Bullwhip-Effect Reversal Is The Major Downside Growth Risk
Bullwhip-Effect Reversal Is The Major Downside Growth Risk
Via blog.VariantPerception.com,
The main downside risk today that the market may…
Via blog.VariantPerception.com,
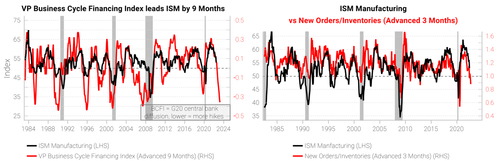
The main downside risk today that the market may not fully appreciate is the reversal of the historically large post-Covid bullwhip effect, which pulled forward a lot of future demand.
The bullwhip effect started with surging consumer goods demand and led to a huge restocking impulse up the supply chain. The below is an excerpt from our July 19th report.
As we highlighted in our July Macro Snapshot:
“ISM new orders to inventory ratio has been collapsing, suggesting this is the beginning of the end of the bullwhip effect. The significant build-up of US retailer inventories is set to exert a strong deflationary force on the economy once the bullwhip effect reverses.”
Leading relationships for ISM manufacturing are bad and still deteriorating.
We are tracking “hard” data to confirm the message from LEIs and the intensity of the industrial slowdown. Absolute USD values of manufacturing new orders and durable goods consumption are still elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels.
More timely hard data confirms the industrial slowdown has started.
Production at US factories declined in June for a second month owing to higher inventories and total industrial production fell for the first time this year (link).
Chemical prices have weakened significantly, signaling falling demand in the face of high prices and weakness in downstream markets. (Ethylene and propylene are key inputs for plastic and household chemical compounds).
Retail sales growth has moderated and has closed the divergence with our retail sales LEI.
We expect further weakness ahead (left-hand chart). Oil consumption as % of GDP has fallen sharply suggesting US consumer resilience is cracking.
* * *
Get the full picture at variantperception.com
Spread & Containment
Five Below makes checkout changes shoppers may not like
The value retailer is discouraging theft at the checkout counter.

Huge retail chains like Walmart (WMT) , Target (TGT) , CVS (CVS) and others have faced a high amount of retail theft, or what they call inventory shrink, since 2020 and have been implementing measures to eliminate those costly losses.
Among the most common measures used by Walmart, Target and some others has been locking up popular items behind glass cases to prevent shoplifting. Customers shopping at these stores have encountered a lot of their favorite products, such as cosmetics, shampoo, over-the-counter drugs and even laundry detergent locked up in those cases.
Related: Target limits self-checkout, makes a change customers will love
Shoppers need to either push a button near the product to alert a worker to unlock the case or, in some situations, run around the store looking for a worker with the proper key to open the case. It's a very inconvenient problem for shoppers, and not all stores are consistent with their lockup policies.
For example, one Walmart store might lock up some of their instant coffee products, while another cross-town Walmart location, or even a Target competitor, doesn't lock up any coffee.
Retail stores have also implemented new self-checkout rules to discourage inventory shrink, but again, stores are inconsistent with their rules. Walmart stores have a 20 items or less rule for their self-checkout lanes to try to steer shoppers with more items to checkout clerks that might help reduce the occurrence of theft. But neither customers, nor workers seem to be observing that rule. Target on March 17 implemented a new 10 items or fewer rule in its self-checkout lanes, but we'll see if anyone enforces it.
These self-checkout requirements are also supposed to speed up the checkout process, but that only works if all the self-check registers are working and an adequate amount of checkout clerks are working registers as well.
The next step for retailers in addressing inventory shrink at self-checkout would be to eliminate self-check altogether.
Pat Greenhouse/The Boston Globe via Getty Images
Five Below cuts back on self-checkout lanes
After finishing the fourth quarter of 2023 with a "higher-than-planned shrink," or higher level of theft than expected in its stores, value retailer Five Below (FIVE) has implemented associate-assisted checkout in all of its stores for 2024, CEO Joel Anderson said on the company's earnings call on March 20.
"In addition, in our high-shrink stores, the primary option for checkout is more of the traditional, over-the-counter associate checkout," Anderson said. "We expect to have 75% of our transactions chain-wide assisted by an associate with a goal of 100% in our highest shrink, highest-risk stores to be fully transacted by an associate."
The retailer also checks receipts and adds guards
"Additionally, in those stores, we’re implementing further mitigation efforts, including receipt checking, additional store payroll and guards. We intend to measure progress as soon as Q2 when we perform a limited number of store counts," Anderson said.
Five Below tested several inventory shrink mitigation initiatives late in the third quarter and into the fourth quarter of 2023, which included product-related tests, front-end initiatives and guard programs, Anderson said in the earnings call. He said the most significant change the Philadelphia-based company made across most of the chain was to limit the number of self-checkout registers that were open, while positioning an associate upfront to further assist customers.
Anderson said he is confident the company's measures will help it over time, but the company has not included any financial impact for shrink reduction in its 2024 guidance. The company, however will aggressively pursue returning to pre-pandemic levels of shrink or offsetting the impact over the next few years, he said.
mitigation pandemicUncategorized
After 625 Days, The Longest Yield Curve Inversion In History
After 625 Days, The Longest Yield Curve Inversion In History
Today is a historic day, as last night – DB’s Jim Reid reminds us – we quietly…
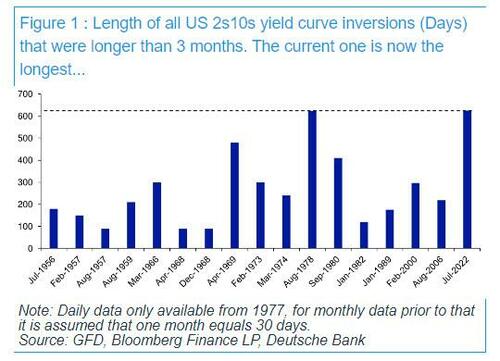
Today is a historic day, as last night - DB's Jim Reid reminds us - we quietly passed the longest continuous US 2s10s inversion in history. After the 2s10s first inverted at the end of March 2022, it has now been continuously inverted for 625 days since July 5th 2022. That exceeds the 624 day inversion from August 1978, which previously held the record.
As regular readers are aware, an inverted yield curve has been the best predictor of a US downturn of any variable through history: the yield curve has always inverted before all of the last 10 US recessions, with a lag that is usually 12-18 months, but some cycles - certainly this one - take longer.... much longer.
In fact, the lack of a recession so far has prompted Red to ask - in his latest Chart of the Day note - if the inverted yield curve recession indicator has failed this cycle?
"Possibly", the DB strategist responds, "but in many ways the yield curve has already accurately predicted many of the drivers that would normally lead to a recession. However, these variables haven't then created recessionary conditions as they normally would have done." He explains:
It led, as it always does, the very sharp deterioration in bank lending standards, and led the declines in bank credit and money supply that are almost unique to this cycle. It was also at the heart of why we had some of the largest bank failures on record with SVB, Signature Bank and First Republic collapsing. A significant part of their failure was a big carry trade that went wrong when the curve inverted.
However, even with the above, a recession - according to the highly political "recession authority" known as the NBER - hasn't materialised. This is perhaps because of the following.
- When lending standards were at their tightest, the borrowing needs of the economy were low relative to previous cycles.
- Excess savings have been unusually high in this cycle (and were revised higher with the GDP revisions last September), so consumers haven't been as exposed to tight credit as they normally are.
- The Fed unveiled a huge series of measures to ensure the regional bank crisis didn't naturally unravel as it would have done in a free market or perhaps in many previous cycles.
- Whilst the Fed’s tightening has been reducing demand, the supply-side of the economy has bounced back strongly from the pandemic disruption, which has further supported growth and made this cycle unique.
So far so good, however, an inverted yield curve should ultimately be a significant headwind for an economy, as capitalism works best when there is a positive return for taking more risk with lending and investments further out the curve. As such, Reid notes, "the rational investor should be prepared to keep more of their money at the front end, or not lend long-term when the curve is inverted" as you are not giving up yield for being able to sleep at night.
So thanks to a historic flood of fiscal stimulus and a daily orgy of new record debt as discussed earlier...
... which means that the US is now running a 6.5% deficit with unemployment near "historical lows", an unheard of event....
... the economy has not succumbed to the inverted yield curve to date, but while it remains inverted the Fed is encouraging more defensive behavior at some point if sentiment changes. As such, the DB strategist concludes that "the quicker we get back to a normal sloping yield curve the safer the system is."
Spread & Containment
Another major retailer cracks down on self-checkout at its stores
The value retailer is discouraging theft at its self-checkout counters by introducing more associate-assisted checkout transactions in its stores.

Huge retail chains like Walmart (WMT) , Target (TGT) , CVS (CVS) and others have faced a high amount of retail theft, or what they call inventory shrink, since 2020 and have been implementing measures to eliminate those costly losses.
Among the most common measures used by Walmart, Target and some others has been locking up popular items behind glass cases to prevent shoplifting. Customers shopping at these stores have encountered a lot of their favorite products, such as cosmetics, shampoo, over-the-counter drugs and even laundry detergent locked up in those cases.
Related: Target limits self-checkout, makes a change customers will love
Shoppers need to either push a button near the product to alert a worker to unlock the case or, in some situations, run around the store looking for a worker with the proper key to open the case. It's a very inconvenient problem for shoppers, and not all stores are consistent with their lockup policies.
For example, one Walmart store might lock up some of their instant coffee products, while another cross-town Walmart location, or even a Target competitor, doesn't lock up any coffee.
Retail stores have also implemented new self-checkout rules to discourage inventory shrink, but again, stores are inconsistent with their rules. Walmart stores have a 20 items or less rule for their self-checkout lanes to try to steer shoppers with more items to checkout clerks that might help reduce the occurrence of theft. But neither customers, nor workers seem to be observing that rule. Target on March 17 implemented a new 10 items or fewer rule in its self-checkout lanes, but we'll see if anyone enforces it.
These self-checkout requirements are also supposed to speed up the checkout process, but that only works if all the self-check registers are working and an adequate amount of checkout clerks are working registers as well.
The next step for retailers in addressing inventory shrink at self-checkout would be to eliminate self-check altogether.
Pat Greenhouse/The Boston Globe via Getty Images
Five Below cuts back on self-checkout lanes
After finishing the fourth quarter of 2023 with a "higher-than-planned shrink," or higher level of theft than expected in its stores, value retailer Five Below (FIVE) has implemented associate-assisted checkout in all of its stores for 2024, CEO Joel Anderson said on the company's earnings call on March 20.
"In addition, in our high-shrink stores, the primary option for checkout is more of the traditional, over-the-counter associate checkout," Anderson said. "We expect to have 75% of our transactions chain-wide assisted by an associate with a goal of 100% in our highest shrink, highest-risk stores to be fully transacted by an associate."
The retailer also checks receipts and adds guards
"Additionally, in those stores, we’re implementing further mitigation efforts, including receipt checking, additional store payroll and guards. We intend to measure progress as soon as Q2 when we perform a limited number of store counts," Anderson said.
Five Below tested several inventory shrink mitigation initiatives late in the third quarter and into the fourth quarter of 2023, which included product-related tests, front-end initiatives and guard programs, Anderson said in the earnings call. He said the most significant change the Philadelphia-based company made across most of the chain was to limit the number of self-checkout registers that were open, while positioning an associate upfront to further assist customers.
Anderson said he is confident the company's measures will help it over time, but the company has not included any financial impact for shrink reduction in its 2024 guidance. The company, however will aggressively pursue returning to pre-pandemic levels of shrink or offsetting the impact over the next few years, he said.
mitigation pandemic-

 Spread & Containment1 week ago
Spread & Containment1 week agoIFM’s Hat Trick and Reflections On Option-To-Buy M&A
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 International2 weeks ago
International2 weeks agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoGOP Efforts To Shore Up Election Security In Swing States Face Challenges



























