Global Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests Market Report 2022-2026: Developed Regions Lead, Developing Economies to Boost Future Growth
Global Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests Market Report 2022-2026: Developed Regions Lead, Developing Economies to Boost Future Growth
PR Newswire
DUBLIN, Sept. 23, 2022
DUBLIN, Sept. 23, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — The “Automated and Rapid Microbi…
Global Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests Market Report 2022-2026: Developed Regions Lead, Developing Economies to Boost Future Growth
PR Newswire
DUBLIN, Sept. 23, 2022
DUBLIN, Sept. 23, 2022 /PRNewswire/ -- The "Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests - Global Market Trajectory & Analytics" report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering.
Global Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests Market to Reach $7.6 Billion by 2026
Amid the COVID-19 crisis, the global market for Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests estimated at US$5.9 Billion in the year 2022, is projected to reach a revised size of US$7.6 Billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% over the analysis period.
GC/CRT (Clinical), one of the segments analyzed in the report, is projected to grow at a 7.4% CAGR to reach US$1 Billion by the end of the analysis period. After a thorough analysis of the business implications of the pandemic and its induced economic crisis, growth in the AISS (clinical) segment is readjusted to a revised 3.4% CAGR for the next 7-year period.
This segment currently accounts for a 10.4% share of the global Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests market. The surge in the occurrences of STDs, such as GC/Chlamydia, HIV and Syphilis, has turned STD rapid tests into the most dynamic and vigorous segment of the market.
Growth in the global is set to be fueled by rising global prevalence of chronic infectious diseases, increasing food safety concerns, growing need for fast and easy diagnosis, rising public-private investments, funding, and research grants, and sustained technological advancements.
Continued technological advancements in terms of improved functionality, efficiency, efficacy, faster results, and accuracy are driving the adoption of microbial testing in academic institutes, research laboratories, hospitals, clinical laboratories, and biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies. Recent advances in proteomics and genomics are contributing to the rapid evolution of new methodologies for microbial identification and quantification.
Rapid advancements in microbial testing help in overcoming limitations such as an extensive period of exposure to pathogenic strains and long procedural times associated with traditional testing methods. In addition, these tests serve as a cost-effective alternative to microbial identification by enabling reduction in the consumable cost per procedure.
The U.S. Market is Estimated at $2.2 Billion in 2022, While China is Forecast to Reach $709.2 Million by 2026
The Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests market in the U.S. is estimated at US$2.2 Billion in the year 2022. The country currently accounts for a 37.1% share in the global market. China, the world's second largest economy, is forecast to reach an estimated market size of US$709.2 Million in the year 2026 trailing a CAGR of 8.6% through the analysis period.
Among the other noteworthy geographic markets are Japan and Canada, each forecast to grow at 4.6% and 5.7% respectively over the analysis period. Within Europe, Germany is forecast to grow at approximately 5% CAGR while Rest of European market (as defined in the study) will reach US$766.1 Million by the end of the analysis period.
North America and Europe represent the leading regional markets, due to technological advancements related to rapid microbial testing, growing incidences of infectious diseases, and increasing food safety concerns. Asia-Pacific region presents considerable growth opportunities due to the rising healthcare expenditure and expanding initiatives for promotion of the use of advanced technologies in rapid microbiology testing.
ABCS (Clinical) Segment to Reach $530.3 Million by 2026
In the global ABCS (Clinical) segment, USA, Canada, Japan, China and Europe will drive the 2.9% CAGR estimated for this segment. These regional markets accounting for a combined market size of US$372.2 Million will reach a projected size of US$456.1 Million by the close of the analysis period.
China will remain among the fastest growing in this cluster of regional markets. Led by countries such as Australia, India, and South Korea, the market in Asia-Pacific is forecast to reach US$32.7 Million by the year 2026, while Latin America will expand at a 3.8% CAGR through the analysis period.
Key Topics Covered:
I. METHODOLOGY
II. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
1. MARKET OVERVIEW
- Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic and Looming Global Recession
- Clinical Microbiology Gains Prominence as Scientists Mobilize United Efforts to Find Ways to Detect, Treat & Vaccinate People Against the Novel Coronavirus
- A New, 20-Minute Assay for COVID-19 Diagnosis
- Automated and Rapid Microbiological Tests: An Introduction
- Enabling Technologies of Automated & Rapid Microbiological Tests
- Clinical Applications of Automated & Rapid Microbiological Tests
- Applications in Non-Clinical Investigations
- Global Market Prospects & Outlook
- Evolutionary Battle against Microbes Drives Market Future
- Clinical Applications Lead the Global Market for Automated and Rapid Microbiological Testing
- Developed Regions Lead, Developing Economies to Boost Future Growth
- Competition
- Recent Market Activity
2. FOCUS ON SELECT PLAYERS (Total 77 Featured)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Abbott Molecular, Inc.
- Aidian Oy
- Beckman Coulter, Inc.
- Becton Dickinson and Company
- bioMerieux SA
- bioMerieux, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc
- Cellabs Pty Ltd
- Cepheid Inc.
- CorisBioconcept SPRL
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- Hologic, Inc.
- MedMira Inc.
- Meridian Bioscience, Inc.
- OraSure Technologies, Inc.
- Oxoid Limited
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Quidel Corporation
- Rapid Micro Biosystems, Inc.
- Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC
- Siemens Healthcare GmbH
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
3. MARKET TRENDS & DRIVERS
- Rapid Diagnostics Bring in a Transformation to Clinical Testing Practices
- Traditional Rapid Microbiological Tests Make Way for New, Probe Tests
- Lab Automation Trend Augurs Well for Microbiological Testing Labs
- Traditional Approaches Give Way to Modern Automated Microbiology Systems
- Microbiology Laboratories Switch to Automation to Push Yields
- Growing Incidence of Infectious Diseases to Fuel Demand for Rapid Microbiology Testing
- Infectious Diseases Remain Major Cause of Death in Under Developed Regions
- Rising Prevalence of Respiratory Infections Drive Market Growth
- Rise in Prevalence of COPD Augments Demand
- Global Prevalence of COPD: Percentage of Men and Women Affected by Age Group
- Influenza Boosts Rapid Test Prospects
- Rise in Pollution Levels Trigger Increase in Respiratory Diseases, Driving Opportunities for Automated Microbiology Tests
- Percentage Share Breakdown of Global Deaths Linked to Air Pollution
- Most Polluted Countries Worldwide: Average PM2.5 concentration (?g/m) for 2020
- Sustained Threat of HIV and Sexually Transmitted Diseases Amplify Need for Rapid Microbiological Testing
- Rapid HIV Tests: A New Age Diagnostic Weapon against the Killer Disease
- Home HIV Testing Emerges as a Lucrative Option
- Advancements in Molecular Diagnostics Drive Market Growth
- Emerging Technologies in Clinical Microbiology Diagnostics Aim at Faster Diagnosis
- Automated Blood Culture Systems: The Gold Standard in the Fight against Bacteremia
- Advancements in Molecular Diagnostics: A Boon for Rapid Microbiological Testing Market
- Biotechnology: A Crucial Step Ahead in the Growing Popularity of Rapid Microbial Tests
- Healthcare Needs of the World's Aging Population: Potential Opportunity in Store
- Increase in Healthcare Spending in Emerging Markets to Propel Demand for Automated Microbiological Testing
- Clinical Microbiology Market Benefits from Digitalization and Robotization Trend
- Integration of Clinical Microbiology with Cloud Computing
- Artificial Intelligence Holds Positive Implications for Automation of Clinical Microbiology
- Point-of-Care Rapid Microbiological Testing: Yet to Realize Its Full Potential.
- Technological Advancements to Drive the Automated Microbiology Testing Market
- Focus on Safe and High-Quality Foods Propels Rapid Microbiological Testing
- Impact of COVID-19 on Food Safety Testing Industry
- Stringent Norms Necessitate Food Safety Testing
- Food Microbiology Testing Market on a Growth Spree
- Rapid and Automated Tests Emerge as an Attractive Solution
- Leading Food Processors Exhibit Inclination Towards Rapid Microbiological Testing
- Automation of Food Microbiology Labs
- Poultry Industry Embraces Rapid Microbiological Testing Technologies
- Rapid Microbial Testing in Dairy Industry
- Real-time PCR/qPCR Technologies Fundamental in Food Safety Testing
- Technical and Cost Related Hurdles Hamper the Microbiology Testing Market
- Rapid Microbiological Testing Gains Significance in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- Key Advantages of Rapid Microbiological Tests for Pharmaceutical Industry
- Growing Importance of Rapid Microbiological Testing for Pharma Laboratories
- Key RMM Technologies for Pharmaceutical Industry
- Adoption of Rapid Methods for QC Microbiology in Biopharmaceuticals
- Advancements in Rapid Microbiological Testing for Pharmaceutical Industry
- Rapid Microbial Testing for Regenerative Medicine: An Emerging Space
- Rapid Microbiological Methods and the Regulatory Environment in Drug Development Industry
- FDA's Requirements for Validation of RMM
- EMA's Guidance on Use of RMMs for Water Testing
- Rapid Microbial Testing Emerges as an Important Means for Quality Control of Advanced Therapies
- Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Throws the Spotlight on Rapid Microbial Testing Tools
- Antimicrobial Vulnerability Testing and Identification of Microbial strains
- Role of Microscopy in Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
- Rising Prominence of NAAT-Driven AST
- Economic Factors Promise Growth for Rapid AST
- Rapid Technologies Gain Momentum in Environment Testing Field
- Deteriorating Quality of Water Throws Emphasis on Water Testing Services
- Percentage of Contaminated Water in Drinking Water Supplies in Africa, Asia, and Latin America and Caribbean
- Key Issues Confronting the Rapid Microbiological Tests Market
4. GLOBAL MARKET PERSPECTIVE
III. REGIONAL MARKET ANALYSIS
IV. COMPETITION
For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/bfkfc8
Media Contact:
Research and Markets
Laura Wood, Senior Manager
press@researchandmarkets.com
For E.S.T Office Hours Call +1-917-300-0470
For U.S./CAN Toll Free Call +1-800-526-8630
For GMT Office Hours Call +353-1-416-8900
U.S. Fax: 646-607-1907
Fax (outside U.S.): +353-1-481-1716
Logo: https://mma.prnewswire.com/media/539438/Research_and_Markets_Logo.jpg
View original content:https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-automated-and-rapid-microbiological-tests-market-report-2022-2026-developed-regions-lead-developing-economies-to-boost-future-growth-301631920.html
SOURCE Research and Markets
Uncategorized
Profits over patients: For-profit nursing home chains are draining resources from care while shifting huge sums to owners’ pockets
Owners of midsize nursing home chains harm the elderly and drain huge sums of money from facilities using opaque accounting practices while government…
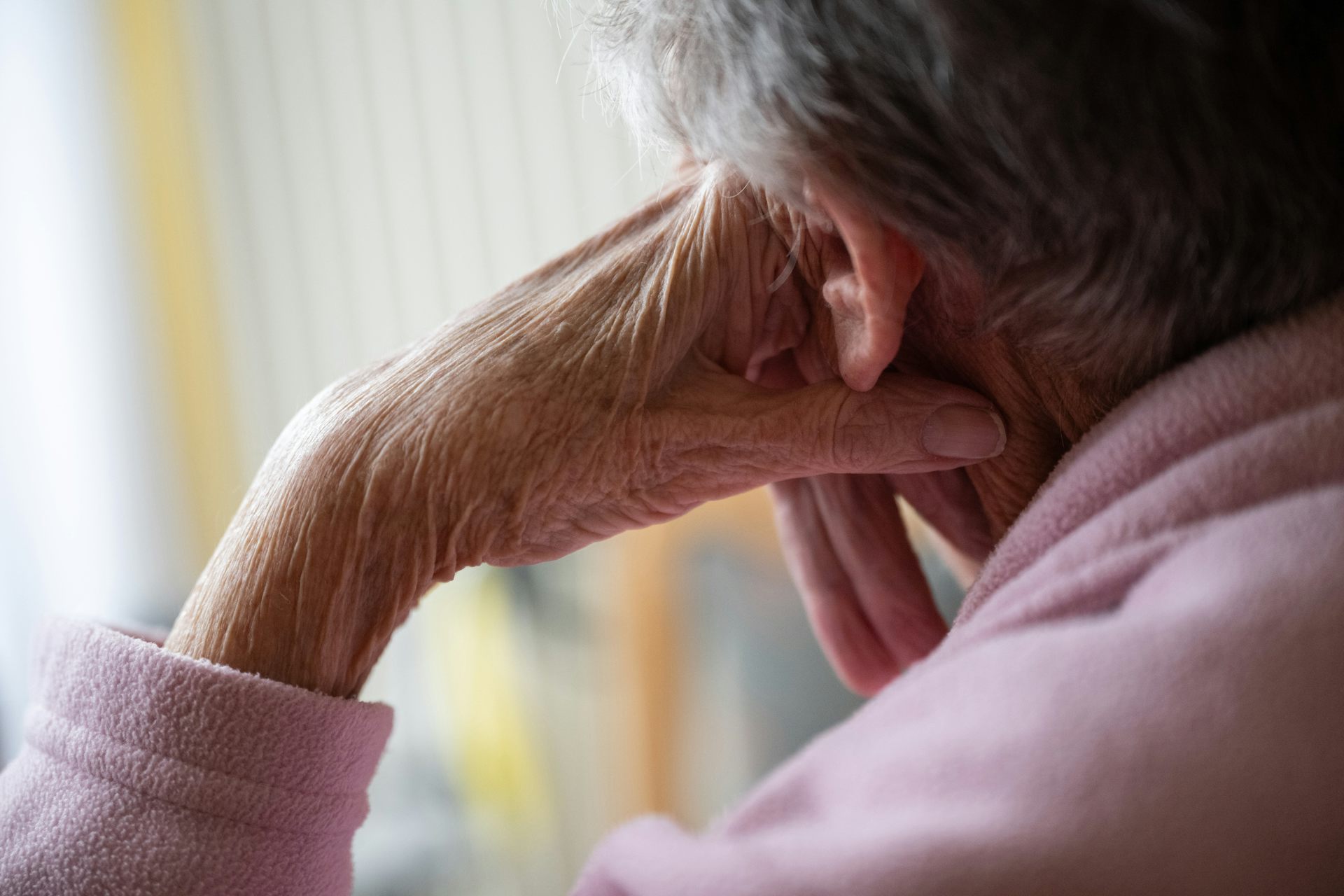

The care at Landmark of Louisville Rehabilitation and Nursing was abysmal when state inspectors filed their survey report of the Kentucky facility on July 3, 2021.
Residents wandered the halls in a facility that can house up to 250 people, yelling at each other and stealing blankets. One resident beat a roommate with a stick, causing bruising and skin tears. Another was found in bed with a broken finger and a bloody forehead gash. That person was allowed to roam and enter the beds of other residents. In another case, there was sexual touching in the dayroom between residents, according to the report.
Meals were served from filthy meal carts on plastic foam trays, and residents struggled to cut their food with dull plastic cutlery. Broken tiles lined showers, and a mysterious black gunk marred the floors. The director of housekeeping reported that the dining room was unsanitary. Overall, there was a critical lack of training, staff and supervision.
The inspectors tagged Landmark as deficient in 29 areas, including six that put residents in immediate jeopardy of serious harm and three where actual harm was found. The issues were so severe that the government slapped Landmark with a fine of over US$319,000 − more than 29 times the average for a nursing home in 2021 − and suspended payments to the home from federal Medicaid and Medicare funds.
But problems persisted. Five months later, inspectors levied six additional deficiencies of immediate jeopardy − the highest level.
Landmark is just one of the 58 facilities run by parent company Infinity Healthcare Management across five states. The government issued penalties to the company almost 4½ times the national average, according to bimonthly data that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services first started to make available in late 2022. All told, Infinity paid nearly $10 million in fines since 2021, the highest among nursing home chains with fewer than 100 facilities.
Infinity Healthcare Management and its executives did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
Race to the bottom
Such sanctions are nothing new for Infinity or other for-profit nursing home chains that have dominated an industry long known for cutting corners in pursuit of profits for private owners. But this race to the bottom to extract profits is accelerating, despite demands by government officials, health care experts and advocacy groups to protect the nation’s most vulnerable citizens.
To uncover the reasons why, The Conversation delved into the nursing home industry, where for-profit facilities make up more than 72% of the nation’s nearly 14,900 facilities. The probe, which paired an academic expert with an investigative reporter, used the most recent government data on ownership, facility information and penalties, combined with CMS data on affiliated entities for nursing homes.
The investigation revealed an industry that places a premium on cost cutting and big profits, with low staffing and poor quality, often to the detriment of patient well-being. Operating under weak and poorly enforced regulations with financially insignificant penalties, the for-profit sector fosters an environment where corners are frequently cut, compromising the quality of care and endangering patient health.
Meanwhile, owners make the facilities look less profitable by siphoning money from the homes through byzantine networks of interconnected corporations. Federal regulators have neglected the problem as each year likely billions of dollars are funneled out of nursing homes through related parties and into owners’ pockets.
More trouble at midsize
Analyzing newly released government data, our investigation found that these problems are most pronounced in nursing homes like Infinity − midsize chains that operate between 11 and 100 facilities. This subsection of the industry has higher average fines per home, lower overall quality ratings, and are more likely to be tagged with resident abuse compared with both the larger and smaller networks. Indeed, while such chains account for about 39% of all facilities, they operate 11 of the 15 most-fined facilities.
With few impediments, private investors who own the midsize chains have swooped in to purchase underperforming homes, expanding their holdings even as larger chains divest and close facilities.
“They are really bad, but the names − we don’t know these names,” said Toby Edelman, senior policy attorney with the Center for Medicare Advocacy, a nonprofit law organization.
In response to The Conversation’s findings on nursing homes and request for an interview, a CMS spokesperson emailed a statement that said the CMS is “unwavering in its commitment to improve safety and quality of care for the more than 1.2 million residents receiving care in Medicare- and Medicaid-certified nursing homes.”
“We support transparency and accountability,” the American Health Care Association/National Center for Assisted Living, a trade organization representing the nursing home industry, wrote in response to The Conversation‘s request for comment. “But neither ownership nor line items on a budget sheet prove whether a nursing home is committed to its residents.”
Ripe for abuse
It often takes years to improve a poor nursing home − or run one into the ground. The analysis of midsize chains shows that most owners have been associated with their current facilities for less than eight years, making it difficult to separate operators who have taken long-term investments in resident care from those who are looking to quickly extract money and resources before closing them down or moving on. These chains control roughly 41% of nursing home beds in the U.S., according to CMS’s provider data, making the lack of transparency especially ripe for abuse.
A churn of nursing home purchases even during the pandemic shows that investors view the sector as highly profitable, especially when staffing costs are kept low and fines for poor care can easily be covered by the money extracted from residents, their families and taxpayers.
A March 2024 study from Lehigh University and the University of California, Los Angeles also shows that costs were inflated when nursing home owners switched to contractors they controlled directly or indirectly. Overall, spending on real estate increased 20.4% and spending on management increased 24.6% when the businesses were affiliated, the research showed.
“This is the model of their care: They come in, they understaff and they make their money,” said Sam Brooks, director of public policy at the Consumer Voice, a national resident advocacy organization. “Then they multiply it over a series of different facilities.”
This is a condensed version of an article from The Conversation’s investigative unit. To find out more about the rise of for-profit nursing homes, financial trickery and what could make the nation’s most vulnerable citizens safer, read the complete version.
Campbell is an adjunct assistant professor at Columbia University and a contributing writer at the Garrison Project, an independent news organization that focuses on mass incarceration and criminal justice.
Harrington is an advisory board member of the nonprofit Veteran's Health Policy Institute and a board member of the nonprofit Center for Health Information and Policy. Harrington served as an expert witness on nursing home litigation cases by residents against facilities owned or operated by Brius and Shlomo Rechnitz in the past and in 2022. She also served as an expert witness in a case against The Citadel Salisbury in North Carolina in 2021.
real estate pandemicInternational
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
According to DB’s Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark…
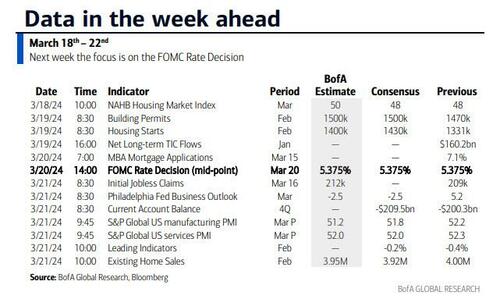
According to DB's Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark week in markets as the last global holdout on negative rates looks set to be removed as the BoJ likely hikes rates from -0.1% tomorrow." That will likely overshadow the FOMC that concludes on Wednesday that will have its own signalling intrigue given recent strong inflation. We also have the RBA meeting tomorrow and the SNB and BoE meetings on Thursday to close out a big week for global central bankers with many EM countries also deciding on policy. We’ll preview the main meetings in more depth below but outside of this we have the global flash PMIs on Thursday as well as inflation reports in Japan (Thursday) and the UK (Wednesday). US housing data also permeates through the week as you'll see in the full global day-by-day week ahead at the end as usual.
Let’s go into detail now, starting with the BoJ tomorrow. We’ve had negative base rates now for 8 years which if is the longest run ever seen for any country in the history of mankind. In fact it is doubtful that pre-historic man was as generous as to charge negative interest rates on lending money prior to this! It also might be one of the longest global runs without any interest rate hikes given the 17 year run that could end tomorrow. So, as Reid puts it, a landmark event.
DB's Chief Japan economist expects the central bank to revise its policy and abandon both NIRP and the multi-tiered current account structure and set rates on all excess reserves at 0.1%. He also sees both the yield curve control (YCC) and the inflation-overshooting commitment ending, replaced by a benchmark for the pace of the bank’s JGB purchasing activity. The house view forecast of 50bps of hikes through 2025 is more hawkish than the market but risks are still tilted to the upside. On Friday, the Japan Trade Union Confederation (Rengo) announced the first tally of the results of this year's shunto spring wage negotiation. The wage increase rate, including the seniority-based wage hike, is 5.28%, which was significantly higher than expected. This year will probably see the highest wage settlements since 1991 which given Japan’s recent history is an incredible turnaround. This wage data news has firmed up expectations for tomorrow.
With regards to the FOMC which concludes on Wednesday, DB economists expect only minor revisions to the meeting statement that saw an overhaul last meeting. With regards to the SEP, the growth and unemployment forecasts are unlikely to change but the 2024 inflation forecasts potentially could; elsewhere, expect the Fed to revise up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast by a tenth to 2.5%, although they see meaningful risks that it gets revised up even higher to 2.6%. In our economists' view, a 2.5% core PCE reading would allow just enough wiggle room to keep the 2024 fed funds rate at 4.6% (75bps of cuts). However, if core PCE inflation were revised up to 2.6%, it would likely entail the Fed moving their base case back to 50bps of cuts, as this would essentially reflect the same forecasts as the September 2023 SEP.
Beyond 2024, DB expect officials to build in less policy easing due to a higher r-star. If two of the eight officials currently at 2.5% move up by 25bps, then the long-run median forecast would edge up to 2.6%. This could be justified by a one-tenth upgrade to the long-run growth forecast. After all this information is released the presser from Powell will of course be heavily scrutinised, especially on how Powell sees recent inflation data. Powell should also provide an update on discussions around QT but it is unlikely they are ready yet to release updated guidance.
One additional global highlight this week might be a big fall in UK inflation on Wednesday, suggesting that headline CPI will slow to 3.4% (vs 4% in January) and core to 4.5% (5.1%). Elsewhere there is plenty of ECB speaker appearances including President Lagarde on Wednesday. They are all highlighted in the day-by-day guide at the end.
Courtesy of DB, here is a day-by-day calendar of events
Monday March 18
- Data: US March New York Fed services business activity, NAHB housing market index, China February retail sales, industrial production, property investment, Eurozone January trade balance, Canada February raw materials, industrial product price index, existing home sales
Tuesday March 19
- Data: US January total net TIC flows, February housing starts, building permits, Japan January capacity utilization, Germany and Eurozone March Zew survey, Eurozone Q4 labour costs, Canada February CPI
- Central banks: BoJ decision, ECB's Guindos speaks, RBA decision
- Auctions: US 20-yr Bond ($13bn, reopening)
Wednesday March 20
- Data: UK February CPI, PPI, RPI, January house price index, China 1-yr and 5-yr loan prime rates, Japan February trade balance, Italy January industrial production, Germany February PPI, Eurozone March consumer confidence, January construction output
- Central banks: Fed's decision, ECB's Lagarde, Lane, De Cos, Schnabel, Nagel and Holzmann speak, BoC summary of deliberations
- Earnings: Tencent, Micron
Thursday March 21
- Data: US, UK, Japan, Germany, France and Eurozone March PMIs, US March Philadelphia Fed business outlook, February leading index, existing home sales, Q4 current account balance, initial jobless claims, UK February public finances, Japan February national CPI, Italy January current account balance, France March manufacturing confidence, February retail sales, ECB January current account, EU27 February new car registrations
- Central banks: BoE decision, SNB decision
- Earnings: Nike, FedEx, Lululemon, BMW, Enel
- Auctions: US 10-yr TIPS ($16bn, reopening)
- Other: European Union summit, through March 22
Friday March 22
- Data: UK March GfK consumer confidence, February retail sales, Germany March Ifo survey, January import price index, Canada January retail sales
* * *
Finally, looking at just the US, Goldman notes that the key economic data releases this week are the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index and existing home sales reports on Thursday. The March FOMC meeting is on Wednesday. The post-meeting statement will be released at 2:00 PM ET, followed by Chair Powell’s press conference at 2:30 PM. There are several speaking engagements from Fed officials this week, including Chair Powell, Vice Chair for Supervision Barr, and President Bostic.
Monday, March 18
- There are no major economic data releases scheduled.
Tuesday, March 19
- 08:30 AM Housing starts, February (GS +9.4%, consensus +7.4%, last -14.8%); Building permits, February (consensus +2.0%, last -0.3%)
Wednesday, March 20
- 02:00 PM FOMC statement, March 19 – March 20 meeting: As discussed in our FOMC preview, we continue to expect the committee to target a first cut in June, but we now expect 3 cuts in 2024 in June, September, and December (vs. 4 previously) given the slightly higher inflation path. We continue to expect 4 cuts in 2025 and now expect 1 final cut in 2026 to an unchanged terminal rate forecast of 3.25-3.5%. The main risk to our expectation is that FOMC participants might be more concerned about the recent inflation data and less convinced that inflation will resume its earlier soft trend. In that case, they might bump up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast to 2.5% and show a 2-cut median.
Thursday, March 21
- 08:30 AM Current account balance, Q4 (consensus -$209.5bn, last -$200.3bn)
- 08:30 AM Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index, March (GS 3.2, consensus -1.3, last 5.2): We estimate that the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index fell 2pt to 3.2 in March. While the measure is elevated relative to other surveys, we expect a boost from the rebound in foreign manufacturing activity and the pickup in US production and freight activity.
- 08:30 AM Initial jobless claims, week ended March 16 (GS 210k, consensus 215k, last 209k): Continuing jobless claims, week ended March 9 (consensus 1,815k, last 1,811k)
- 09:45 AM S&P Global US manufacturing PMI, March preliminary (consensus 51.8, last 52.2): S&P Global US services PMI, March preliminary (consensus 52.0, last 52.3)
- 10:00 AM Existing home sales, February (GS +1.2%, consensus -1.6%, last +3.1%)
- 02:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair Michael for Supervision Barr will participate in a fireside chat in Ann Arbor, MI with students and faculty. A moderated Q&A is expected. On February 14, Barr said the Fed is “confident we are on a path to 2% inflation,” but the recent report showing prices rose faster than anticipated in January “is a reminder that the path back to 2% inflation may be a bumpy one.” Barr also noted that “we need to see continued good data before we can begin the process of reducing the federal funds rate.”
Friday, March 22
- 09:00 AM Fed Reserve Chair Powell speaks: The Federal Reserve Board will host a Fed Listens event in Washington D.C. on “Transitioning to the Post-Pandemic Economy.” Chair Powell will deliver opening remarks. Vice Chair Phillip Jefferson and Fed Governor Michelle Bowman will moderate conversations with leaders from various organizations. On March 6, Chair Powell noted in his congressional testimony that if the economy evolves broadly as expected, it will likely be appropriate to begin dialing back policy restraint at some point this year.
- 12:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Michael Barr will participate in a virtual event on “International Economic and Monetary Design.” A moderated Q&A is expected.
- 04:00 PM Atlanta Fed President Bostic (FOMC voter) speaks: Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic will participate in a moderated conversation at the 2024 Household Finance Conference in Atlanta. On March 4, Bostic said, “I need to see more progress to feel fully confident that inflation is on a sure path to averaging 2% over time.” Bostic also noted, “I expect the first interest rate cut, which I have penciled in for the third quarter, will be followed by a pause in the following meeting.”
Source: DB, Goldman, BofA
International
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
Key Events This Week: Central Banks Galore Including A Historic Rate Hike By The BOJ
According to DB’s Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark…

According to DB's Jim Reid, "this could be a landmark week in markets as the last global holdout on negative rates looks set to be removed as the BoJ likely hikes rates from -0.1% tomorrow." That will likely overshadow the FOMC that concludes on Wednesday that will have its own signalling intrigue given recent strong inflation. We also have the RBA meeting tomorrow and the SNB and BoE meetings on Thursday to close out a big week for global central bankers with many EM countries also deciding on policy. We’ll preview the main meetings in more depth below but outside of this we have the global flash PMIs on Thursday as well as inflation reports in Japan (Thursday) and the UK (Wednesday). US housing data also permeates through the week as you'll see in the full global day-by-day week ahead at the end as usual.
Let’s go into detail now, starting with the BoJ tomorrow. We’ve had negative base rates now for 8 years which if is the longest run ever seen for any country in the history of mankind. In fact it is doubtful that pre-historic man was as generous as to charge negative interest rates on lending money prior to this! It also might be one of the longest global runs without any interest rate hikes given the 17 year run that could end tomorrow. So, as Reid puts it, a landmark event.
DB's Chief Japan economist expects the central bank to revise its policy and abandon both NIRP and the multi-tiered current account structure and set rates on all excess reserves at 0.1%. He also sees both the yield curve control (YCC) and the inflation-overshooting commitment ending, replaced by a benchmark for the pace of the bank’s JGB purchasing activity. The house view forecast of 50bps of hikes through 2025 is more hawkish than the market but risks are still tilted to the upside. On Friday, the Japan Trade Union Confederation (Rengo) announced the first tally of the results of this year's shunto spring wage negotiation. The wage increase rate, including the seniority-based wage hike, is 5.28%, which was significantly higher than expected. This year will probably see the highest wage settlements since 1991 which given Japan’s recent history is an incredible turnaround. This wage data news has firmed up expectations for tomorrow.
With regards to the FOMC which concludes on Wednesday, DB economists expect only minor revisions to the meeting statement that saw an overhaul last meeting. With regards to the SEP, the growth and unemployment forecasts are unlikely to change but the 2024 inflation forecasts potentially could; elsewhere, expect the Fed to revise up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast by a tenth to 2.5%, although they see meaningful risks that it gets revised up even higher to 2.6%. In our economists' view, a 2.5% core PCE reading would allow just enough wiggle room to keep the 2024 fed funds rate at 4.6% (75bps of cuts). However, if core PCE inflation were revised up to 2.6%, it would likely entail the Fed moving their base case back to 50bps of cuts, as this would essentially reflect the same forecasts as the September 2023 SEP.
Beyond 2024, DB expect officials to build in less policy easing due to a higher r-star. If two of the eight officials currently at 2.5% move up by 25bps, then the long-run median forecast would edge up to 2.6%. This could be justified by a one-tenth upgrade to the long-run growth forecast. After all this information is released the presser from Powell will of course be heavily scrutinised, especially on how Powell sees recent inflation data. Powell should also provide an update on discussions around QT but it is unlikely they are ready yet to release updated guidance.
One additional global highlight this week might be a big fall in UK inflation on Wednesday, suggesting that headline CPI will slow to 3.4% (vs 4% in January) and core to 4.5% (5.1%). Elsewhere there is plenty of ECB speaker appearances including President Lagarde on Wednesday. They are all highlighted in the day-by-day guide at the end.
Courtesy of DB, here is a day-by-day calendar of events
Monday March 18
- Data: US March New York Fed services business activity, NAHB housing market index, China February retail sales, industrial production, property investment, Eurozone January trade balance, Canada February raw materials, industrial product price index, existing home sales
Tuesday March 19
- Data: US January total net TIC flows, February housing starts, building permits, Japan January capacity utilization, Germany and Eurozone March Zew survey, Eurozone Q4 labour costs, Canada February CPI
- Central banks: BoJ decision, ECB's Guindos speaks, RBA decision
- Auctions: US 20-yr Bond ($13bn, reopening)
Wednesday March 20
- Data: UK February CPI, PPI, RPI, January house price index, China 1-yr and 5-yr loan prime rates, Japan February trade balance, Italy January industrial production, Germany February PPI, Eurozone March consumer confidence, January construction output
- Central banks: Fed's decision, ECB's Lagarde, Lane, De Cos, Schnabel, Nagel and Holzmann speak, BoC summary of deliberations
- Earnings: Tencent, Micron
Thursday March 21
- Data: US, UK, Japan, Germany, France and Eurozone March PMIs, US March Philadelphia Fed business outlook, February leading index, existing home sales, Q4 current account balance, initial jobless claims, UK February public finances, Japan February national CPI, Italy January current account balance, France March manufacturing confidence, February retail sales, ECB January current account, EU27 February new car registrations
- Central banks: BoE decision, SNB decision
- Earnings: Nike, FedEx, Lululemon, BMW, Enel
- Auctions: US 10-yr TIPS ($16bn, reopening)
- Other: European Union summit, through March 22
Friday March 22
- Data: UK March GfK consumer confidence, February retail sales, Germany March Ifo survey, January import price index, Canada January retail sales
* * *
Finally, looking at just the US, Goldman notes that the key economic data releases this week are the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index and existing home sales reports on Thursday. The March FOMC meeting is on Wednesday. The post-meeting statement will be released at 2:00 PM ET, followed by Chair Powell’s press conference at 2:30 PM. There are several speaking engagements from Fed officials this week, including Chair Powell, Vice Chair for Supervision Barr, and President Bostic.
Monday, March 18
- There are no major economic data releases scheduled.
Tuesday, March 19
- 08:30 AM Housing starts, February (GS +9.4%, consensus +7.4%, last -14.8%); Building permits, February (consensus +2.0%, last -0.3%)
Wednesday, March 20
- 02:00 PM FOMC statement, March 19 – March 20 meeting: As discussed in our FOMC preview, we continue to expect the committee to target a first cut in June, but we now expect 3 cuts in 2024 in June, September, and December (vs. 4 previously) given the slightly higher inflation path. We continue to expect 4 cuts in 2025 and now expect 1 final cut in 2026 to an unchanged terminal rate forecast of 3.25-3.5%. The main risk to our expectation is that FOMC participants might be more concerned about the recent inflation data and less convinced that inflation will resume its earlier soft trend. In that case, they might bump up their 2024 core PCE inflation forecast to 2.5% and show a 2-cut median.
Thursday, March 21
- 08:30 AM Current account balance, Q4 (consensus -$209.5bn, last -$200.3bn)
- 08:30 AM Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index, March (GS 3.2, consensus -1.3, last 5.2): We estimate that the Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index fell 2pt to 3.2 in March. While the measure is elevated relative to other surveys, we expect a boost from the rebound in foreign manufacturing activity and the pickup in US production and freight activity.
- 08:30 AM Initial jobless claims, week ended March 16 (GS 210k, consensus 215k, last 209k): Continuing jobless claims, week ended March 9 (consensus 1,815k, last 1,811k)
- 09:45 AM S&P Global US manufacturing PMI, March preliminary (consensus 51.8, last 52.2): S&P Global US services PMI, March preliminary (consensus 52.0, last 52.3)
- 10:00 AM Existing home sales, February (GS +1.2%, consensus -1.6%, last +3.1%)
- 02:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair Michael for Supervision Barr will participate in a fireside chat in Ann Arbor, MI with students and faculty. A moderated Q&A is expected. On February 14, Barr said the Fed is “confident we are on a path to 2% inflation,” but the recent report showing prices rose faster than anticipated in January “is a reminder that the path back to 2% inflation may be a bumpy one.” Barr also noted that “we need to see continued good data before we can begin the process of reducing the federal funds rate.”
Friday, March 22
- 09:00 AM Fed Reserve Chair Powell speaks: The Federal Reserve Board will host a Fed Listens event in Washington D.C. on “Transitioning to the Post-Pandemic Economy.” Chair Powell will deliver opening remarks. Vice Chair Phillip Jefferson and Fed Governor Michelle Bowman will moderate conversations with leaders from various organizations. On March 6, Chair Powell noted in his congressional testimony that if the economy evolves broadly as expected, it will likely be appropriate to begin dialing back policy restraint at some point this year.
- 12:00 PM Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Barr speaks: Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Michael Barr will participate in a virtual event on “International Economic and Monetary Design.” A moderated Q&A is expected.
- 04:00 PM Atlanta Fed President Bostic (FOMC voter) speaks: Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic will participate in a moderated conversation at the 2024 Household Finance Conference in Atlanta. On March 4, Bostic said, “I need to see more progress to feel fully confident that inflation is on a sure path to averaging 2% over time.” Bostic also noted, “I expect the first interest rate cut, which I have penciled in for the third quarter, will be followed by a pause in the following meeting.”
Source: DB, Goldman, BofA
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Spread & Containment5 days ago
Spread & Containment5 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International1 week ago
International1 week agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















