Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) has been shown to be an excellent means of understanding the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in communities. It is now used in multiple areas across the world to track the prevalence of the virus, serving as a proxy for determining the status of COVID-19. Of particular importance is that WBE can be used to estimate the prevalence of COVID-19, including asymptomatic cases. However, one of the major drawbacks of WBE for SARS-CoV-2 has been that the traditional method was not very sensitive, and low viral loads could not be reliably detected.
A team of scientists from Hokkaido University and Shionogi & Co, Ltd., have developed a simple, rapid, highly sensitive method for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. The method, EPISENS-S, which does not require specialised equipment, was described in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Japan has had the lowest number of cases per capita. Thus, the viral loads in sewage have also been lower, and much more difficult to evaluate using established WBE methods—due to their low sensitivity. Prior work by the research team showed that the SARS-CoV-2 virus was associated with solids in sewage, so they focused on developing a method to analyse the solid phase of wastewater.
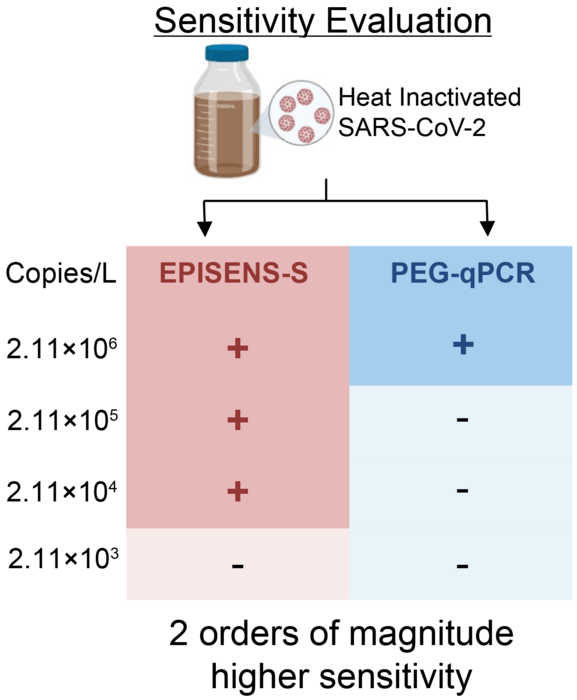
The method they developed, EPISENS-S, involves centrifuging collected wastewater samples to separate all the solids in the samples. The solids were then treated with a commercially available kit to extract all the RNA; the RNA was then reverse transcribed and amplified to obtain a substantial amount of DNA copies. A separate set of samples was subjected to treatment with polyethylene glycol followed by RNA extraction and reverse transcription to synthesize DNA: the method that is currently widely implemented in Japan. The DNA obtained from each of these methods was subjected to quantitative PCR (qPCR).
The team found that the EPISENS-S method is approximately 100 times more sensitive than the polyethylene glycol method. They used EPISENS-S to conduct a long-term analysis of wastewater from two sewage treatment plants in Sapporo city, and found that there was a high correlation between changes in RNA concentrations in the collected samples and changes in the number of reported cases in the city. EPISENS-S can also detect and quantify the Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV), which is associated with fecal matter and is used as an internal control.
EPISENS-S provides a way to track COVID-19 cases that are asymptomatic, as well as those that have not been clinically confirmed. In addition, it has great potential to continue tracking the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 as vaccination rates increase. Finally, EPISENS-S could also be adapted to track other viral diseases with low infection numbers and viral loads.
Journal
Science of The Total Environment
DOI
10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157101
Method of Research
Experimental study
Article Title
The efficient and practical virus identification system with enhanced sensitivity for solids (EPISENS-S): A rapid and cost-effective SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection method for routine wastewater surveillance
Article Publication Date
8-Aug-2022