Uncategorized
China Focus releases a new feature on A Must for Global Growth
China Focus releases a new feature on A Must for Global Growth
PR Newswire
BEIJING, Nov. 21, 2022
BEIJING, Nov. 21, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — China Focus releases a new feature on A Must for Global Growth. The feature is contributed by Michael Zakkour w…
China Focus releases a new feature on A Must for Global Growth
PR Newswire
BEIJING, Nov. 21, 2022
BEIJING, Nov. 21, 2022 /PRNewswire/ -- China Focus releases a new feature on A Must for Global Growth. The feature is contributed by Michael Zakkour who is founder and CEO of U.S.-based consulting firms 5 New Digital and China BrightStar.
The Fifth China International Import Expo (CIIE) took place in Shanghai on November 5-10. The event was established in 2018 as a way to encourage and assist foreign companies to connect with and sell their products to Chinese companies, debut new products for consumers and to strengthen trade between China and the world.
The main takeaways from the event are that China is open for business, Chinese companies want foreign industrial and consumer products, and the national goal of driving the Chinese economy through consumption is on track.
This year's event was a reminder that, over the last three years, due to the impact of COVID-19, supply chain disruptions and global economic realities, a great many things have changed in international commerce and in the way global businesses and business people have had to interact.
In a statement released to the media in October, the U.S. China Business Council (USCBC) noted that "it's still business, though not as usual."
Thus, the mission of the expo made it all the more important in reestablishing a sense of normalcy and setting a roadmap for growth in international trade. The event highlighted the importance of China to the global economy as a consumer of foreign industrial, technology and consumer products.
The CIIE also sent a clear message about how important Chinese consumers are to global companies, to global economic growth and how China's consumer economy is especially important to U.S. manufacturers, brands and new technology companies.
The USCBC noted that more than 200 U.S. companies attended the event, including 32 members, making the U.S. delegation the largest at the expo.
"As the largest delegation at the show, U.S. companies are sending a message that they have confidence in the market, that growth will continue, and government leaders will find ways to preserve the commercial side of the relationship and the millions of jobs in both countries that depend on it," the council said.
Chinese consumers
With all the changes in the international business scene, are Chinese consumers no longer important to global brands and retailers? Is it, with the exception of only the biggest companies in the world, too hard, too expensive and too risky to win over Chinese consumers? Does the rise of local hero brands and products mean Chinese consumers are giving up on foreign brands?
The answer to all these questions is a resounding no. It would be a mistake for global companies to view current headwinds in China's consumption as something approaching a permanent change in tastes and desires or a long-term downturn in spending.
China is, like the rest of the world, experiencing the negative economic and social effects of a pandemic, global inflationary pressure, geopolitical conflicts, and a period where major changes in technology, consumer demands, supply chains and data science are rewriting the rules and norms of retail and consumption.
Is spending down in China today? Yes, it is, and it's a problem that is plaguing retailers, e-commerce giants and brands around the world as consumer spending dips in Europe, North America, and the rest of Asia.
We have also seen a drop in the valuations of many legacy retailers and brands around the world, including many luxury companies.
Is Chinese consumer sentiment as strong as we are accustomed to it being during the "shopping period" that starts in October, peaks during the November 11 Shopping Festival initiated by China's e-commerce giant Alibaba and runs through the December 12 and Chinese New Year events? No.
The bottom line is that spending and consumer sentiment are down almost universally and inflation and uncertainty about the future are on the minds of almost all global consumers and the companies that make and sell them everything from footwear to couches to TVs.
Long-term strategies
As always, the strategy for and commitment to China must be long-term and companies need to be patient, stay flexible and understand that the country is still the second largest consumer market in the world and is still maturing.
In 2014, there was a significant downturn in spending on luxury goods in China. Executives from New York, Paris and Milan were panicking and thinking the end of the China luxury boom had come.
Yes, the China luxury downturn was real, but don't panic, hold steady and plan for the future.
This was the perfect time to start building out digital commerce, e-commerce and digital experiences for Chinese consumers so that when things improved, they would be well-positioned for a new era of growth in China based on the integration of online/offline technology for unified commerce.
The market bottomed at about $33 billion in sales in 2015-17, but by 2019 the market had grown to $49 billion. While the pandemic dropped sales again to $40 billion in 2020 and $42 billion in 2021, sales are expected to advance to $53 billion in 2022 and hit $60 billion by 2025, according to a report by global consulting firm McKinsey.
The lesson is clear: Had the luxury companies panicked, fled, stopped investing and innovating because of a temporary downtown, they might have lost out on what's up to an average of 25 percent of their global sales.
Global producers and merchants also can use this time to conduct deep market, consumer and product research. Demand is changing, not disappearing. The products people want, where and how they want to buy them, purchase motivators, and the continued torrid growth of e-commerce and integrated retail should all be subject to review and improvement.
As the hundreds of companies that took part in the CIIE know, Chinese consumers are vital to their futures; and as China knows, a robust consumer economy is crucial to its growth.
Contact: Bai Shi
Tel: 008610-68996995
Email: baishi@cnfocus.com
Logo - https://mma.prnewswire.com/media/1952219/logo_china_focus_Logo.jpg
View original content to download multimedia:https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/china-focus-releases-a-new-feature-on-a-must-for-global-growth-301683742.html
SOURCE China Focus
Uncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
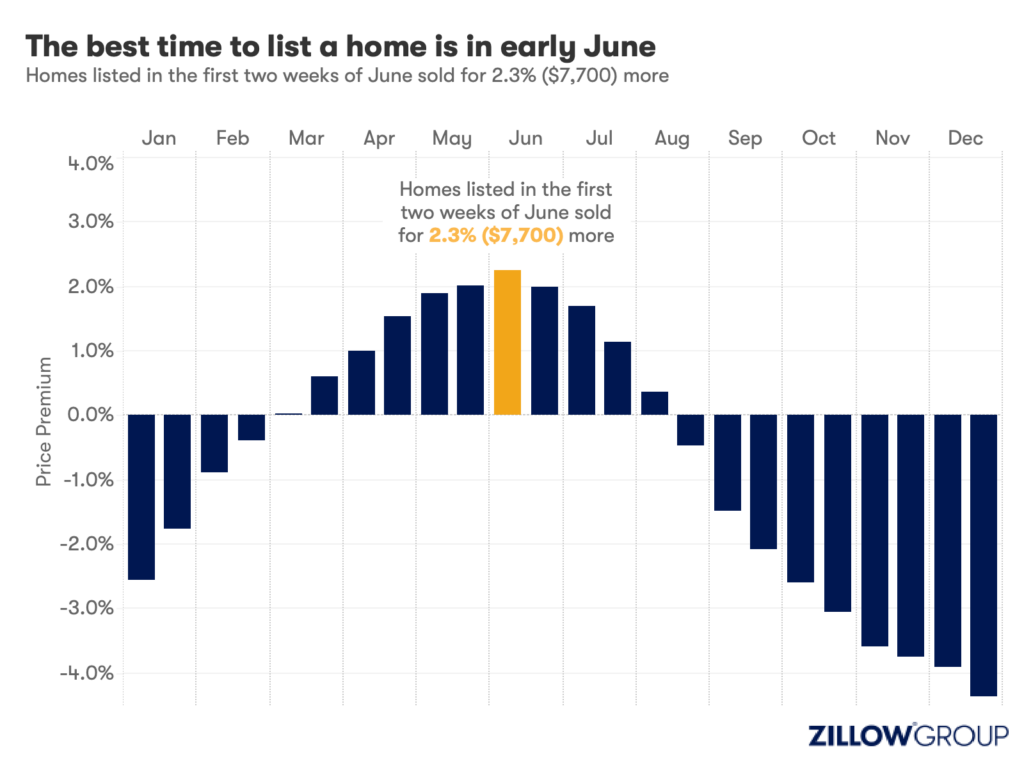
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
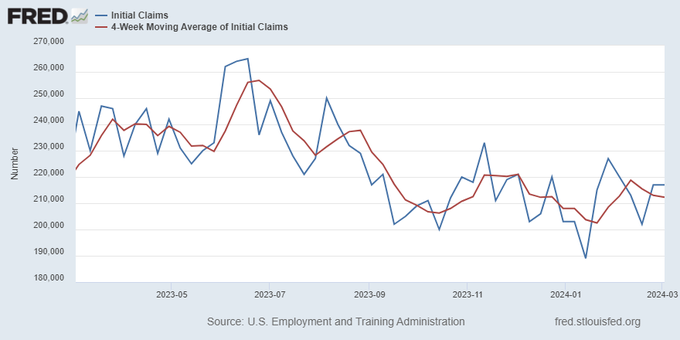
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





