From CRISPR to glowing proteins to optogenetics – scientists’ most powerful technologies have been borrowed from nature
Three pioneering technologies have forever altered how researchers do their work and promise to revolutionize medicine, from correcting genetic disorders to treating degenerative brain diseases.

Watson and Crick, Schrödinger and Einstein all made theoretical breakthroughs that have changed the world’s understanding of science.
Today big, game-changing ideas are less common. New and improved techniques are the driving force behind modern scientific research and discoveries. They allow scientists – including chemists like me – to do our experiments faster than before, and they shine light on areas of science hidden to our predecessors.
Three cutting-edge techniques – the gene-editing tool CRISPR, fluorescent proteins and optogenetics – were all inspired by nature. Biomolecular tools that have worked for bacteria, jellyfish and algae for millions of years are now being used in medicine and biological research. Directly or indirectly, they will change the lives of everyday people.
Bacterial defense systems as genetic editors
Bacteria and viruses battle themselves and one another. They are at constant biochemical war, competing for scarce resources.
One of the weapons that bacteria have in their arsenal is the CRISPR-Cas system. It is a genetic library consisting of short repeats of DNA gathered over time from hostile viruses, paired with a protein called Cas that can cut viral DNA as if with scissors. In the natural world, when bacteria are attacked by viruses whose DNA has been stored in the CRISPR archive, the CRISPR-Cas system hunts down, cuts and destroys the viral DNA.
Scientists have repurposed these weapons for their own use, with groundbreaking effect. Jennifer Doudna, a biochemist based at the University of California, Berkeley, and French microbiologist Emmanuelle Charpentier shared the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry for the development of CRISPR-Cas as a gene-editing technique.

The Human Genome Project has provided a nearly complete genetic sequence for humans and given scientists a template to sequence all other organisms. However, before CRISPR-Cas, we researchers didn’t have the tools to easily access and edit the genes in living organisms. Today, thanks to CRISPR-Cas, lab work that used to take months and years and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars can be done in less than a week for just a few hundred dollars.
There are more than 10,000 genetic disorders caused by mutations that occur on only one gene, the so-called single-gene disorders. They affect millions of people. Sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease are among the most well-known of these disorders. These are all obvious targets for CRISPR therapy because it is much simpler to fix or replace just one defective gene rather than needing to correct errors on multiple genes.
For example, in preclinical studies, researchers injected an encapsuled CRISPR system into patients born with a rare genetic disease, transthyretin amyloidosis, that causes fatal nerve and heart conditions. Preliminary results from the study demonstrated that CRISPR-Cas can be injected directly into patients in such a way that it can find and edit the faulty genes associated with a disease. In the six patients included in this landmark work, the encapsuled CRISPR-Cas minimissiles reached their target genes and did their job, causing a significant drop in a misfolded protein associated with the disease.
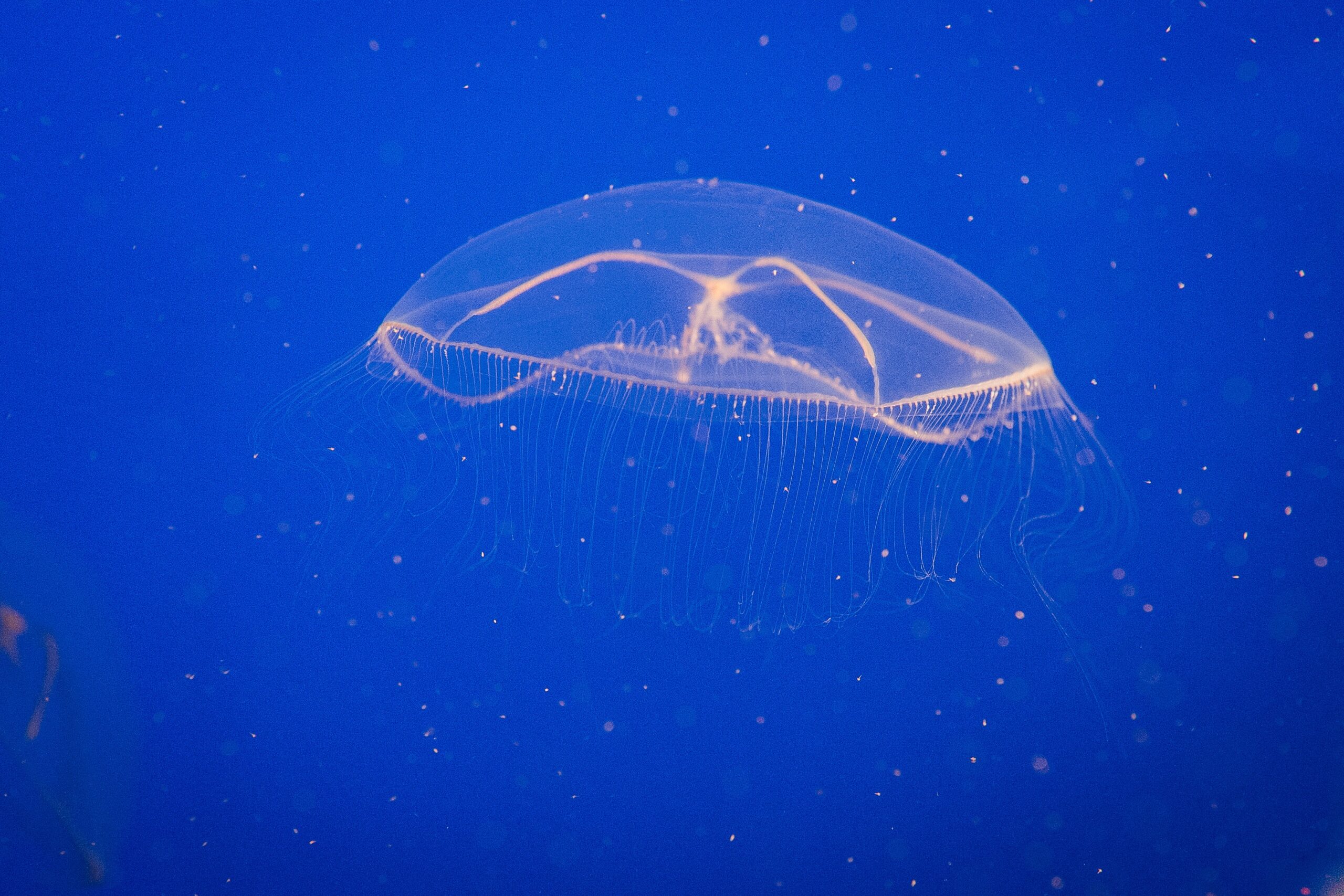
Jellyfish light up the microscopic world
The crystal jellyfish, Aequorea victoria, which drifts aimlessly in the northern Pacific, has no brain, no anus and no poisonous stingers. It is an unlikely candidate to ignite a revolution in biotechnology. Yet on the periphery of its umbrella, it has about 300 photo-organs that give off pinpricks of green light that have changed the way science is conducted.
This bioluminescent light in the jellyfish stems from a luminescent protein called aequorin and a fluorescent molecule called green fluorescent protein, or GFP. In modern biotechnology GFP acts as a molecular lightbulb that can be fused to other proteins, allowing researchers to track them and to see when and where proteins are being made in the cells of living organisms. Fluorescent protein technology is used in thousands of labs every day and has resulted in the awarding of two Nobel Prizes, one in 2008 and the other in 2014. And fluorescent proteins have now been found in many more species.

This technology proved its utility once again when researchers created genetically modified COVID-19 viruses that express GFP. The resulting fluorescence makes it possible to follow the path of the viruses as they enter the respiratory system and bind to surface cells with hairlike structures.
Algae let us play the brain neuron by neuron
When algae, which depend on sunlight for growth, are placed in a large aquarium in a darkened room, they swim around aimlessly. But if a lamp is turned on, the algae will swim toward the light. The single-celled flagellates – so named for the whiplike appendages they use to move around – don’t have eyes. Instead, they have a structure called an eyespot that distinguishes between light and darkness. The eyespot is studded with light-sensitive proteins called channelrhodopsins.
In the early 2000s, researchers discovered that when they genetically inserted these channelrhodopsins into the nerve cells of any organism, illuminating the channelrhodopsins with blue light caused neurons to fire. This technique, known as optogenetics, involves inserting the algae gene that makes channelrhodopsin into neurons. When a pinpoint beam of blue light is shined on these neurons, the channelrhodopsins open up, calcium ions flood through the neurons and the neurons fire.
Using this tool, scientists can stimulate groups of neurons selectively and repeatedly, thereby gaining a more precise understanding of which neurons to target to treat specific disorders and diseases. Optogenetics might hold the key to treating debilitating and deadly brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.

But optogenetics isn’t only useful for understanding the brain. Researchers have used optogenetic techniques to partially reverse blindness and have found promising results in clinical trials using optogenetics on patients with retinitis pigmentosa, a group of genetic disorders that break down retinal cells. And in mouse studies, the technique has been used to manipulate heartbeat and regulate bowel movements of constipated mice.
What else lies within nature’s toolbox?
What undiscovered techniques does nature still hold for us?
According to a 2018 study, people represent just 0.01% of all living things by mass but have caused the loss of 83% of all wild mammals and half of all plants in our brief time on Earth. By annihilating nature, humankind might be losing out on new, powerful and life-altering techniques without having even imagined them.
[Over 100,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today.]
After all, no one could have foreseen that the discovery of three groundbreaking processes derived from nature could change the way science is done.
Marc Zimmer received funding from NIH for his fluorescent protein research.
clinical trials preclinical genome genetic therapy dna covid-19Government
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
Survey Shows Declining Concerns Among Americans About COVID-19
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat"…
A new survey reveals that only 20% of Americans view covid-19 as "a major threat" to the health of the US population - a sharp decline from a high of 67% in July 2020.
What's more, the Pew Research Center survey conducted from Feb. 7 to Feb. 11 showed that just 10% of Americans are concerned that they will catch the disease and require hospitalization.
"This data represents a low ebb of public concern about the virus that reached its height in the summer and fall of 2020, when as many as two-thirds of Americans viewed COVID-19 as a major threat to public health," reads the report, which was published March 7.
According to the survey, half of the participants understand the significance of researchers and healthcare providers in understanding and treating long COVID - however 27% of participants consider this issue less important, while 22% of Americans are unaware of long COVID.
What's more, while Democrats were far more worried than Republicans in the past, that gap has narrowed significantly.
"In the pandemic’s first year, Democrats were routinely about 40 points more likely than Republicans to view the coronavirus as a major threat to the health of the U.S. population. This gap has waned as overall levels of concern have fallen," reads the report.
More via the Epoch Times;
The survey found that three in ten Democrats under 50 have received an updated COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older.
Moreover, 66 percent of Democrats ages 65 and older have received the updated COVID-19 vaccine, while only 24 percent of Republicans ages 65 and older have done so.
“This 42-point partisan gap is much wider now than at other points since the start of the outbreak. For instance, in August 2021, 93 percent of older Democrats and 78 percent of older Republicans said they had received all the shots needed to be fully vaccinated (a 15-point gap),” it noted.
COVID-19 No Longer an Emergency
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently issued its updated recommendations for the virus, which no longer require people to stay home for five days after testing positive for COVID-19.
The updated guidance recommends that people who contracted a respiratory virus stay home, and they can resume normal activities when their symptoms improve overall and their fever subsides for 24 hours without medication.
“We still must use the commonsense solutions we know work to protect ourselves and others from serious illness from respiratory viruses, this includes vaccination, treatment, and staying home when we get sick,” CDC director Dr. Mandy Cohen said in a statement.
The CDC said that while the virus remains a threat, it is now less likely to cause severe illness because of widespread immunity and improved tools to prevent and treat the disease.
“Importantly, states and countries that have already adjusted recommended isolation times have not seen increased hospitalizations or deaths related to COVID-19,” it stated.
The federal government suspended its free at-home COVID-19 test program on March 8, according to a website set up by the government, following a decrease in COVID-19-related hospitalizations.
According to the CDC, hospitalization rates for COVID-19 and influenza diseases remain “elevated” but are decreasing in some parts of the United States.
International
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says “I Would Support”
Rand Paul Teases Senate GOP Leader Run – Musk Says "I Would Support"
Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump…

Republican Kentucky Senator Rand Paul on Friday hinted that he may jump into the race to become the next Senate GOP leader, and Elon Musk was quick to support the idea. Republicans must find a successor for periodically malfunctioning Mitch McConnell, who recently announced he'll step down in November, though intending to keep his Senate seat until his term ends in January 2027, when he'd be within weeks of turning 86.
So far, the announced field consists of two quintessential establishment types: John Cornyn of Texas and John Thune of South Dakota. While John Barrasso's name had been thrown around as one of "The Three Johns" considered top contenders, the Wyoming senator on Tuesday said he'll instead seek the number two slot as party whip.
Paul used X to tease his potential bid for the position which -- if the GOP takes back the upper chamber in November -- could graduate from Minority Leader to Majority Leader. He started by telling his 5.1 million followers he'd had lots of people asking him about his interest in running...
Thousands of people have been asking if I'd run for Senate leadership...
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
...then followed up with a poll in which he predictably annihilated Cornyn and Thune, taking a 96% share as of Friday night, with the other two below 2% each.
????????️VOTE NOW ????️ ???? Who would you like to be the next Senate leader?
— Rand Paul (@RandPaul) March 8, 2024
Elon Musk was quick to back the idea of Paul as GOP leader, while daring Cornyn and Thune to follow Paul's lead by throwing their names out for consideration by the Twitter-verse X-verse.
I would support Rand Paul and suspect that other candidates will not actually run polls out of concern for the results, but let’s see if they will!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 8, 2024
Paul has been a stalwart opponent of security-state mass surveillance, foreign interventionism -- to include shoveling billions of dollars into the proxy war in Ukraine -- and out-of-control spending in general. He demonstrated the latter passion on the Senate floor this week as he ridiculed the latest kick-the-can spending package:
This bill is an insult to the American people. The earmarks are all the wasteful spending that you could ever hope to see, and it should be defeated. Read more: https://t.co/Jt8K5iucA4 pic.twitter.com/I5okd4QgDg
— Senator Rand Paul (@SenRandPaul) March 8, 2024
In February, Paul used Senate rules to force his colleagues into a grueling Super Bowl weekend of votes, as he worked to derail a $95 billion foreign aid bill. "I think we should stay here as long as it takes,” said Paul. “If it takes a week or a month, I’ll force them to stay here to discuss why they think the border of Ukraine is more important than the US border.”
Don't expect a Majority Leader Paul to ditch the filibuster -- he's been a hardy user of the legislative delay tactic. In 2013, he spoke for 13 hours to fight the nomination of John Brennan as CIA director. In 2015, he orated for 10-and-a-half-hours to oppose extension of the Patriot Act.
Among the general public, Paul is probably best known as Capitol Hill's chief tormentor of Dr. Anthony Fauci, who was director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease during the Covid-19 pandemic. Paul says the evidence indicates the virus emerged from China's Wuhan Institute of Virology. He's accused Fauci and other members of the US government public health apparatus of evading questions about their funding of the Chinese lab's "gain of function" research, which takes natural viruses and morphs them into something more dangerous. Paul has pointedly said that Fauci committed perjury in congressional hearings and that he belongs in jail "without question."
Musk is neither the only nor the first noteworthy figure to back Paul for party leader. Just hours after McConnell announced his upcoming step-down from leadership, independent 2024 presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy, Jr voiced his support:
Mitch McConnell, who has served in the Senate for almost 40 years, announced he'll step down this November.
— Robert F. Kennedy Jr (@RobertKennedyJr) February 28, 2024
Part of public service is about knowing when to usher in a new generation. It’s time to promote leaders in Washington, DC who won’t kowtow to the military contractors or…
In a testament to the extent to which the establishment recoils at the libertarian-minded Paul, mainstream media outlets -- which have been quick to report on other developments in the majority leader race -- pretended not to notice that Paul had signaled his interest in the job. More than 24 hours after Paul's test-the-waters tweet-fest began, not a single major outlet had brought it to the attention of their audience.
That may be his strongest endorsement yet.
Government
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While “Waiting” For Deporation, Asylum
The Great Replacement Loophole: Illegal Immigrants Score 5-Year Work Benefit While "Waiting" For Deporation, Asylum
Over the past several…
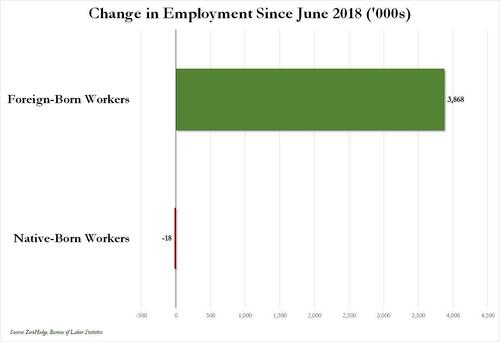
Over the past several months we've pointed out that there has been zero job creation for native-born workers since the summer of 2018...
... and that since Joe Biden was sworn into office, most of the post-pandemic job gains the administration continuously brags about have gone foreign-born (read immigrants, mostly illegal ones) workers.
And while the left might find this data almost as verboten as FBI crime statistics - as it directly supports the so-called "great replacement theory" we're not supposed to discuss - it also coincides with record numbers of illegal crossings into the United States under Biden.
In short, the Biden administration opened the floodgates, 10 million illegal immigrants poured into the country, and most of the post-pandemic "jobs recovery" went to foreign-born workers, of which illegal immigrants represent the largest chunk.

'But Tyler, illegal immigrants can't possibly work in the United States whilst awaiting their asylum hearings,' one might hear from the peanut gallery. On the contrary: ever since Biden reversed a key aspect of Trump's labor policies, all illegal immigrants - even those awaiting deportation proceedings - have been given carte blanche to work while awaiting said proceedings for up to five years...
... something which even Elon Musk was shocked to learn.
Wow, learn something new every day https://t.co/8MDtEEZGam
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 10, 2024
Which leads us to another question: recall that the primary concern for the Biden admin for much of 2022 and 2023 was soaring prices, i.e., relentless inflation in general, and rising wages in particular, which in turn prompted even Goldman to admit two years ago that the diabolical wage-price spiral had been unleashed in the US (diabolical, because nothing absent a major economic shock, read recession or depression, can short-circuit it once it is in place).
Well, there is one other thing that can break the wage-price spiral loop: a flood of ultra-cheap illegal immigrant workers. But don't take our word for it: here is Fed Chair Jerome Powell himself during his February 60 Minutes interview:
PELLEY: Why was immigration important?
POWELL: Because, you know, immigrants come in, and they tend to work at a rate that is at or above that for non-immigrants. Immigrants who come to the country tend to be in the workforce at a slightly higher level than native Americans do. But that's largely because of the age difference. They tend to skew younger.
PELLEY: Why is immigration so important to the economy?
POWELL: Well, first of all, immigration policy is not the Fed's job. The immigration policy of the United States is really important and really much under discussion right now, and that's none of our business. We don't set immigration policy. We don't comment on it.
I will say, over time, though, the U.S. economy has benefited from immigration. And, frankly, just in the last, year a big part of the story of the labor market coming back into better balance is immigration returning to levels that were more typical of the pre-pandemic era.
PELLEY: The country needed the workers.
POWELL: It did. And so, that's what's been happening.
Translation: Immigrants work hard, and Americans are lazy. But much more importantly, since illegal immigrants will work for any pay, and since Biden's Department of Homeland Security, via its Citizenship and Immigration Services Agency, has made it so illegal immigrants can work in the US perfectly legally for up to 5 years (if not more), one can argue that the flood of illegals through the southern border has been the primary reason why inflation - or rather mostly wage inflation, that all too critical component of the wage-price spiral - has moderated in in the past year, when the US labor market suddenly found itself flooded with millions of perfectly eligible workers, who just also happen to be illegal immigrants and thus have zero wage bargaining options.
None of this is to suggest that the relentless flood of immigrants into the US is not also driven by voting and census concerns - something Elon Musk has been pounding the table on in recent weeks, and has gone so far to call it "the biggest corruption of American democracy in the 21st century", but in retrospect, one can also argue that the only modest success the Biden admin has had in the past year - namely bringing inflation down from a torrid 9% annual rate to "only" 3% - has also been due to the millions of illegals he's imported into the country.
We would be remiss if we didn't also note that this so often carries catastrophic short-term consequences for the social fabric of the country (the Laken Riley fiasco being only the latest example), not to mention the far more dire long-term consequences for the future of the US - chief among them the trillions of dollars in debt the US will need to incur to pay for all those new illegal immigrants Democrat voters and low-paid workers. This is on top of the labor revolution that will kick in once AI leads to mass layoffs among high-paying, white-collar jobs, after which all those newly laid off native-born workers hoping to trade down to lower paying (if available) jobs will discover that hardened criminals from Honduras or Guatemala have already taken them, all thanks to Joe Biden.
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
























