VANCOUVER, BC, Oct. 6, 2022 /PRNewswire/ - First Mining Gold Corp. ("First Mining" or the "Company") (TSX: FF) (OTCQX: FFMGF) (FRANKFURT: FMG) is pleased to announce it has filed on SEDAR a Technical Report prepared in accordance with National Instrument 43-101 Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects ("NI 43-101") on the Duparquet Gold Project ("Duparquet" or the "Project") titled "NI 43-101 Technical Report and Mineral Resource Estimate Update for the Duparquet Project, Quebec, Canada," dated October 6, 2022 with an effective date of September 12, 2022.
The full Mineral Resource Estimate ("MRE") Technical Report prepared by InnovExplo Inc. in Val-d'Or (Quebec), can be found on the Company's website at www.firstmininggold.com and on SEDAR under the Company's issuer profile at www.sedar.com.
The Duparquet Gold Project is a multi-million ounce advanced exploration and mining development asset located in the Abitibi region of the province of Quebec, approximately 50 km north of the city of Rouyn-Noranda. The Duparquet deposit hosts a gold Resource of 3.4 Moz in the Measured and Indicated category, and an additional 1.6 Moz Au Inferred Resource derived from the master database of drill data, which contains 904 holes totalling 270,119m and 173,831 sampled intervals. Existing infrastructure at the Project site includes paved provincial highways from Rouyn-Noranda to the south and LaSarre to the north and direct access to Quebec's hydroelectric power grid. In addition, the near-by communities of Duparquet, Ruoyn-Noranda and LaSarre have strong histories of sustainable mining practices.
Table 1: Duparquet Gold Project Mineral Resource Estimate
Area
| Cut-off
| Measured Resource
| Indicated Resource
| Inferred Resource
|
(mining
method)
| (g/t)
| Tonnage (t)
| Au
| Ounces
| Tonnage (t)
| Au
| Ounces
| Tonnage (t)
| Au
| Ounces
|
|
| (g/t)
| (g/t)
| (g/t)
|
Open Pit
| 0.40
| 163,700
| 1.37
| 7,200
| 59,410,600
| 1.52
| 2,909,600
| 28,333,000
| 1.07
| 970,400
|
UG Mining
| 1.50
| -
| -
| -
| 5,506,900
| 2.26
| 399,300
| 9,038,900
| 2.29
| 665,600
|
Tailings
| 0.40
| 19,900
| 2.03
| 1,300
| 4,105,200
| 0.93
| 123,200
| -
| -
| -
|
Total
|
| 183,600
| 1.43
| 8,500
| 69,022,700
| 1.55
| 3,432,100
| 37,371,900
| 1.36
| 1,636,000
|
Notes to accompany the Mineral Resource Estimate:
- The independent and qualified persons for the mineral resource estimate, as defined by NI 43 101, are Marina Iund, P.Geo., Carl Pelletier, P.Geo., Simon Boudreau, P.Eng. from InnovExplo Inc. and Guy Comeau, P.Eng. from Soutex. The effective date of the estimate is September 12, 2022.
- These mineral resources are not mineral reserves, as they do not have demonstrated economic viability. There is currently insufficient data to define these Inferred mineral resources as Indicated or Measured mineral resources and it is uncertain if further exploration will result in upgrading them to an Indicated or Measured mineral resource category. The mineral resource estimate follows current CIM Definition Standards.
- The results are presented in situ and undiluted and have reasonable prospects of economic viability.
- In-pit and Underground estimates encompass sixty (60) mineralized domains and one dilution envelop using the grade of the adjacent material when assayed or a value of zero when not assayed; The tailings estimate encompass four (4) zones.
- In-pit and Underground: High-grade capping of 25 g/t Au; Tailings: High-grade capping of 13.0 g/t Au for Zone 1, 3.5 g/t Au for Zone 2, 1.7 g/t Au for Zone 3 and 2.2 g/t Au for Zone 4. High-grade capping supported by statistical analysis was done on raw assay data before compositing.
- In-pit and Underground: The estimate used a sub-block model in GEOVIA SURPAC 2021 with a unit block size of 5m x 5m x 5m and a minimum block size of 1.25m x 1.25m x1.25m. Grade interpolation was obtained by ID2 using hard boundaries. Tailings: The estimate used a block model in GEOVIA GEMS with a block size of 5m x 5m x 1m. Grade interpolation was obtained by ID2 using hard boundaries.
- In-pit and Underground: A density value of 2.73 g/cm3 was used for the mineralized domains and the envelope. A density value of 2.00 g/cm3 was used for the overburden. A density value of 1.00 g/cm3 was used for the excavation solids (drifts and stopes) assumed to be filled with water. Tailings: A fixed density of 1.45 g/cm3 was used in zones and waste.
- In-pit and Underground: The mineral resource estimate is classified as Measured, Indicated and Inferred. The measured category is defined by blocks having a volume of at least 25% within an envelope built at a distance of 10 m around existing channel samples. The Indicated category is defined by blocks meeting at least one (1) of the following conditions: Blocks falling within a 15-m buffer surrounding existing stopes and/or blocks for which the average distance to composites is less than 45 m. A clipping polygon was generated to constrain Indicated resources for each of the sixty (60) mineralized domains. Only the blocks for which reasonable geological and grade continuity have been demonstrated were selected. All remaining interpolated blocks were classified as Inferred resources. Blocks interpolated in the envelope were all classified as Inferred resources. Tailings: The Measured and Indicated categories were defined based on the drill hole spacing (Measured: Zones 1 and 2 = 30m x 30m grid; Indicated: Zone 3 = 100m x 100m grid and Zone 4 = 200m x 200m grid).
- In-pit and Underground: The mineral resource estimate is locally pit-constrained with a bedrock slope angle of 50° and an overburden slope angle of 30°. The out-pit mineral resource met the reasonable prospect for eventual economic extraction by having constraining volumes applied to any blocks (potential underground extraction scenario) using DSO. It is reported at a rounded cut-off grade of 0.4 g/t Au (in-pit and tailings) and 1.5 g/t Au (UG). The cut-off grades were calculated using the following parameters: mining cost = CA$70.00 (UG); processing cost = CA$11.9 to 17.0; G&A = CA$8.75; refining and selling costs = CA$ 5.00; gold price = US$ 1,650/oz; USD:CAD exchange rate = 1.31; and mill recovery = 93.9%. The cut-off grades should be re-evaluated in light of future prevailing market conditions (metal prices, exchange rates, mining costs etc.).
- The number of metric tons and ounces was rounded to the nearest hundred, following the recommendations in NI 43 101. Any discrepancies in the totals are due to rounding effects.
- The authors are not aware of any known environmental, permitting, legal, title-related, taxation, socio-political, or marketing issues, or any other relevant issue not reported in the Technical Report, that could materially affect the Mineral Resource Estimate.
Table 2: Cut-off grade sensitivity for the in-pit and underground portions of the Duparquet Gold Project
Area
(Mining Method)
| Cut-off
(g/t)
| Measured Resource
| Indicated Resource
| Inferred Resource
|
Tonnage (t)
| Au
(g/t)
| Ounces
| Tonnage (t)
| Au
(g/t)
| Ounces
| Tonnage (t)
| Au
(g/t)
| Ounces
|
Open Pit
| 0.7
| 137,321
| 1.53
| 6,755
| 23,142,210
| 2.05
| 1,525,279
| 2,592,695
| 1.62
| 135,038
|
0.65
| 141,757
| 1.5
| 6,836
| 25,666,698
| 1.98
| 1,633,902
| 3,334,098
| 1.48
| 158,647
|
0.6
| 149,158
| 1.46
| 7,001
| 32,690,577
| 1.86
| 1,954,908
| 5,716,620
| 1.34
| 246,283
|
0.55
| 154,634
| 1.42
| 7,060
| 36,556,977
| 1.77
| 2,080,340
| 7,727,020
| 1.23
| 305,568
|
0.5
| 156,938
| 1.41
| 7,122
| 41,152,335
| 1.70
| 2,253,068
| 11,007,061
| 1.13
| 400,881
|
0.45
| 161,081
| 1.39
| 7,187
| 53,548,726
| 1.58
| 2,722,586
| 22,032,449
| 1.16
| 824,601
|
0.4
| 163,709
| 1.37
| 7,222
| 59,410,612
| 1.52
| 2,909,551
| 28,332,980
| 1.07
| 970,424
|
0.35
| 165,800
| 1.36
| 7,248
| 66,307,600
| 1.46
| 3,117,172
| 37,354,222
| 0.96
| 1,147,282
|
UG Mining
| 1.9
| -
| -
| -
| 5,891,904
| 2.67
| 505,871
| 7,168,869
| 2.91
| 669,750
|
1.7
| -
| -
| -
| 5,224,787
| 2.47
| 414,153
| 7,378,504
| 2.51
| 595,956
|
1.5
| -
| -
| -
| 5,506,861
| 2.26
| 399,356
| 9,038,871
| 2.29
| 665,629
|
1.3
| -
| -
| -
| 5,302,381
| 2.10
| 357,603
| 11,459,118
| 2.05
| 756,440
|
Tailings
| 0.6
| 19,000
| 2.10
| 1,284
| 4,104,400
| 0.93
| 123,189
| -
| -
| -
|
0.5
| 19,400
| 2.07
| 1,290
| 4,104,800
| 0.93
| 123,196
| -
| -
| -
|
0.45
| 19,600
| 2.06
| 1,295
| 4,105,000
| 0.93
| 123,200
| -
| -
| -
|
0.4
| 19,900
| 2.03
| 1,297
| 4,105,200
| 0.93
| 123,203
| -
| -
| -
|
0.35
| 20,000
| 2.02
| 1,299
| 4,105,400
| 0.93
| 123,206
| -
| -
| -
|
InnovExplo Inc., the authors of the Technical Report, concluded that:
- The database supporting the 2022 MRE is complete, valid and up to date.
- Geological and gold-grade continuity has been demonstrated for all 72 mineralized zones.
- The key parameters of the 2022 MRE (density, capping, compositing, interpolation, search ellipsoid, etc.) are supported by data and statistical and/or geostatistical analysis.
- The 2022 MRE includes measured, indicated and inferred resources for a combination of two mining scenarios: open pit and selective underground. The 2022 MRE complies with CIM Definition Standards and CIM Guidelines.
- Two cut-off grades of 0.40 and 1.50 g/t Au were used, corresponding to potential open pit and selective underground mining scenarios.
- Cut-off grades were calculated at a gold price of US$1,650 per troy ounce and an exchange rate of 1.31 USD/CAD, using reasonable mining, processing and G&A costs.
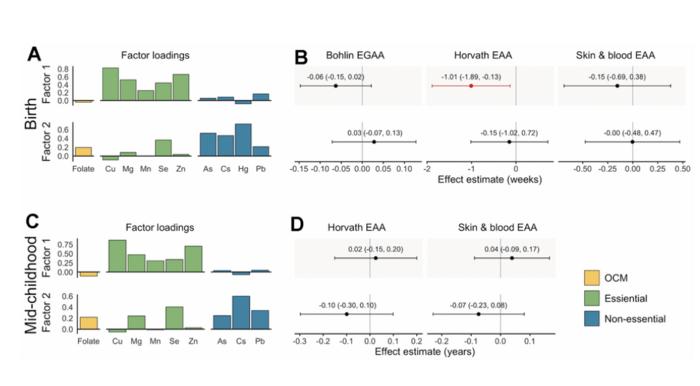
- In a combined pit and selective underground mining scenario, the Project contains an estimated M+I Resource of 65,081,200 t at 1.58 g/t Au for 3,316,100 oz of gold and an Inferred Resource of 37,371,900 t at 1.36 g/t Au for 1,636,000 oz of gold. The Project also contains the Beattie mine tailings with an estimated M+I Resource of 4,125,100 t at 0.94 g/t Au for 124,500 oz of gold.
- The results of the 2022 MRE represent a 10.5% increase in the M+I Resource and a 13.4% increase in the Inferred Resource compared to the previous 2014 MRE of Poirier et al., 2014. The increase in the M+I Resource is due to a deeper optimized shell and the updated economic parameters. The same reasons combined with the addition of 55 drill holes explain the increase in Inferred resources.
- Based on metallurgical tests, the Duparquet project appears amenable to standard gold recovery processes. A combination of flotation, pressure oxidation and cyanide leach processes has shown a gold recovery ranging from 94.7% to 96.5%.
- Additional diamond drilling on multiple zones would likely upgrade some of the Inferred Resource to the Indicated category and/or add to the Inferred Resource since most of the mineralized zones have not been fully explored at depth or close to surface infrastructures.
Qualified Persons
The independent and qualified persons for the MRE, as defined by National Instrument 43-101 Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects, are Marina Iund, P.Geo., Carl Pelletier, P.Geo., Simon Boudreau, P.Eng. from InnovExplo and Guy Comeau P.Eng. from Soutex. The effective date of the estimate is September 12, 2022.
Mr. Louis Martin P.Geo., (OGQ 0364), a consultant of First Mining, is a "Qualified Person" for the purposes of National Instrument 43-101 Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects, and he has reviewed and approved the scientific and technical disclosure contained in this news release.
About First Mining Gold Corp.
First Mining is a gold developer advancing two of the largest gold projects in Canada, the Springpole Gold Project in northwestern Ontario, where we have commenced a Feasibility Study and permitting activities are on-going with a draft Environmental Impact Statement ("EIS") for the project published in June 2022, and the Duparquet, Pitt and Duquesne Gold Projects in Quebec, a collection of advanced stage development assets located on the Destor-Porcupine Fault in the prolific Abitibi region. First Mining also owns the Cameron project in Ontario and a portfolio of gold project interests including the Pickle Crow gold project (being advanced in partnership with Auteco Minerals Ltd.), the Hope Brook gold project (being advanced in partnership with Big Ridge Gold Corp.), an equity interest in Treasury Metals Inc., and a portfolio of 21 gold royalties.
First Mining was established in 2015 by Mr. Keith Neumeyer, founding President and CEO of First Majestic Silver Corp.
ON BEHALF OF FIRST MINING GOLD CORP.
Daniel W. Wilton
Chief Executive Officer and Director
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This news release includes certain "forward-looking information" and "forward-looking statements" (collectively "forward-looking statements") within the meaning of applicable Canadian and United States securities legislation including the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this news release. Forward-looking statements are frequently, but not always, identified by words such as "expects", "anticipates", "believes", "plans", "projects", "intends", "estimates", "envisages", "potential", "possible", "strategy", "goals", "opportunities", "objectives", or variations thereof or stating that certain actions, events or results "may", "could", "would", "might" or "will" be taken, occur or be achieved, or the negative of any of these terms and similar expressions.
Forward-looking statements in this news release relate to future events or future performance and reflect current estimates, predictions, expectations or beliefs regarding future events. All forward-looking statements are based on First Mining's or its consultants' current beliefs as well as various assumptions made by them and information currently available to them. There can be no assurance that such statements will prove to be accurate, and actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. Forward-looking statements reflect the beliefs, opinions and projections on the date the statements are made and are based upon a number of assumptions and estimates that, while considered reasonable by the respective parties, are inherently subject to significant business, economic, competitive, political and social uncertainties and contingencies. Such factors include, without limitation the Company's business, operations and financial condition potentially being materially adversely affected by the outbreak of epidemics, pandemics or other health crises, such as COVID-19, and by reactions by government and private actors to such outbreaks; risks to employee health and safety as a result of the outbreak of epidemics, pandemics or other health crises, such as COVID-19, that may result in a slowdown or temporary suspension of operations at some or all of the Company's mineral properties as well as its head office; fluctuations in the spot and forward price of gold, silver, base metals or certain other commodities; fluctuations in the currency markets (such as the Canadian dollar versus the U.S. dollar); changes in national and local government, legislation, taxation, controls, regulations and political or economic developments; risks and hazards associated with the business of mineral exploration, development and mining (including environmental hazards, industrial accidents, unusual or unexpected formations, pressures, cave-ins and flooding); the presence of laws and regulations that may impose restrictions on mining; employee relations; relationships with and claims by local communities, indigenous populations and other stakeholders; availability and increasing costs associated with mining inputs and labour; the speculative nature of mineral exploration and development; title to properties.; and the additional risks described in the Company's Annual Information Form for the year ended December 31, 2021 filed with the Canadian securities regulatory authorities under the Company's SEDAR profile at www.sedar.com, and in the Company's Annual Report on Form 40-F filed with the SEC on EDGAR.
First Mining cautions that the foregoing list of factors that may affect future results is not exhaustive. When relying on our forward-looking statements to make decisions with respect to First Mining, investors and others should carefully consider the foregoing factors and other uncertainties and potential events. First Mining does not undertake to update any forward-looking statement, whether written or oral, that may be made from time to time by the Company or on our behalf, except as required by law.
Cautionary Note to United States Investors
The Company is a "foreign private issuer" as defined in Rule 3b-4 under the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and is eligible to rely upon the Canada-U.S. Multi-Jurisdictional Disclosure System, and is therefore permitted to prepare the technical information contained herein in accordance with the requirements of the securities laws in effect in Canada, which differ from the requirements of the securities laws currently in effect in the United States. Accordingly, information concerning mineral deposits set forth herein may not be comparable with information made public by companies that report in accordance with U.S. standards.
Technical disclosure contained in this news release has not been prepared in accordance with the requirements of United States securities laws and uses terms that comply with reporting standards in Canada with certain estimates prepared in accordance with NI 43-101.
NI 43-101 is a rule developed by the Canadian Securities Administrators that establishes standards for all public disclosure an issuer makes of scientific and technical information concerning the issuer's material mineral projects.
View original content to download multimedia:https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/first-mining-files-ni-43-101-technical-report-on-the-updated-mineral-resource-estimate-for-the-duparquet-gold-project-quebec-301643040.html
SOURCE First Mining Gold Corp.