Escobar: ‘Samarkand Spirit’ To Be Driven By “Responsible Powers” Russia & China
Escobar: ‘Samarkand Spirit’ To Be Driven By "Responsible Powers" Russia & China
Authored by Pepe Escobar,
The SCO summit of Asian power…
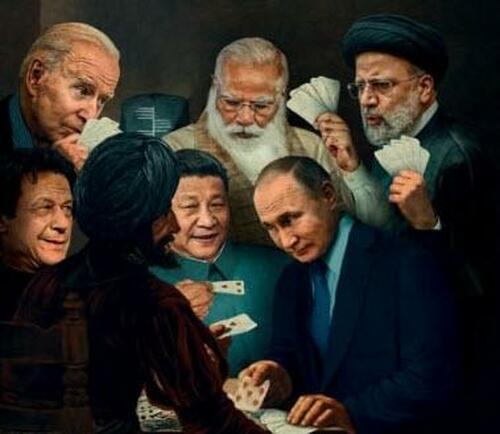

The SCO summit of Asian power players delineated a road map for strengthening the multipolar world...
Amidst serious tremors in the world of geopolitics, it is so fitting that this year’s Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) heads of state summit should have taken place in Samarkand – the ultimate Silk Road crossroads for 2,500 years.
When in 329 BC Alexander the Great reached the then Sogdian city of Marakanda, part of the Achaemenid empire, he was stunned: “Everything I have heard about Samarkand it’s true, except it is even more beautiful than I had imagined.”
Fast forward to an Op-Ed by Uzbekistan’s President Shavkat Mirziyoyev published ahead of the SCO summit, where he stresses how Samarkand now “can become a platform that is able to unite and reconcile states with various foreign policy priorities.”
After all, historically, the world from the point of view of the Silk Road landmark has always been “perceived as one and indivisible, not divided. This is the essence of a unique phenomenon – the ‘Samarkand spirit’.”
And here Mirziyoyev ties the “Samarkand Spirit” to the original SCO “Shanghai Spirit” established in early 2001, a few months before the events of September 11, when the world was forced into strife and endless war, almost overnight.
All these years, the culture of the SCO has been evolving in a distinctive Chinese way. Initially, the Shanghai Five were focused on fighting terrorism – months before the US war of terror (italics mine) metastasized from Afghanistan to Iraq and beyond.
Over the years, the initial “three no’s” – no alliance, no confrontation, no targeting any third party – ended up equipping a fast, hybrid vehicle whose ‘four wheels’ are ‘politics, security, economy, and humanities,’ complete with a Global Development Initiative, all of which contrast sharply with the priorities of a hegemonic, confrontational west.
Arguably the biggest takeaway of this week’s Samarkand summit is that Chinese President Xi Jinping presented China and Russia, together, as “responsible global powers” bent on securing the emergence of multipolarity, and refusing the arbitrary “order” imposed by the United States and its unipolar worldview.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov pronounced Xi’s bilateral conversation with President Vladimir Putin as “excellent.” Xi Jinping, previous to their meeting, and addressing Putin directly, had already stressed the common Russia-China objectives:
“In the face of the colossal changes of our time on a global scale, unprecedented in history, we are ready with our Russian colleagues to set an example of a responsible world power and play a leading role in order to put such a rapidly changing world on the trajectory of sustainable and positive development.”
Later, in the preamble to the heads of state meeting, Xi went straight to the point: it is important to “prevent attempts by external forces to organize ‘color revolutions’ in the SCO countries.” Well, Europe wouldn’t be able to tell, because it has been color-revolutionized non-stop since 1945.
Putin, for his part, sent a message that will be ringing all across the Global South: “Fundamental transformations have been outlined in world politics and economics, and they are irreversible.” (italics mine)
Iran: it’s showtime
Iran was the guest star of the Samarkand show, officially embraced as the 9th member of the SCO. President Ebrahim Raisi, significantly, stressed before meeting Putin that “Iran does not recognize sanctions against Russia.” Their strategic partnership will be enhanced. On the business front, a hefty delegation comprising leaders of 80 large Russian companies will be visiting Tehran next week.
The increasing Russia-China-Iran interpolation – the three top drivers of Eurasia integration – scares the hell out of the usual suspects, who may be starting to grasp how the SCO represents, in the long run, a serious challenge to their geoeconomic game. So, as every grain of sand in every Heartland desert is already aware, the geopolitical pressure against the trio will increase exponentially.
And then there was the mega-crucial Samarkand trilateral: Russia-China-Mongolia. There were no official leaks, but this trio arguably discussed the Power of Siberia-2 gas pipeline – the interconnector to be built across Mongolia; and Mongolia’s enhanced role in a crucial Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) connectivity corridor, now that China is not using the Trans-Siberian route for exports to Europe because of sanctions.
Putin briefed Xi on all aspects of Russia’s Special Military Operation (SMO) in Ukraine, and arguably answered some really tough questions, many of them circulating wildly on the Chinese web for months now.
Which brings us to Putin’s presser at the end of the summit – with virtually all questions predictably revolving around the military theater in Ukraine.
The key takeaway from the Russian president: “There are no changes on the SMO plan. The main tasks are being implemented.” On peace prospects, it is Ukraine that “is not ready to talk to Russia.” And overall, “it is regrettable that the west had the idea to use Ukraine to try to collapse Russia.”
On the fertilizer soap opera, Putin remarked, “food supply, energy supply, they (the west) created these problems, and now are trying to resolve them at the expense of someone else” – meaning the poorest nations. “European countries are former colonial powers and they still have this paradigm of colonial philosophy. The time has come to change their behavior, to become more civilized.”
On his meeting with Xi Jinping: “It was just a regular meeting, it’s been quite some time we haven’t had a meeting face to face.” They talked about how to “expand trade turnover” and circumvent the “trade wars caused by our so-called partners,” with “expansion of settlements in national currencies not progressing as fast as we want.”
Strenghtening multipolarity
Putin’s bilateral with India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi could not have been more cordial – on a “very special friendship” register – with Modi calling for serious solutions to the food and fuel crises, actually addressing the west. Meanwhile, the State Bank of India will be opening special rupee accounts to handle Russia-related trade.
This is Xi’s first foreign trip since the Covid pandemic. He could do it because he’s totally confident of being awarded a third term during the Communist Party Congress next month in Beijing. Xi now controls and/or has allies placed in at least 90 percent of the Politburo.
The other serious reason was to recharge the appeal of BRI in close connection to the SCO. China’s ambitious BRI project was officially launched by Xi in Astana (now Nur-Sultan) nine years ago. It will remain the overarching Chinese foreign policy concept for decades ahead.
BRI’s emphasis on trade and connectivity ties in with the SCO’s evolving multilateral cooperation mechanisms, congregating nations focusing on economic development independent from the hazy, hegemonic “rules-based order.” Even India under Modi is having second thoughts about relying on western blocs, where New Delhi is at best a neo-colonized “partner.”
So Xi and Putin, in Samarkand, for all practical purposes delineated a road map for strengthening multipolarity – as stressed by the final Samarkand declaration signed by all SCO members.
The Kazakh puzzle
There will be bumps on the road aplenty. It’s no accident that Xi started his trip in Kazakhstan – China’s mega-strategic western rear, sharing a very long border with Xinjiang. The tri-border at the dry port of Khorgos – for lorries, buses and trains, separately – is quite something, an absolutely key BRI node.
The administration of President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev in Nur-Sultan (soon to be re-named Astana again) is quite tricky, swinging between eastern and western political orientations, and infiltrated by Americans as much as during the era of predecessor Nursultan Nazarbayev, Kazakhstan’s first post-USSR president.
Earlier this month, for instance, Nur-Sultan, in partnership with Ankara and British Petroleum (BP) – which virtually rules Azerbaijan – agreed to increase the volume of oil on the Baku-Tblisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline to up to 4 million tons a month by the end of this year. Chevron and ExxonMobil, very active in Kazakhstan, are part of the deal.
The avowed agenda of the usual suspects is to “ultimately disconnect the economies of Central Asian countries from the Russian economy.” As Kazakhstan is a member not only of the Russian-led Eurasia Economic Union (EAEU), but also the BRI, it is fair to assume that Xi – as well as Putin – discussed some pretty serious issues with Tokayev, told him to grasp which way the wind is blowing, and advised him to keep the internal political situation under control (see the aborted coup in January, when Tokayev was de facto saved by the Russian-led Collective Security Treaty Organization [CSTO]).
There’s no question Central Asia, historically known as a “box of gems” at the center of the Heartland, striding the Ancient Silk Roads and blessed with immense natural wealth – fossil fuels, rare earth metals, fertile agrarian lands – will be used by the usual suspects as a Pandora’s box, releasing all manner of toxic tricks against legitimate Eurasian integration.
That’s in sharp contrast with West Asia, where Iran in the SCO will turbo-charge its key role of crossroads connectivity between Eurasia and Africa, in connection with the BRI and the International North-South Transportation Corridor (INSTC).
So it’s no wonder that the UAE, Bahrain and Kuwait, all in West Asia, do recognize which way the wind is blowing. The three Persian Gulf states received official SCO ‘partner status’ in Samarkand, alongside the Maldives and Myanmar.
A cohesion of goals
Samarkand also gave an extra impulse to integration along the Russian-conceptualized Greater Eurasia Partnership – which includes the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) – and that, just two weeks after the game-changing Eastern Economic Forum (EEF) held in Vladivostok, on Russia’s strategic Pacific coast.
Moscow’s priority at the EAEU is to implement a union-state with Belarus (which looks bound to become a new SCO member before 2024), side-by-side with closer integration with the BRI. Serbia, Singapore and Iran have trade agreements with the EAEU too.
The Greater Eurasian Partnership was proposed by Putin in 2015 – and it’s getting sharper as the EAEU commission, led by Sergey Glazyev, actively designs a new financial system, based on gold and natural resources and counter-acting the Bretton Woods system. Once the new framework is ready to be tested, the key disseminator is likely to be the SCO.
So here we see in play the full cohesion of goals – and the interaction mechanisms – deployed by the Greater Eurasia Partnership, BRI, EAEU, SCO, BRICS+ and the INSTC. It’s a titanic struggle to unite all these organizations and take into account the geoeconomic priorities of each member and associate partner, but that’s exactly what’s happening, at breakneck speed.
In this connectivity feast, practical imperatives range from fighting local bottlenecks to setting up complex multi-party corridors – from the Caucasus to Central Asia, from Iran to India, everything discussed in multiple roundtables.
Successes are already notable: from Russia and Iran introducing direct settlements in rubles and rials, to Russia and China increasing their trade in rubles and yuan to 20 percent – and counting. An Eastern Commodity Exchange may be soon established in Vladivostok to facilitate trade in futures and derivatives with the Asia-Pacific.
China is the undisputed primary creditor/investor in infrastructure across Central Asia. Beijing’s priorities may be importing gas from Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan and oil from Kazakhstan, but connectivity is not far behind.
The $5 billion construction of the 600 km-long Pakistan-Afghanistan-Uzbekistan (Pakafuz) railway will deliver cargo from Central Asia to the Indian Ocean in only three days instead of 30. And that railway will be linked to Kazakhstan and the already in progress 4,380 km-long Chinese-built railway from Lanzhou to Tashkent, a BRI project.
Nur-Sultan is also interested in a Turkmenistan-Iran-Türkiye railway, which would connect its port of Aktau on the Caspian Sea with the Persian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea.
Türkiye, meanwhile, still a SCO observer and constantly hedging its bets, slowly but surely is trying to strategically advance its own Pax Turcica, from technological development to defense cooperation, all that under a sort of politico-economic-security package. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan did discuss it in Samarkand with Putin, as the latter later announced that 25 percent of Russian gas bought by Ankara will be paid in rubles.
Welcome to Great Game 2.0
Russia, even more than China, knows that the usual suspects are going for broke. In 2022 alone, there was a failed coup in Kazakhstan in January; troubles in Badakhshan, in Tajikistan, in May; troubles in Karakalpakstan in Uzbekistan in June; the non-stop border clashes between Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan (both presidents, in Samarkand, at least agreed on a ceasefire and to remove troops from their borders).
And then there is recently-liberated Afghanistan – with no less than 11 provinces crisscrossed by ISIS-Khorasan and its Tajik and Uzbek associates. Thousands of would-be Heartland jihadis have made the trip to Idlib in Syria and then back to Afghanistan – ‘encouraged’ by the usual suspects, who will use every trick under the sun to harass and ‘isolate’ Russia from Central Asia.
So Russia and China should be ready to be involved in a sort of immensely complex, rolling Great Game 2.0 on steroids, with the US/NATO fighting united Eurasia and Turkiye in the middle.
On a brighter note, Samarkand proved that at least consensus exists among all the players at different institutional organizations that: technological sovereignty will determine sovereignty; and that regionalization – in this case Eurasian – is bound to replace US-ruled globalization.
These players also understand that the Mackinder and Spykman era is coming to a close – when Eurasia was ‘contained’ in a semi-disassembled shape so western maritime powers could exercise total domination, contrary to the national interests of Global South actors.
It’s now a completely different ball game. As much as the Greater Eurasia Partnership is fully supported by China, both favor the interconnection of BRI and EAEU projects, while the SCO shapes a common environment.
Yes, this is an Eurasian civilizational project for the 21st century and beyond. Under the aegis of the ‘Spirit of Samarkand.’
International
Beloved mall retailer files Chapter 7 bankruptcy, will liquidate
The struggling chain has given up the fight and will close hundreds of stores around the world.

It has been a brutal period for several popular retailers. The fallout from the covid pandemic and a challenging economic environment have pushed numerous chains into bankruptcy with Tuesday Morning, Christmas Tree Shops, and Bed Bath & Beyond all moving from Chapter 11 to Chapter 7 bankruptcy liquidation.
In all three of those cases, the companies faced clear financial pressures that led to inventory problems and vendors demanding faster, or even upfront payment. That creates a sort of inevitability.
Related: Beloved retailer finds life after bankruptcy, new famous owner
When a retailer faces financial pressure it sets off a cycle where vendors become wary of selling them items. That leads to barren shelves and no ability for the chain to sell its way out of its financial problems.
Once that happens bankruptcy generally becomes the only option. Sometimes that means a Chapter 11 filing which gives the company a chance to negotiate with its creditors. In some cases, deals can be worked out where vendors extend longer terms or even forgive some debts, and banks offer an extension of loan terms.
In other cases, new funding can be secured which assuages vendor concerns or the company might be taken over by its vendors. Sometimes, as was the case with David's Bridal, a new owner steps in, adds new money, and makes deals with creditors in order to give the company a new lease on life.
It's rare that a retailer moves directly into Chapter 7 bankruptcy and decides to liquidate without trying to find a new source of funding.
Image source: Getty Images
The Body Shop has bad news for customers
The Body Shop has been in a very public fight for survival. Fears began when the company closed half of its locations in the United Kingdom. That was followed by a bankruptcy-style filing in Canada and an abrupt closure of its U.S. stores on March 4.
"The Canadian subsidiary of the global beauty and cosmetics brand announced it has started restructuring proceedings by filing a Notice of Intention (NOI) to Make a Proposal pursuant to the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act (Canada). In the same release, the company said that, as of March 1, 2024, The Body Shop US Limited has ceased operations," Chain Store Age reported.
A message on the company's U.S. website shared a simple message that does not appear to be the entire story.
"We're currently undergoing planned maintenance, but don't worry we're due to be back online soon."
That same message is still on the company's website, but a new filing makes it clear that the site is not down for maintenance, it's down for good.
The Body Shop files for Chapter 7 bankruptcy
While the future appeared bleak for The Body Shop, fans of the brand held out hope that a savior would step in. That's not going to be the case.
The Body Shop filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy in the United States.
"The US arm of the ethical cosmetics group has ceased trading at its 50 outlets. On Saturday (March 9), it filed for Chapter 7 insolvency, under which assets are sold off to clear debts, putting about 400 jobs at risk including those in a distribution center that still holds millions of dollars worth of stock," The Guardian reported.
After its closure in the United States, the survival of the brand remains very much in doubt. About half of the chain's stores in the United Kingdom remain open along with its Australian stores.
The future of those stores remains very much in doubt and the chain has shared that it needs new funding in order for them to continue operating.
The Body Shop did not respond to a request for comment from TheStreet.
bankruptcy pandemic canadaGovernment
Are Voters Recoiling Against Disorder?
Are Voters Recoiling Against Disorder?
Authored by Michael Barone via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
The headlines coming out of the Super…

Authored by Michael Barone via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
The headlines coming out of the Super Tuesday primaries have got it right. Barring cataclysmic changes, Donald Trump and Joe Biden will be the Republican and Democratic nominees for president in 2024.
With Nikki Haley’s withdrawal, there will be no more significantly contested primaries or caucuses—the earliest both parties’ races have been over since something like the current primary-dominated system was put in place in 1972.
The primary results have spotlighted some of both nominees’ weaknesses.
Donald Trump lost high-income, high-educated constituencies, including the entire metro area—aka the Swamp. Many but by no means all Haley votes there were cast by Biden Democrats. Mr. Trump can’t afford to lose too many of the others in target states like Pennsylvania and Michigan.
Majorities and large minorities of voters in overwhelmingly Latino counties in Texas’s Rio Grande Valley and some in Houston voted against Joe Biden, and even more against Senate nominee Rep. Colin Allred (D-Texas).
Returns from Hispanic precincts in New Hampshire and Massachusetts show the same thing. Mr. Biden can’t afford to lose too many Latino votes in target states like Arizona and Georgia.
When Mr. Trump rode down that escalator in 2015, commentators assumed he’d repel Latinos. Instead, Latino voters nationally, and especially the closest eyewitnesses of Biden’s open-border policy, have been trending heavily Republican.
High-income liberal Democrats may sport lawn signs proclaiming, “In this house, we believe ... no human is illegal.” The logical consequence of that belief is an open border. But modest-income folks in border counties know that flows of illegal immigrants result in disorder, disease, and crime.
There is plenty of impatience with increased disorder in election returns below the presidential level. Consider Los Angeles County, America’s largest county, with nearly 10 million people, more people than 40 of the 50 states. It voted 71 percent for Mr. Biden in 2020.
Current returns show county District Attorney George Gascon winning only 21 percent of the vote in the nonpartisan primary. He’ll apparently face Republican Nathan Hochman, a critic of his liberal policies, in November.
Gascon, elected after the May 2020 death of counterfeit-passing suspect George Floyd in Minneapolis, is one of many county prosecutors supported by billionaire George Soros. His policies include not charging juveniles as adults, not seeking higher penalties for gang membership or use of firearms, and bringing fewer misdemeanor cases.
The predictable result has been increased car thefts, burglaries, and personal robberies. Some 120 assistant district attorneys have left the office, and there’s a backlog of 10,000 unprosecuted cases.
More than a dozen other Soros-backed and similarly liberal prosecutors have faced strong opposition or have left office.
St. Louis prosecutor Kim Gardner resigned last May amid lawsuits seeking her removal, Milwaukee’s John Chisholm retired in January, and Baltimore’s Marilyn Mosby was defeated in July 2022 and convicted of perjury in September 2023. Last November, Loudoun County, Virginia, voters (62 percent Biden) ousted liberal Buta Biberaj, who declined to prosecute a transgender student for assault, and in June 2022 voters in San Francisco (85 percent Biden) recalled famed radical Chesa Boudin.
Similarly, this Tuesday, voters in San Francisco passed ballot measures strengthening police powers and requiring treatment of drug-addicted welfare recipients.
In retrospect, it appears the Floyd video, appearing after three months of COVID-19 confinement, sparked a frenzied, even crazed reaction, especially among the highly educated and articulate. One fatal incident was seen as proof that America’s “systemic racism” was worse than ever and that police forces should be defunded and perhaps abolished.
2020 was “the year America went crazy,” I wrote in January 2021, a year in which police funding was actually cut by Democrats in New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, and Denver. A year in which young New York Times (NYT) staffers claimed they were endangered by the publication of Sen. Tom Cotton’s (R-Ark.) opinion article advocating calling in military forces if necessary to stop rioting, as had been done in Detroit in 1967 and Los Angeles in 1992. A craven NYT publisher even fired the editorial page editor for running the article.
Evidence of visible and tangible discontent with increasing violence and its consequences—barren and locked shelves in Manhattan chain drugstores, skyrocketing carjackings in Washington, D.C.—is as unmistakable in polls and election results as it is in daily life in large metropolitan areas. Maybe 2024 will turn out to be the year even liberal America stopped acting crazy.
Chaos and disorder work against incumbents, as they did in 1968 when Democrats saw their party’s popular vote fall from 61 percent to 43 percent.
Views expressed in this article are opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of The Epoch Times or ZeroHedge.
Government
Veterans Affairs Kept COVID-19 Vaccine Mandate In Place Without Evidence
Veterans Affairs Kept COVID-19 Vaccine Mandate In Place Without Evidence
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
The…
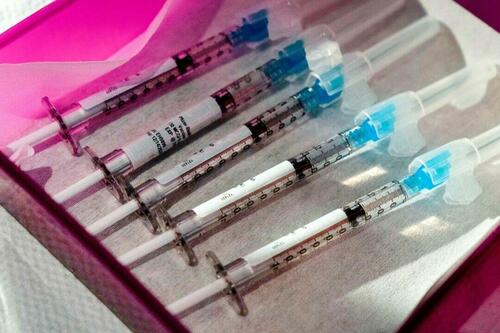
Authored by Zachary Stieber via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) reviewed no data when deciding in 2023 to keep its COVID-19 vaccine mandate in place.
VA Secretary Denis McDonough said on May 1, 2023, that the end of many other federal mandates “will not impact current policies at the Department of Veterans Affairs.”
He said the mandate was remaining for VA health care personnel “to ensure the safety of veterans and our colleagues.”
Mr. McDonough did not cite any studies or other data. A VA spokesperson declined to provide any data that was reviewed when deciding not to rescind the mandate. The Epoch Times submitted a Freedom of Information Act for “all documents outlining which data was relied upon when establishing the mandate when deciding to keep the mandate in place.”
The agency searched for such data and did not find any.
“The VA does not even attempt to justify its policies with science, because it can’t,” Leslie Manookian, president and founder of the Health Freedom Defense Fund, told The Epoch Times.
“The VA just trusts that the process and cost of challenging its unfounded policies is so onerous, most people are dissuaded from even trying,” she added.
The VA’s mandate remains in place to this day.
The VA’s website claims that vaccines “help protect you from getting severe illness” and “offer good protection against most COVID-19 variants,” pointing in part to observational data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that estimate the vaccines provide poor protection against symptomatic infection and transient shielding against hospitalization.
There have also been increasing concerns among outside scientists about confirmed side effects like heart inflammation—the VA hid a safety signal it detected for the inflammation—and possible side effects such as tinnitus, which shift the benefit-risk calculus.
President Joe Biden imposed a slate of COVID-19 vaccine mandates in 2021. The VA was the first federal agency to implement a mandate.
President Biden rescinded the mandates in May 2023, citing a drop in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations. His administration maintains the choice to require vaccines was the right one and saved lives.
“Our administration’s vaccination requirements helped ensure the safety of workers in critical workforces including those in the healthcare and education sectors, protecting themselves and the populations they serve, and strengthening their ability to provide services without disruptions to operations,” the White House said.
Some experts said requiring vaccination meant many younger people were forced to get a vaccine despite the risks potentially outweighing the benefits, leaving fewer doses for older adults.
“By mandating the vaccines to younger people and those with natural immunity from having had COVID, older people in the U.S. and other countries did not have access to them, and many people might have died because of that,” Martin Kulldorff, a professor of medicine on leave from Harvard Medical School, told The Epoch Times previously.
The VA was one of just a handful of agencies to keep its mandate in place following the removal of many federal mandates.
“At this time, the vaccine requirement will remain in effect for VA health care personnel, including VA psychologists, pharmacists, social workers, nursing assistants, physical therapists, respiratory therapists, peer specialists, medical support assistants, engineers, housekeepers, and other clinical, administrative, and infrastructure support employees,” Mr. McDonough wrote to VA employees at the time.
“This also includes VA volunteers and contractors. Effectively, this means that any Veterans Health Administration (VHA) employee, volunteer, or contractor who works in VHA facilities, visits VHA facilities, or provides direct care to those we serve will still be subject to the vaccine requirement at this time,” he said. “We continue to monitor and discuss this requirement, and we will provide more information about the vaccination requirements for VA health care employees soon. As always, we will process requests for vaccination exceptions in accordance with applicable laws, regulations, and policies.”
The version of the shots cleared in the fall of 2022, and available through the fall of 2023, did not have any clinical trial data supporting them.
A new version was approved in the fall of 2023 because there were indications that the shots not only offered temporary protection but also that the level of protection was lower than what was observed during earlier stages of the pandemic.
Ms. Manookian, whose group has challenged several of the federal mandates, said that the mandate “illustrates the dangers of the administrative state and how these federal agencies have become a law unto themselves.”
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





















