Domino’s Pizza Stock Faces a Major Problem (And, It’s Not The Noid)
A factor the pizza chain can’t control may impact the return Domino’s shares deliver to investors in 2022.

A factor the pizza chain can't control may impact the return Domino's shares deliver to investors in 2022.
Domino's (DPZ) - Get Domino's Pizza, Inc. Report owns 22% of the quick-serve (QSR) market share for pizza in the United States and 20% globally. The company has nearly $18 billion in global sales from its 18,380 stores, of which 98% operate under a franchise model.
Those numbers seem huge, but Domino's CEO Richard Allison, speaking at a virtual conference, pointed out that the QSR pizza market stands at $81 billion globally, split nearly equally between the U.S. ($40 billion) and the rest of the world ($41 billion). He also noted that fragmentation in the market opens up opportunities for his company to add share.
"As we think about the share opportunity out into the future, if you look at the U.S., for example, the top four players only make up about a 52% share," he said. "It's more fragmented than some of the other QSR categories out there."
In the long-term, that's a huge opportunity for Domino's but the company does face some significant shorter-term headwinds, according to its CEO.
Image Source: Domino's.
Domino's Faces Some Expensive Problems
Allison explained that his chain's huge scale has helped it during the Covid-19 pandemic. "As we look forward to growing the business well into the future, the muscle that comes from that substantial marketing fund is also an important part of our scale advantage."
Domino's, however, can't leverage its size to get itself out of every problem. Allison expects that the chain's bottom line will be hurt by rising prices for the ingredients it needs to make the items on its menu.
"We expect unprecedented increases in our food basket cost versus 2021 of 8-10%, which is three to four times what we would normally see in a year," he said. "I think many of you are aware of the significant inflation across the U.S. economy and how that is hitting many of the inputs that we have for our business from meats to cheese to some of the grains that go into the production of our products."
The CEO said he also expects to see wage inflation in 2022, which he sees impacting the entire industry including Domino's.
What Is Domino's Doing to Combat Rising Expenses?
"In light of some of these costs we are going to make some changes to our national offers in 2022," Allison said.
The first of those, he added, will hit menus "in a couple of weeks" and it relates to the Domino's $7.99 carryout offer. Instead of changing the price, Domino's plans to give customers less food.
"We're not going to change the headline number because the equity in that number is so important," he said. "But we are going to move that offer to online only and we're going to change the count on our chicken -- our wings and boneless -- from 10 pieces to eight pieces to recognize some of the costs we are incurring."
Allison said that including less chicken lowers the cost while moving to online-only has benefits as well.
"One is a higher ticket. Two is a lower cost to serve because we're not having to answer the phones, and third is that we get access to critical data."
Need expert advice on Fast-Food Stocks?
The Action Alerts PLUS team beat the S&P, Dow, and Nasdaq in 2021. Don’t miss your opportunity to grow your portfolio with the AAP team. Follow along with the AAP portfolio so you know what stocks to buy and sell!
Try Action Alerts PLUS for free!
nasdaq stocks pandemic covid-19
Uncategorized
Wall Street Bonuses Fall For Second Year To 2019 Lows Amid Capital Markets Freeze
Wall Street Bonuses Fall For Second Year To 2019 Lows Amid Capital Markets Freeze
Wall Street bonuses have declined for two consecutive years,…
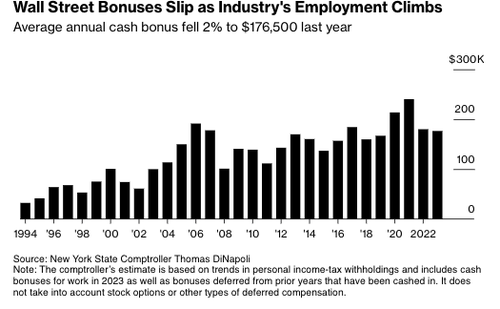
Wall Street bonuses have declined for two consecutive years, falling to levels last seen in 2019, according to the latest yearly figures released by New York State Comptroller Thomas P. DiNapoli. This trend is occurring amidst a multi-year downturn in capital markets due to the Federal Reserve's interest rate hiking cycle.
According to the report, the average Wall Street cash bonus fell 2% to $176,500 in 2023, the lowest level since 2019. The drop was far less than the 25% plunge in 2022. Last year's bonus pool was $33.8 billion, unchanged from the previous year but far less than the $42.7 billion during the stock market mania in 2021.
"Wall Street's average cash bonuses dipped slightly from last year, with continued market volatility and more people joining the securities workforce," DiNapoli said in a news release on Tuesday.
He continued: "While these bonuses affect income tax revenues for the state and city, both budgeted for larger declines so the impact on projected revenues should be limited."
"The securities industry's continued strength should not overshadow the broader economic picture in New York, where we need all sectors to enjoy full recovery from the pandemic," he added.
Despite the slump, the report said Wall Street's profits rose 1.8% last year, "but firms have taken a more cautious approach to compensation, and more employees have joined the securities industry, which accounts for the slight decline in the average bonus."
The report showed the industry employed 198,500 people in 2023, up from 191,600 the prior year. This expansion occurred during a period when US banks laid off 23,000 jobs.
Given that swaps traders and economists at Goldman Sachs Group are forecasting fewer Fed interest-rate cuts this year, a higher-for-longer rates environment will continue to discourage capital-market activity.
There's about a 50% chance of a June cut. Over the last several months, the Fed's interest-rate target implied by overnight index swaps and SOFR futures went from 700bps of cuts to currently 292bps of cuts for the full year.
Any delay in the easing cycle will only mean another year of depressed bonuses for Wall Street.
Uncategorized
Caitlin Clark, Coach Prime, and Linsanity: The Anatomy of a Viewership ‘Craze’
This is a trying time for sports on television as the industry fights the headwinds of cord-cutting and media fragmentation. Television networks and leagues…
This is a trying time for sports on television as the industry fights the headwinds of cord-cutting and media fragmentation. Television networks and leagues have taken measures that just a short time ago would have been considered extreme, desperate, or some combination of the two: an In-Season Tournament in the NBA; MLB in an Iowa cornfield; NASCAR inside the L.A. Coliseum. These efforts have been met with moderate success from a viewership standpoint, but they are not the type of needle-movers that drastically impact viewership in the aggregate. That type of shift requires a unicorn, and the last year has featured two: Caitlin Clark and Deion Sanders.
Clark has spent the past season breaking records on and off the court. Her Iowa Hawkeyes played in two of the four most watched college basketball games this season — regardless of gender. Both her record-breaking game against Ohio State and Big Ten Tournament championship win against Nebraska attracted over three million viewers. Only two men’s games, a Thanksgiving NFL lead-out between Michigan State and Arizona on FOX (5.18m), and a Duke-UNC game on ESPN (3.08m) also eclipsed the three million mark. Clark’s Big Ten Tournament semifinal against Michigan was the most watched women’s sporting event ever measured on Big Ten Network (1.08m). The championship game on CBS was the network’s most watched college basketball game of the year, men’s or women’s (pending results from this past weekend).
Of the six most watched women’s college basketball games this year, Clark played in five. Last year’s LSU-Iowa championship game delivered 9.9m viewers, the most ever for a women’s college game in the Nielsen people-meter era (dates back to 1988). The list could go on.
Deion Sanders — aka Coach Prime — transcended the sport of college football for a moment last fall. On his way to becoming Sports Illustrated Sportsperson of the Year, the Prime-fueled Colorado Buffaloes played in five of the fifteen most-watched regular season games of the year, more than any other school. Through the first five weeks of the season, Colorado played in either the first or second most-watched game of the week. Incredibly, that includes a Week 3 game against Colorado State that averaged 9.3 million viewers on ESPN, despite not kicking off until after 10 PM ET. That game drew four million more viewers than the second-most watched game that week, Georgia-South Carolina in the afternoon window on CBS. All of this for a team that won just one game the previous season.
Such viewership anomalies do not happen in a bubble; they are products of larger, media-driven forces. Think of last summer’s “Barbenheimer” craze for instance. Those two blockbuster films almost single-handedly lifted the box office from its pandemic-era depths. As many Hollywood analysts pointed out, the organic social media trend spurred from the strange juxtaposition of both movies being released on the same day led them to sell more tickets. Established media operations then picked up the story and fed into the trend. Social media isn’t always wagging the tail of traditional media, it can go both ways. The key to a true ‘craze’ however, is breaking through everywhere, no matter the media one consumes.
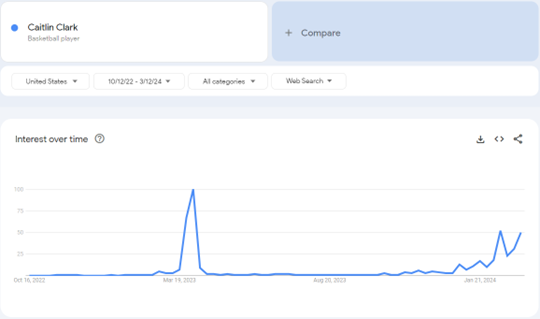
Maybe the most comparable sports craze in recent memory to the Clark-Sanders charged viewership of this past year is Linsanity. For a few weeks in 2012, New York Knicks guard Jeremy Lin broke out in a series of masterful performances that captured the imagination of the basketball world. Lin helped MSG Network improve its ratings by 82% through mid-February compared to the previous season — an absurd jump. However, Linsanity is perhaps also the most illustrative of another key factor in these viewership crazes: by definition, they are fleeting.
A look at Google search trends (below) puts these anomalies into perspective. Linsanity lasted about three weeks. Prime Time at Colorado was able to break through for about a month. Clark’s 2023 spike held for a few weeks in March, though her spike started much earlier this season, beginning to trend up in January. The lesson here, these massive viewership crazes are nice to have, can potentially raise the floor of a sport on the margins, but cannot be relied on for sustained viewership long term.
Caitlin Clark
Deion Sanders
Jeremy Lin
This isn’t to say these anomalies are without value. Networks have realized that facilitating these crazes help maintain healthy viewership in a difficult television environment. Thus, manufacturing these short-lived spikes could prove to be a key component of network’s strategies into the future. Last year for instance, FOX sent its Big Noon Kickoff show to a Colorado game four of the first five weeks of the season to help jump-start the Deion Sanders media blitz. ESPN’s College GameDay also setup shop in Boulder for the Week 3 game against Colorado State, the same week CBS’s 60 Minutes aired a Deion Sanders story.
As for Clark, ESPN recently announced that for the first time, it will embed a reporter (Holly Rowe) with Iowa for the team’s upcoming NCAA Tournament run. FOX gave Clark special treatment as well. When the network aired Caitlin Clark games this season, they would have her stat line permanently fixed on the scorebug. They livestreamed a “Caitlin Clark Cam” on TikTok. FOX even reportedly offered Clark an NIL package to incentivize her to play in college another year.
Of course, these crazes cannot solely be manufactured by the networks. There must be some truly organic interest in the subject for any of this to be possible. Between Clark and Sanders, there’s evidence to suggest that such crazes are becoming more frequent. Two in one year is notable when the last similar instance was Linsanity in 2012. This is partly due to the networks’ willingness to feed into these stories, though the growing desire in public life for shared experiences should not be discounted either.
Record-setting viewership has become commonplace for sporting events that have found ways to break into the monoculture. To be sure, some of that is because of Nielsen’s changes to out-of-home viewing measurements, though arguably the reason a property like the NFL has been so successful lately is because of its ubiquity in American life. Clark and Sanders have been able to simulate similar far-reaching appeal to generate viewership, albeit for shorter periods of time, and orders of magnitude smaller than the NFL.
A level of cultish personality, elite talent, or both seems prerequisite for a viewership craze to start. The level to which television networks will find ways to capitalize on these circumstances in the future remains to be seen. As traditional media fights for survival, with live sports as a main component, replicating Clark or Sanders-esque media booms may well become a substantial part of the formula. The next few years will be telling about how much influence traditional media still has in its agenda-setting role, and how far they’ll be willing to go to facilitate a media-induced frenzy.
The post Caitlin Clark, Coach Prime, and Linsanity: The Anatomy of a Viewership ‘Craze’ appeared first on Sports Media Watch.
fed pandemic treatmentSpread & Containment
Gates-backed PhIII study tuberculosis vaccine study gets underway
A large study of an experimental vaccine for the world’s biggest infectious disease has finally kicked off in South Africa.
The Bill & Melinda Gates…

A large study of an experimental vaccine for the world’s biggest infectious disease has finally kicked off in South Africa.
The Bill & Melinda Gates Medical Research Institute (MRI) will test a tuberculosis vaccine’s ability to prevent latent infections from causing potentially deadly lung disease. Last summer the nonprofit said it would foot $400 million of the estimated $550 million cost of running the 20,000-person Phase III trial.
It’s a pivotal moment for a vaccine whose origins date back 25 years when scientists identified two proteins that triggered strong immunity to the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. A fusion of those proteins, paired with the tree bark-derived adjuvant that helps power GSK’s shingles shot, comprise the so-called M72 vaccine.
After decades of failures in the field, the vaccine impressed scientists in 2018 when GSK found that it was 54% efficacious at preventing lung disease in a 3,600-person Phase IIb study.
But the Big Pharma decided that a full-blown trial was too expensive to conduct on its own. Gates MRI stepped in to license the vaccine in early 2020, right before the Covid pandemic shifted global vaccine priorities towards the coronavirus, further stalling the tuberculosis shot.
“There’s been frustration that it’s taken so long to get this trial up and running,” Thomas Scriba, deputy director of immunology for the South African Tuberculosis Vaccine Initiative, told Endpoints News last summer.
At last, the vaccine is getting a chance to prove itself in a bigger study. If successful, it could lead to the first new shot for tuberculosis in over a century.
Emilio Emini, CEO of the Gates MRI, told Endpoints that the initial results may come in roughly four to six years. “Hopefully this will galvanize a refocus on TB,” he said. “It’s been ignored for many, many years. We can’t ignore it anymore.”
A substantial impact
Even though an existing vaccine helps protect babies and children against severe tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for the disease still causes roughly 10 million new cases and 500,000 deaths each year.
 Emilio Emini
Emilio EminiBy vaccinating adolescents and adults who test positive for infections but don’t have symptoms of lung disease, the Gates MRI hopes the shot will help prevent mild infections from becoming severe ones, curtail transmission of the bug, which is predominantly driven by people with lung disease, and reduce deaths.
“The impact would be substantial,” Emini said. But he cautioned that the biology behind mild and severe diseases is still mysterious. “The reality is that no one really knows what keeps it under control.”
The study, which will take place at 60 sites across seven countries, will include some people who are not infected with tuberculosis to ensure that the vaccine is safe in that broader population.
“Having to pre-test everybody is not going to make the vaccine easy to deliver,” Emini said. If the vaccine is ultimately approved, it will likely be used in targeted communities with high tuberculosis, rather than across a whole country, he added. “In practice, you would immunize everybody in those populations.”
Emini described the Gates MRI’s rights to the vaccine as “close to a worldwide license.” GSK retained rights to commercialize the vaccine in certain countries but declined to specify which ones.
A spokesperson for GSK said that the company “has around 30 assets under development specifically for global health … none of which are expected to generate significant return on investment.”
“It is not sustainable or practical in the longer term for GSK to deliver all of these alone. So we continue to work on M72, but in partnership with others,” the spokesperson added.
If the shot works, Emini said that the Gates MRI will sublicense it to a manufacturer that will be responsible for making and marketing the vaccine. The details are still being worked out, he noted.
vaccine pandemic coronavirus deaths new cases transmission africa-

 Spread & Containment6 days ago
Spread & Containment6 days agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
























