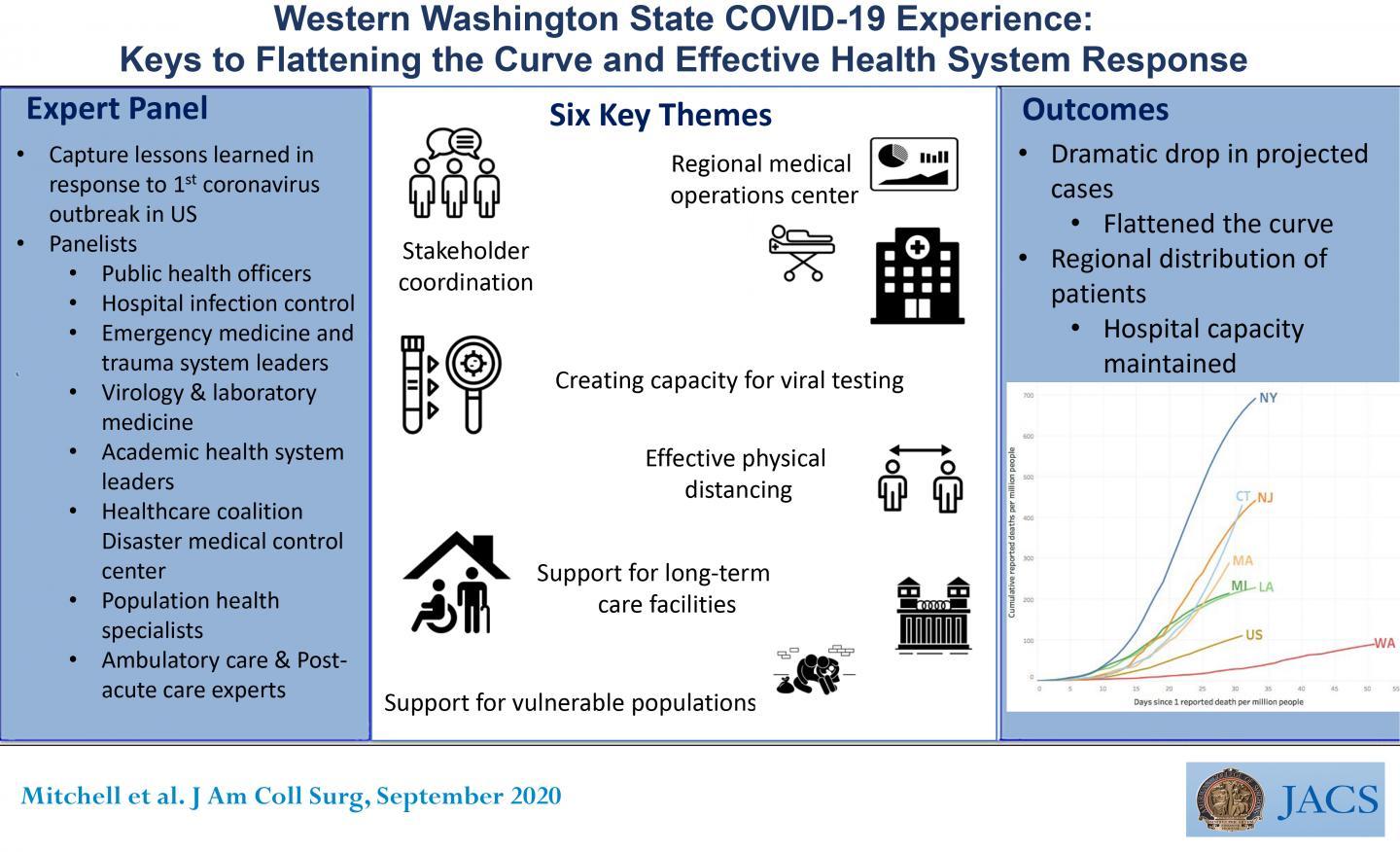
CHICAGO (June 16, 2020): Despite having the first confirmed case of coronavirus and the first major COVID-19 outbreak in the United States, the state of Washington implemented a response plan that kept its death rate the lowest among all states that have had major outbreaks. A multidisciplinary consensus panel of 26 experts analyzed western Washington’s response and identified six key factors that contributed to “flattening the curve” in the state. They report on their findings in an “article in press” on the Journal of the American College of Surgeons website ahead of print.
The six pillars of the COVID-19 response identified by the consensus panel are early communication and coordination among stakeholders, regional coordination and situational awareness of the healthcare system, rapid development and access to testing, proactive management of long-term care facilities (LTCF) and vulnerable populations and effective physical distancing in the community.
As of June 5, Washington State had 22,729 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 1,138 ensuing deaths, a rate of about 5 percent. The overall death rate in the United States is 5.7 percent, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data. New York State, by comparison, has had more than 380,000 confirmed cases and 30,000 deaths, a death rate of 8 percent.
“Along with the governor’s stay at home and physical distancing orders, preexisting relationships across the healthcare system were critical in facilitating this response,” said corresponding author Eileen M. Bulger, MD, FACS, chief of trauma at Harborview Medical Center in Seattle and Chair of the American College of Surgeons (ACS) Committee on Trauma. The consensus panel noted that early communication and coordination among the various hospitals systems, emergency medical services, and LTCFs was pivotal in the response.
Days after the first case was identified on January 21, the Northwest Healthcare Response Network (NWHRN) coordinated with other entities–Public Health Seattle and King County (PHSKC), Harborview Medical Center Infection, Prevention and Control, the Washington Department of Health (DOH), and the Washington State Hospital Association, among others–to create communications channels across individual health systems. NWHRN is a non-profit coalition comprised of 3,000 health care organizations in 15 counties and 25 contiguous sovereign tribal nations in western Washington that collaborates on disaster preparedness and response.
“Normally we exist in a competitive landscape,” said lead author Steven H. Mitchell, MD, medical director of the emergency department at Harborview Medical Center and medical director of the Western Washington Regional COVID Coordination Center (WRC), “but there was great willingness for each system and entity to do what they could to address the region’s needs.”
By the end of February, the first cluster of cases was identified at a Kirkland LTCF and the first COVID-19 death occurred in King County. Dr. Mitchell noted that as the outbreak unfolded, the stakeholders recognized the need for increased infrastructure to support a coordinated response and the WRC was established as a regional medical operations center. The WRC realized LTCFs “were going to be significantly impacted,” he said. However, there was no communication mechanism in place with those facilities. The NWHRN and WRC partnered with Microsoft (based in suburban Redmond), the state hospital association, and state DOH to build a communication platform to track critical hospital capacity data and leverage relationships between hospitals and LTCFs. This software platform will also support tracking of cases in LTCFs with mandatory reporting to the DOH.
Another key component of the response was the ability of the University of Washington virology laboratory to rapidly develop viral testing and make it widely available. Dr. Bulger called the virology lab staff “heroes in this response.” She added, “They recognized very early that there would be a need for widespread testing that would likely exceed the capability of the state laboratory. They worked to develop their own testing platform and validate the test so that they could begin receiving samples from the initial outbreak.” As of June 5, 383,587 people have been tested for SARS-CoV-2 in Washington.
To proactively engage LTCFs, health systems and PHSKC developed strike teams to provide them with on-site support. “Our geriatrics and post-acute care physicians have had longstanding relationships with many of the skilled nursing facilities, and each healthcare system has a group of LTCFs that they routinely work with for patient discharges, so they organized these strike teams to support these facilities,” Dr. Bulger said. That on-site support includes COVID-19 testing for residents and staff and training for personal protective equipment and effective isolation and quarantine. “We were able to keep many of these patients in the nursing facilities and not overwhelm the hospitals by evacuating entire facilities,” she said.
In addition to people in LTCFs, the response identified other vulnerable populations: minority and immigrant communities and non-English speakers; the homeless; and people in jails and prisons. PHSKC has convened nine task forces and community advisory groups to engage diverse populations. To service the homeless, King County added shelter space, hand-washing stations, and a call center along with locations where they can access isolation and quarantine services.
The WRC, Dr. Bulger noted, is built on the RMOC model first established in Texas and since promoted by the ACS Committee on Trauma to support disaster response. “The RMOC structure is a vital resource that I believe needs to be established in every community in the United States,” Dr. Bulger said. The Department of Health and Human Services office of Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR), which provides funding for regional coalitions, has promoted this approach as “Medical Operations Coordination Cells.”
“Each region should begin to organize itself in this way because whether it’s a pandemic or other type of large-scale disaster that occurs, it’s critical for regions to prepare to develop communication structures that support situational awareness and patient distribution strategies,” Dr. Mitchell said. “Otherwise, facilities get overwhelmed and patients suffer.”
The authors proposed these “lessons learned” as a roadmap for preparation for future outbreaks, as well as establishing a lasting infrastructure which will strengthen the health systems response to all future mass casualty events and save lives.
###
The authors have no relevant disclosures.
Coauthors are senior author John B. Lynch, MD, MPH, of the Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the University of Washington, Seattle; Herbert C. Duber, MD, MPH; and Vicki L. Sakata, MD, of the Northwest Healthcare Response Network, Tukwilla, Wash.; James Lewis, MD, and Jeffrey S. Duchin, MD, of Public Health – Seattle and King County; Keith R. Jerome, MD, PhD, of the University of Washington and the Vaccine and Infectious Disease Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle; and Alexander L. Greninger, MD, PhD, MS, MPhil, Thuan D. Ong, MD, MPH, Stephen C. Morris, MD, MPH, Lisa D. Chew, MD, MPH, Tom M. Haffner, BS, Geoffrey S. Baird, MD, PhD, Susan A. Stern, MD, Timothy H. Dellit, MD, Louise Simpson, MHA, Onora Lien, MA, Nancy K. Sugg, MD, Meagan Kay, DVM, Benjamin Sanders, MD, MPH, Margaret D. Lukoff, MD, Sabine von Preyss-Friedman, MD, Matias Valenzuela, PhD, Chloe Bryson-Cahn, MD1, Vanessa A. Makarewicz, MN, and Hanh Pan, MHA, all of the University of Washington.
“FACS” designates that a surgeon is a Fellow of the American College of Surgeons.
Citation: Western Washington State’s COVID-19 Experience: The Keys to Flattening the Curve & An Effective Health System Response. Journal of American College of Surgeons. DOI: https:/
About the American College of Surgeons
The American College of Surgeons is a scientific and educational organization of surgeons that was founded in 1913 to raise the standards of surgical practice and improve the quality of care for all surgical patients. The College is dedicated to the ethical and competent practice of surgery. Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients. The College has more than 82,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. For more information, visit http://www.