From anxiety about the state of the world to ongoing waves of Covid-19, the stresses we face can seem relentless and even overwhelming. Worse, these stressors can cause chronic inflammation in our bodies. Chronic inflammation is linked to serious conditions such as cardiovascular disease and cancer – and may also affect our thinking and behavior.
A new hypothesis published in Frontiers in Science suggests the negative impacts may extend far further.
“We propose that stress, inflammation, and consequently impaired cognition in individuals can scale up to communities and populations,” explained lead author Prof Yoram Vodovotz of the University of Pittsburgh, USA.
“This could affect the decision-making and behavior of entire societies, impair our cognitive ability to address complex issues like climate change, social unrest, and infectious disease – and ultimately lead to a self-sustaining cycle of societal dysfunction and environmental degradation,” he added.
Bodily inflammation ‘mapped’ in the brain
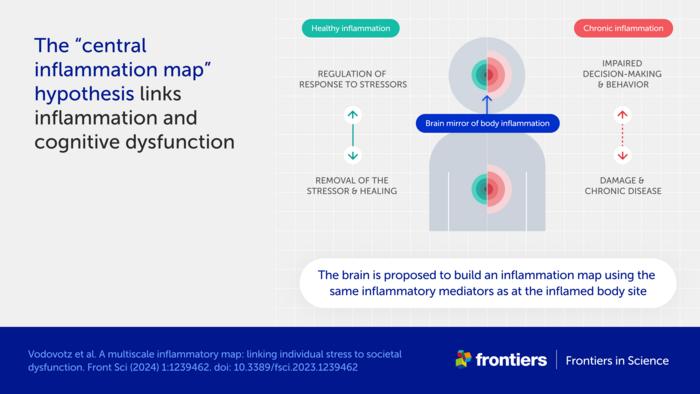
One central premise to the hypothesis is an association between chronic inflammation and cognitive dysfunction.
“The cause of this well-known phenomenon is not currently known,” said Vodovotz. “We propose a mechanism, which we call the ‘central inflammation map’.”
The authors’ novel idea is that the brain creates its own copy of bodily inflammation. Normally, this inflammation map allows the brain to manage the inflammatory response and promote healing.
When inflammation is high or chronic, however, the response goes awry and can damage healthy tissues and organs. The authors suggest the inflammation map could similarly harm the brain and impair cognition, emotion, and behavior.
Accelerated spread of stress and inflammation online
A second premise is the spread of chronic inflammation from individuals to populations.
“While inflammation is not contagious per se, it could still spread via the transmission of stress among people,” explained Vodovotz.
The authors further suggest that stress is being transmitted faster than ever before, through social media and other digital communications.
“People are constantly bombarded with high levels of distressing information, be it the news, negative online comments, or a feeling of inadequacy when viewing social media feeds,” said Vodovotz. “We hypothesize that this new dimension of human experience, from which it is difficult to escape, is driving stress, chronic inflammation, and cognitive impairment across global societies.”
Inflammation as a driver of social and planetary disruption
These ideas shift our view of inflammation as a biological process restricted to an individual. Instead, the authors see it as a multiscale process linking molecular, cellular, and physiological interactions in each of us to altered decision-making and behavior in populations – and ultimately to large-scale societal and environmental impacts.
“Stress-impaired judgment could explain the chaotic and counter-intuitive responses of large parts of the global population to stressful events such as climate change and the Covid-19 pandemic,” explained Vodovotz.
“An inability to address these and other stressors may propagate a self-fulfilling sense of pervasive danger, causing further stress, inflammation, and impaired cognition in a runaway, positive feedback loop,” he added.
The fact that current levels of global stress have not led to widespread societal disorder could indicate an equally strong stabilizing effect from “controllers” such as trust in laws, science, and multinational organizations like the United Nations.
“However, societal norms and institutions are increasingly being questioned, at times rightly so as relics of a foregone era,” said Prof Paul Verschure of Radboud University, the Netherlands, and a co-author of the article. “The challenge today is how we can ward off a new adversarial era of instability due to global stress caused by a multi-scale combination of geopolitical fragmentation, conflicts, and ecological collapse amplified by existential angst, cognitive overload, and runaway disinformation.”
Reducing social media exposure as part of the solution
The authors developed a mathematical model to test their ideas and explore ways to reduce stress and build resilience.
“Preliminary results highlight the need for interventions at multiple levels and scales,” commented co-author Prof Julia Arciero of Indiana University, USA.
“While anti-inflammatory drugs are sometimes used to treat medical conditions associated with inflammation, we do not believe these are the whole answer for individuals,” said Dr David Katz, co-author and a specialist in preventive and lifestyle medicine based in the US. “Lifestyle changes such as healthy nutrition, exercise, and reducing exposure to stressful online content could also be important.”
“The dawning new era of precision and personalized therapeutics could also offer enormous potential,” he added.
At the societal level, the authors suggest creating calm public spaces and providing education on the norms and institutions that keep our societies stable and functioning.
“While our ‘inflammation map’ hypothesis and corresponding mathematical model are a start, a coordinated and interdisciplinary research effort is needed to define interventions that would improve the lives of individuals and the resilience of communities to stress. We hope our article stimulates scientists around the world to take up this challenge,” Vodovotz concluded.
The article is part of the Frontiers in Science multimedia article hub ‘A multiscale map of inflammatory stress’. The hub features a video, an explainer, a version of the article written for kids, and an editorial, viewpoints, and policy outlook from other eminent experts: Prof David Almeida (Penn State University, USA), Prof Pietro Ghezzi (University of Urbino Carlo Bo, Italy), and Dr Ioannis P Androulakis (Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, USA).
Journal
Frontiers in Science
DOI
10.3389/1239462
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
A multiscale inflammatory map: linking individual stress to societal dysfunction
Article Publication Date
12-Mar-2024
COI Statement
YV is a cofounder of, and stakeholder in, Immunetrics, Inc. and a consultant to Anuna AI. PFMJV is the founder of, and stakeholder in, Eodyne Systems s.l. and Sapiens5 Holding BV. DLK was employed by Tangelo – Intend, Inc. Neither these companies nor the funders mentioned above were involved in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication. The companies mentioned above also did not provide funding for the study. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors YV and PV declared that they are editorial board members of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.