollar’s direction.
In FX, the Bloomberg Dollar Spot Index reversed early losses and extended Friday’s advance to rise against all Group-of-10 peers apart from the safe-haven Japanese yen which was in its sixth consecutive session of gains versus the dollar, up around 0.4% at 104.185. Japan has public holidays on Monday and Tuesday this week, meaning volumes are thin in Asian trading. The euro dipped against the dollar, sliding to $1.1791 while the safe Swiss franc rose against both the dollar and euro.
The yuan headed for a third straight daily drop, the longest slide since July, as the greenback advanced. The onshore yuan slipped 0.14% to 6.7793 a dollar as of 5:53 p.m. in Shanghai after earlier rising as much as 0.2%. A measure of the dollar’s strength rose in the afternoon as risk appetite took a hit on concern that the climbing number of virus cases across Europe could lead to travel restrictions and cripple an economic recovery. Despite the retreat over past few days, the onshore yuan has surged 4.3% in the third quarter, on pace for the best performance on record. The rally has come as the greenback is set for its weakest quarter in a decade and amid investor optimism over China economy.
The Turkish lira continued to plumb record lows with Moody's adding more fuel to the fire warning that the country has almost depleted its buffers against a Balance of Payments crisis.
In rates, Treasuries jumped after risk sentiment deteriorated in global markets. Yields were lower by 5.5bp across long-end of the curve, flattening 2s10s, 5s30s by 3.1bp and 3.5bp; 10-year yields richer by 3.8bp at 0.655%. Treasuries bull flatten from London open after cash markets closed in Asia for Japan holiday. Risk-off backdrop supports long-end of the curve with S&P e-minis lower by 1.6% and Estoxx 50 dropping 3% over European morning session. U.S. 2-, 5-, 7-year sales due this week for comb. $155b, while Fed chair Powell is due to speak three times. In Europe, the benchmark 10-year German bund yield was down 2 basis points at -0.507% with most high-rated euro zone government bond yields down by a similar amount. The European Central Bank will review how long its emergency pandemic bond-purchase scheme should go on, the Financial Times reported. The European Council meets in a summit on Thursday and Friday this week.
Elsewhere, oil prices fell, with Brent crude down 1.8% at $42.39 a barrel while WTI was down 1.9% at $40.34 a barrel. Gold prices slumped, hit by the rising dollar, with spot gold down to $1,931 per ounce at 730am ET>
Data include the Chicago Fed National Activity Index. No major earnings are expected.
Market Snapshot
- S&P 500 futures down 1.8% to 3,262.75
- STOXX Europe 600 down 2.2% to 360.69
- MXAP down 0.6% to 172.88
- MXAPJ down 1% to 563.47
- Nikkei up 0.2% to 23,360.30
- Topix up 0.5% to 1,646.42
- Hang Seng Index down 2.1% to 23,950.69
- Shanghai Composite down 0.6% to 3,316.94
- Sensex down 0.9% to 38,482.09
- Australia S&P/ASX 200 down 0.7% to 5,822.62
- Kospi down 1% to 2,389.39
- Brent futures down 2% to $42.29/bbl
- German 10Y yield fell 2.6 bps to -0.511%
- Euro down 0.3% to $1.1807
- Italian 10Y yield rose 0.7 bps to 0.756%
- Spanish 10Y yield fell 0.2 bps to 0.283%
- Gold spot down 0.5% to $1,940.89
- U.S. Dollar Index up 0.3% to 93.19
Top Overnight News
- U.S. deaths related to Covid-19 approached 200,000 and the nation’s new cases rose in line with a one-week average. Former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb said he expects the U.S. to experience “at least one more cycle” of the virus in the fall and winter
- The dollar’s weakest quarter in a decade may get even worse as investors respond to the effects that massive American equity-market gains have had on the composition of their portfolios
- The European Union will unleash as many green bonds as the world issued last year, testing the level of investor interest in financing a shift toward cleaner economies
- Democratic presidential nominee Joe Biden blasted Republican efforts to speed through a replacement for the late Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg on the Supreme Court, warning that such a process would “inflict irreversible damage” on the country
- Britain is at a “critical point” in the coronavirus pandemic, Prime Minister Boris Johnson will be told on Monday, as concern mounts that a second lockdown may be needed to stop the renewed spread of the disease.
- The European Central Bank has launched a review of its pandemic bond-buying program to consider how long it should continue and whether its exceptional flexibility should be extended to older programs, the Financial Times reported, citing two Governing Council members that it didn’t identify
- New Zealand cabinet has confirmed that gathering limits in Auckland will ease from Sept 23 while they will be lifted entirely for the rest of the country tonight, Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern said Monday
- Oil steadied following its biggest weekly gain since June as a lack of clarity over the global energy demand recovery was balanced by the possibility that Saudi Arabia could press for more OPEC+ output cuts
A quick look at global markets courtesy of NewsSquawk:
Asian equity markets were subdued and US equity futures traded choppy after last Friday’s losses on Wall St amid quadruple witching and continued tech woes, with risk appetite also dampened by holiday conditions as Japanese participants observe a 4-day weekend. ASX 200 (-0.7%) was negative with losses in metal miners and financials underperforming in the broad weakness across its sectors aside from Health Care and Energy, while KOSPI (-1.0%) swung from gains and losses on varied COVID-19 headlines with South Korea to extend level 2 social distancing curbs by an additional week but will also be distributing emergency funds from the 4th extra budget within days. Hang Seng (-2.0%) and Shanghai Composite (-0.6%) were downbeat with HSBC shares slumping to a 25-year low in Hong Kong after a leaked document noted that the bank had permitted GBP 62mln to be moved to Hong Kong in suspicious transactions during 2013-2014 despite being warned by a regulator, while Standard Chartered also declined after being implicated by the ‘FinCEN’ leak, and other reports noted concerns HSBC and Standard Chartered could be frozen out of the US banking system in the event of a further escalation US-China tensions. Elsewhere, Tencent shares were pressured amid uncertainty regarding its US future despite a California judge halting President Trump's ban on WeChat downloads, while weekend news that President Trump gave his blessing to the TikTok-Oracle-Walmart deal, also did little to spur risk appetite.
Top Asian News
- Hedge Funds Raise Long Aussie Bets to 2018 High on China Rebound
- Amundi Sanguine on Indonesian Bonds on Attractive Real Yields
- China Tried to Dramatize Its Handling of the Virus. It Backfired
- SCG Packaging Seeks to Raise Up to $1.27 Billion in Thai IPO
Stocks in Europe see deep losses across the board (Euro Stoxx 50 -3%) as the region coat-tailed on the downbeat APAC handover before extending on losses amid an intensifying risk averse tone and a number of sector-specific factors. Firstly, Travel & Leisure resides as the marked underperformer as the resurging cases across Europe trigger warning bells for the sector, with some of the region’s worst performers including the likes IAG (-12%), Tui (-8.6%), easyJet (-8.4%), Carnival (-8.0%), Lufthansa (-7.7%) and Ryanair (-7.1%). Secondly, the European banking sector plumbs the depths in light of a leaked US government document accused HSBC (-5%), Standard Chartered (-4.4%), Barclays (-6.2%), Deutsche Bank (-5.6%), JPM (-3.6% premkt) and BNY Mellon (-2.5% premkt) of moving large sums of illegal cash for shady characters and criminal networks. The documents center around the number of SAR's (Suspicious Activity Reports) sent to US authorities between 1999 and 2017. The Basic Resources and Oil & Gas sectors are also among the laggards. As such, the UK’s FTSE 100 (-3.4%) underperforms the region despite a softer Sterling, given its heavy exposure to the aforementioned sectors. In terms of other movers and shakers, United Internet (-24%) and 1&1 Drillisch (-27%) reside as the biggest losers in Europe after cutting their respective FY EBTIDA guidance, whilst their spat with Telefonica (-3.6%) intensified over its subsidiary Telefonica Deutschland (-3.4) being accused of raising user costs significantly from July. Elsewhere, Rolls-Royce (-8.5%) holds onto its losses amid reports that the group is planning to raise as much as GBP 2.5bln to brace itself for another demand decline for aircraft engines. As such, Leonardo (-6.0%) continues falling despite an early halt, whilst Safran (-4.4%) is also pressured in sympathy. Finally, the Norwegian government has proposed that its Sovereign Wealth Fund should invest more within the US stock market and less within Europe.
Top European News
- Unilever’s Dutch Investors Said to Approve Single Headquarters
- European Stocks Drop Most Since July as HSBC Leads Bank Slump
- Sweden Loosens Purse Strings With Virus Stimulus Budget
- U.K. House Prices Up Most Since 2016 as Britons Seek More Space
In FX, although the Dollar has regained some poise amidst more pronounced risk aversion at the start of a new week, Usd/Jpy continues to decline alongside Yen crosses in the absence of Japanese market participants for ‘Old Age Day’. The headline pair has now breached another key chart if not major technical level in the form of July 31’s 104.20 low and there is little in the way of 104.00 to stop a 250+ pip cumulative fall from this month’s early peaks, especially given another holiday on Tuesday (Autumnal Equinox). However, it remains to be seen whether a 103.00 print provokes some verbal intervention from the MoF, and for now greater safe-haven demand for the Jpy is keeping the Usd index relatively capped beyond 93.000 within a 93.322-92.746 band.
- AUD/CAD/CHF - All succumbing to the increasingly sour tone and deterioration in broad sentiment as the Aussie loses 0.7300+ status vs its US counterpart, the Loonie retreats through 1.3200 with added fuel from a reversal in crude prices and the Franc falls back below 0.9100, albeit holding above 1.0800 against the Euro following latest weekly Swiss bank sight deposit balances showing perhaps surprise declines ahead of the SNB. Question is, are these coincidental or significant in advance of a more official shift in policy to be revealed at Thursday’s quarterly review?
- NZD/EUR/GBP - The Kiwi is back-pedalling further from Friday’s near 0.6800 peak vs its US peer and 1.0800+ apex on the Aud/Nzd cross even though NZ PM Adern scaled down the country’s COVID-19 alert level outside of Auckland again, while the Euro is retesting bids/support around 1.1800 and Sterling has recoiled over a big figure to sub-1.2850 on the ongoing rise of the pandemic across Europe.
- SCANDI/EM - A sea of red as risk assets tumble, while the aforementioned downturn in oil takes a heavier toll on the Norwegian Crown compared to the Swedish Krona that seems to be deriving some traction from upbeat commentary by the nation’s Finance Minister. Similarly, the Yuan is drawing a degree of comfort from a steady PBoC Cny fixing, net liquidity injection and unchanged loan prime rates to offset other less favourable issues like the ongoing Sino-US spat and reports from China’s top infectious disease expert warning that a 2nd wave is inevitable. Conversely, diplomatic strains and the retracement in Brent are undermining the Lira and Rouble again, while the Rand has unwounded all and more of its post-SARB gains.
In commodities, WTI and Brent front month futures continue to decline with losses driven by the broader risk averse sentiment coupled with a firmer Dollar and the prospect of dwindling demand given the resurgence of COVID-19 prompting talks of renewed lockdown measures. Furthermore, on the supply side of the equation, Libya’s NOC said it will lift the force majeure at ports and facilities that were deemed safe, with the gradual return of Libyan oil raising questions in terms of an OPEC quota for the country. WTI Nov resides around USD 40.50/bbl, having declined from a high ~41.50/bbl, whilst Brent Nov hovers just under USD 42.50/bbl vs. a high of USD 43.30/bbl. Another thing to keep on the radar – unconfirmed twitter reports noted that Saudi King Salman is reportedly in a critical condition, albeit nothing has been seen since on this front, with participants likely to dwell on the future of the Kingdom’s oil policy should he be replaced. Elsewhere, precious metal prices succumb to the Dollar, with spot gold now losing ground below the USD 1950/oz mark having traded on either side of the level in APAC hours. Spot silver meanwhile extends losses below USD 26.50/oz after printing a high just shy of USD 27/oz earlier in the session. In terms of base metals, LME copper is pressured by the broader equity sell-off and the firmer Buck, whilst Dalian iron ore futures slipped over 2% amid the soured risk tone and sluggish downstream demand.
US Event Calendar
- 8:30am: Chicago Fed Nat Activity Index, est. 1.2, prior 1.2
- 12pm: Household Change in Net Worth, prior $6.55t deficit
DB's Jim Reid concludes the overnight wrap
one of the reasons we have a widening bias for credit into year-end ( see our YE outlook here from a couple of weeks back) is that it seemed inevitable to us that we’d see a second wave causing confusion and chaos to many government’s strategies. Well as we sweltered in a pretty hot late September weekend here in the U.K. (and across much of Europe) the fact that the virus is already spreading quite rapidly is a big worry. It doesn’t feel like fatalities are going to be as big as an issue as they were in the first wave but it really is hard to understand what the strategies of governments are at the moment. They pretty much all don’t want a further wide scale lockdown but they also don’t want the virus to spread. Its not going to be easy to solve for both and as such It’s going to be a pretty difficult few months ahead if September is seeing numbers as high as they are already. I personally didn’t think these type of numbers would take place until well into October. Expect lots more restrictions over the days and weeks ahead, especially in Europe.
The latest on virus is that its spread has continued in the Europe with France reporting 37,282 new cases in the last 3 days, the highest since pandemic began. The 7 day average of new cases for France stands at 10,123,versus 8,161 a week ago. Over in the UK, the 3-day number stands at 12,661, the highest since May 9 with Health Secretary Matt Hancock not ruling out that London office employees might have to work from home again this week as Chief Medical Officer Chris Whitty is set to warn on today that the UK is at a “critical point.” Meanwhile, the LBC radio reported yesterday that London Mayor Sadiq Khan will recommend tightened rules for the capital today. Across the other side of world, South Korea reported 70 new cases yesterday, the lowest since the second wave began. However, the country is set to strengthen social distancing rules from September 28 to October 11, which will be designated as special quarantine period as the country celebrates Chuseok holidays from September 30 to October 4. So restrictions are tightening in even successful virus fighting places.
The weekend political press has also been full of news after US Supreme Court Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg passed away late Friday night following a long battle with cancer. Afterwards, President Trump said that he would put forth a nominee to fill the seat and Senate Majority Leader McConnell said “President Trump’s nominee will receive a vote on the floor of the United States Senate,” indicating that Republican leadership will try to fill the seat ahead of the election.This represents a turn in the Majority leader’s thinking from 2016, where he did not allow a floor vote for then-President Obama’s nominee in an election year. The nomination and confirmation process will introduce a new element to an election not least because the court can hold sway over highly contentious issues like healthcare, abortion rights and gun law.
It brings lots of fascinating scenarios to the table. If Trump succeeds at getting his nomination through before the election there will be a 6-3 Republican bias to the Supreme Court which as discussed could have policy ramifications for the US for a generation. Democrats are up in arms that the Republicans won’t wait until after the election and are suggesting that may do extraordinary things to address the balance (like adding new judges to the bench) if they gain control of both the Senate and the White House. Congress altered the size of the bench seven times in the first eighty years of the republic (ranging from 5 to 10 justices) but this has not changed since the Judiciary Act of 1869. However getting the current Senate to confirm a nominee won’t be straight forward for Mr Trump as the GOP only hold a 53-47 majority in the Senate (with Vice President Pence serving as the tie-breaker) and a few members have already made noises that they don’t think a new judge should be added this close to the election. So even more drama added to an election campaign.
Another interesting weekend story is of China revealing how it will manage its “unreliable entity list” that aims to punish firms, organizations or individuals that pose a threat or potential threat to China’s sovereignty, national security, development and business interests; and those that discriminate against or harm Chinese businesses, organizations or individuals. According to details, penalties will include restrictions on trade, investment and visas of any company, country, group or person that appears on its “unreliable entity list.” The Global Times has carried an article that HSBC is a possible candidate and is down -2.91% to the lowest level it has traded since the 2008 financial crisis.
In overall trading, the Hang Seng (-0.95%) is leading the declines this morning not helped by this. Other Asian markets have also started the week on a weak footing with the Shanghai Comp (-0.41%), Kospi (-0.29%) and Asx (-0.54%) all down along with S&P 500 futures (-0.21%). In fx, all G-10 currencies are trading strong against the greenback with the US dollar index down -0.21%.
In other news, the FT reported that the ECB has launched a review of its pandemic bond-buying program to consider how long it should continue and whether its exceptional flexibility should be extended to older programs. The report added that the review is expected to be discussed by policy makers next month.
Looking to this week now, the flash PMIs on Wednesday will probably get the most attention due to it being one of the first glimpses of September economic performance around the world. Economic and social restrictions are mounting again in various places due to the virus but it may be a bit too early to see their impact in these numbers.
It’ll also be worth keeping an eye on Germany’s Ifo survey on Thursday, which has so far been rising each month since its April low, even as it remains below its pre-pandemic level. The consensus is looking for a further increase to 93.8, which would be just 2 points below its level in February.
Meanwhile Fed Chair Powell will be speaking three times before congressional committees. He’ll be appearing tomorrow before the House Financial Services Panel about the CARES Act. Then on Wednesday he’ll be appearing on the House Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Crisis, before Thursday sees him speak before the Senate Banking Committee on the CARES Act once again. Otherwise, there’ll be remarks from Fed Vice Chair Quarles on the economic outlook, while Bank of England Governor Bailey will be speaking twice next week.
There’ll also a special European Council summit on Thursday and Friday. As well as taking stock of the Covid-19 pandemic, the agenda includes a discussion of the single market, industrial policy and digital transformation, along with the EU’s external relations. Brexit may get a small mention as relationships between the EU and the U.K. are just about hanging by enough of a thread enough to merit it. The day by day calendar of the week ahead is at the end.
Recapping last week now and equity markets continued to feel the pullback in mega-cap tech stocks. The S&P 500 dropped -0.64% (-1.12% Friday) to six week lows, having declined for a third straight week for the first time since October 2019. The index is now down -7.30% from 2 Sept highs. The NASDAQ also fell a third week in a row itself, declining -0.56% (-1.07% Friday) and is now down -10.48% from recent highs. Meanwhile European equities edged higher for a second straight week with the Stoxx 600 ending the week +0.22% higher (-0.66% Friday). While the broader index rose on the week, many individual bourses across Europe finished lower with the DAX (-0.66%), FTSE 100 (-0.42%), FTSE MIB (-1.49%), CAC 40 (-1.11%) and IBEX (-0.19%) all posting losses as Covid-19 caseloads continue to rise throughout western Europe, prompting some restrictions to be reinstated. Asian equities were mixed with the CSI 300 up +2.37% on the week, while the Nikkei (-0.20%) and the Kospi (+0.66%) saw smaller weekly moves.
Similar to risk assets, core sovereign bonds were mixed on the week. US 10yr Treasury yields rose +2.8bps (+0.5bps Friday) to finish at 0.694%, while 10yr Bund yields were down -0.4bps (+0.6bps Friday) to -0.49% and gilts were largely unchanged (+0.1bps) at 0.18%. The dollar fell -0.44% on the week after rising in 3 of the previous 4 weeks. This in part supported gold’s +0.53% rise on the week, while copper gained +2.62%. However, the largest move in commodities was in oil. Brent (+8.34%) and WTI (+10.13%) rose in part on news that Russia and Saudi Arabia would push their fellow OPEC+ members on keeping to quotas.
On the data front from Friday, UK August retail sales rose more than expected and up +0.6% MoM (+0.4% expected) and +4.3% YoY (+4.2% expected). In Germany, August PPI was -1.2% YoY, up from last month’s -1.7% reading and slightly higher than expected (-1.4%). While in the US, the preliminary reading of the University of Michigan Sentiment survey showed an +4.9pt increase to 78.9 (75.0 expected), which is the highest since March.
International
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
Illegal Immigrants Leave US Hospitals With Billions In Unpaid Bills
By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal…

By Autumn Spredemann of The Epoch Times
Tens of thousands of illegal immigrants are flooding into U.S. hospitals for treatment and leaving billions in uncompensated health care costs in their wake.
The House Committee on Homeland Security recently released a report illustrating that from the estimated $451 billion in annual costs stemming from the U.S. border crisis, a significant portion is going to health care for illegal immigrants.
With the majority of the illegal immigrant population lacking any kind of medical insurance, hospitals and government welfare programs such as Medicaid are feeling the weight of these unanticipated costs.
Apprehensions of illegal immigrants at the U.S. border have jumped 48 percent since the record in fiscal year 2021 and nearly tripled since fiscal year 2019, according to Customs and Border Protection data.
Last year broke a new record high for illegal border crossings, surpassing more than 3.2 million apprehensions.
And with that sea of humanity comes the need for health care and, in most cases, the inability to pay for it.
In January, CEO of Denver Health Donna Lynne told reporters that 8,000 illegal immigrants made roughly 20,000 visits to the city’s health system in 2023.
The total bill for uncompensated care costs last year to the system totaled $140 million, said Dane Roper, public information officer for Denver Health. More than $10 million of it was attributed to “care for new immigrants,” he told The Epoch Times.
Though the amount of debt assigned to illegal immigrants is a fraction of the total, uncompensated care costs in the Denver Health system have risen dramatically over the past few years.
The total uncompensated costs in 2020 came to $60 million, Mr. Roper said. In 2022, the number doubled, hitting $120 million.
He also said their city hospitals are treating issues such as “respiratory illnesses, GI [gastro-intenstinal] illnesses, dental disease, and some common chronic illnesses such as asthma and diabetes.”
“The perspective we’ve been trying to emphasize all along is that providing healthcare services for an influx of new immigrants who are unable to pay for their care is adding additional strain to an already significant uncompensated care burden,” Mr. Roper said.
He added this is why a local, state, and federal response to the needs of the new illegal immigrant population is “so important.”
Colorado is far from the only state struggling with a trail of unpaid hospital bills.

Dr. Robert Trenschel, CEO of the Yuma Regional Medical Center situated on the Arizona–Mexico border, said on average, illegal immigrants cost up to three times more in human resources to resolve their cases and provide a safe discharge.
“Some [illegal] migrants come with minor ailments, but many of them come in with significant disease,” Dr. Trenschel said during a congressional hearing last year.
“We’ve had migrant patients on dialysis, cardiac catheterization, and in need of heart surgery. Many are very sick.”
He said many illegal immigrants who enter the country and need medical assistance end up staying in the ICU ward for 60 days or more.
A large portion of the patients are pregnant women who’ve had little to no prenatal treatment. This has resulted in an increase in babies being born that require neonatal care for 30 days or longer.
Dr. Trenschel told The Epoch Times last year that illegal immigrants were overrunning healthcare services in his town, leaving the hospital with $26 million in unpaid medical bills in just 12 months.
ER Duty to Care
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986 requires that public hospitals participating in Medicare “must medically screen all persons seeking emergency care … regardless of payment method or insurance status.”
The numbers are difficult to gauge as the policy position of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is that it “will not require hospital staff to ask patients directly about their citizenship or immigration status.”
In southern California, again close to the border with Mexico, some hospitals are struggling with an influx of illegal immigrants.
American patients are enduring longer wait times for doctor appointments due to a nursing shortage in the state, two health care professionals told The Epoch Times in January.
A health care worker at a hospital in Southern California, who asked not to be named for fear of losing her job, told The Epoch Times that “the entire health care system is just being bombarded” by a steady stream of illegal immigrants.
“Our healthcare system is so overwhelmed, and then add on top of that tuberculosis, COVID-19, and other diseases from all over the world,” she said.

A newly-enacted law in California provides free healthcare for all illegal immigrants residing in the state. The law could cost taxpayers between $3 billion and $6 billion per year, according to recent estimates by state and federal lawmakers.
In New York, where the illegal immigration crisis has manifested most notably beyond the southern border, city and state officials have long been accommodating of illegal immigrants’ healthcare costs.
Since June 2014, when then-mayor Bill de Blasio set up The Task Force on Immigrant Health Care Access, New York City has worked to expand avenues for illegal immigrants to get free health care.
“New York City has a moral duty to ensure that all its residents have meaningful access to needed health care, regardless of their immigration status or ability to pay,” Mr. de Blasio stated in a 2015 report.
The report notes that in 2013, nearly 64 percent of illegal immigrants were uninsured. Since then, tens of thousands of illegal immigrants have settled in the city.
“The uninsured rate for undocumented immigrants is more than three times that of other noncitizens in New York City (20 percent) and more than six times greater than the uninsured rate for the rest of the city (10 percent),” the report states.
The report states that because healthcare providers don’t ask patients about documentation status, the task force lacks “data specific to undocumented patients.”
Some health care providers say a big part of the issue is that without a clear path to insurance or payment for non-emergency services, illegal immigrants are going to the hospital due to a lack of options.
“It’s insane, and it has been for years at this point,” Dana, a Texas emergency room nurse who asked to have her full name omitted, told The Epoch Times.
Working for a major hospital system in the greater Houston area, Dana has seen “a zillion” migrants pass through under her watch with “no end in sight.” She said many who are illegal immigrants arrive with treatable illnesses that require simple antibiotics. “Not a lot of GPs [general practitioners] will see you if you can’t pay and don’t have insurance.”
She said the “undocumented crowd” tends to arrive with a lot of the same conditions. Many find their way to Houston not long after crossing the southern border. Some of the common health issues Dana encounters include dehydration, unhealed fractures, respiratory illnesses, stomach ailments, and pregnancy-related concerns.
“This isn’t a new problem, it’s just worse now,” Dana said.

Medicaid Factor
One of the main government healthcare resources illegal immigrants use is Medicaid.
All those who don’t qualify for regular Medicaid are eligible for Emergency Medicaid, regardless of immigration status. By doing this, the program helps pay for the cost of uncompensated care bills at qualifying hospitals.
However, some loopholes allow access to the regular Medicaid benefits. “Qualified noncitizens” who haven’t been granted legal status within five years still qualify if they’re listed as a refugee, an asylum seeker, or a Cuban or Haitian national.
Yet the lion’s share of Medicaid usage by illegal immigrants still comes through state-level benefits and emergency medical treatment.
A Congressional report highlighted data from the CMS, which showed total Medicaid costs for “emergency services for undocumented aliens” in fiscal year 2021 surpassed $7 billion, and totaled more than $5 billion in fiscal 2022.
Both years represent a significant spike from the $3 billion in fiscal 2020.
An employee working with Medicaid who asked to be referred to only as Jennifer out of concern for her job, told The Epoch Times that at a state level, it’s easy for an illegal immigrant to access the program benefits.
Jennifer said that when exceptions are sent from states to CMS for approval, “denial is actually super rare. It’s usually always approved.”
She also said it comes as no surprise that many of the states with the highest amount of Medicaid spending are sanctuary states, which tend to have policies and laws that shield illegal immigrants from federal immigration authorities.
Moreover, Jennifer said there are ways for states to get around CMS guidelines. “It’s not easy, but it can and has been done.”
The first generation of illegal immigrants who arrive to the United States tend to be healthy enough to pass any pre-screenings, but Jennifer has observed that the subsequent generations tend to be sicker and require more access to care. If a family is illegally present, they tend to use Emergency Medicaid or nothing at all.
The Epoch Times asked Medicaid Services to provide the most recent data for the total uncompensated care that hospitals have reported. The agency didn’t respond.
Continue reading over at The Epoch Times
International
Fuel poverty in England is probably 2.5 times higher than government statistics show
The top 40% most energy efficient homes aren’t counted as being in fuel poverty, no matter what their bills or income are.

The cap set on how much UK energy suppliers can charge for domestic gas and electricity is set to fall by 15% from April 1 2024. Despite this, prices remain shockingly high. The average household energy bill in 2023 was £2,592 a year, dwarfing the pre-pandemic average of £1,308 in 2019.
The term “fuel poverty” refers to a household’s ability to afford the energy required to maintain adequate warmth and the use of other essential appliances. Quite how it is measured varies from country to country. In England, the government uses what is known as the low income low energy efficiency (Lilee) indicator.
Since energy costs started rising sharply in 2021, UK households’ spending powers have plummeted. It would be reasonable to assume that these increasingly hostile economic conditions have caused fuel poverty rates to rise.
However, according to the Lilee fuel poverty metric, in England there have only been modest changes in fuel poverty incidence year on year. In fact, government statistics show a slight decrease in the nationwide rate, from 13.2% in 2020 to 13.0% in 2023.
Our recent study suggests that these figures are incorrect. We estimate the rate of fuel poverty in England to be around 2.5 times higher than what the government’s statistics show, because the criteria underpinning the Lilee estimation process leaves out a large number of financially vulnerable households which, in reality, are unable to afford and maintain adequate warmth.

Energy security
In 2022, we undertook an in-depth analysis of Lilee fuel poverty in Greater London. First, we combined fuel poverty, housing and employment data to provide an estimate of vulnerable homes which are omitted from Lilee statistics.
We also surveyed 2,886 residents of Greater London about their experiences of fuel poverty during the winter of 2022. We wanted to gauge energy security, which refers to a type of self-reported fuel poverty. Both parts of the study aimed to demonstrate the potential flaws of the Lilee definition.
Introduced in 2019, the Lilee metric considers a household to be “fuel poor” if it meets two criteria. First, after accounting for energy expenses, its income must fall below the poverty line (which is 60% of median income).
Second, the property must have an energy performance certificate (EPC) rating of D–G (the lowest four ratings). The government’s apparent logic for the Lilee metric is to quicken the net-zero transition of the housing sector.
In Sustainable Warmth, the policy paper that defined the Lilee approach, the government says that EPC A–C-rated homes “will not significantly benefit from energy-efficiency measures”. Hence, the focus on fuel poverty in D–G-rated properties.
Generally speaking, EPC A–C-rated homes (those with the highest three ratings) are considered energy efficient, while D–G-rated homes are deemed inefficient. The problem with how Lilee fuel poverty is measured is that the process assumes that EPC A–C-rated homes are too “energy efficient” to be considered fuel poor: the main focus of the fuel poverty assessment is a characteristic of the property, not the occupant’s financial situation.
In other words, by this metric, anyone living in an energy-efficient home cannot be considered to be in fuel poverty, no matter their financial situation. There is an obvious flaw here.
Around 40% of homes in England have an EPC rating of A–C. According to the Lilee definition, none of these homes can or ever will be classed as fuel poor. Even though energy prices are going through the roof, a single-parent household with dependent children whose only income is universal credit (or some other form of benefits) will still not be considered to be living in fuel poverty if their home is rated A-C.
The lack of protection afforded to these households against an extremely volatile energy market is highly concerning.
In our study, we estimate that 4.4% of London’s homes are rated A-C and also financially vulnerable. That is around 171,091 households, which are currently omitted by the Lilee metric but remain highly likely to be unable to afford adequate energy.
In most other European nations, what is known as the 10% indicator is used to gauge fuel poverty. This metric, which was also used in England from the 1990s until the mid 2010s, considers a home to be fuel poor if more than 10% of income is spent on energy. Here, the main focus of the fuel poverty assessment is the occupant’s financial situation, not the property.
Were such alternative fuel poverty metrics to be employed, a significant portion of those 171,091 households in London would almost certainly qualify as fuel poor.
This is confirmed by the findings of our survey. Our data shows that 28.2% of the 2,886 people who responded were “energy insecure”. This includes being unable to afford energy, making involuntary spending trade-offs between food and energy, and falling behind on energy payments.
Worryingly, we found that the rate of energy insecurity in the survey sample is around 2.5 times higher than the official rate of fuel poverty in London (11.5%), as assessed according to the Lilee metric.
It is likely that this figure can be extrapolated for the rest of England. If anything, energy insecurity may be even higher in other regions, given that Londoners tend to have higher-than-average household income.
The UK government is wrongly omitting hundreds of thousands of English households from fuel poverty statistics. Without a more accurate measure, vulnerable households will continue to be overlooked and not get the assistance they desperately need to stay warm.
Torran Semple receives funding from Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) grant EP/S023305/1.
John Harvey does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
european uk pandemicGovernment
Looking Back At COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes
After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked,…

After having moved from Canada to the United States, partly to be wealthier and partly to be freer (those two are connected, by the way), I was shocked, in March 2020, when President Trump and most US governors imposed heavy restrictions on people’s freedom. The purpose, said Trump and his COVID-19 advisers, was to “flatten the curve”: shut down people’s mobility for two weeks so that hospitals could catch up with the expected demand from COVID patients. In her book Silent Invasion, Dr. Deborah Birx, the coordinator of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, admitted that she was scrambling during those two weeks to come up with a reason to extend the lockdowns for much longer. As she put it, “I didn’t have the numbers in front of me yet to make the case for extending it longer, but I had two weeks to get them.” In short, she chose the goal and then tried to find the data to justify the goal. This, by the way, was from someone who, along with her task force colleague Dr. Anthony Fauci, kept talking about the importance of the scientific method. By the end of April 2020, the term “flatten the curve” had all but disappeared from public discussion.
Now that we are four years past that awful time, it makes sense to look back and see whether those heavy restrictions on the lives of people of all ages made sense. I’ll save you the suspense. They didn’t. The damage to the economy was huge. Remember that “the economy” is not a term used to describe a big machine; it’s a shorthand for the trillions of interactions among hundreds of millions of people. The lockdowns and the subsequent federal spending ballooned the budget deficit and consequent federal debt. The effect on children’s learning, not just in school but outside of school, was huge. These effects will be with us for a long time. It’s not as if there wasn’t another way to go. The people who came up with the idea of lockdowns did so on the basis of abstract models that had not been tested. They ignored a model of human behavior, which I’ll call Hayekian, that is tested every day.
These are the opening two paragraphs of my latest Defining Ideas article, “Looking Back at COVID’s Authoritarian Regimes,” Defining Ideas, March 14, 2024.
Another excerpt:
That wasn’t the only uncertainty. My daughter Karen lived in San Francisco and made her living teaching Pilates. San Francisco mayor London Breed shut down all the gyms, and so there went my daughter’s business. (The good news was that she quickly got online and shifted many of her clients to virtual Pilates. But that’s another story.) We tried to see her every six weeks or so, whether that meant our driving up to San Fran or her driving down to Monterey. But were we allowed to drive to see her? In that first month and a half, we simply didn’t know.
Read the whole thing, which is longer than usual.
(0 COMMENTS) budget deficit coronavirus covid-19 white house fauci trump canada-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International7 days ago
International7 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Spread & Containment2 days ago
Spread & Containment2 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex

























