Government
Futures Slide, Nat Gas Soars As Traders Return From Holiday
Futures Slide, Nat Gas Soars As Traders Return From Holiday
Equity futures fell, Treasury yields rose and nat gas prices soared to the highest…
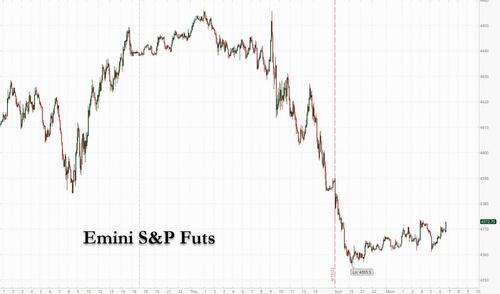
Equity futures fell, Treasury yields rose and nat gas prices soared to the highest since 2008 as US markets reopened after a three-day holiday weekend while the U.K. and euro-zone markets remain closed. Nasdaq 100 futures led the retreat, falling 0.3% at 730 a.m. EDT after tumbling as much as 0.8%, and signaling a bearish start to the week after the U.S. market was closed on Friday for a holiday. S&P 500 futures also dropped 0.2%, while European markets remained closed on Monday. Oil was flat, while a cautious overall investor mood bolstered the dollar and gold. The USDJPY was set for the longest winning streak on record.
Nat gas soared another 3%, rising to the highest level since 2008.
“We think inflation is no longer a net positive for earnings growth given the impact on costs that are now showing up in margins,” Morgan Stanley strategists led by Michael Wilson wrote in a note. The effects of soaring prices “are now more likely to be a headwind to growth.”
In U.S. premarket trading, Twitter rose after Elon Musk said the economic interests of the board are not aligned with shareholders as the social media company took steps to ward off his takeover attempt. Meanwhile, DiDi Global plummeted after the company said it will hold an extraordinary general meeting on May 23 to vote on delisting its shares from the New York Stock Exchange.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell may reinforce bets that the central bank will raise interest rates by a half point in May when he speaks at an event on Thursday. Later that day he’s due to participate in a panel hosted by the International Monetary Fund. Investors will also focus on earnings and guidance as companies from Bank of America to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation report on Monday.
The pattern across markets suggests investors remain uncertain whether high inflation has peaked or not. Price pressures are being fanned by supply-chain snarls from China’s Covid restrictions and disruptions to commodity flows due to the war. Concern is growing that the U.S. economy faces a downturn as the Fed pivots toward aggressive policy tightening to contain the cost of living. History suggests the Fed will face a difficult task in tightening policy to cool inflation without causing a U.S. recession, according to Goldman Sachs Group Inc. It put the odds of a contraction at about 35% over the next two years.
“Major regime change is rarely smooth in either geopolitics or economics, and markets are under-pricing these risks,” Eric Robertsen, chief strategist at Standard Chartered Bank Plc, wrote in a note. “We are increasingly concerned about a summer of turbulence and volatility.”
Meanwhile, in its latest downbeat note, Morgan Stanley wrote that the positive effects from inflation on earnings growth for U.S. firms have peaked as rising costs trim their margins and price pressures caused by the Ukraine war hit consumers.
U.S. index futures followed a decline in Asia-Pacific stocks, which were sapped by Japan and China, despite the latter reporting stronger than expected GDP while March economic data confirmed that recent lockdowns have crippled the local economy. Markets in Australia, Hong Kong and much of Europe remain shut for Easter.
Asian stocks dropped for a second day in holiday-thinned trading amid continued concern over the impact of inflation and efforts to contain it on global economic growth. The MSCI Asia Pacific Index fell as much as 1.1%, with India, Vietnam and Japan leading losses among national benchmarks. Mumbai-listed IT giants were among the biggest drags on the regional gauge after disappointing results from Infosys due to surging wages. Hong Kong and Australia remained closed for Easter holidays. Energy stocks outperformed after oil climbed on political unrest in Libya and Russia’s warning of the potential for record prices if more nations ban its products. Concerns of energy-driven inflation and moves by the Federal Reserve and other central banks to combat it have driven the recent global equity selloff, with tech stocks bearing the brunt in Asia. Meanwhile, China reported faster economic growth for the first quarter, while retail sales in March showed the first monthly decline since July 2020, as markets brace for the impact of the latest Covid outbreaks and lockdowns. The nation’s central bank refrained from lowering interest rates Friday, disappointing investors who had been looking for a cut. China Jitters Mount as Easing Calls Echo Across Trading Floors “China’s first quarter GDP was a bit stronger than expected, but what matters now is how the economy is doing after lockdowns in Shanghai so I see very limited impact on markets,” said Ayako Sera, a market strategist at Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Bank. “I would think we are just seeing a calm before the storm.”
In geopolitics, Ukrainian officials said the remaining defenders of Mariupol are encircled by Russian forces but have not surrendered the strategically important port city, as a deadly strike was reported in Lviv near the Polish border. Ukrainian officials will be in Washington for this week’s meetings of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank to seek financial support.
In rates, Treasuries were higher across the curve by ~1bp, led by longer-maturity issues; 10- and 30-year yields reached new YTD highs, steepening the curve. 10-year Treasury yields edged down one point to 2.83% in the Asia session after rising as much as 5bps earlier in the session to 2.88% and rising 13 basis points last week; 30-year as much as 4.4bp to 2.96%; 2s10s and 5s30s spreads are wider but remain inside last week’s ranges, when both steepened sharply for a second straight week as traders dialed back the total amount of Fed tightening that’s expected following smaller-than-expected increase in the March core CPI. Yields climbed during Asia session amid speculation the market will move further toward pricing in a half-point rate increase by the Fed at its May meeting, already almost fully priced in.
In FX, a gauge of the dollar rose against all its Group-of-10 peers; The New Zealand and Australian dollars led declines while the Japanese yen outperformed, swinging between gains and losses as BOJ Governor Haruhiko Kuroda said the currency’s rapid moves were fueling negative effects on the economy. The dollar extended its advance for a 12th day versus the yen, the longest winning streak on record, according to data going back five decades compiled by Bloomberg. USD/JPY up by as much as 0.3% to 126.79; one-week risk reversals at a 35 basis-point premium in favor of the topside. Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda said a weak yen is good for the economy, although a rapid drop can disrupt corporate planning.
“With several markets closed for holiday today, the low liquidity may potentially amplify the risk-off market moves, aiding to support the dollar strength,” said Jun Rong Yeap, market strategist at IG Asia Pte.
The currency market stuck to the trading patterns of recent days as a holiday-thinned session on Monday brought low volumes in spot and options markets alike.
Market Snapshot
- S&P 500 futures down 0.4% to 4,371.75
- MXAP down 0.9% to 172.33
- MXAPJ down 0.7% to 572.84
- Nikkei down 1.1% to 26,799.71
- Topix down 0.9% to 1,880.08
- Hang Seng Index up 0.7% to 21,518.08
- Shanghai Composite down 0.5% to 3,195.52
- Sensex down 2.2% to 57,073.46
- Australia S&P/ASX 200 up 0.6% to 7,523.43
- Kospi down 0.1% to 2,693.21
- Brent Futures down 0.4% to $111.27/bbl
- Gold spot up 0.7% to $1,991.92
- U.S. Dollar Index up 0.22% to 100.72
Top Overnight News from Bloomberg
- U.S. natural gas prices surged to the highest level in over 13 years as robust demand tests drillers’ ability to expand supplies
- China reported its biggest decline in consumer spending and worst unemployment rate since the early months of the pandemic as Covid lockdowns put a strain on the world’s second- largest economy
- Shanghai reported its first deaths as the biggest Covid flareup China has faced during the pandemic prompted more cities around the country to impose restrictions on their residents
- The odds of an economic contraction in the U.S. over the next two years are about 35%, according to Goldman Sachs Group Inc.
- Long-maturity Treasuries are contending with their biggest drawdown on record, according to their most popular exchange-traded fund
- Japan’s giant investors look set to bet on yen weakness continuing and boost their purchases of Treasuries over the rest of the year
A more detailed look at global markets courtesy of Newsquawk
Asian stocks traded mostly negative and US equity futures were also subdued amid a higher yield environment as gains in energy prices stoked inflationary' concerns, while market sentiment was also clouded by the mass holiday closures for Easter Monday and with participants reflecting on the recent PBoC actions and Chinese GDP data. Nikkei 225 (-1.6%) underperformed and fell beneath the 27k level with the index not helped by a choppy currency as officials continued their jawboning including BoJ Governor Kuroda who stated the recent Yen weakening has been quite sharp and that an excessively weak Yen or the currency's rapid depreciation can have a further negative impact but is basically positive overall. KOSPI (+0.1%) was indecisive after North Korea conducted projectile launches a day after the 110th birth anniversary of leader Kim's late grandfather and state founder Kim II Sung, while the US and South Korea are also to begin their spring training exercises this week. Shanghai Comp. (-0.8%) was negative following the PBoC’s recent actions including the narrower than expected 25bps RRR cut on Friday which follows the central bank's surprise decision to keep its 1-year MLF rate unchanged and with headwinds from the ongoing COVID-19 concerns in China where more cities tightened controls and Shanghai reported its first fatalities from the current outbreak but also recently unveiled plans to resume production in the city. Furthermore, stronger than expected Chinese GDP growth for Q1 and Industrial Production in March failed to spur risk appetite, as the data only partially took into account the latest restrictions including the lockdown in Shanghai that began in late March, while Retail Sales disappointed and the Unemployment Rate increased. As a reminder, markets in Australia. New Zealand and Hong Kong were closed for holiday and there are also mass closures across Europe including the UK for Easter Monday.
Top Asian News
- Larsen Said to Weigh Merging Tech Arms Into $22 Billion Firm
- Sri Lanka Must Show IMF Sustainable Debt Plan to Secure Aid
- Tesla Shanghai Sets Out Hand Washing, Sleeping Plans for Workers
- DiDi Shares Plunge in U.S. Premarket on Plan for Delisting Vote
Europe remains closed for the Easter holiday
US Event Calendar
- 10:00: April NAHB Housing Market Index, est. 77, prior 79
Central Banks
- 16:00: Fed’s Bullard Discusses the U.S. Economy and Monetary Policy
Government
Buyouts can bring relief from medical debt, but they’re far from a cure
Local governments are increasingly buying – and forgiving – their residents’ medical debt.
One in 10 Americans carry medical debt, while 2 in 5 are underinsured and at risk of not being able to pay their medical bills.
This burden crushes millions of families under mounting bills and contributes to the widening gap between rich and poor.
Some relief has come with a wave of debt buyouts by county and city governments, charities and even fast-food restaurants that pay pennies on the dollar to clear enormous balances. But as a health policy and economics researcher who studies out-of-pocket medical expenses, I think these buyouts are only a partial solution.
A quick fix that works
Over the past 10 years, the nonprofit RIP Medical Debt has emerged as the leader in making buyouts happen, using crowdfunding campaigns, celebrity engagement, and partnerships in the private and public sectors. It connects charitable buyers with hospitals and debt collection companies to arrange the sale and erasure of large bundles of debt.
The buyouts focus on low-income households and those with extreme debt burdens. You can’t sign up to have debt wiped away; you just get notified if you’re one of the lucky ones included in a bundle that’s bought off. In 2020, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services reviewed this strategy and determined it didn’t violate anti-kickback statutes, which reassured hospitals and collectors that they wouldn’t get in legal trouble partnering with RIP Medical Debt.
Buying a bundle of debt saddling low-income families can be a bargain. Hospitals and collection agencies are typically willing to sell the debt for steep discounts, even pennies on the dollar. That’s a great return on investment for philanthropists looking to make a big social impact.
And it’s not just charities pitching in. Local governments across the country, from Cook County, Illinois, to New Orleans, have been directing sizable public funds toward this cause. New York City recently announced plans to buy off the medical debt for half a million residents, at a cost of US$18 million. That would be the largest public buyout on record, although Los Angeles County may trump New York if it carries out its proposal to spend $24 million to help 810,000 residents erase their debt.
Nationally, RIP Medical Debt has helped clear more than $10 billion in debt over the past decade. That’s a huge number, but a small fraction of the estimated $220 billion in medical debt out there. Ultimately, prevention would be better than cure.
Preventing medical debt is trickier
Medical debt has been a persistent problem over the past decade even after the reforms of the 2010 Affordable Care Act increased insurance coverage and made a dent in debt, especially in states that expanded Medicaid. A recent national survey by the Commonwealth Fund found that 43% of Americans lacked adequate insurance in 2022, which puts them at risk of taking on medical debt.
Unfortunately, it’s incredibly difficult to close coverage gaps in the patchwork American insurance system, which ties eligibility to employment, income, age, family size and location – all things that can change over time. But even in the absence of a total overhaul, there are several policy proposals that could keep the medical debt problem from getting worse.
Medicaid expansion has been shown to reduce uninsurance, underinsurance and medical debt. Unfortunately, insurance gaps are likely to get worse in the coming year, as states unwind their pandemic-era Medicaid rules, leaving millions without coverage. Bolstering Medicaid access in the 10 states that haven’t yet expanded the program could go a long way.
Once patients have a medical bill in hand that they can’t afford, it can be tricky to navigate financial aid and payment options. Some states, like Maryland and California, are ahead of the curve with policies that make it easier for patients to access aid and that rein in the use of liens, lawsuits and other aggressive collections tactics. More states could follow suit.
Another major factor driving underinsurance is rising out-of-pocket costs – like high deductibles – for those with private insurance. This is especially a concern for low-wage workers who live paycheck to paycheck. More than half of large employers believe their employees have concerns about their ability to afford medical care.
Lowering deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums could protect patients from accumulating debt, since it would lower the total amount they could incur in a given time period. But if the current system otherwise stayed the same, then premiums would have to rise to offset the reduction in out-of-pocket payments. Higher premiums would transfer costs across everyone in the insurance pool and make enrolling in insurance unreachable for some – which doesn’t solve the underinsurance problem.
Reducing out-of-pocket liability without inflating premiums would only be possible if the overall cost of health care drops. Fortunately, there’s room to reduce waste. Americans spend more on health care than people in other wealthy countries do, and arguably get less for their money. More than a quarter of health spending is on administrative costs, and the high prices Americans pay don’t necessarily translate into high-value care. That’s why some states like Massachusetts and California are experimenting with cost growth limits.
Momentum toward policy change
The growing number of city and county governments buying off medical debt signals that local leaders view medical debt as a problem worth solving. Congress has passed substantial price transparency laws and prohibited surprise medical billing in recent years. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau is exploring rule changes for medical debt collections and reporting, and national credit bureaus have voluntarily removed some medical debt from credit reports to limit its impact on people’s approval for loans, leases and jobs.
These recent actions show that leaders at all levels of government want to end medical debt. I think that’s a good sign. After all, recognizing a problem is the first step toward meaningful change.
Erin Duffy receives funding from Arnold Ventures.
congress trump pandemicGovernment
Student Loan Forgiveness Is Robbing Peter To Pay Paul
Student Loan Forgiveness Is Robbing Peter To Pay Paul
Via SchiffGold.com,
With President Biden’s Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE)…

With President Biden’s Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) plan set to extend more student loan relief to borrowers this summer, the federal government is pretending it can wave a magic wand to make debts disappear. But the truth of student debt “relief” is that they’re simply shifting the burden to everyone else, robbing Peter to pay Paul and funneling more steam into an inflation pressure cooker that’s already set to burst.
Starting July 1st, new rules go into effect that change the discretionary income requirements for their payment plans from 10% to only 5% for undergraduates, leading to lower payments for millions. Some borrowers will even have their owed balances revert to zero.
What the plan doesn’t describe, predictably, is how that burden will be shifted to the rest of the country by stealing value out of their pockets via new taxes or increased inflation, which still simmering well above levels seen in early 2020 before the Fed printed trillions in Covid “stimulus” money. They’re rewarding students who took out loans they can’t afford and punishing those who paid their way or repaid their loans, attending school while living within their means. And they’re stealing from the entire country to finance it.
Biden actually claims that a continuing Covid “emergency” is what gives him the authority to offer student loan forgiveness to begin with. As with any “temporary” measure that gives state power a pretense to grow, or gives them an excuse to collect more revenue (I’m looking at you, federal income tax), COVID-19 continues to be the gift that keeps on giving for power and revenue-hungry politicians even as the CDC reclassifies the virus as a threat similar to the seasonal flu.
The SAVE plan takes the burden of billions of dollars in owed payments away from students and adds it to a national debt that’s already ballooning to the tune of a mind-boggling trillion dollars every 3 months. If all student loan debt were forgiven, according to the Brookings Institution, it would surpass the cumulative totals for the past 20 years for multiple existing tax credits and welfare programs:
“Forgiving all student debt would be a transfer larger than the amounts the nation has spent over the past 20 years on unemployment insurance, larger than the amount it has spent on the Earned Income Tax Credit, and larger than the amount it has spent on food stamps.”
Ironically enough, adding hundreds of billions to the national debt from Biden’s program is likely to cause the most pain to the very demographics the Biden administration claims to be helping with its plan: poor people, anyone who skipped college entirely or paid their loans back, and other already overly-indebted young adults, whose purchasing power is being rapidly eroded by out-of-control government spending and central bank monetary shenanigans. It effectively transfers even more wealth from the poor to the wealthy, a trend that Covid-era measures have taken to new extremes.
As Ron Paul pointed out in a recent op-ed for the Eurasia Review:
“…these loans will be paid off in part by taxpayers who did not go to college, paid their own way through school, or have already paid off their student loans. Since those with college degrees tend to earn more over time than those without them, this program redistributes wealth from lower to higher income Americans.”
Even some progressives are taking aim at the plan, not because it shifts the debt burden to other Americans, but because it will require cutting welfare or sacrificing other expensive social programs promised by Biden such as universal pre-K. For these critics, the issue isn’t so much that spending and debt are totally out of control, but that they’re being funneled into the wrong issues.
Progressive “solutions” always seem to take the form of slogans like “tax the wealthy,” a feel-good bromide that for lawmakers always seems to translate into increased taxes for the middle and lower-upper class. Meanwhile, the .01% continue to avoid taxes through offshore accounts, money laundering trickery dressed up as philanthropy, and general de facto ownership of the system through channels like political donations and aggressive lobbying.
If new waves of college applicants expect loan forgiveness plans to continue, it also encourages schools to continue raising tuition and motivates prospective students to continue with even more irresponsible borrowing.
This puts pressure on the Fed to keep interest rates lower to help accommodate waves of new student loan applicants from sparkly-eyed young borrowers who figure they’ll never really have to pay the money back.
With the Fed already expected to cut rates this year despite inflation not being properly under control, the loan forgiveness scheme is just one of many factors conspiring to cause inflation to start running hotter again, spiraling out of control, as the entire country is forced to pay the hidden tax of price increases for all their basic needs.
International
Analyst reviews Apple stock price target amid challenges
Here’s what could happen to Apple shares next.

They said it was bound to happen.
It was Jan. 11, 2024 when software giant Microsoft (MSFT) briefly passed Apple (AAPL) as the most valuable company in the world.
Microsoft's stock closed 0.5% higher, giving it a market valuation of $2.859 trillion.
It rose as much as 2% during the session and the company was briefly worth $2.903 trillion. Apple closed 0.3% lower, giving the company a market capitalization of $2.886 trillion.
"It was inevitable that Microsoft would overtake Apple since Microsoft is growing faster and has more to benefit from the generative AI revolution," D.A. Davidson analyst Gil Luria said at the time, according to Reuters.
The two tech titans have jostled for top spot over the years and Microsoft was ahead at last check, with a market cap of $3.085 trillion, compared with Apple's value of $2.684 trillion.
Analysts noted that Apple had been dealing with weakening demand, including for the iPhone, the company’s main source of revenue.
Demand in China, a major market, has slumped as the country's economy makes a slow recovery from the pandemic and competition from Huawei.
Sales in China of Apple's iPhone fell by 24% in the first six weeks of 2024 compared with a year earlier, according to research firm Counterpoint, as the company contended with stiff competition from a resurgent Huawei "while getting squeezed in the middle on aggressive pricing from the likes of OPPO, vivo and Xiaomi," said senior Analyst Mengmeng Zhang.
“Although the iPhone 15 is a great device, it has no significant upgrades from the previous version, so consumers feel fine holding on to the older-generation iPhones for now," he said.
Big plans for China
Counterpoint said that the first six weeks of 2023 saw abnormally high numbers with significant unit sales being deferred from December 2022 due to production issues.
Apple is planning to open its eighth store in Shanghai – and its 47th across China – on March 21.
Related: Tech News Now: OpenAI says Musk contract 'never existed', Xiaomi's EV, and more
The company also plans to expand its research centre in Shanghai to support all of its product lines and open a new lab in southern tech hub Shenzhen later this year, according to the South China Morning Post.
Meanwhile, over in Europe, Apple announced changes to comply with the European Union's Digital Markets Act (DMA), which went into effect last week, Reuters reported on March 12.
Beginning this spring, software developers operating in Europe will be able to distribute apps to EU customers directly from their own websites instead of through the App Store.
"To reflect the DMA’s changes, users in the EU can install apps from alternative app marketplaces in iOS 17.4 and later," Apple said on its website, referring to the software platform that runs iPhones and iPads.
"Users will be able to download an alternative marketplace app from the marketplace developer’s website," the company said.
Apple has also said it will appeal a $2 billion EU antitrust fine for thwarting competition from Spotify (SPOT) and other music streaming rivals via restrictions on the App Store.
The company's shares have suffered amid all this upheaval, but some analysts still see good things in Apple's future.
Bank of America Securities confirmed its positive stance on Apple, maintaining a buy rating with a steady price target of $225, according to Investing.com.
The firm's analysis highlighted Apple's pricing strategy evolution since the introduction of the first iPhone in 2007, with initial prices set at $499 for the 4GB model and $599 for the 8GB model.
BofA said that Apple has consistently launched new iPhone models, including the Pro/Pro Max versions, to target the premium market.
Analyst says Apple selloff 'overdone'
Concurrently, prices for previous models are typically reduced by about $100 with each new release.
This strategy, coupled with installment plans from Apple and carriers, has contributed to the iPhone's installed base reaching a record 1.2 billion in 2023, the firm said.
More Tech Stocks:
- Analyst unveils new Facebook stock price target after earnings
- Billionaire George Soros sold this popular semiconductor stock
- Ark’s Cathie Wood just traded 3 popular tech stocks
Apple has effectively shifted its sales mix toward higher-value units despite experiencing slower unit sales, BofA said.
This trend is expected to persist and could help mitigate potential unit sales weaknesses, particularly in China.
BofA also noted Apple's dominance in the high-end market, maintaining a market share of over 90% in the $1,000 and above price band for the past three years.
The firm also cited the anticipation of a multi-year iPhone cycle propelled by next-generation AI technology, robust services growth, and the potential for margin expansion.
On Monday, Evercore ISI analysts said they believed that the sell-off in the iPhone maker’s shares may be “overdone.”
The firm said that investors' growing preference for AI-focused stocks like Nvidia (NVDA) has led to a reallocation of funds away from Apple.
In addition, Evercore said concerns over weakening demand in China, where Apple may be losing market share in the smartphone segment, have affected investor sentiment.
And then ongoing regulatory issues continue to have an impact on investor confidence in the world's second-biggest company.
“We think the sell-off is rather overdone, while we suspect there is strong valuation support at current levels to down 10%, there are three distinct drivers that could unlock upside on the stock from here – a) Cap allocation, b) AI inferencing, and c) Risk-off/defensive shift," the firm said in a research note.
Related: Veteran fund manager picks favorite stocks for 2024
stocks pandemic recovery european europe eu china-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges
























