Uncategorized
7 biggest crypto collapses of 2022 the industry would like to forget
A look at some of the biggest disappointments in the crypto space form this year as the industry readies itself for better things to come.
…

A look at some of the biggest disappointments in the crypto space form this year as the industry readies itself for better things to come.
2022 has been a bumpy year for the cryptocurrency market, with one of the worst bear markets on record and the downfall of some major platforms within the space. The global economy is beginning to feel the consequences of the pandemic, and clearly, this has had an influence on the crypto industry.
Below is a breakdown of some of the biggest disappointments in the crypto space this year.
Axie Infinity’s Ronin Bridge hacked
In March of this year, Ronin, the blockchain network that runs the popular nonfungible token (NFT) crypto game Axie Infinity, was hacked for $625 million. The hacker took 173,600 Ether (ETH) and 25.5 million USD Coin (USDC) from the Ronin bridge in two transactions.
When the Lazarus Group started its attack, five of the nine private keys for the Ronin Network’s cross-chain bridge were hacked. With this vote, they authorized two withdrawals totaling $25.5 million in USDC and 173,600 ETH.
According to the Ronin group, Axie Infinity’s issues began in November 2021, when its user base had expanded to an untenable size. Consequently, the corporation’s safety rules had to be relaxed to fulfill client demand. After the initial phase of fast development was completed, the firm reduced its safety procedures.
Bridge hacks have accounted for 2/3 of the $3B that has been stolen from DeFi.@AxieInfinity's @Ronin_Network bridge hack has been the largest to date at $600M lost. pic.twitter.com/5IAuTqShMO
— Messari (@MessariCrypto) August 30, 2022
The main difficulty was a lack of a suitably decentralized network created by game developer Sky Mavis. The hacker acquired access to the private keys of five of Sky Mavis’ Ronin Chain’s nine validator nodes, enabling them to compromise the network. When the hackers gained control of five nodes, they essentially controlled over half of the network and were free to accept or deny whatever transactions they wanted. They obtained ETH and USDC via falsifying withdrawals.
The crime occurred on March 23, but it was only noticed on March 29, when a user reported being unable to withdraw 5,000 ETH from the Ronin bridge ATM. In the aftermath of the attack, Axie Infinity developers raised $150 million to reimburse the affected users.
TerraUSD/LUNA collapse
On May 7, when over $2 billion in TerraUSD (UST) was unstaked (removed from the Anchor Protocol), hundreds of millions of United States dollars were quickly liquidated. It’s unclear if this was a deliberate attack on the Terra blockchain or a response to rising interest rates. Because of the enormous outflow of cash, the price of UST fell from $1 to $0.91. As a result, market players started trading $0.90 in UST for $1 in Terra (LUNA).
When a considerable amount of UST was moved out, the stablecoin depegged. The availability of LUNA increased as more people sold their UST during the panic.

Following this fall, cryptocurrency marketplaces started to suspend trading pairs such as LUNA and UST. Following the initial accident in May, Do Kwon disclosed a rehabilitation plan for LUNA, and things seemed to improve. However, the currency’s value eventually fell. It was abandoned almost as soon as it began. Finally, Terra launched a whole new currency known as LUNA 2.0.
Investors lost a combined $60 billion due to the panic selling that accompanied the decline of TerraUSD Classic (USTC) and Luna Classic (LUNC), a related token.
On Sept. 14, a South Korean court issued an arrest warrant for Do Kwon. This happened four months after Terraform Labs’ LUNA and UST tokens collapsed. Do Kwon and five others were detained for allegedly violating regional market restrictions.
Three Arrows Capital collapse
When LUNA and Terra collapsed, the crypto hedge fund Three Arrows Capital (3AC), which had a peak market valuation of more than $560 million, suffered significantly. 3AC had invested heavily in several troubled cryptocurrency projects, including the play-to-earn game Axie Infinity, which lost $625 million to a North Korean hack this year, and the centralized cryptocurrency exchange BlockFi, which laid off hundreds of employees in mid-June.
The UST collapse shattered investor confidence and expedited the slide of cryptocurrencies, which was already underway as part of a bigger flight from risk. A flood of margin calls from 3AC’s lenders sought repayment, but the firm lacked the funds to meet the requests. In addition, many of the company’s counterparties could not meet their investors’ expectations, many of whom were retail investors promised 20% annual returns.
Related: Santas and Grinches: The heroes and villains of 2022
The crypto hedge fund eventually collapsed after taking on major directional trades and borrowing from over 20 institutions, and the founders defaulted on its payments.
Because the founders would not appear in court, the lawsuit proceeded without them. In a leaked court document filed with the Singapore High Court, the Singapore government was asked to accept liquidation proceedings and work with liquidators. As liquidators try to wind down the failed crypto business of Three Arrows Capital, U.S. Bankruptcy Judge Martin Glenn has issued subpoenas to the company’s founders.
Voyager Digital’s fall
On July 6, prominent cryptocurrency investment firm Voyager Digital filed for bankruptcy after crypto hedge fund 3AC defaulted on a $650 million loan. 3AC received a significant loan from Voyager with no security. When 3AC defaulted on all of its obligations and its owners left, Voyager lost a significant sum of customer money.
Trading, withdrawals, and deposits were all suspended when Voyager reported that 3AC would not repay its loan. In June, Sam Bankman-Fried, billionaire CEO of trading firms FTX and Alameda Research, presented Voyager with a $500 million line of credit to help them weather the market collapse.
On July 5, 2022, Voyager Digital Holdings filed for bankruptcy in the Southern District of New York. According to Voyager Digital, the corporation owes between $1 billion and $10 billion to its more than 100,000 debtors. Despite its debts, however, the company believes it has assets worth between $1 and $10 billion. They also guarantee that adequate money is available to pay off the company’s unsecured creditors.
In a September court filing, insolvent cryptocurrency broker Voyager Digital revealed that it would auction off its remaining assets.

Celsius crash and liquidity crisis
Celsius’s value plummeted on July 13, 2022, when one of the main crypto businesses, Celsius Network, declared bankruptcy. As the price of cryptocurrencies fell, investors on the Celsius network started withdrawing their Bitcoin (BTC) holdings in search of safer alternatives.
Consequently, panicked investors left Celsius in volume. Despite stating they were forced to do so due to “extreme market conditions,” Celsius Network halted BTC withdrawals, swaps and transfers on June 12. Users of the site understandably thought that Celsius had declared bankruptcy and would be unable to refund their money. The value of the Celsius cryptocurrency plummeted by 70% in only a few hours and fell further in the days that followed.
The crypto market has seen a significant sell-off due to the insecurity and falling prices of many major cryptocurrencies, which corresponded with the drop in the price of Celsius. In addition, due to escalating cash flow issues, Celsius announced 23% layoffs on July 3, 2022. When the time came, the company filed for bankruptcy on July 13, 2022.
Celsius had total liabilities of $6.6 billion and assets of $3.8 billion, resulting in a $1.2 billion hole in the company’s balance sheet due to the court ruling.
FTX collapse
FTX and its U.S. equivalent, FTX.US, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on Nov. 11. The exchanges collapsed due to a lack of liquidity and money mismanagement, resulting in a large number of withdrawals from fearful investors.
Following the announcement of bankruptcy, FTX.US briefly restricted withdrawals on Nov. 11, despite earlier promises that FTX.US would be unaffected by FTX’s liquidity concerns. On the evening of Nov. 11, an alleged hack took more than $600 million from FTX wallets. The assault was revealed by FTX in its assistance channel on the instant-messaging network Telegram.
PSA: If you have a bank account linked to FTX US, change your bank account password and stop sharing data immediately.
— Mike McGuiness ᵍᵐ (@mikemcg0) November 12, 2022
Below is a screenshot of my bank account, which they tried accessing 40 mins ago pic.twitter.com/sdnaUFEzOW
According to some Twitter users, hackers were also attempting to get access to FTX-linked bank accounts. Plaid, a company that connects consumer bank accounts with financial applications, responded to “concerning public reports” by denying FTX access to their products, claiming that they had no proof that their tools had been used unlawfully.
Bankman-Fried was arrested in the Bahamas on Dec. 12 at the request of the U.S. government, which wanted him extradited for eight criminal offenses, including wire fraud and conspiracy to defraud investors. Bankman-Fried was eventually deported to the United States and is awaiting trial after posting a $250 million bail.
BlockFi bankruptcy
The collapse of FTX earlier in the month generated fear and uncertainty across the market. BlockFi, another cryptocurrency exchange, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on Nov. 28. With assets and liabilities ranging from $1 billion to $10 billion, the firm had over 100,000 creditors. In addition, they had a $275,000,000 debt to Sam Bankman-Fried’s American subsidiary, FTX US. The application shows that the largest client has a balance of $28 million.
Following the demise of Three Arrows Capital, multiple firms, including the crypto company that operates a trading exchange and an interest-bearing custodial service for cryptocurrencies, had serious liquidity issues.
Related: Women who made a contribution to the crypto industry in 2022
BlockFi agreed earlier this year to accept a credit package from FTX worth up to $400 million to help it weather a liquidity restriction caused by the exchange’s exposure to the TerraUSD stablecoin’s collapse. As a result of these concerns, BlockFi was reliant on the performance of the cryptocurrency exchange FTX, which may now jeopardize its financial stability.
While 2022 may have been a tough year for the crypto market, there may be a silver lining. Investor sentiment seems to be improving, and the crypto market has always recovered from previous bear markets and platform collapses. The events of 2022 could pave the way for new platforms to learn from the mistakes of their predecessors.
cryptocurrency bitcoin blockchain crypto btc link pandemic cryptoUncategorized
Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more
New Zillow research suggests the spring home shopping season may see a second wave this summer if mortgage rates fall
The post Homes listed for sale in…
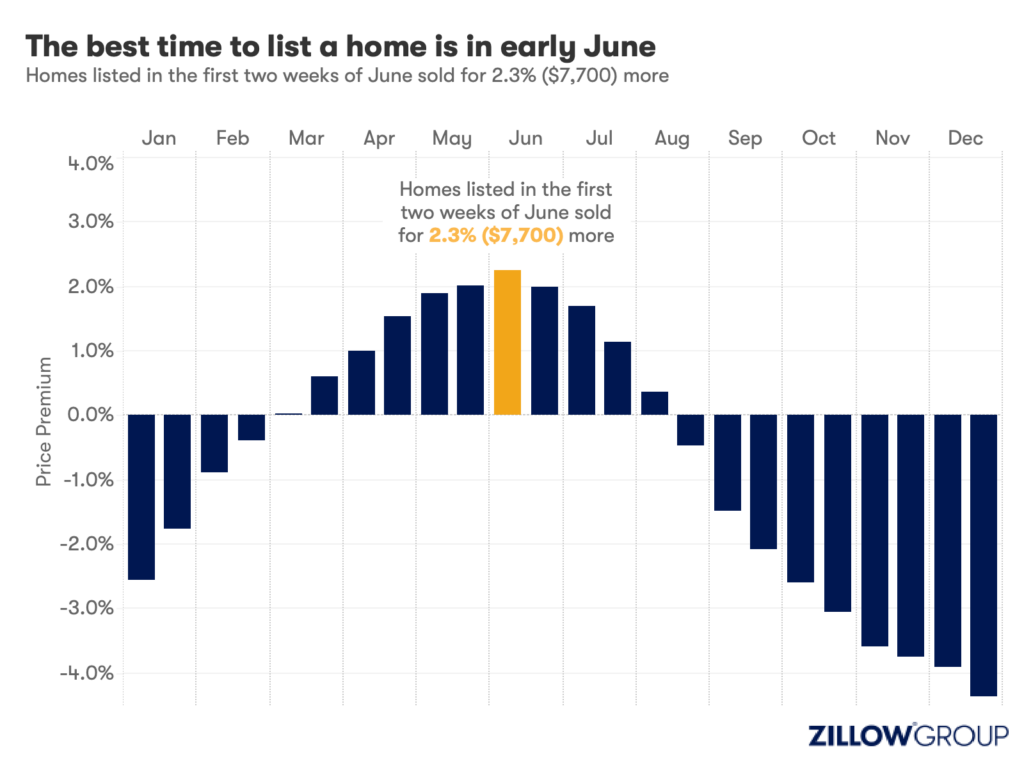
- A Zillow analysis of 2023 home sales finds homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more.
- The best time to list a home for sale is a month later than it was in 2019, likely driven by mortgage rates.
- The best time to list can be as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York and Philadelphia.
Spring home sellers looking to maximize their sale price may want to wait it out and list their home for sale in the first half of June. A new Zillow® analysis of 2023 sales found that homes listed in the first two weeks of June sold for 2.3% more, a $7,700 boost on a typical U.S. home.
The best time to list consistently had been early May in the years leading up to the pandemic. The shift to June suggests mortgage rates are strongly influencing demand on top of the usual seasonality that brings buyers to the market in the spring. This home-shopping season is poised to follow a similar pattern as that in 2023, with the potential for a second wave if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates midyear or later.
The 2.3% sale price premium registered last June followed the first spring in more than 15 years with mortgage rates over 6% on a 30-year fixed-rate loan. The high rates put home buyers on the back foot, and as rates continued upward through May, they were still reassessing and less likely to bid boldly. In June, however, rates pulled back a little from 6.79% to 6.67%, which likely presented an opportunity for determined buyers heading into summer. More buyers understood their market position and could afford to transact, boosting competition and sale prices.
The old logic was that sellers could earn a premium by listing in late spring, when search activity hit its peak. Now, with persistently low inventory, mortgage rate fluctuations make their own seasonality. First-time home buyers who are on the edge of qualifying for a home loan may dip in and out of the market, depending on what’s happening with rates. It is almost certain the Federal Reserve will push back any interest-rate cuts to mid-2024 at the earliest. If mortgage rates follow, that could bring another surge of buyers later this year.
Mortgage rates have been impacting affordability and sale prices since they began rising rapidly two years ago. In 2022, sellers nationwide saw the highest sale premium when they listed their home in late March, right before rates barreled past 5% and continued climbing.
Zillow’s research finds the best time to list can vary widely by metropolitan area. In 2023, it was as early as the second half of February in San Francisco, and as late as the first half of July in New York. Thirty of the top 35 largest metro areas saw for-sale listings command the highest sale prices between May and early July last year.
Zillow also found a wide range in the sale price premiums associated with homes listed during those peak periods. At the hottest time of the year in San Jose, homes sold for 5.5% more, a $88,000 boost on a typical home. Meanwhile, homes in San Antonio sold for 1.9% more during that same time period.
| Metropolitan Area | Best Time to List | Price Premium | Dollar Boost |
| United States | First half of June | 2.3% | $7,700 |
| New York, NY | First half of July | 2.4% | $15,500 |
| Los Angeles, CA | First half of May | 4.1% | $39,300 |
| Chicago, IL | First half of June | 2.8% | $8,800 |
| Dallas, TX | First half of June | 2.5% | $9,200 |
| Houston, TX | Second half of April | 2.0% | $6,200 |
| Washington, DC | Second half of June | 2.2% | $12,700 |
| Philadelphia, PA | First half of July | 2.4% | $8,200 |
| Miami, FL | First half of June | 2.3% | $12,900 |
| Atlanta, GA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $8,700 |
| Boston, MA | Second half of May | 3.5% | $23,600 |
| Phoenix, AZ | First half of June | 3.2% | $14,700 |
| San Francisco, CA | Second half of February | 4.2% | $50,300 |
| Riverside, CA | First half of May | 2.7% | $15,600 |
| Detroit, MI | First half of July | 3.3% | $7,900 |
| Seattle, WA | First half of June | 4.3% | $31,500 |
| Minneapolis, MN | Second half of May | 3.7% | $13,400 |
| San Diego, CA | Second half of April | 3.1% | $29,600 |
| Tampa, FL | Second half of June | 2.1% | $8,000 |
| Denver, CO | Second half of May | 2.9% | $16,900 |
| Baltimore, MD | First half of July | 2.2% | $8,200 |
| St. Louis, MO | First half of June | 2.9% | $7,000 |
| Orlando, FL | First half of June | 2.2% | $8,700 |
| Charlotte, NC | Second half of May | 3.0% | $11,000 |
| San Antonio, TX | First half of June | 1.9% | $5,400 |
| Portland, OR | Second half of April | 2.6% | $14,300 |
| Sacramento, CA | First half of June | 3.2% | $17,900 |
| Pittsburgh, PA | Second half of June | 2.3% | $4,700 |
| Cincinnati, OH | Second half of April | 2.7% | $7,500 |
| Austin, TX | Second half of May | 2.8% | $12,600 |
| Las Vegas, NV | First half of June | 3.4% | $14,600 |
| Kansas City, MO | Second half of May | 2.5% | $7,300 |
| Columbus, OH | Second half of June | 3.3% | $10,400 |
| Indianapolis, IN | First half of July | 3.0% | $8,100 |
| Cleveland, OH | First half of July | 3.4% | $7,400 |
| San Jose, CA | First half of June | 5.5% | $88,400 |
The post Homes listed for sale in early June sell for $7,700 more appeared first on Zillow Research.
federal reserve pandemic home sales mortgage rates interest ratesUncategorized
February Employment Situation
By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000…

By Paul Gomme and Peter Rupert
The establishment data from the BLS showed a 275,000 increase in payroll employment for February, outpacing the 230,000 average over the previous 12 months. The payroll data for January and December were revised down by a total of 167,000. The private sector added 223,000 new jobs, the largest gain since May of last year.

Temporary help services employment continues a steep decline after a sharp post-pandemic rise.


Average hours of work increased from 34.2 to 34.3. The increase, along with the 223,000 private employment increase led to a hefty increase in total hours of 5.6% at an annualized rate, also the largest increase since May of last year.

The establishment report, once again, beat “expectations;” the WSJ survey of economists was 198,000. Other than the downward revisions, mentioned above, another bit of negative news was a smallish increase in wage growth, from $34.52 to $34.57.

The household survey shows that the labor force increased 150,000, a drop in employment of 184,000 and an increase in the number of unemployed persons of 334,000. The labor force participation rate held steady at 62.5, the employment to population ratio decreased from 60.2 to 60.1 and the unemployment rate increased from 3.66 to 3.86. Remember that the unemployment rate is the number of unemployed relative to the labor force (the number employed plus the number unemployed). Consequently, the unemployment rate can go up if the number of unemployed rises holding fixed the labor force, or if the labor force shrinks holding the number unemployed unchanged. An increase in the unemployment rate is not necessarily a bad thing: it may reflect a strong labor market drawing “marginally attached” individuals from outside the labor force. Indeed, there was a 96,000 decline in those workers.


Earlier in the week, the BLS announced JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey) data for January. There isn’t much to report here as the job openings changed little at 8.9 million, the number of hires and total separations were little changed at 5.7 million and 5.3 million, respectively.

As has been the case for the last couple of years, the number of job openings remains higher than the number of unemployed persons.

Also earlier in the week the BLS announced that productivity increased 3.2% in the 4th quarter with output rising 3.5% and hours of work rising 0.3%.

The bottom line is that the labor market continues its surprisingly (to some) strong performance, once again proving stronger than many had expected. This strength makes it difficult to justify any interest rate cuts soon, particularly given the recent inflation spike.
unemployment pandemic unemploymentUncategorized
Mortgage rates fall as labor market normalizes
Jobless claims show an expanding economy. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
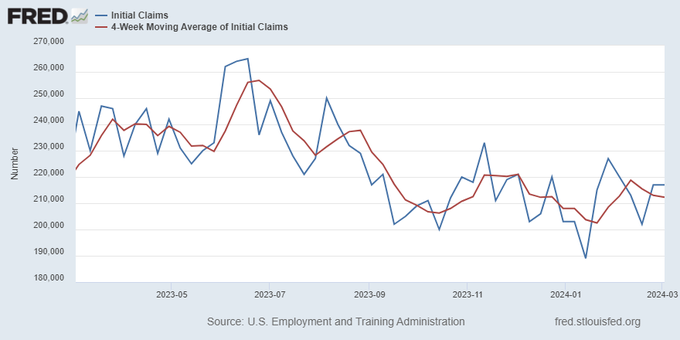
Everyone was waiting to see if this week’s jobs report would send mortgage rates higher, which is what happened last month. Instead, the 10-year yield had a muted response after the headline number beat estimates, but we have negative job revisions from previous months. The Federal Reserve’s fear of wage growth spiraling out of control hasn’t materialized for over two years now and the unemployment rate ticked up to 3.9%. For now, we can say the labor market isn’t tight anymore, but it’s also not breaking.
The key labor data line in this expansion is the weekly jobless claims report. Jobless claims show an expanding economy that has not lost jobs yet. We will only be in a recession once jobless claims exceed 323,000 on a four-week moving average.
From the Fed: In the week ended March 2, initial claims for unemployment insurance benefits were flat, at 217,000. The four-week moving average declined slightly by 750, to 212,250
Below is an explanation of how we got here with the labor market, which all started during COVID-19.
1. I wrote the COVID-19 recovery model on April 7, 2020, and retired it on Dec. 9, 2020. By that time, the upfront recovery phase was done, and I needed to model out when we would get the jobs lost back.
2. Early in the labor market recovery, when we saw weaker job reports, I doubled and tripled down on my assertion that job openings would get to 10 million in this recovery. Job openings rose as high as to 12 million and are currently over 9 million. Even with the massive miss on a job report in May 2021, I didn’t waver.
Currently, the jobs openings, quit percentage and hires data are below pre-COVID-19 levels, which means the labor market isn’t as tight as it once was, and this is why the employment cost index has been slowing data to move along the quits percentage.

3. I wrote that we should get back all the jobs lost to COVID-19 by September of 2022. At the time this would be a speedy labor market recovery, and it happened on schedule, too
Total employment data
4. This is the key one for right now: If COVID-19 hadn’t happened, we would have between 157 million and 159 million jobs today, which would have been in line with the job growth rate in February 2020. Today, we are at 157,808,000. This is important because job growth should be cooling down now. We are more in line with where the labor market should be when averaging 140K-165K monthly. So for now, the fact that we aren’t trending between 140K-165K means we still have a bit more recovery kick left before we get down to those levels.

From BLS: Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 275,000 in February, and the unemployment rate increased to 3.9 percent, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Job gains occurred in health care, in government, in food services and drinking places, in social assistance, and in transportation and warehousing.
Here are the jobs that were created and lost in the previous month:

In this jobs report, the unemployment rate for education levels looks like this:
- Less than a high school diploma: 6.1%
- High school graduate and no college: 4.2%
- Some college or associate degree: 3.1%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher: 2.2%

Today’s report has continued the trend of the labor data beating my expectations, only because I am looking for the jobs data to slow down to a level of 140K-165K, which hasn’t happened yet. I wouldn’t categorize the labor market as being tight anymore because of the quits ratio and the hires data in the job openings report. This also shows itself in the employment cost index as well. These are key data lines for the Fed and the reason we are going to see three rate cuts this year.
recession unemployment covid-19 fed federal reserve mortgage rates recession recovery unemployment-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoAll Of The Elements Are In Place For An Economic Crisis Of Staggering Proportions
-

 Uncategorized1 month ago
Uncategorized1 month agoCathie Wood sells a major tech stock (again)
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoCalifornia Counties Could Be Forced To Pay $300 Million To Cover COVID-Era Program
-

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks agoApparel Retailer Express Moving Toward Bankruptcy
-

 Uncategorized4 weeks ago
Uncategorized4 weeks agoIndustrial Production Decreased 0.1% in January
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoWalmart launches clever answer to Target’s new membership program
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoEyePoint poaches medical chief from Apellis; Sandoz CFO, longtime BioNTech exec to retire
-

 Uncategorized3 weeks ago
Uncategorized3 weeks agoRFK Jr: The Wuhan Cover-Up & The Rise Of The Biowarfare-Industrial Complex





